Exam 1- Microanatomy/Quizzes/Iclicker
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
166 Terms
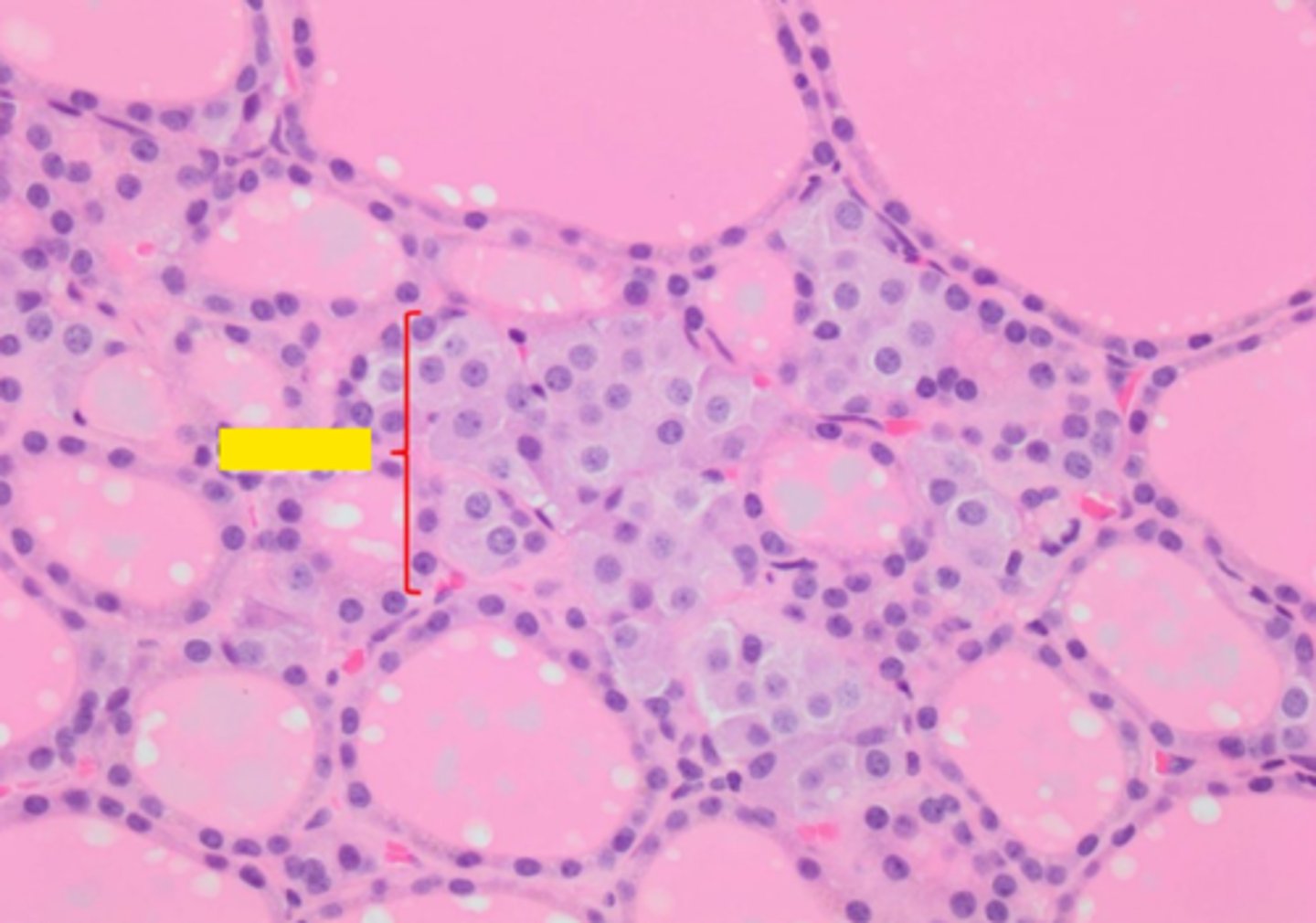
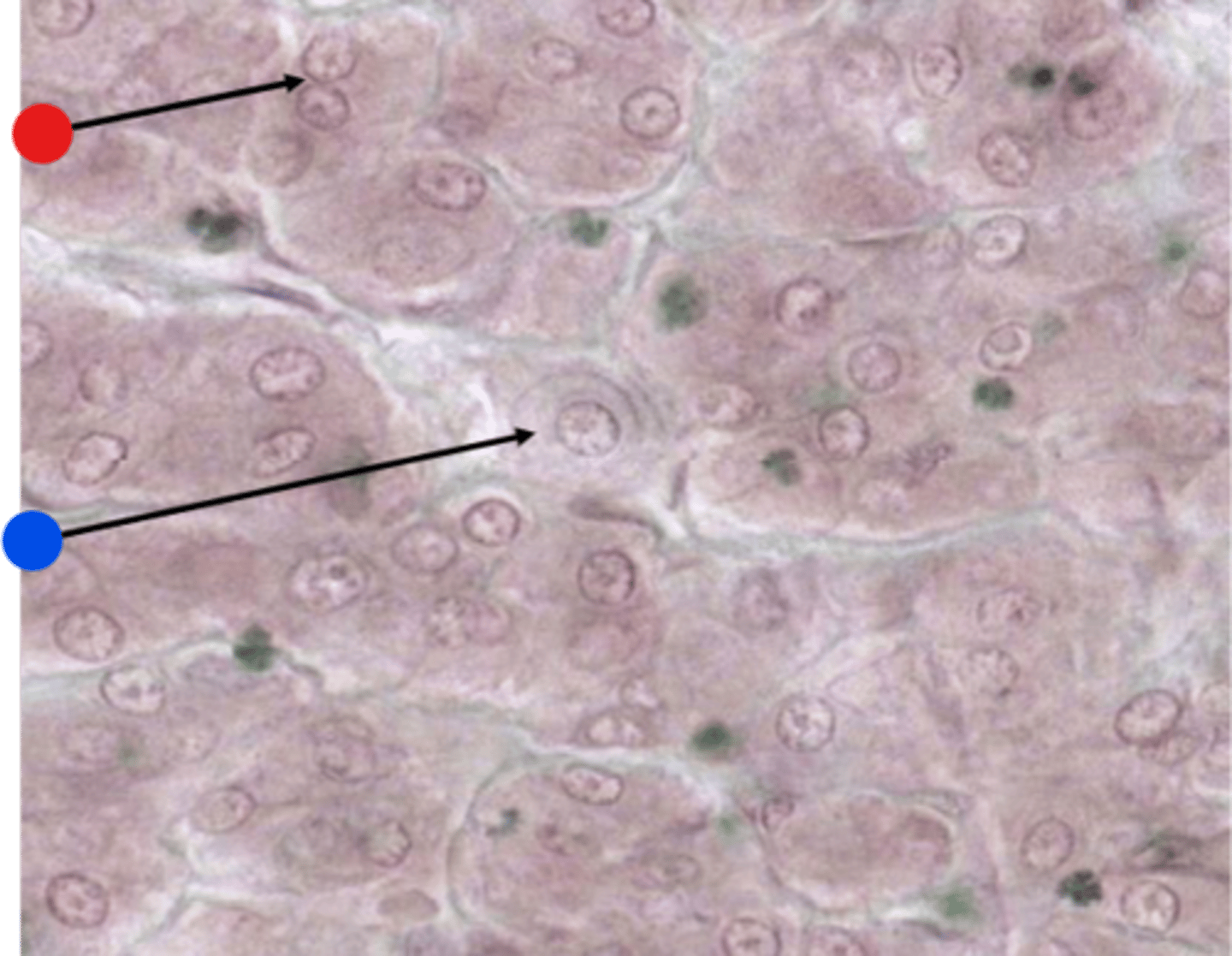
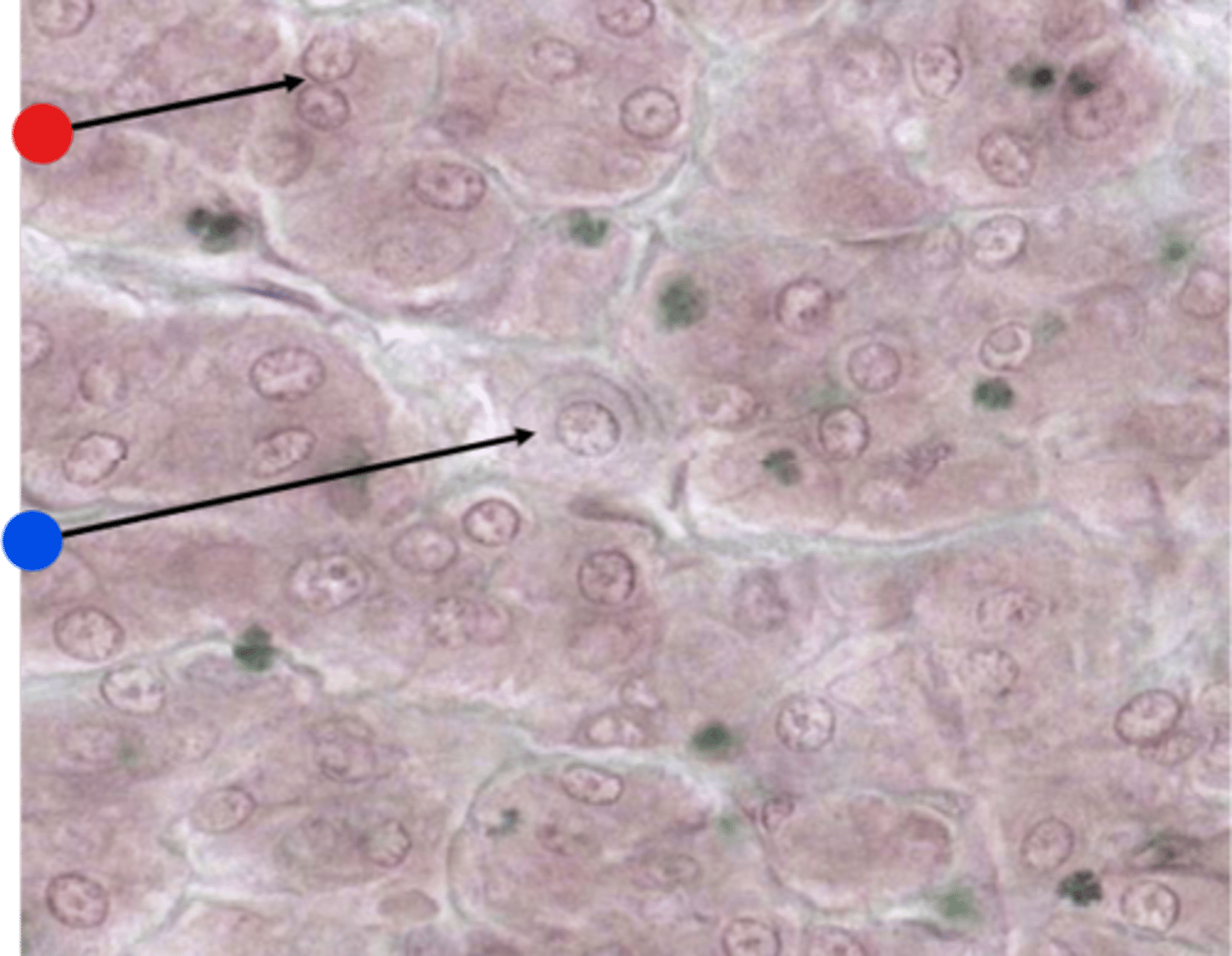
Thyroid Follicle
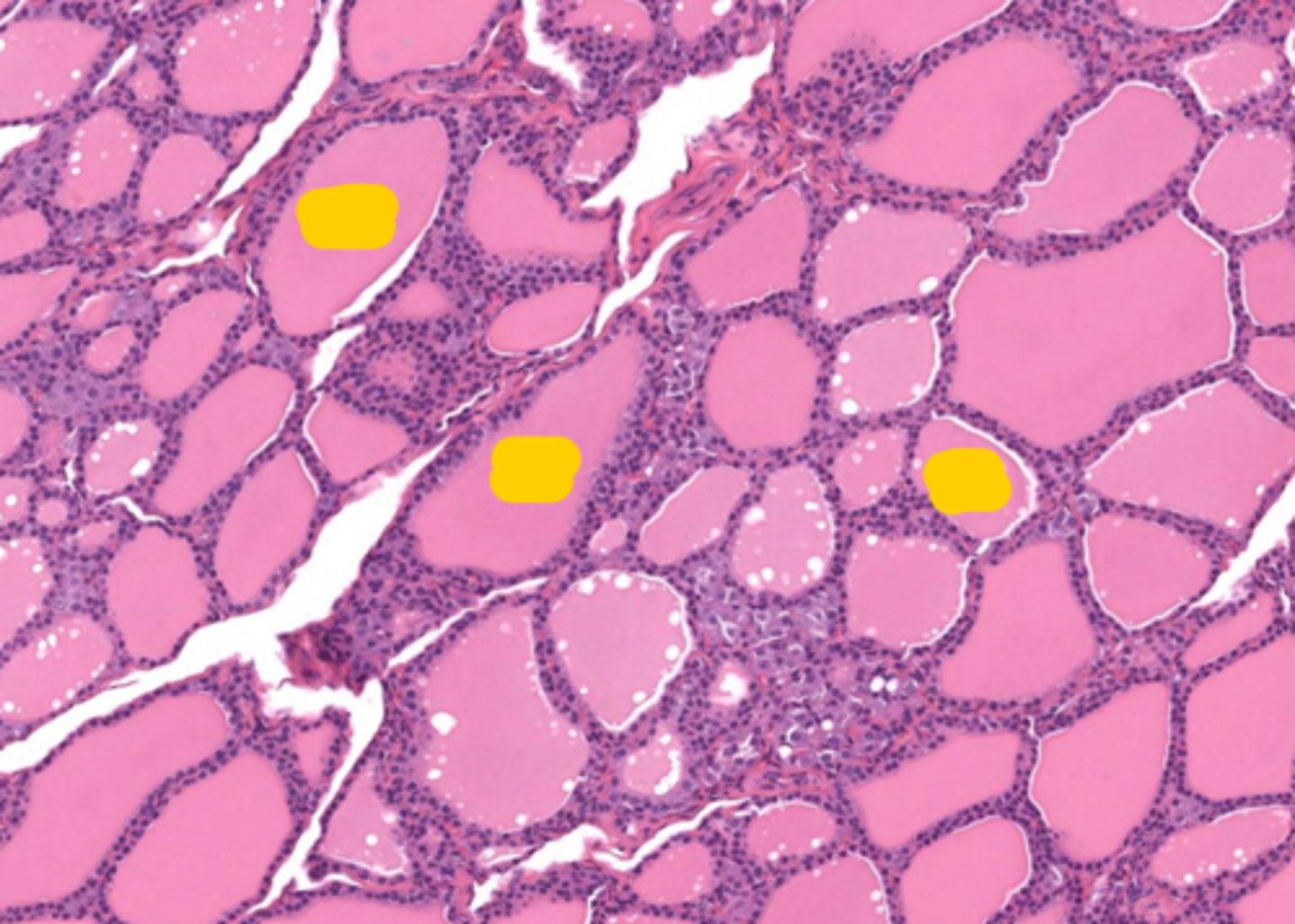
simple cuboidal thyroid follicular epithelium
What type of epithelium is shown with the arrows?
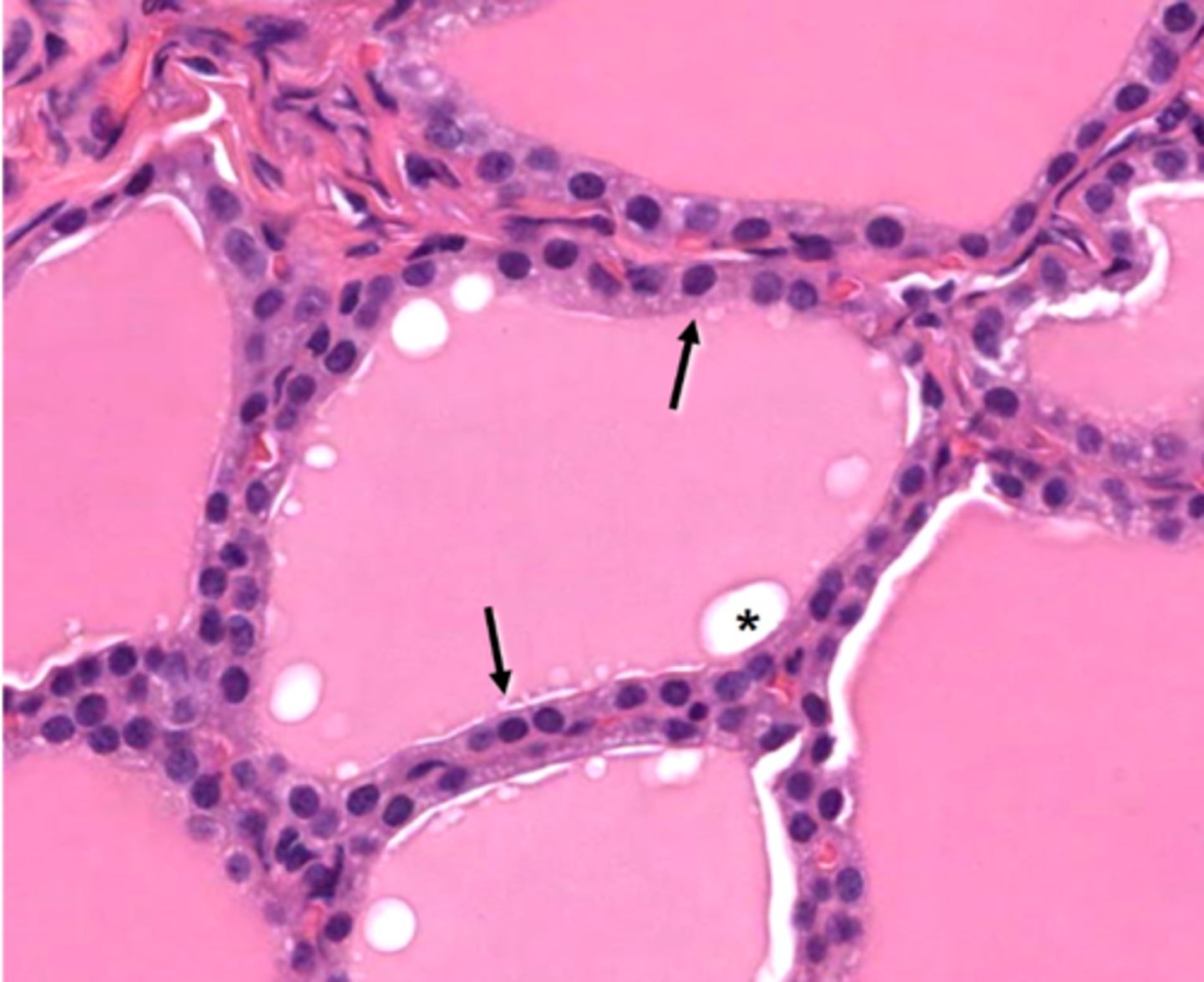
luminal membrane of the epithelial cells
*
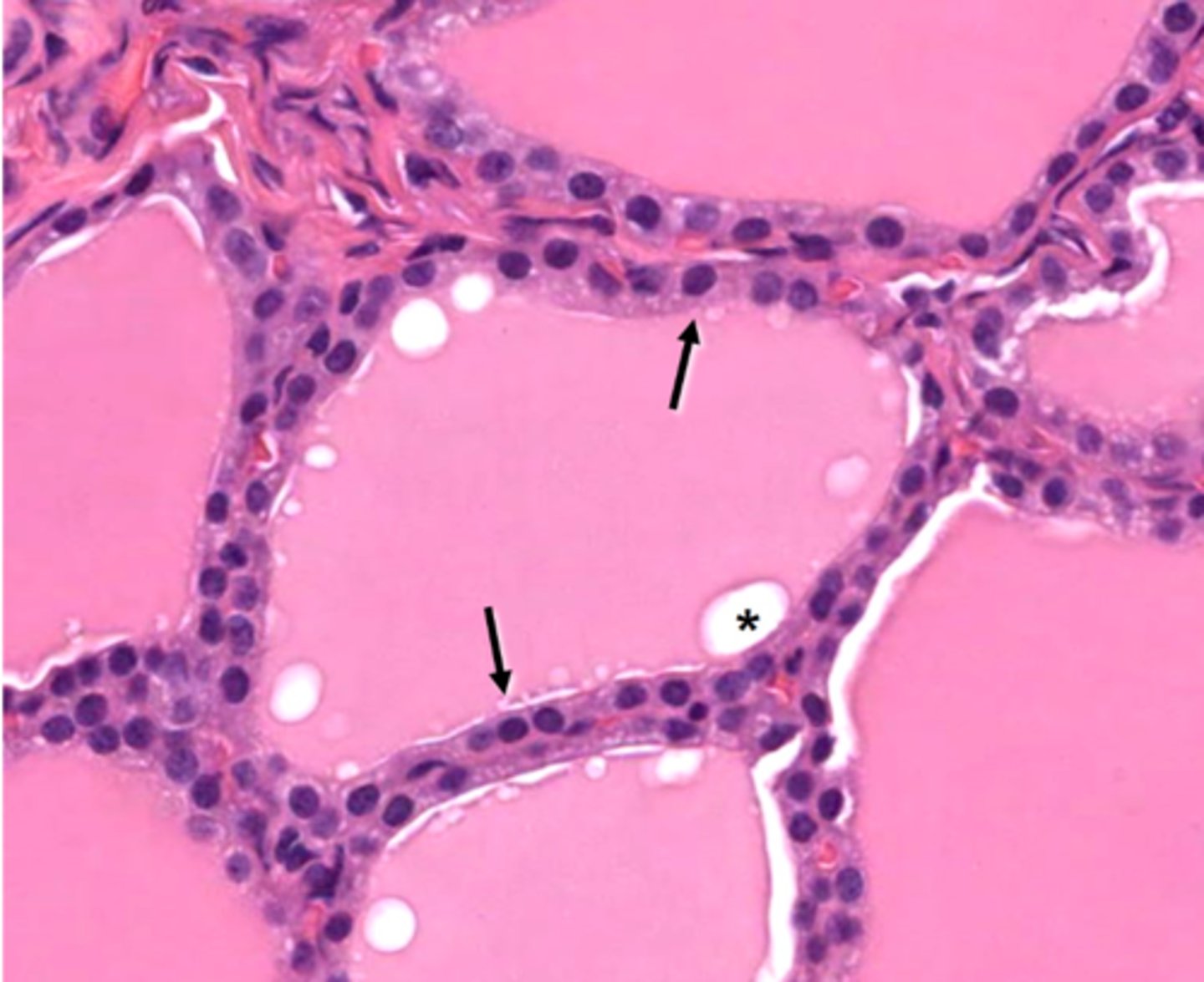
Colloid
a protein rich fluid containing thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid follicular epithelium is called what?
Thyroid medullary cells (C cells)
pituitary gland
thalamus
orange
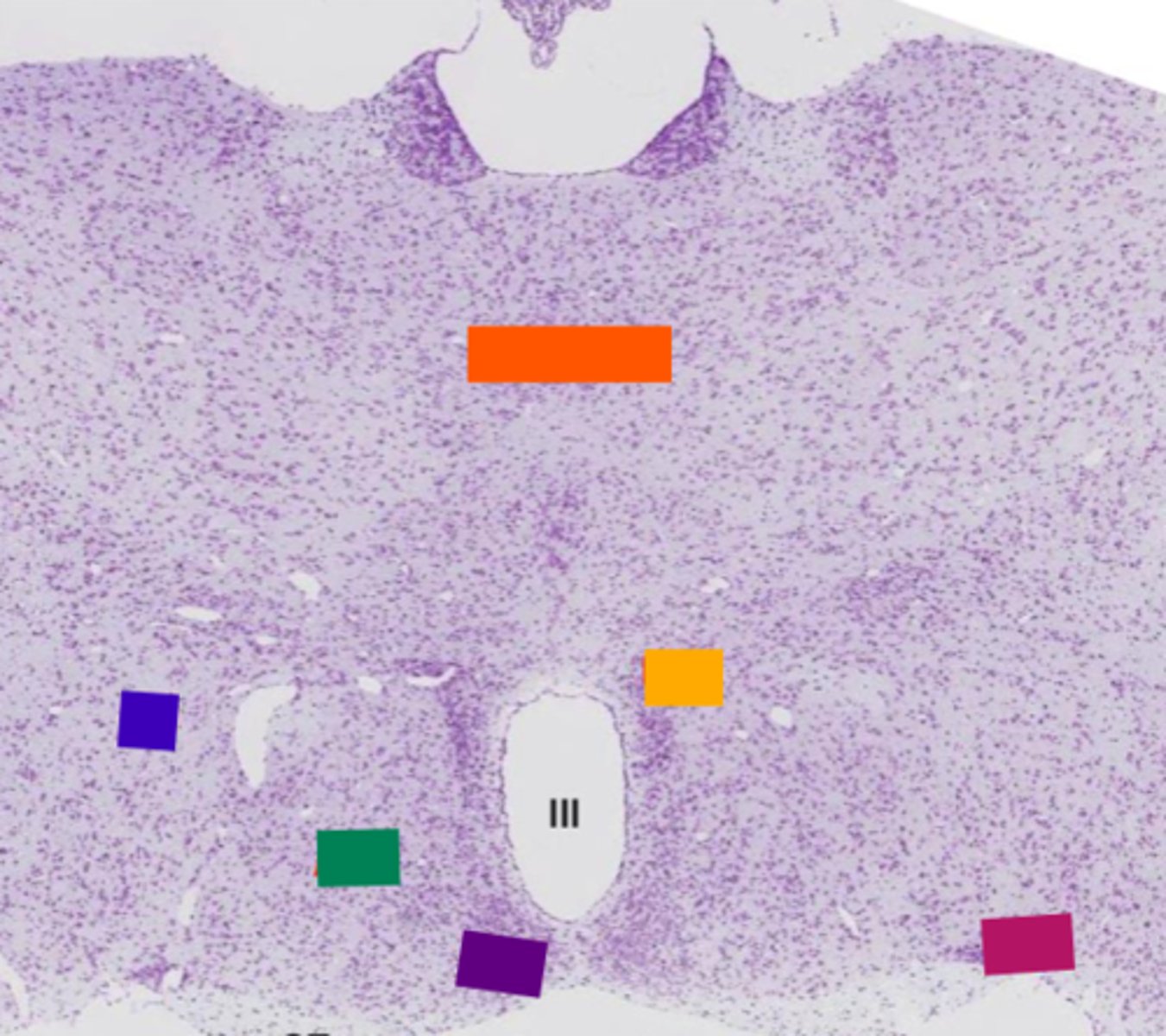
lateral hypothalamic area
blue
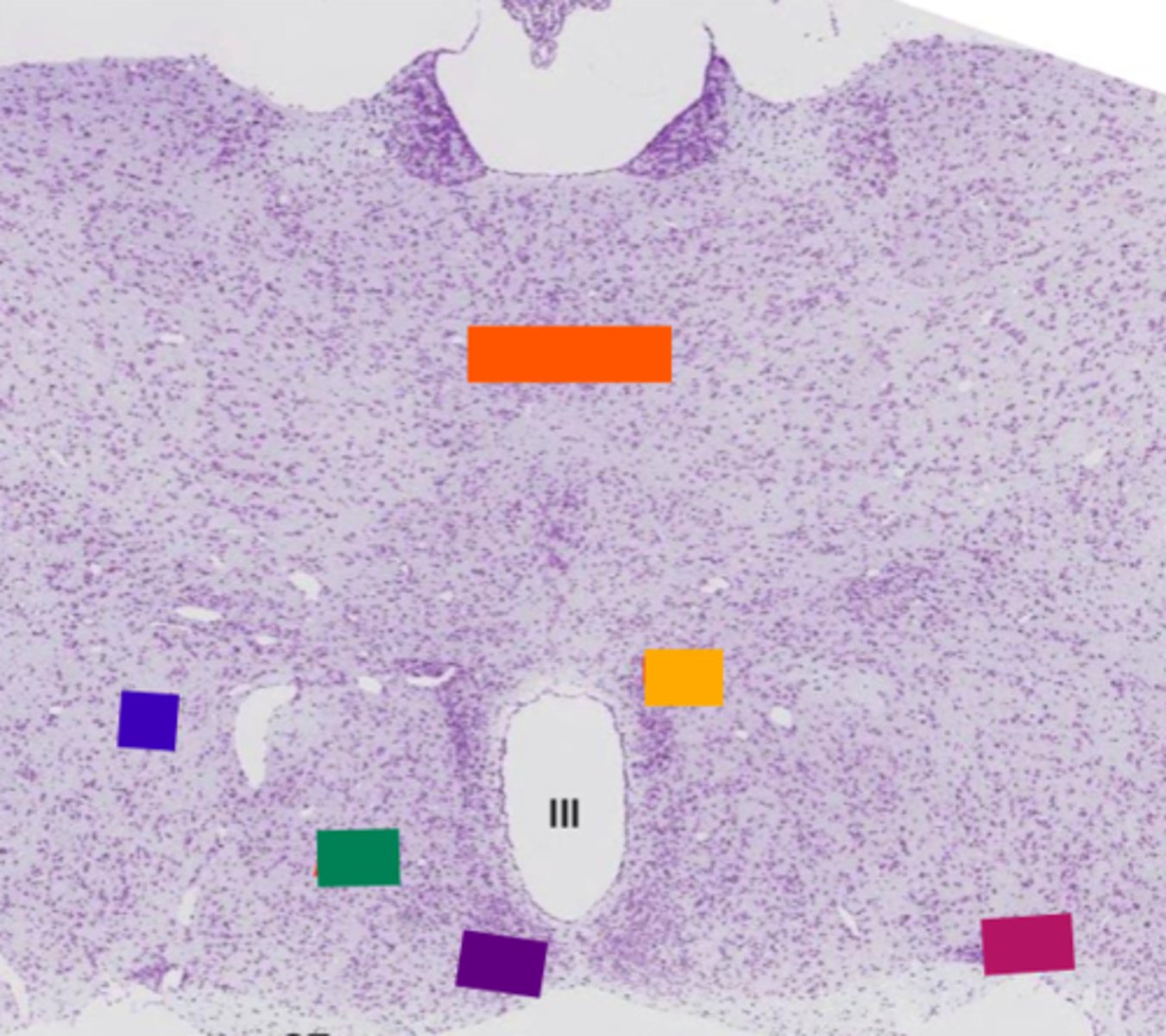
anterior hypothalamic area
green
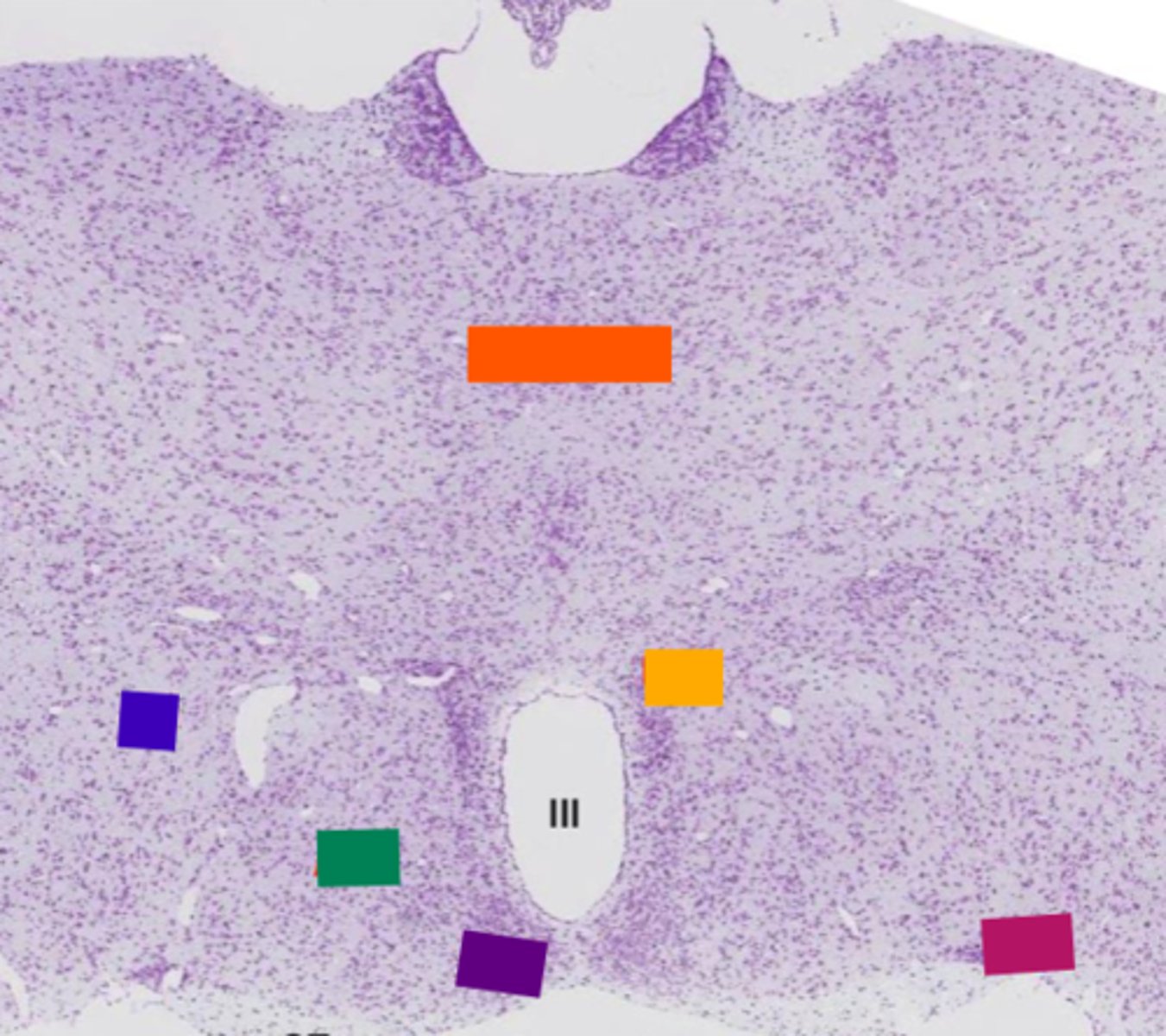
suprachiasmatic nucleus
purple
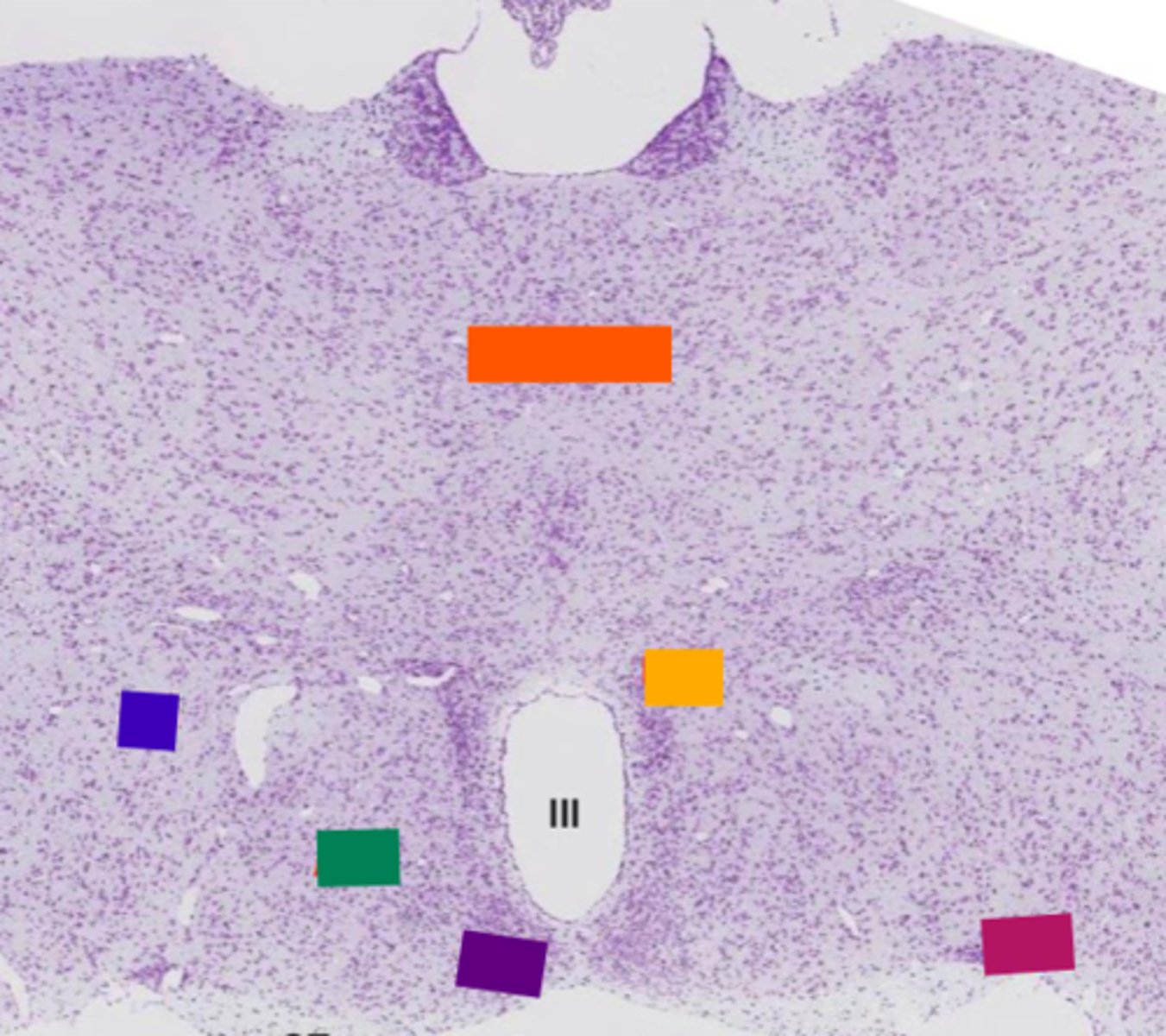
hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus
yellow
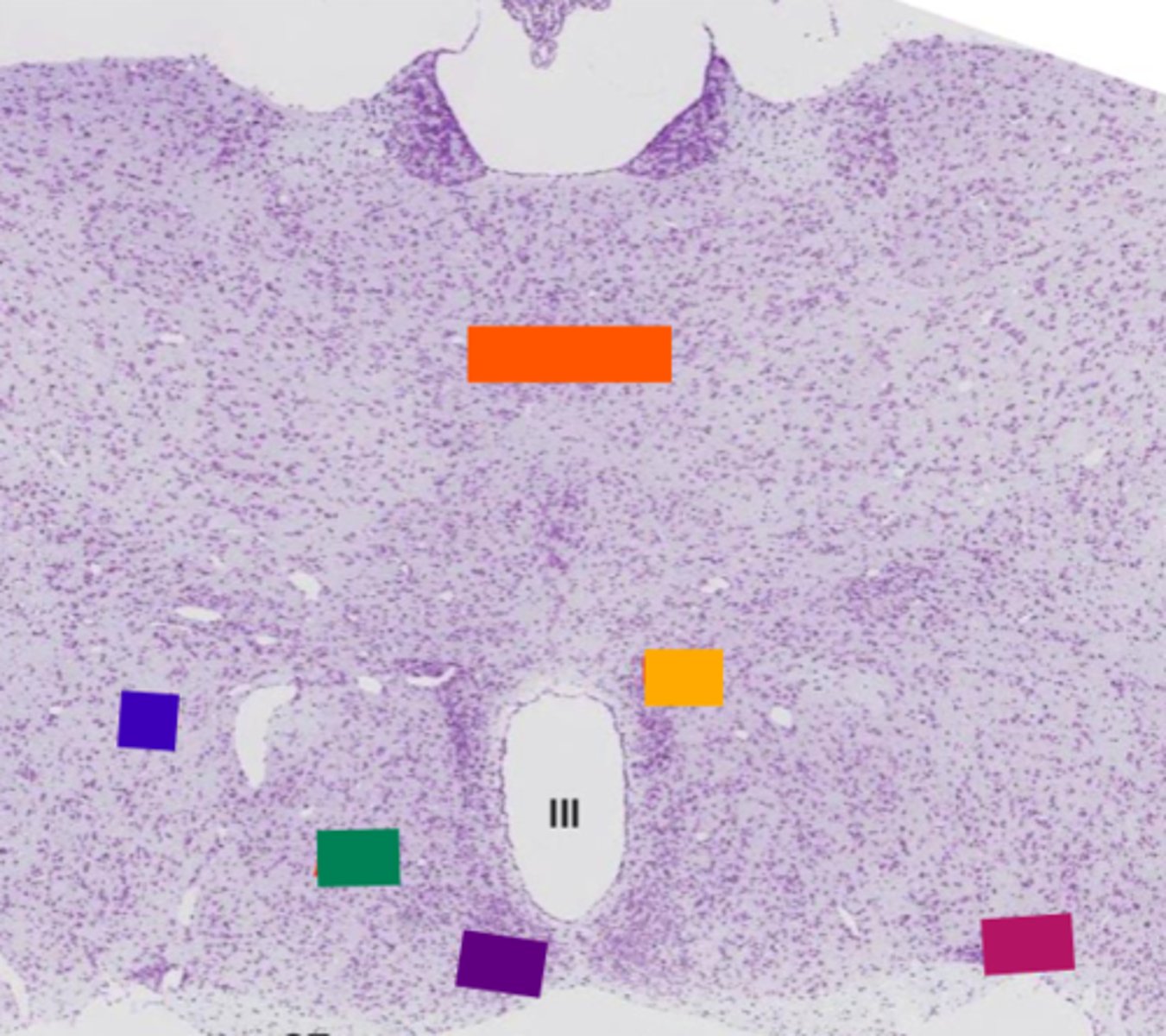
supraoptic nucleus
pink
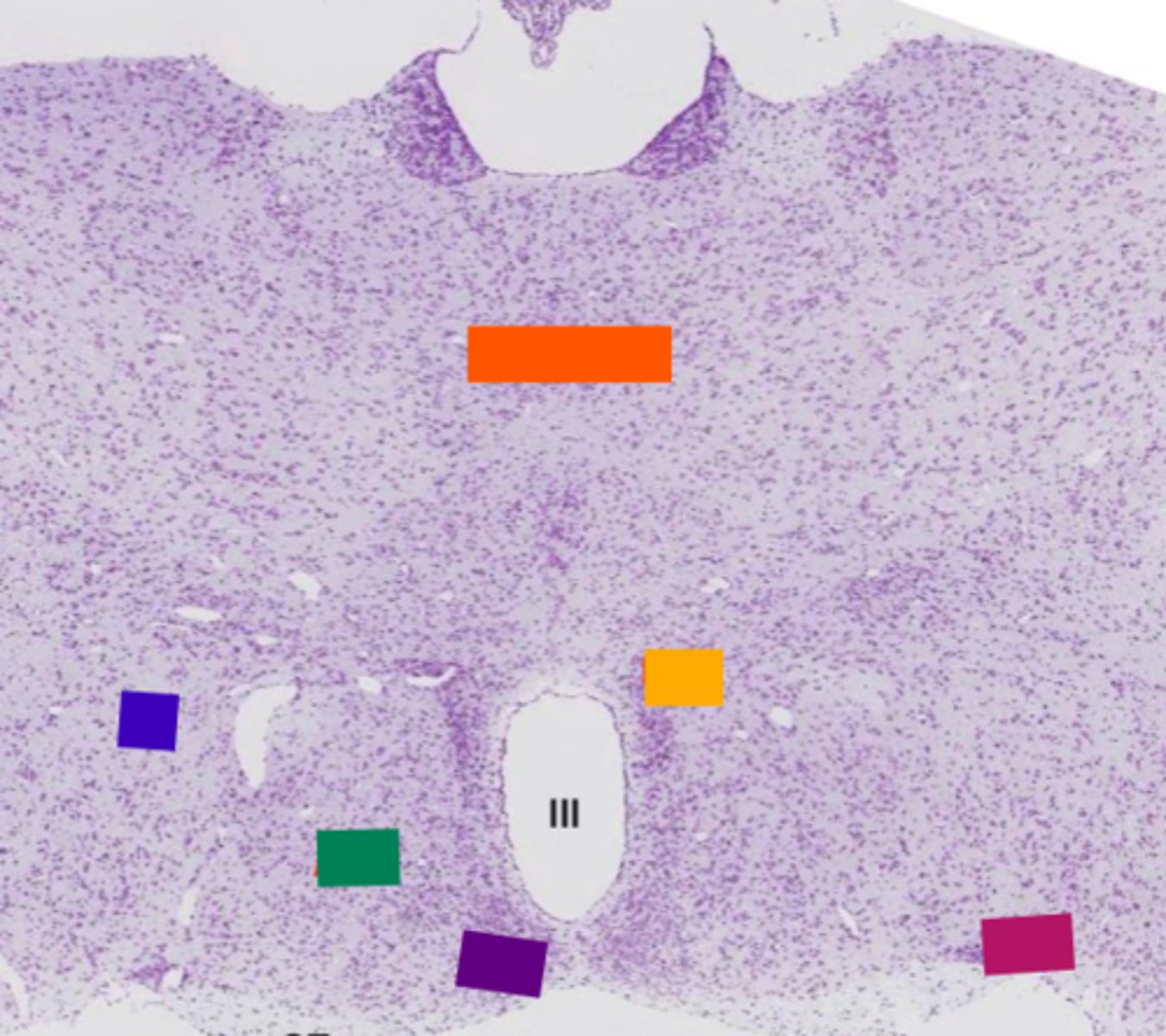
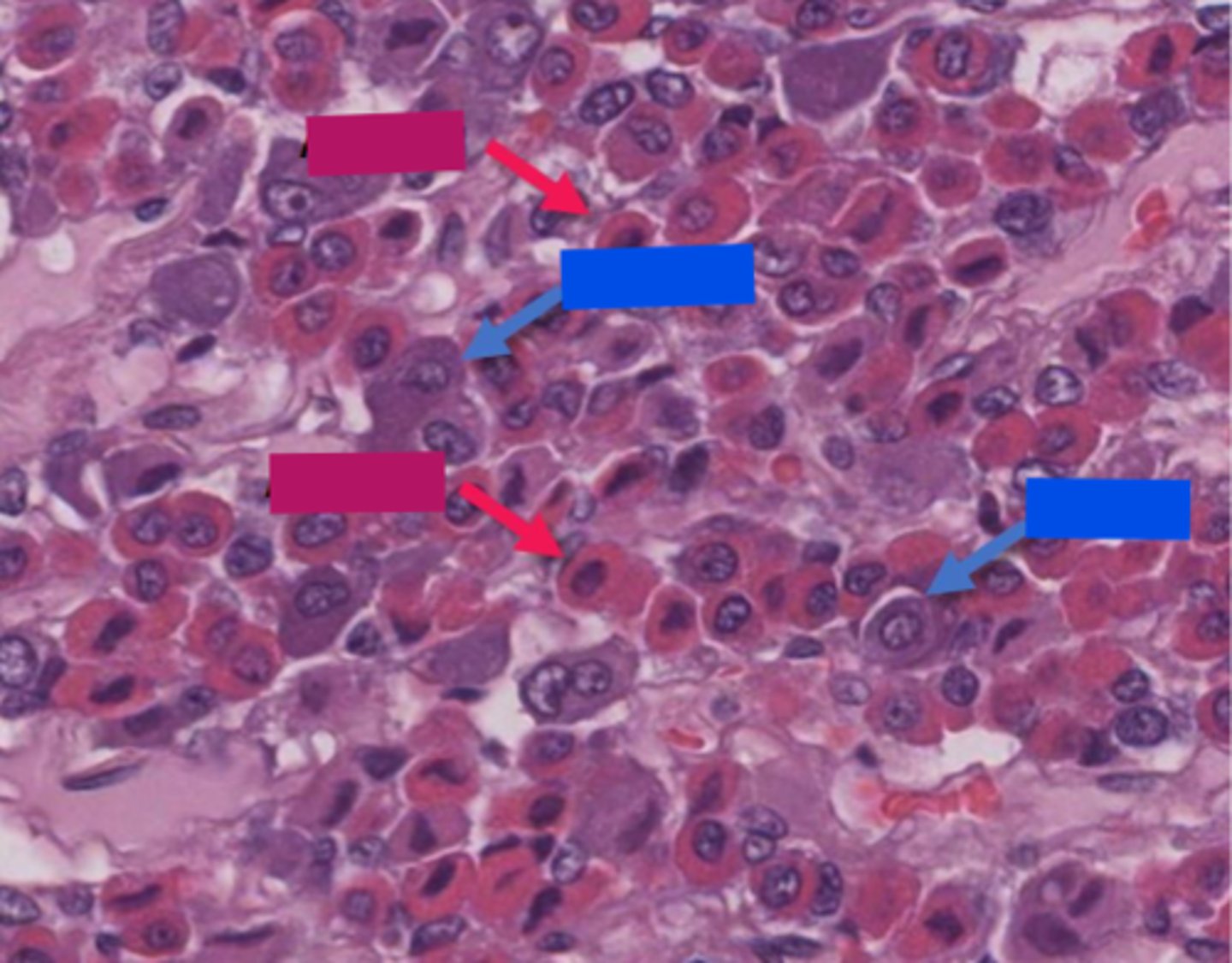
basophil
blue
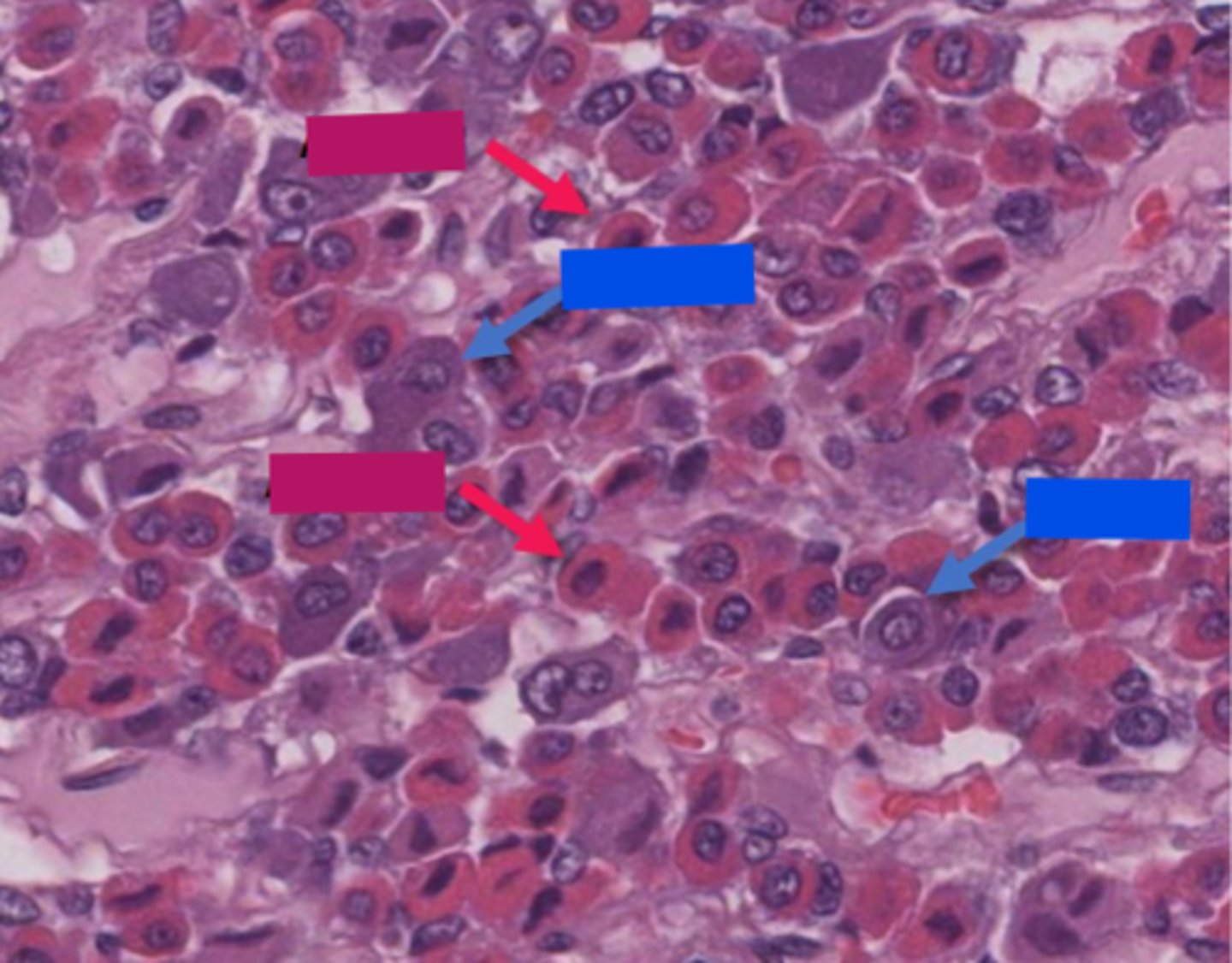
Acidophil
red
the glycoprotein thyroglobulin
What is stored in the colloid?
The thyroid gland produces the hormones in response to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland
How are T3 and T4 formed?
the hormone calcitonin
What is produced by parafollicular cells (aka C-cells)?
chief cells
yellow
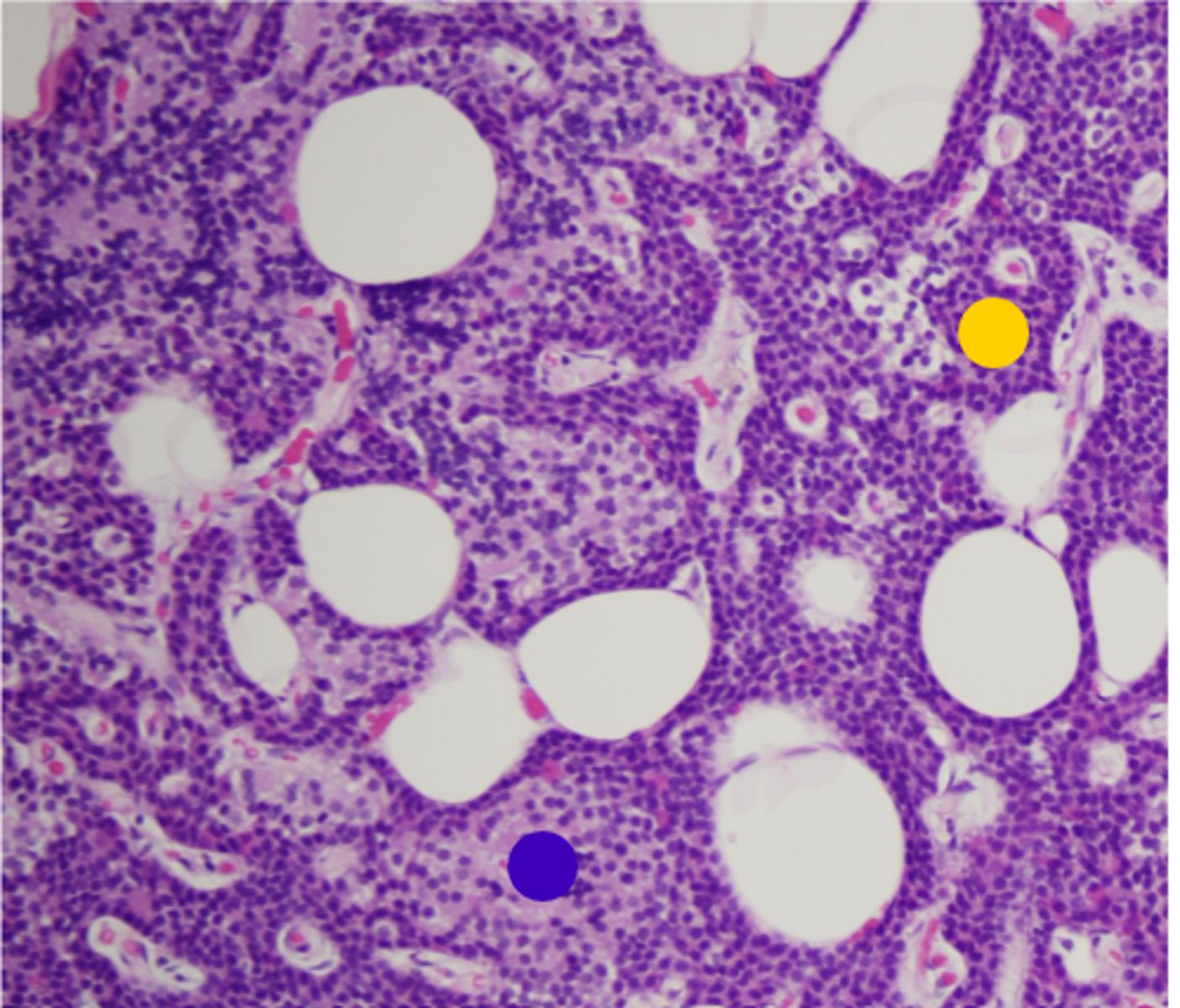
oxyphil cells
blue
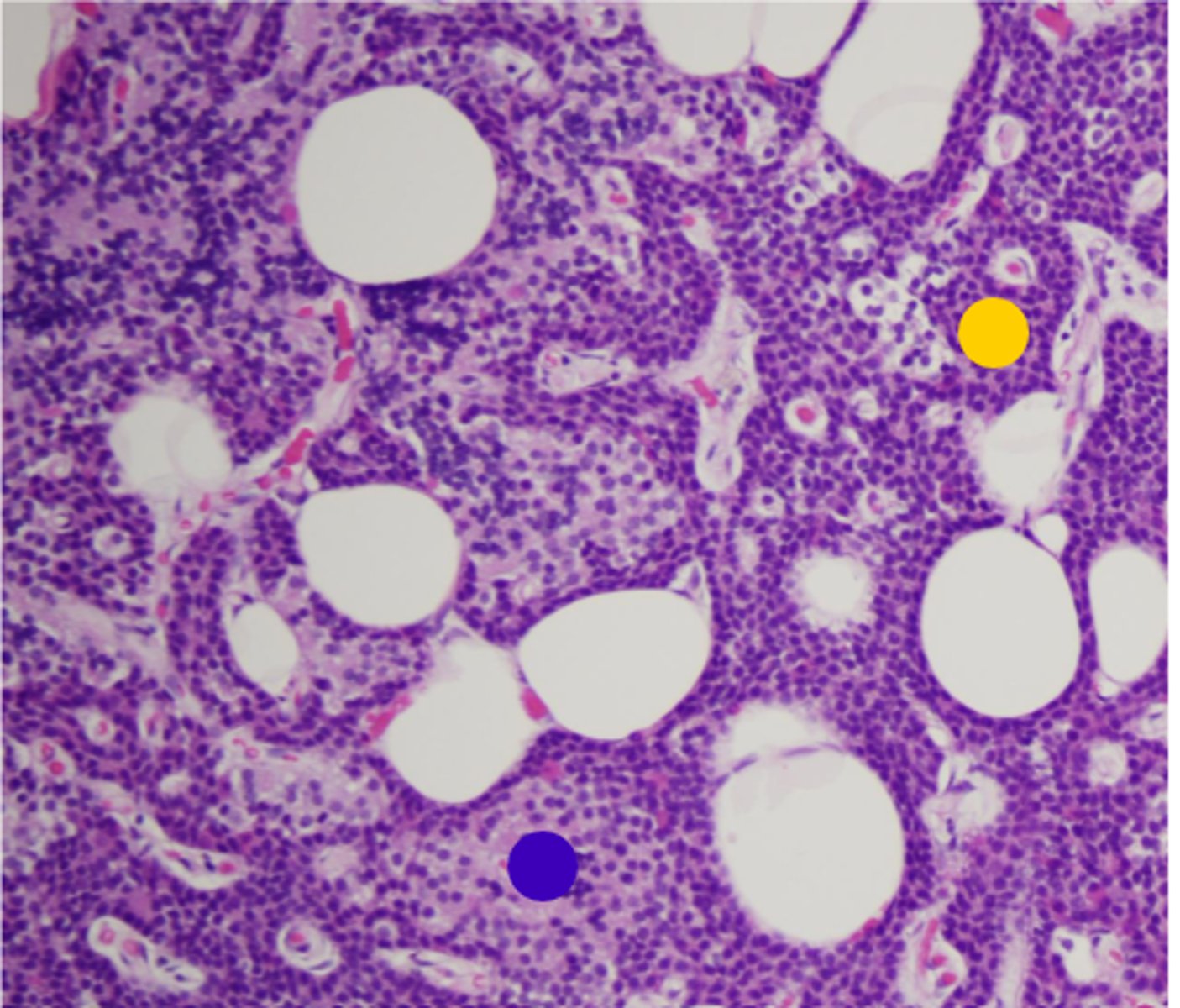
Capsule
blue
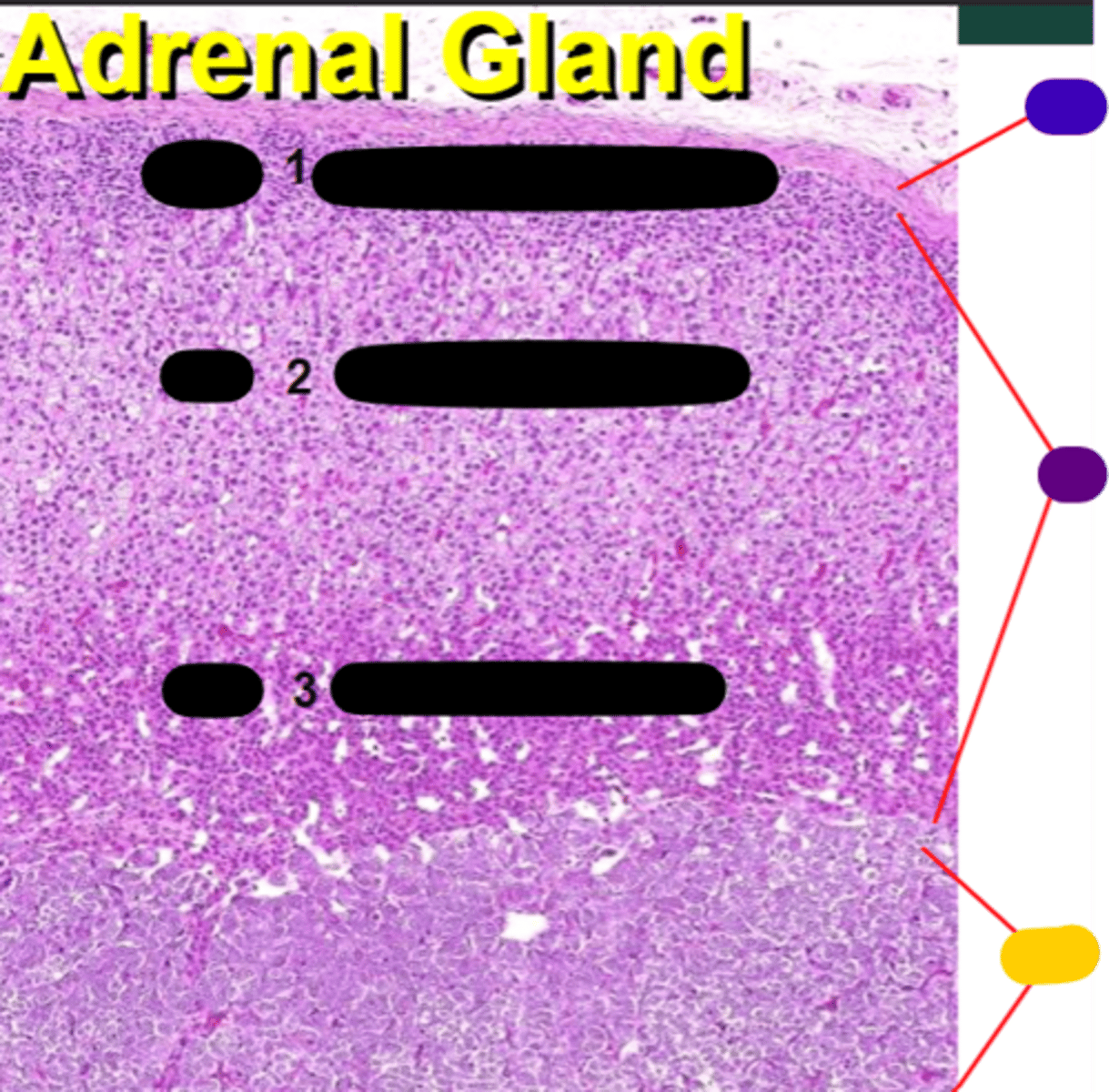
cortex
purple
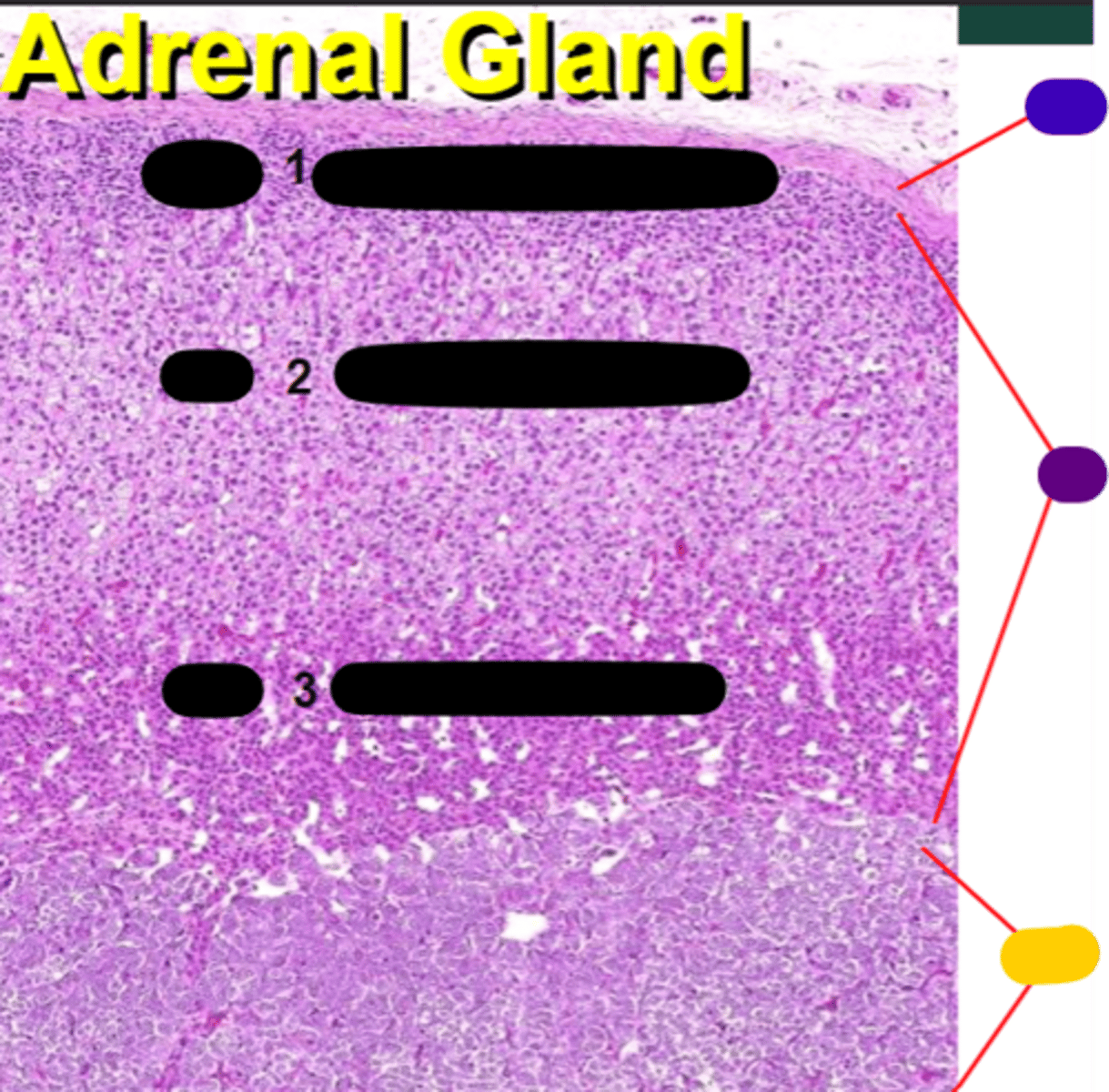
medulla
yellow
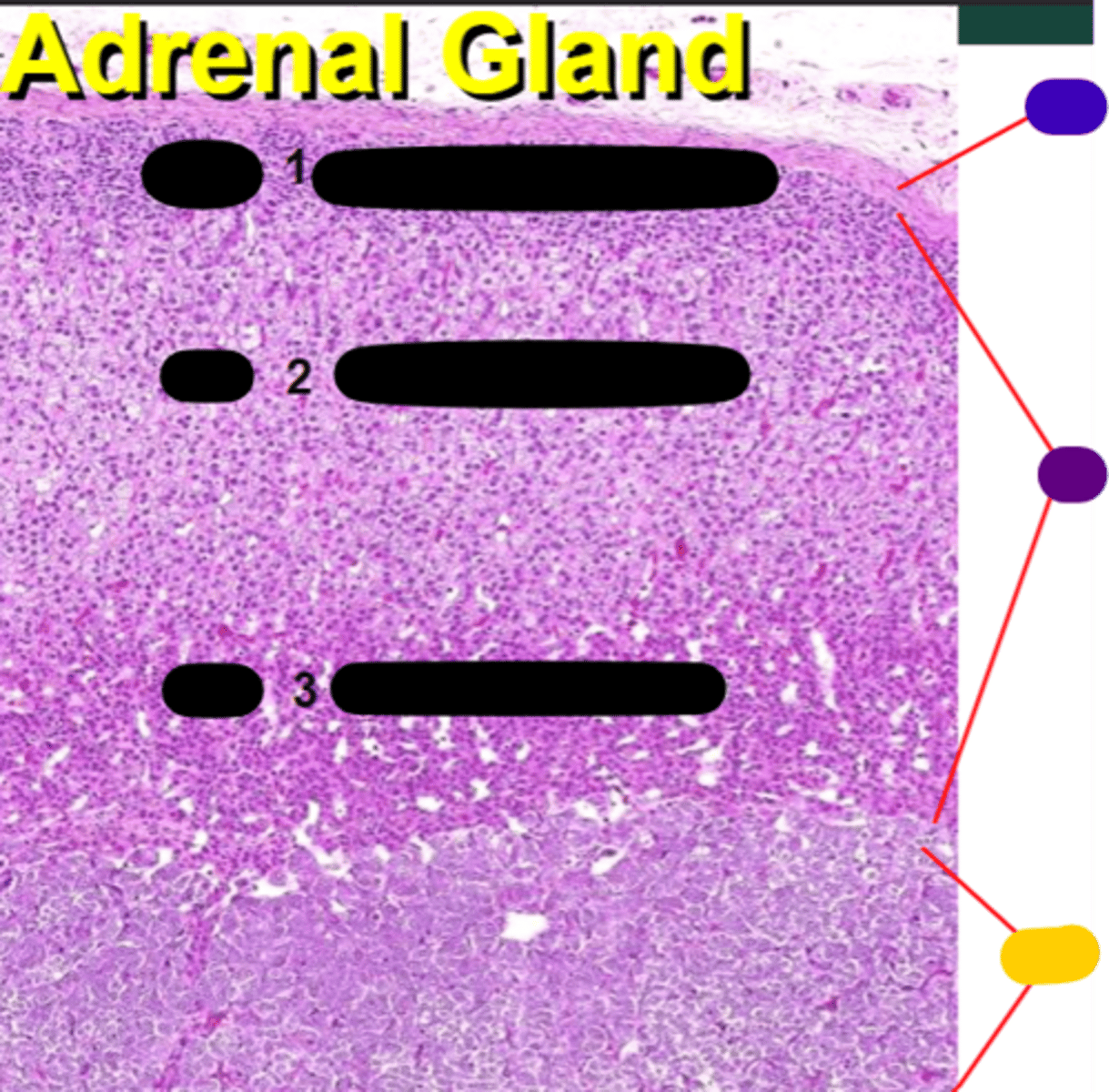
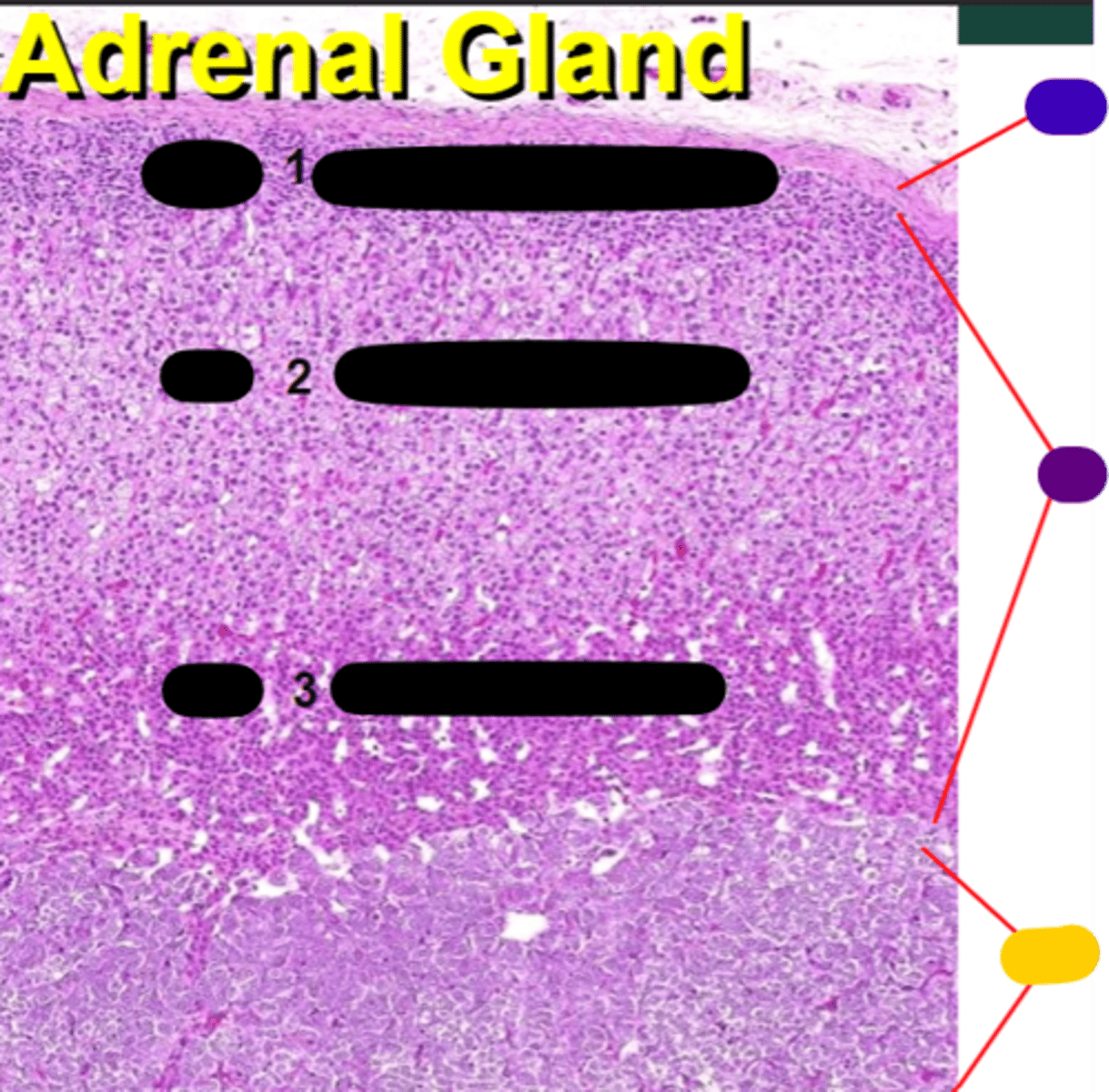
Zona glomerulosa
1
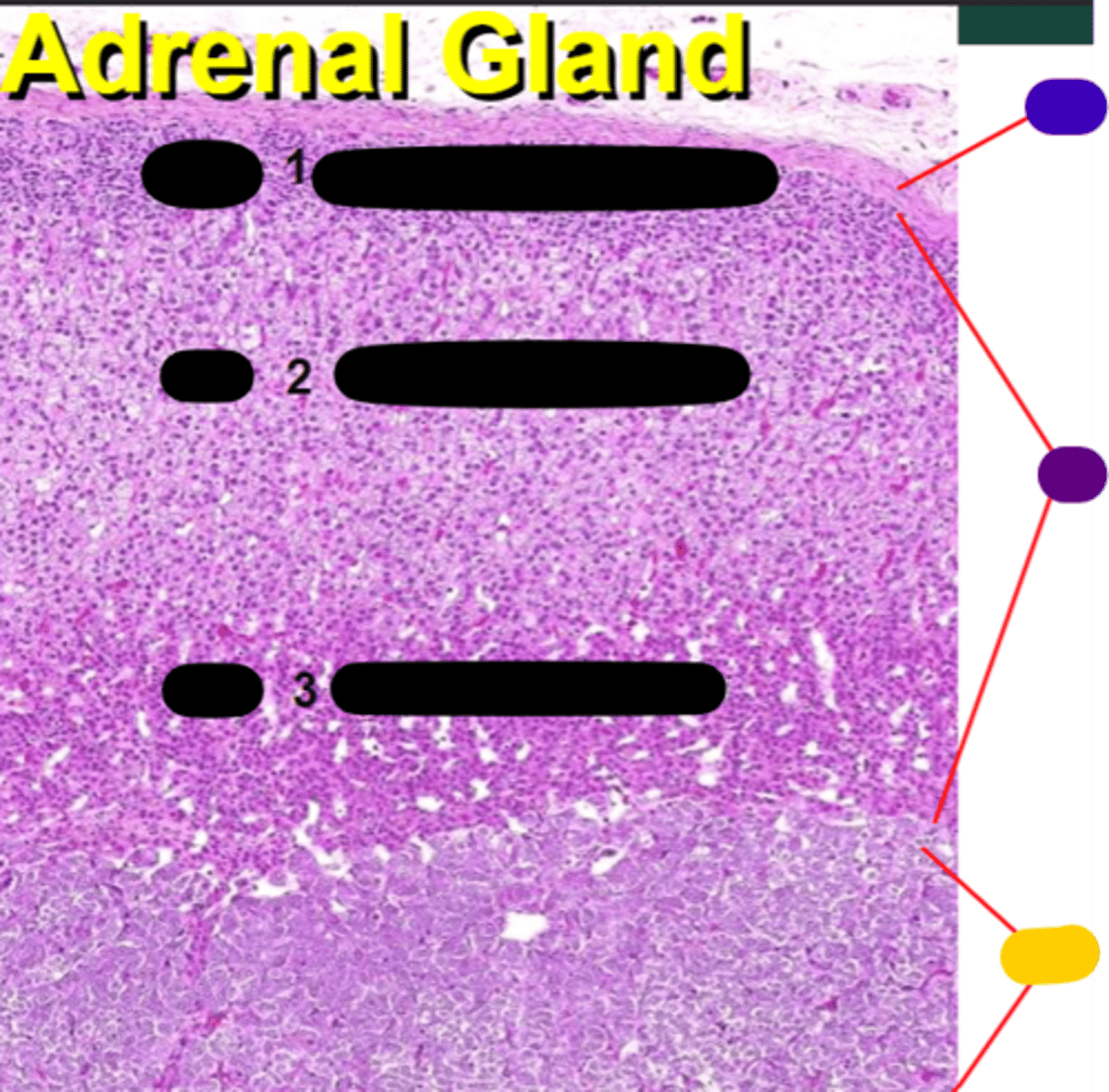
Zona fasciculata
2
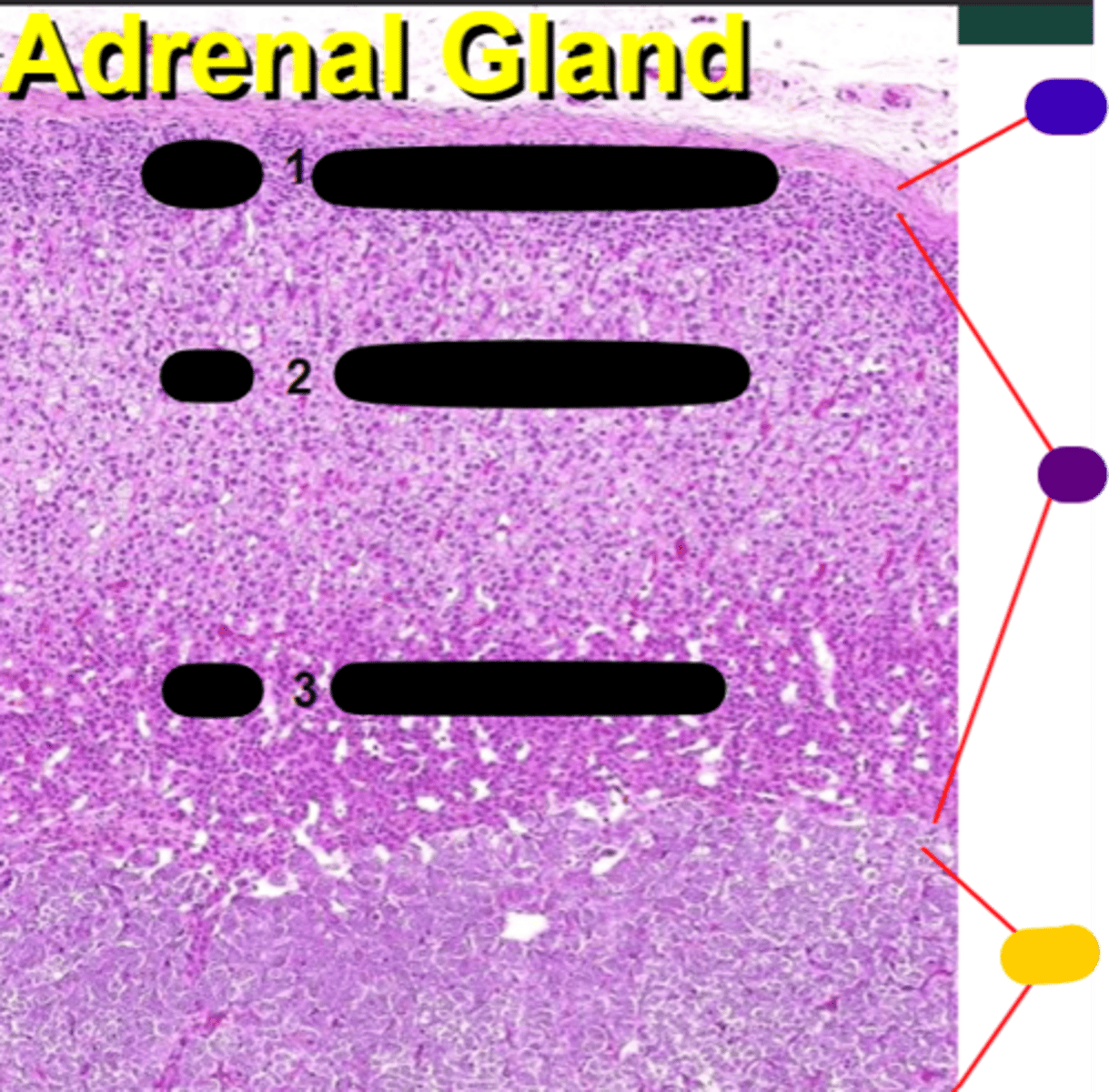
Zona reticularis
3
Sugar - Secrete glucocorticoids
Sex steroids - Secrete androgens and glucocorticoids
Chromaffin cells
red
Sympathetic Ganglion cell
blue
Exocrine pancreas
red arrow
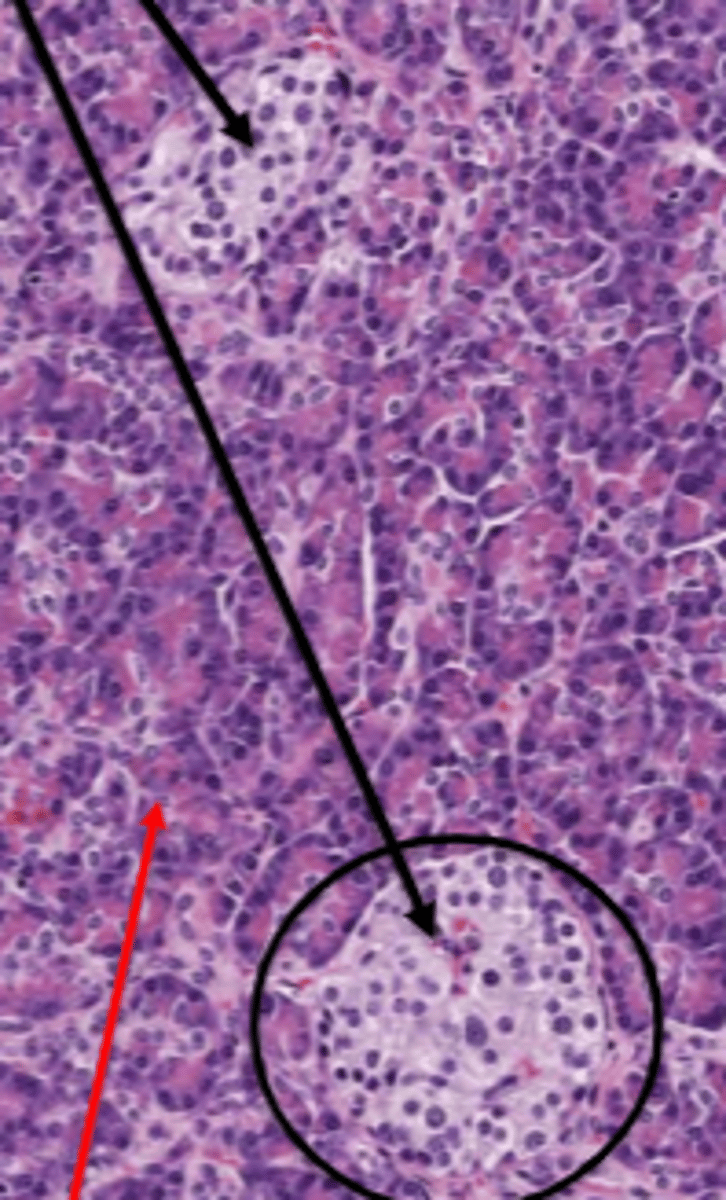
Islets of Langerhans
black arrow
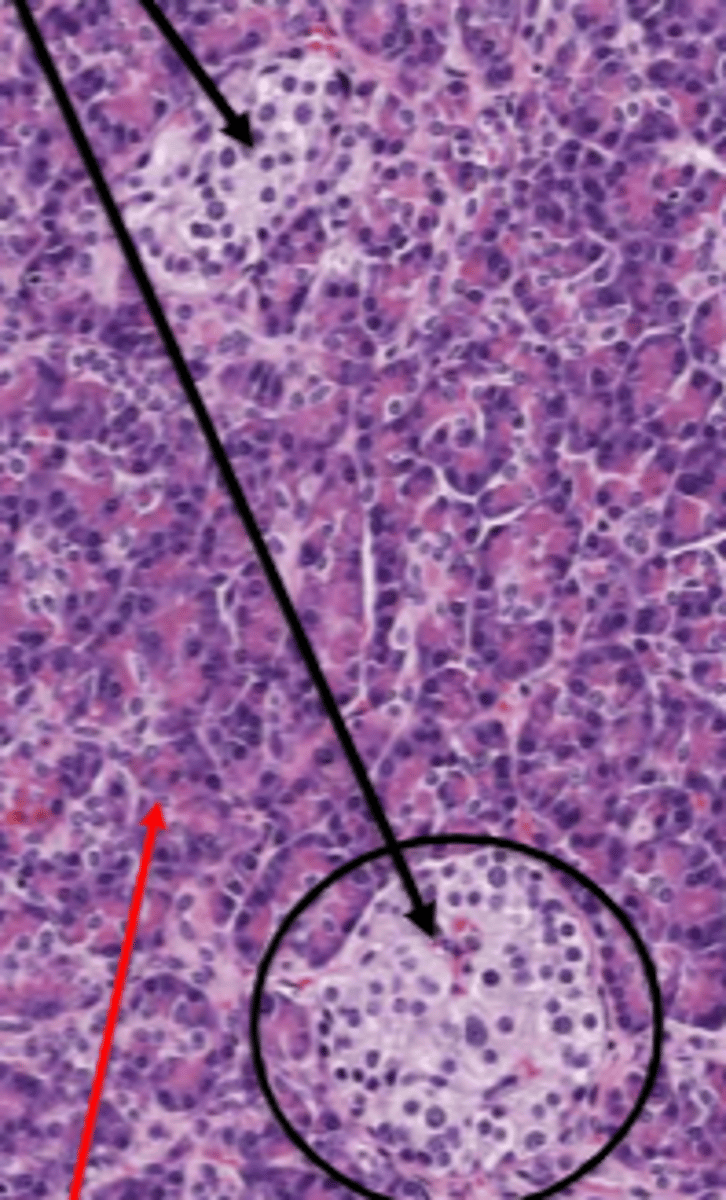
nucleus
orange
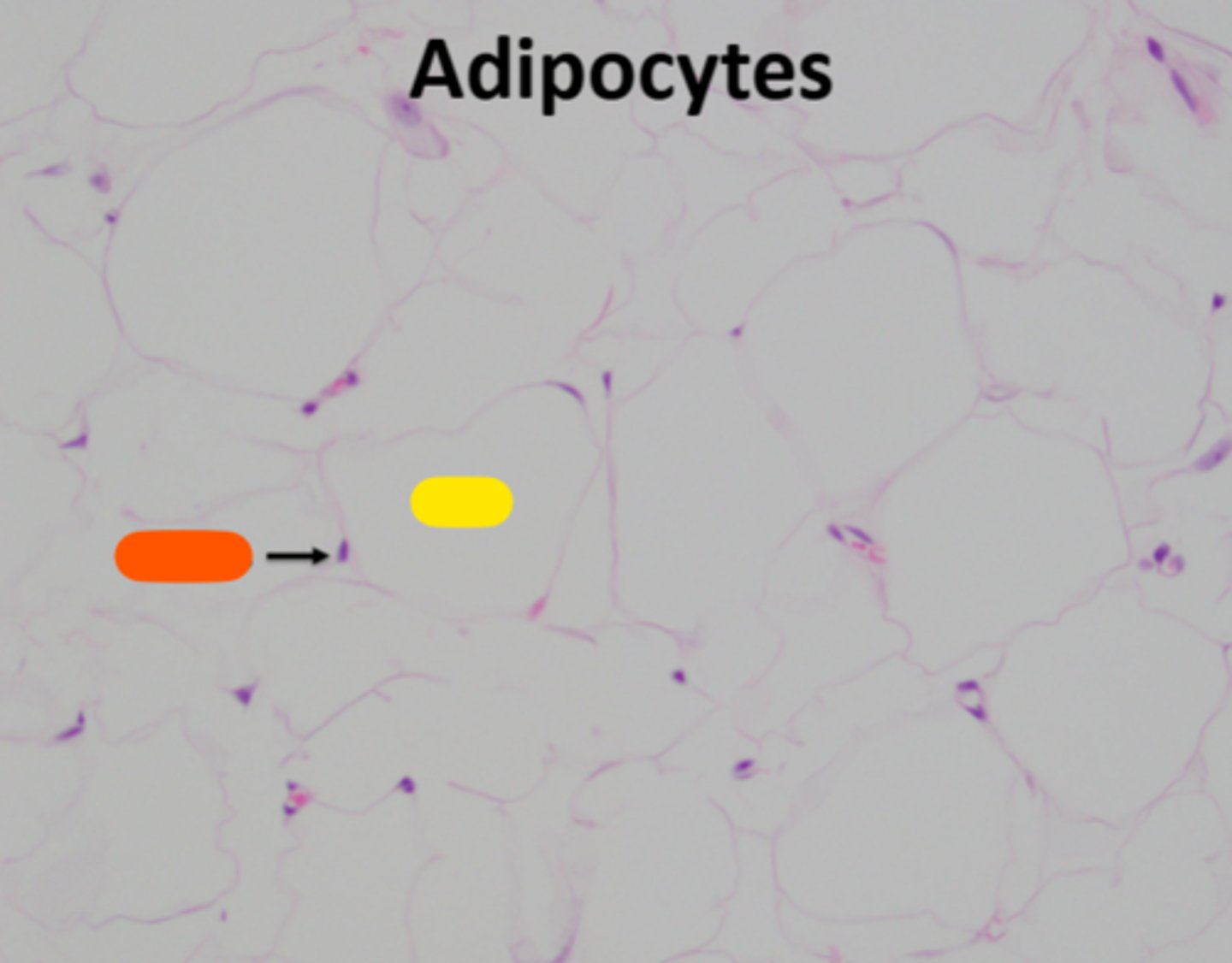
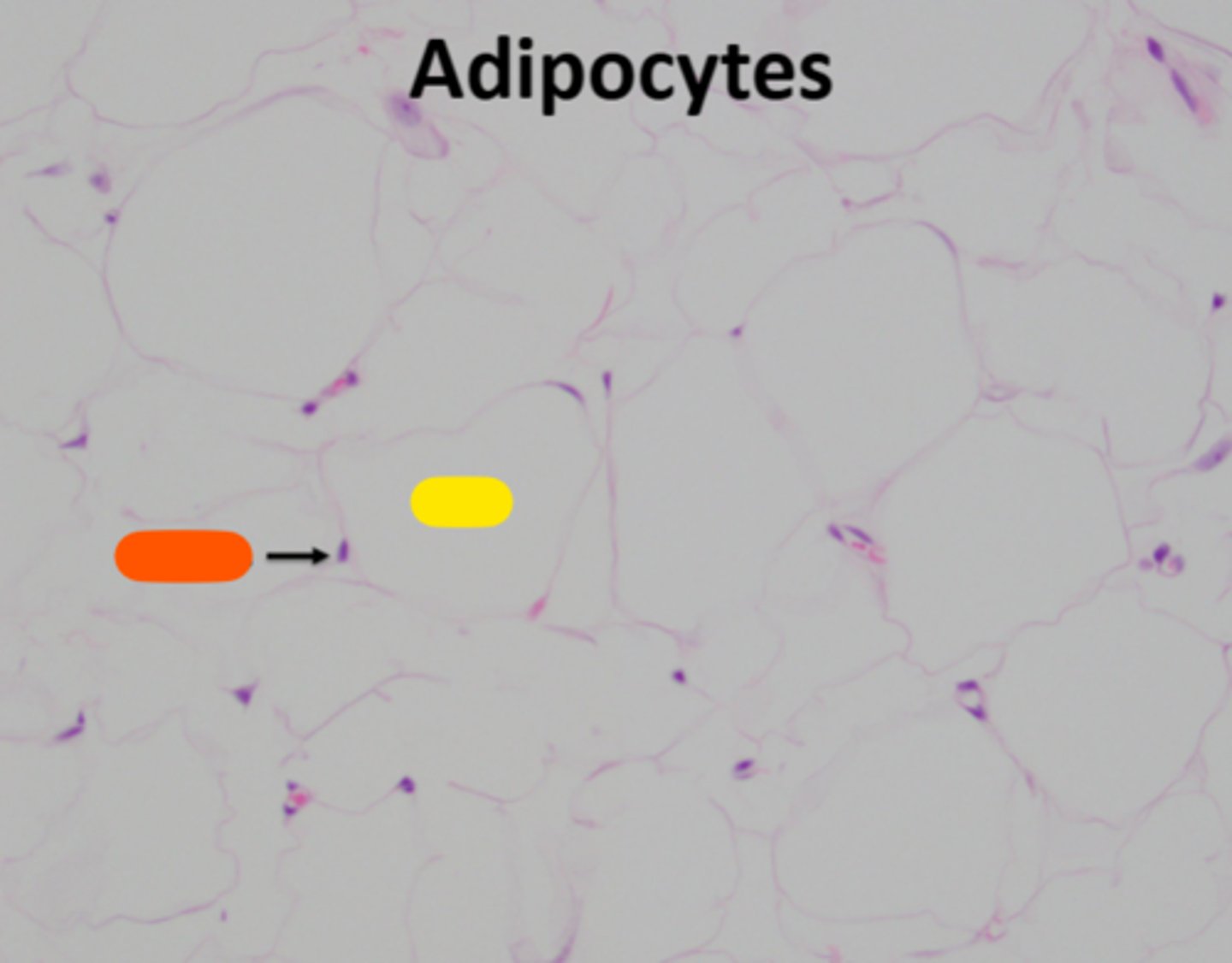
lipid
yellow
True
T or F: Serum is be the sample needed for a thyroid panel.
Low PiO2
Select the cause of hypoxemia that is typically associated with a normal AaDO2
a) V/Q mismatch
b) Low PiO2
c) Right-to-Left shunt
d) Diffusion impairment
Horse
Which species does not have a gallbladder?
True
T or F: The cannon bone in the cow is made of up fused 3rd and 4th metacarpal bones.
True
T or F: The endocrine system and the nervous system play a major role in homeostasis.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Proteins/peptides, steroids, and amines are categories of hormones. Which one of the following proteins is a hormone?
a) Oxytocin
b) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
c) Mineralocorticoids
d) Progesterone
e) Dopamine
False
T or F: The hypothalmus secretes stimulating hormones.
disrupted body temperature, growth, milk production
Damage to the hypothalmus can result in what signs? Please choose the most correct answer.
a. disrupted body temperature, growth, milk production
b. disrupted digestion, metabolism, sodium and water balance
c. disrupted sleep cycles, fractures, sex characteristics
the yellowish clear fluid you pipette off the top of a spun down red top tube
Serum is:
a. the yellowish clear fluid you pipette off the top of a spun down red top tube
b. the yellowish clear fluid you pipette off the top of a spun down purple top tube
c. the yellowish clear fluid you pipette off the top of a spun down green top tube
d. the contents of a purple top tube before it is spun down
False
T or F: Growth Hormone Increases protein production, increases fat stores, and conserves carbohydrates.
increased blood glucose
Which of these inhibits Growth Hormone secretion?
a. decreased free fatty acids
b. starvation
c. increased blood glucose
duodenocolic ligament
Which item is not associated with the horse cecum?
a. haustra
b. duodenocolic ligament
c. ventral band
d. Ileocecal fold
ventrodorsal
Name this view
True
T or F: The fetlock of the horse is also called the metacarpophalangeal joint.
kidney, spleen, large colon
If I were to ultrasound the left dorsal quadrant of the abdomen I would most commonly see:
a. kidney, cecum, duodenum
b. kidney, spleen, large colon
c. kidney, stomach, pelvic flexure
d. spleen, liver, small intestine
Paraventricular nucleus (PVN)
Supraoptic nucleus (SON)
Which hypothalamic nucleus produces the hormones of the posterior pituitary?
a. Suprachiasmatic nucleus
b. Paraventricular nucleus
c. Supraoptic nucleus
d. Arcuate nucleus
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
Prolactin
Growth Hormone
Which of the following hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary? Choose all that apply.
a. Oxytocin
b. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
c. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone
d. Prolactin
e. Growth Hormone
hair coat
hooves
body condition score
For an endocrine physical exam, what items should be a focus?
a. hair coat
b. hooves
c. body condition score
d. lung sounds
Tip of the frog
Where would I put pressure with hoof testers if I was concerned about laminitis (this is a painful condition in the horse where the tip of the coffin bone rotates downwards)?
a. Tip of the frog
b. Seat of corn
c. on the sole near the quarter
d. across the heels
Tyrosine and iodide are critical for the synthesis of thyroid hormones
Which of the following is true regarding the synthesis and storage of thyroid hormones? (Choose the single most appropriate answer)
a. Thyroid hormone is a protein hormone
b. Tyrosine and iodide are critical for the synthesis of thyroid hormones
c. In the thyroid follicles, intracellular iodide concentrations are much lower than extracellular concentrations
d. The majority of T3 is formed inside the thyroid gland
increase
After thyroidectomy, serum TSH levels will (Choose the single most appropriate answer)
a. decrease.
b. remain unchanged.
c. increase.
Cervical swelling due to enlargement of the thyroid gland(s); usually from blockade of thyroid hormone synthesis due to iodine deficiency or inhibition of thyroperoxidase (e.g. sulfonamides). Can occur with hyperthyroidism and neoplasia as well.
What is goiter and its usual etiology?
a. Cervical swelling due to enlargement of the thyroid gland(s); usually from blockade of thyroid hormone synthesis due to iodine deficiency or inhibition of thyroperoxidase (e.g. sulfonamides). Can occur with hyperthyroidism and neoplasia as well.
b. Weight gain or difficulty losing weight; usually from lack of catabolic actions of T3 and T4
c. Nonpruritic hair loss; usually due to T4 and T3 deficiency resulting in loss of the cycle of hair growth and shedding
d. Weight loss and hyperactivity; usually due to behavioral and metabolic effects of excess T3 and T4
TSH, T4 and T3, Thyroglobulin autoantibody
A canine diagnostic thyroid panel assesses thyroid-related pituitary function as __________, thyroid hormone production and activation as _________________, and screens for autoimmune thyroid disease using _____________.
a. TRH, TSH, IL-10
b. TSH, T4 and T3, Thyroglobulin autoantibody
c. TRH, rT3 and T4, TSH autoantibody
d. TSH stimulation, T3, Thyroglobulin autoantibody
True
T or F: Hypoventilation is characterized by increased PaCO2.
Thyroid hormone synthesis
The main use of iodine in the body is:
a. Thyroid hormone synthesis
b. Muscle growth
c. Peristalsis
d. Phagocytosis
night
The pineal gland (in the continental USA) is most active at:
a. night
b. day
c. twilight
Increased heart rate
Which of the following signs would you expect to occur in hyperthyroidism? (Choose the single most appropriate answer)
a. Increased heart rate
b. Lethargy and dullness
c. Lack of appetite
d. None of the above
Thyroid hormone levels will not change
Which of the following would happen if you inject TSH into a dog that has primary hypothyroidism?
a. Thyroid hormone levels will increase
b. Thyroid hormone levels will not change
c. Thyroid hormone levels will decrease
IGF-1
In the case of a dwarf german shepherd, what hormone would we be most clinically relevant to measure?
a. GH
b. IGF-1
c. ACTH
d. GHRH
Growth hormone is a protein hormone
Which of the following is true regarding the synthesis and storage of growth hormone and related areas?
a. Growth hormone is a protein hormone
b. Cholesterol is critical for the synthesis of growth hormone
c. The source of growth hormone is the posterior pituitary.
d. The majority of IGF-1 is formed inside the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism is more common in dogs
Which of the following is true regarding hypothyroidism in companion animals?
a. Hypothyroidism is more common in cats
b. Hypothyroidism is more common in dogs
c. Hypocholesterolemia (decreased blood cholesterol) is a common feature of hypothyroidism in dogs
d. Animals suspected of hypothyroidism do very well in cold winters.
e. None of the above
Right-to-left shunts
Supplemental oxygen does not substantially improve the hypoxemia caused by which of the following mechanisms?
a) Right-to-left shunts
b) Alveolar hypoventilation
c) Low PiO2
d) V/Q mismatch
e) Diffusion impairment
Excess thyroid hormones are catabolic
Which of the following is true regarding the actions of thyroid hormones?
a. Thyroid hormones inhibit heat production
b. Excess thyroid hormones are catabolic
c. Thyroid hormones are not involved in the regulation of blood cholesterol
d. None of the above
Hypothalamus or pituitary
Black pin
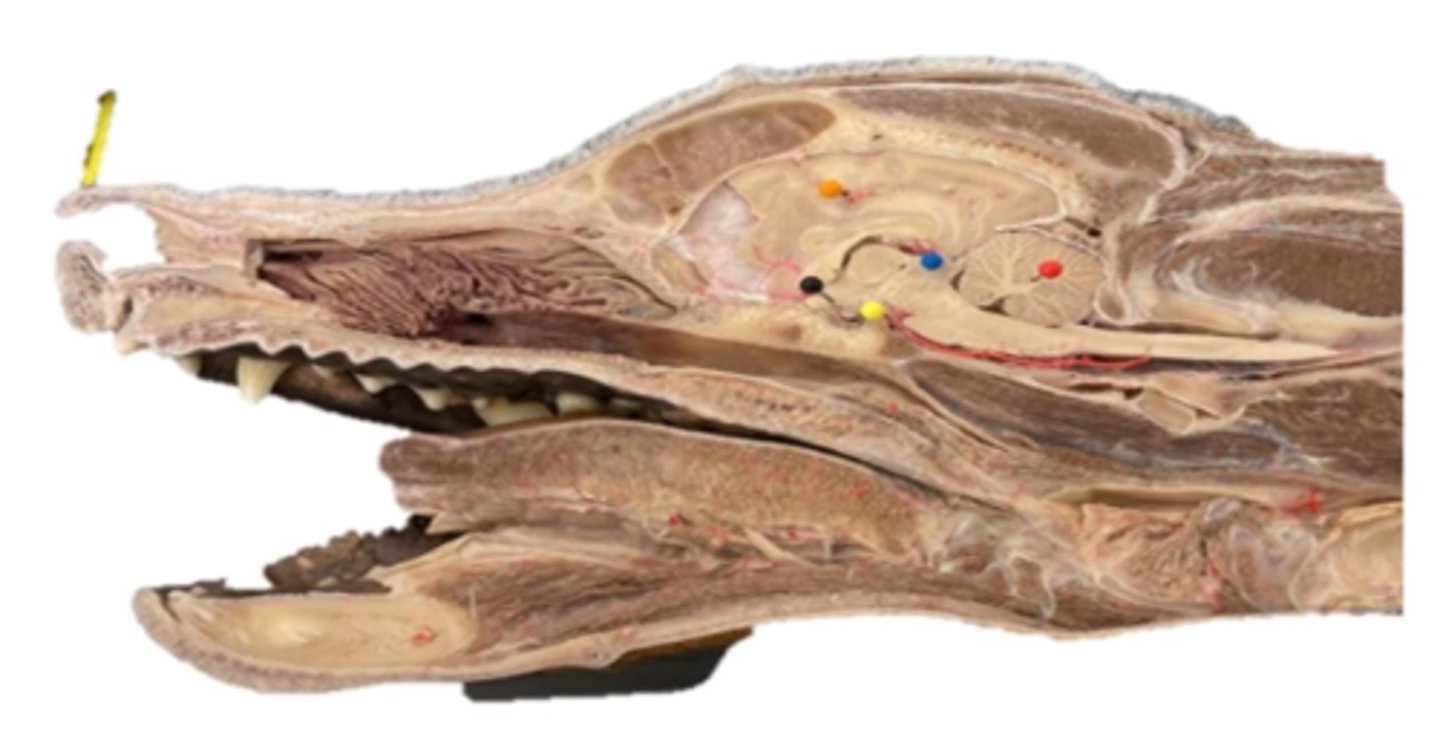
adrenal gland
What is this?
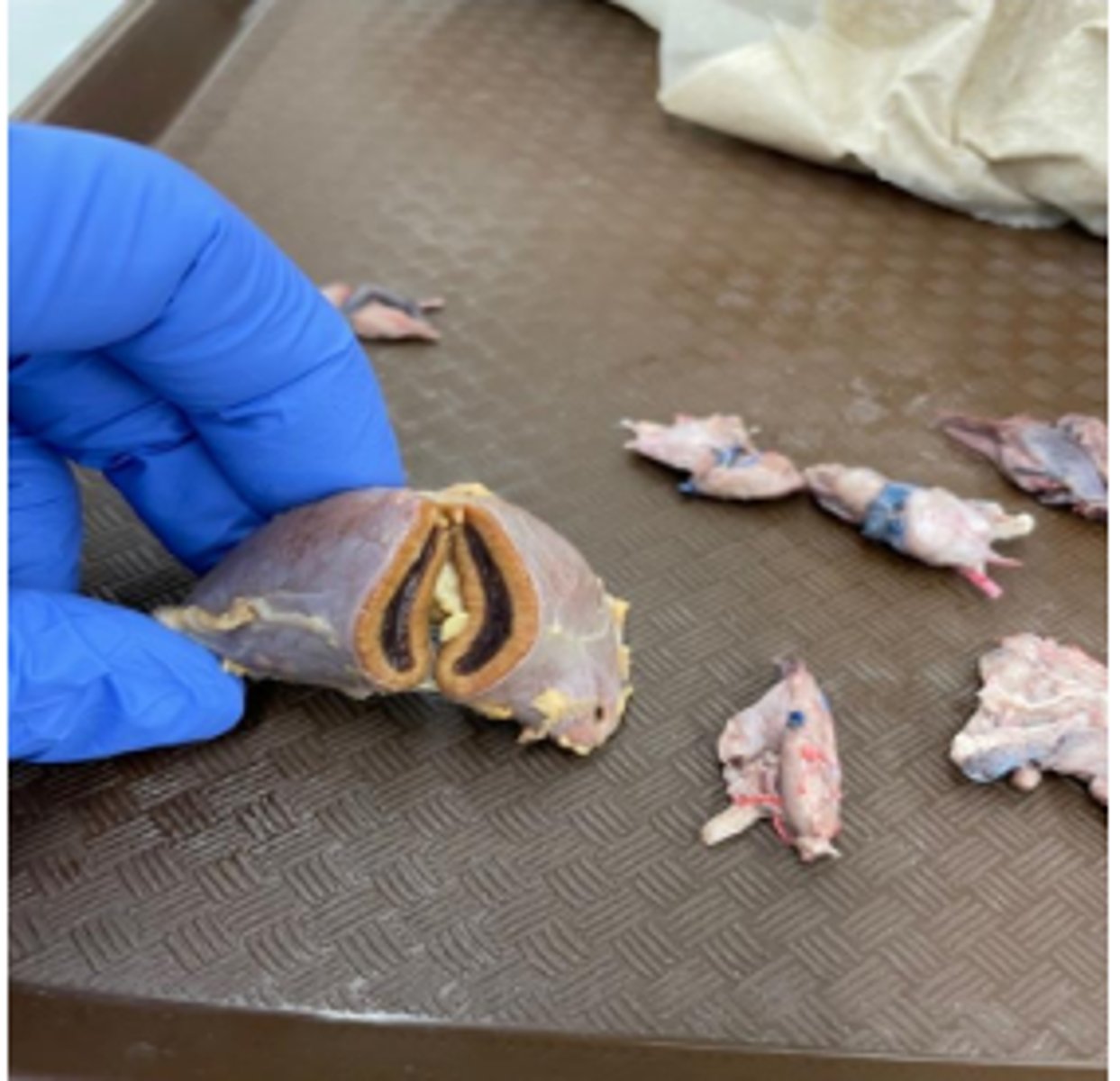
No
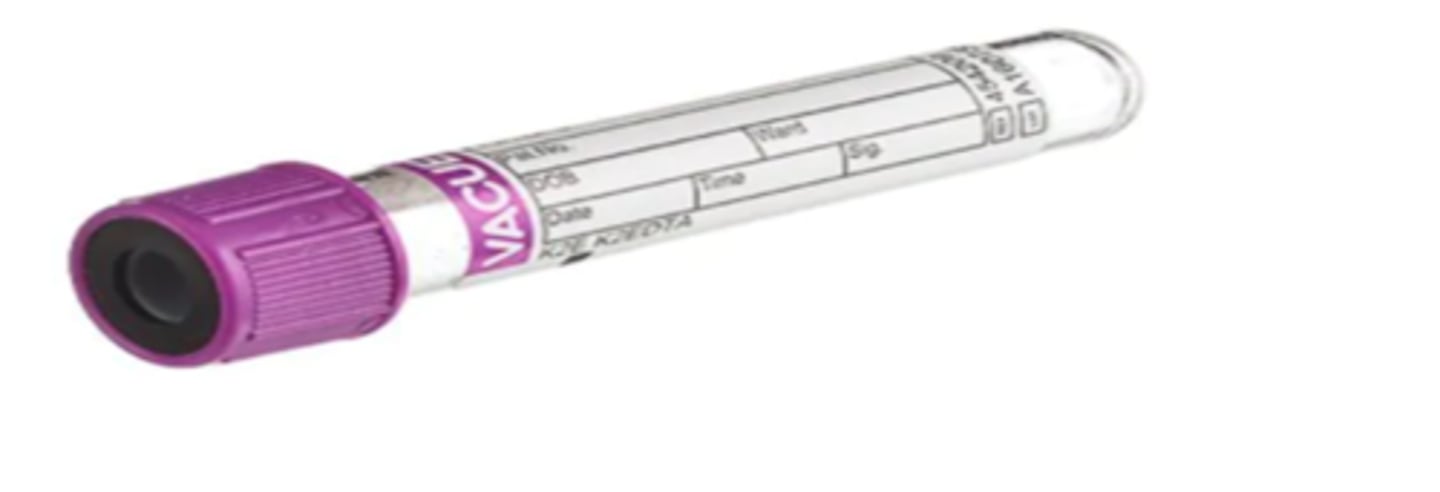
If the lab asks for plasma, is it ok to send this tube?

The median eminence
The space into which the hypothalamic hormones are released is known as...
orange
Where is the hypothalamus
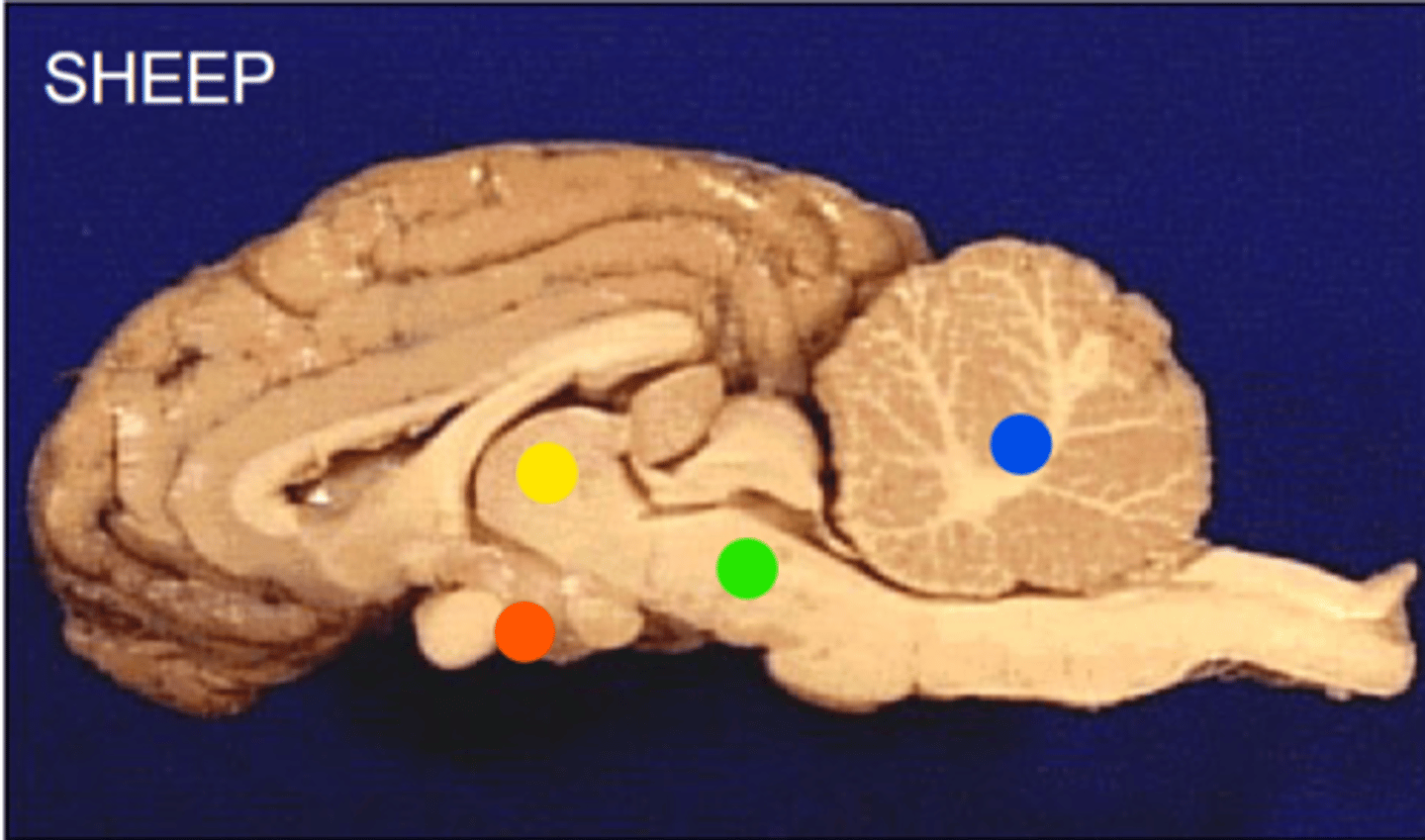
Tyrosine-derived
Dopamine belongs to which biochemical class of hormones:
G-protein coupled
Which class of receptors do dopamine and growth hormone releasing hormone use in the anterior pituitary:
Ventromedial nucleus
Steroidogenic factor-1 is important for the development and function of which hypothalamic nucleus:
pars nervosa
green
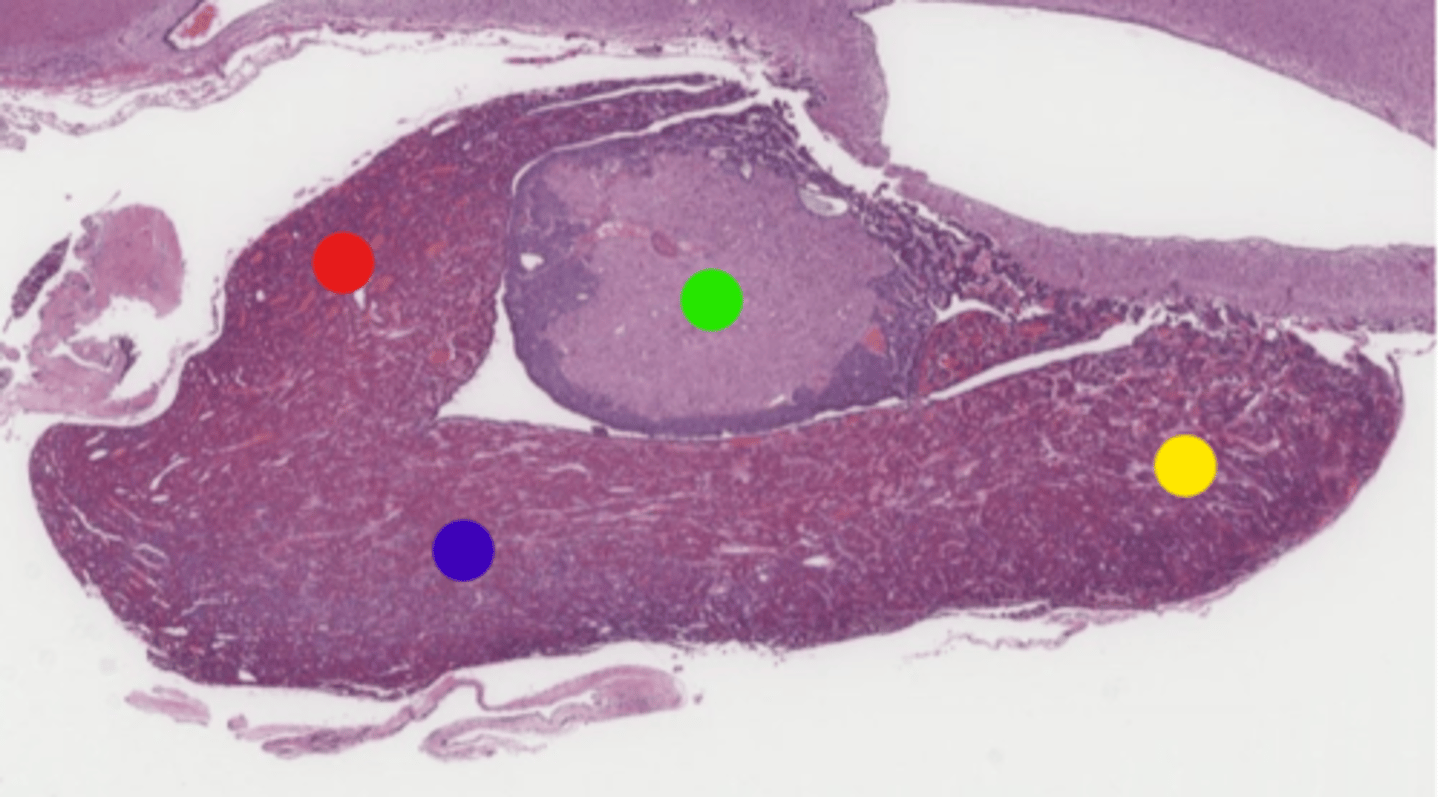
Rathke's pouch
The structure from which the anterior pituitary develops is known as the:
Glycoprotein hormones
Thyroid stimulating hormone belongs to which biochemical class of hormones:
JAK/STAT receptors
Which class of receptors do prolactin and growth hormone use in their target tissues:
Somatotrope
Pit-1 is important for the development and function of which anterior pituitary cell type:
Follicle
Sometimes called the functional unit of the thyroid gland. It is lined with thyroid epithelial cells and filled with proteinaceous colloid.
hormone
What is a chemical messenger?
melatonin
This is secreted by the pineal gland to help you sleep at night
plasma
This is the fluid part of blood which has blood clotting factors in it
scintigraphy
Medical imaging technique using detection of light caused by accumulation of radioactive or chemiluminescent contrast agents. This is frequently used in the diagnosis of thyroid disorder and is permitted by the sequestration of iodine and similar compounds within the thyroid glands.
thyroglobulin
Large lipoprotein produced by the thyroid gland that is plentiful within the colloid of the thyroid follicle viewed as the molecular location for most of thyroid hormone synthesis. This is also a frequent target of autoimmune disease during autoimmune thyroiditis, the most common cause of hypothyroidism in dogs
BCS
This is the abbreviation for the scoring system used to document horse obesity
oxytocin
This stimulates milk let down
colloid
Protein rich liquid that fills the thyroid follicle. The amount of colloid depends upon the amount of thyroid hormone synthesis.
somatotroph
This cell type produces hGH to promote growth
MSH
(melanocyte-stimulating hormone)
Abbreviation for the hormone which increases skin pigmentation
goiter
Enlargement of the thyroid glands. The most common cause is accumulation of colloid due to blockade of thyroid hormone synthesis when iodine is deficient.
adrenal gland: cortisol
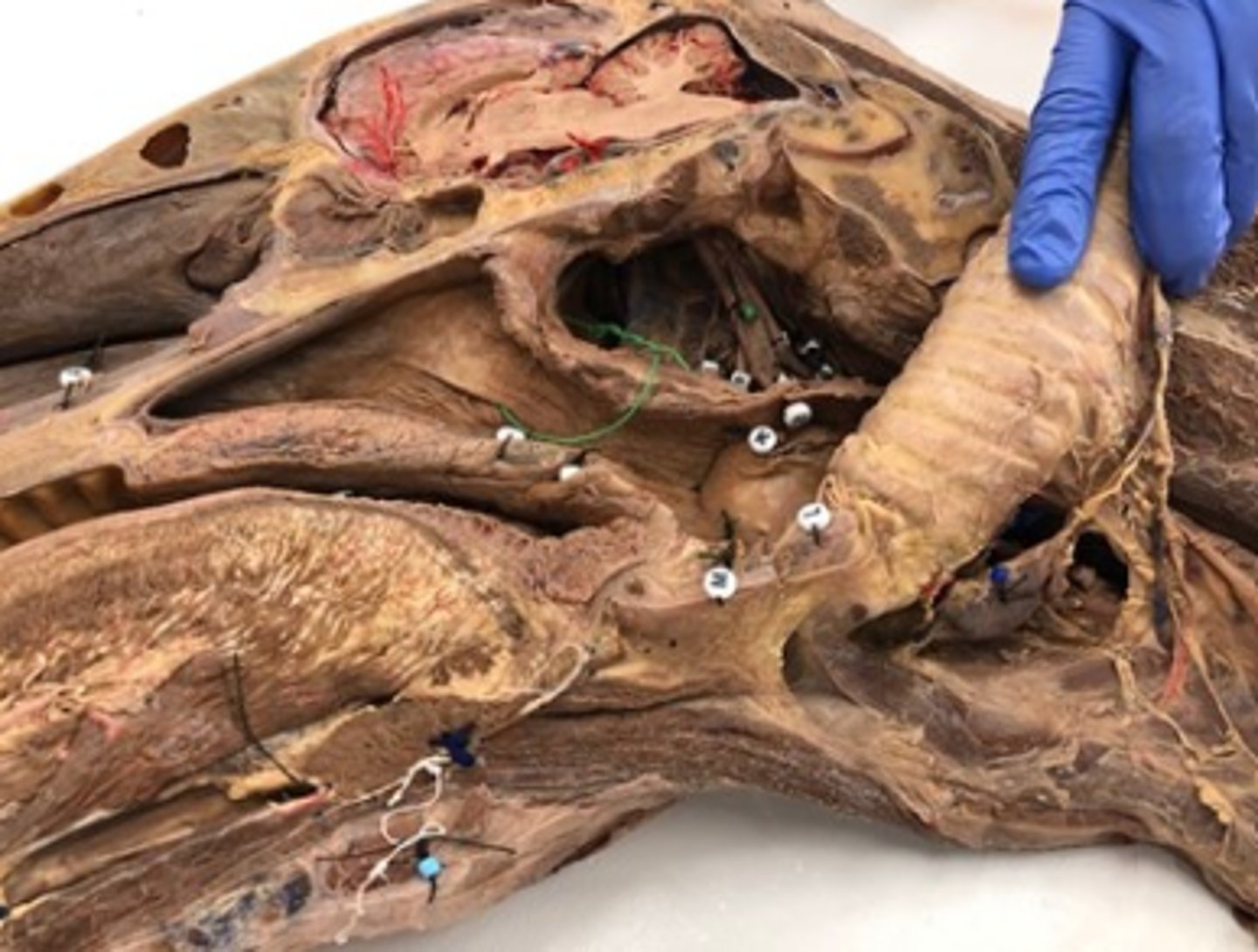
Select a hormone produced in the endocrine organ labeled with the yellow beads.
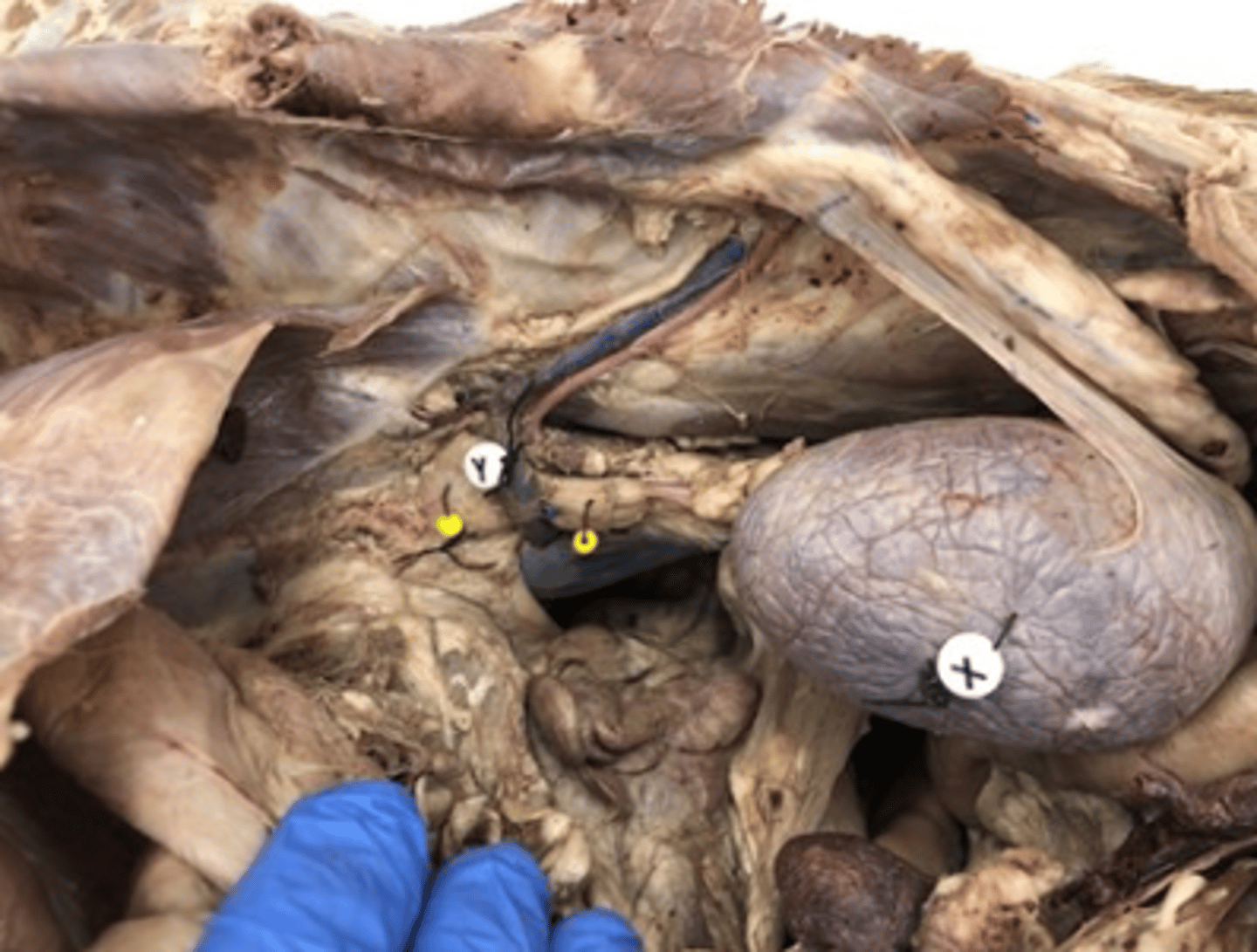
adipose
What endocrine organ is visable in this image?
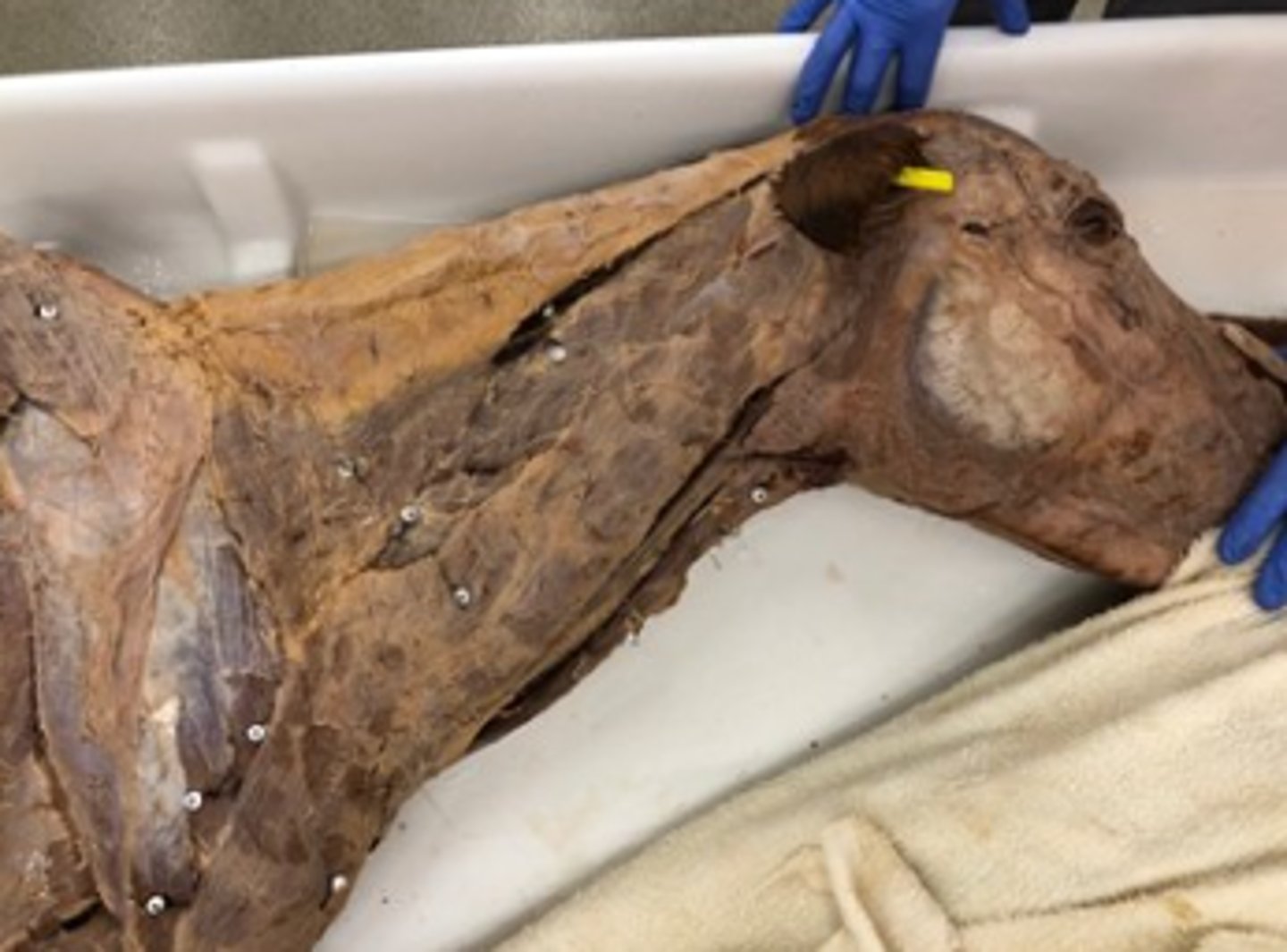
thyroid
What endocrine organ is the blue bead on?
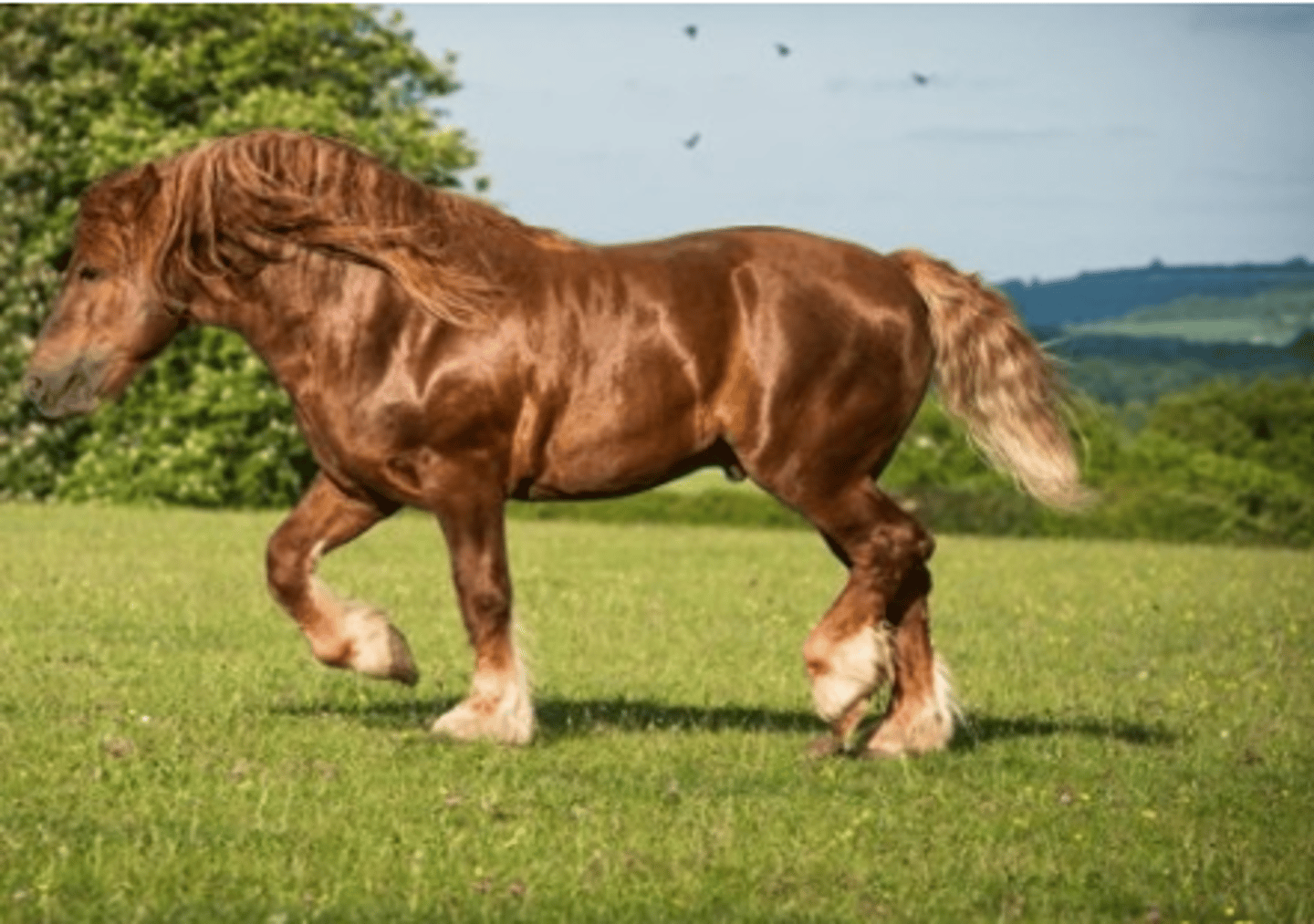
8
What BCS would you say this horse is?

A
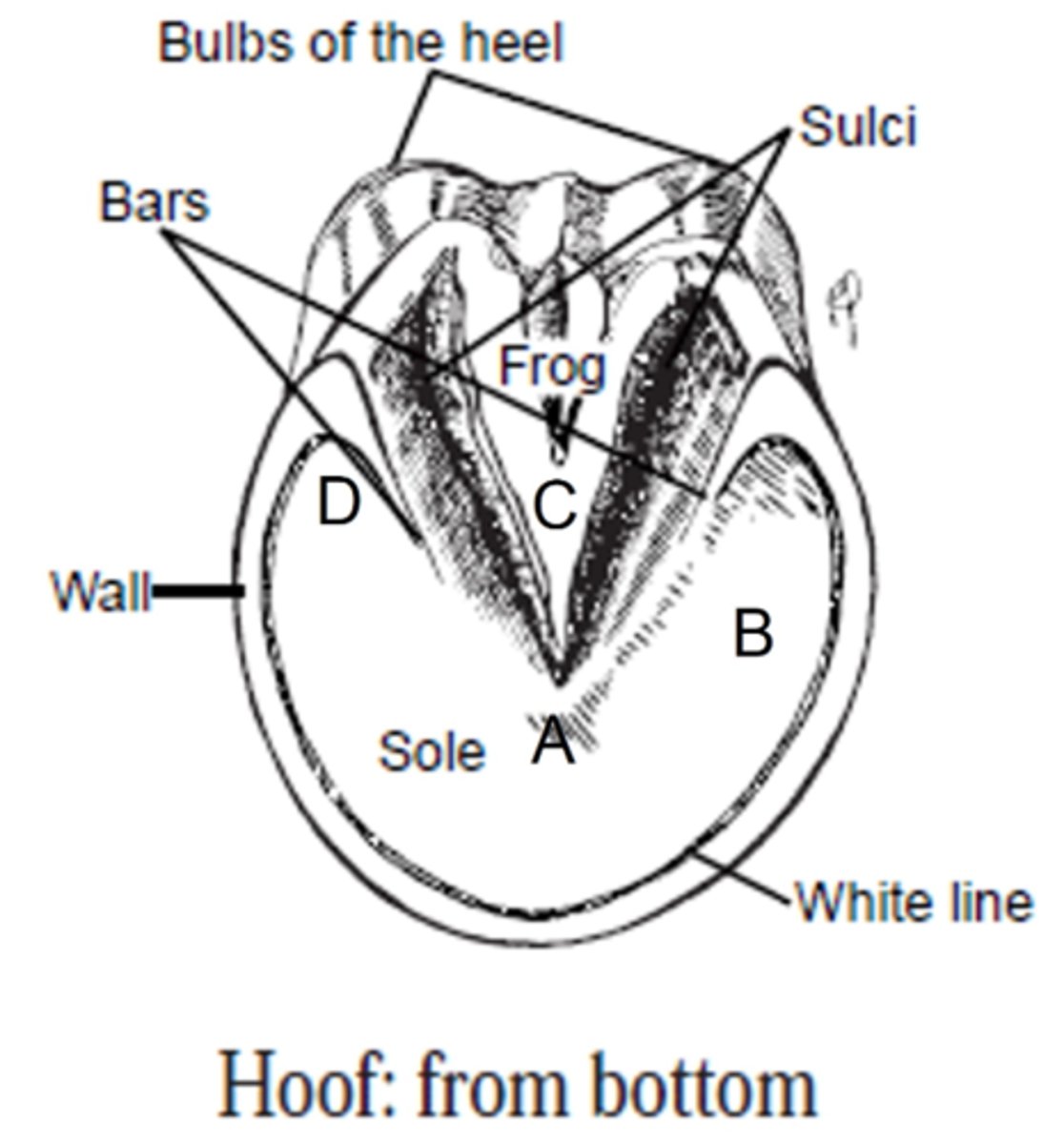
What letter is the place where you could expect to find laminitic pain secondary to endocrine disease?
True
T or F: Plasma is the top yellowish fluid you see after a purple top is spun down.
nuclear scintigraphy
MRI
Ultrasound
What diagnostic imaging techniques can be used to best assess/image endocrine organs? Please SELECT ALL of the most correct answers.
a. MRI
b. Ultrasound
c. nuclear scintigraphy
d. radiographs
Blood
What is the most common item sampled to evaluate endocrine disease?
thyroid follicular cells make T3 and T4, which contribute to growth and differentiation, metabolic rate
Which statement is most correct?
a. Thryoid Follicular cells make T3 and T4, which contribute to growth and differentiation, metabolic rate
b. Thyroid parafollicular cells make calcitonin which relates to magnesium storage.
c. T3 is higher in circulation, T4 is more potent
d. T3/T4 is stored in the colloid.