ORGO 2 EXAM 3
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
NaBH4 reduction how many steps
1 step
LiAlH4 reduction how many steps
2 steps
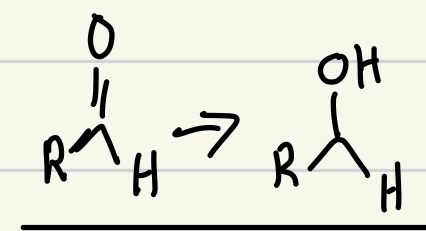
NaBH4 or LiAlH4 good reducing agent
Both NaBH4 and LiAlH4
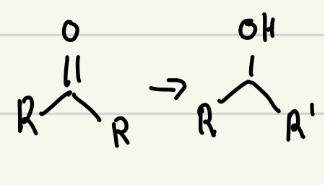
NaBH4 or LiAlH4 good reducing agent
Both NaBH4 and LiAlH4
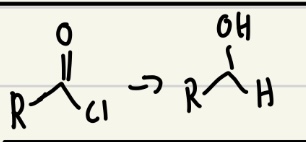
NaBH4 or LiAlH4 good reducing agent
Both NaBH4 and LiAlH4
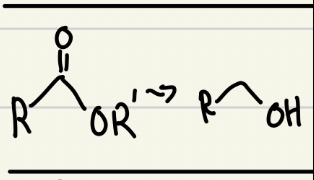
NaBH4 or LiAlH4 good reducing agent
Only LiAlH4
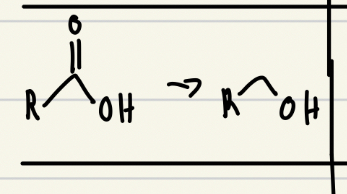
NaBH4 or LiAlH4 good reducing agent
Only LiAlH4
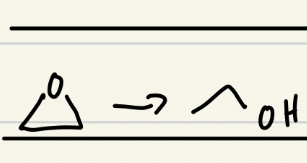
NaBH4 or LiAlH4 good reducing agent
Only LiAlH4
Grignard reagent + formaldehyde makes
Primary Alcohol
Grignard reagent + aldehyde makes
Secondary alcohol
Grignard reagent + ketone makes
Tertiary alcohol
Grignard reagent + acid chloride makes
Tertiary alcohol, Cl is LG
(This is made after an acid workup)
Grignard reagent + epoxide makes
Primary alcohol with 2 extra carbons
MgBr strong nucleophile, attacks less hinder Carbon
Grignard reagent + CO2 makes
Carboxylic acid after acid workup
Limitations of Grignard reagent
Protic reagents such as water, alcohols, amines because grignard is very strong base
Acid catalyzed ring opening of epoxides steps with reagents, FINAL PRODUCT
Protonation, oxygen attacks H+
Ring opening, H2O attacks more substituted carbon
Deprotonation, water attack H+ on other water
FINAL PRODUCT: Anti-diol
Base catalyzed ring opening of epoxides, steps, final product
Nucleophile (-OH) attack on less hindered Carbon
Protonation, (by water)
Final Product: Anti-diol
What constitutes reduction
Loss of O or O2
Loss of X2
Gain of H
What constitutes oxidation
Gaining of O
Gaining X2
Loss of H
Primary alcohol → aldehyde reagents
PCC, CH2Cl2
Primary alcohol → Carboxylic acid reagents
Na2Cr2O7 , H2SO4
Secondary alcohol → Ketone reagents
PCC / CH2Cl2
OR
Na2Cr2O7 / H2SO4
How to make symmetrical ether
Bimolecular dehydration of alcohol
Bimolecular vs unimolecular dehydration of alcohol
Unimolecular - higher temp, makes alkene
Bimolecular- 2 reactants, lower temp, makes symmetrical ether + H2O
Bimolecular dehydration of alcohol reagents
H2SO4 , Heat (lower)
To make asymmetrical ether
Williamson ether synthesis
Williamson ether synthesis reagents
NaH
Alkyl halide (SN2)
Primary alcohol → alkyl halide reagents for Cl, Br, and I
Chloride: SOCl2
Bromide: PBr3
Iodide: P/I2
Secondary alcohol → alkyl halide reagents for Cl, Br, and I
Chloride: SOCl2
Bromide: PBr3
Iodide: P/I2
Tertiary alcohol → alkyl halide reagents for Cl, Br, and I
Chloride: HCl
Bromide: HBr
Iodide:HI
Converting OH to good LG using tosylate or tosyl chloride TsCl steps reagents
TsCl, pyridine
NaX
Tosylate method scheme
ROH → R-OTs → R-X
-OTs
Very good LG