PSYC 308: Abnormal Behavior - Test 2 Flashcards
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
Stress
Perception of challenges to wellbeing.
Allostatic load
biological cost of adapting to stress
Stressors
External demands causing stress.
Coping Strategies
Efforts to manage stressors.
Chronic Stress
Long-term stress exposure.
Acute Stress
a short-term psychological and/or physiological response to a stressful event or situation
Social Readjustment Rating Scale (SRRS)
Checklist used for self-reported stressful events to assess stress levels.
Holmes and Rahe
Developers of the SRRS.
SRRS Scores
Indicate likelihood of stress-related illness.
300+ SRRS Score
High stress; 80% illness chance.
150-299 SRRS Score
Moderate stress; roughly 50% illness chance.
150 or less SRRS Score
Low stress; low illness probability.
Allostatic Load
Biological cost of stress responses.
Autonomic Nervous System
Part of peripheral nervous system activated by stress.
Cytokines
Chemical messengers in immune response.
Proinflammatory Cytokines
proteins secreted by immune cells that promote inflammation and support immune system response.
Anti-inflammatory Cytokines
Reduce immune response effects. They help regulate the immune response by reducing inflammation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Inflammation
Part of the response to chronic stress; can be a cytokine imbalance. Contributes to the physical symptoms related tot chronic stress.
Cortisol
Hormone produced for and regulating stress response.
Adjustment Disorder
Maladaptive response to common stressor.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
a mental health condition that develops after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as a life-threatening situation, violence, or natural disaster
Symptoms of PTSD
4 clusters of related symptoms.
Intrusion: Involuntary and distressing memories, nightmares, flashbacks
Avoidance: of thoughts, feelings, conversations, people, places, activities, etc that remind of the traumatic event.
Negative Cognition and Mood: Persistent negative beliefs, distorted memories, difficulty concentrating/making decisions, feelings of guilt, shame, or detachment
Hyperarousal: Irritability or outbursts of anger, Difficulty sleeping, Hypervigilance (excessive alertness), and Startle responses.
Acute Stress Disorder
Diagnosis requires:
1. Exposure to a traumatic event
2. Development of symptoms within 3 days of the event
3. Symptoms persist for at least 3 days and no longer than 1 month
4. Symptoms meet specific diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5)
Avoidance Symptoms of stress disorders
Avoiding trauma-related stimuli.
Negative Cognitions
Feelings of self-blame, detachment and negative beliefs related to stress disorders.
Arousal Symptoms of stress disorders
Hypervigilance and exaggerated startle response.
Causal Factors of PTSD
nature of trauma, individual risk factors, sociocultural risk factors
Stress Inoculation Training
Building resilience through coping skills. Often used favor individuals who have or will see combat
Psychological Debriefing
Post-trauma support sessions.
EMDR
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing therapy. Used in treatment of stress disorders especially PTSD
Cognitive-Behavioural Treatments (CBT)
Therapy focusing on exposure and cognition, altering negative cognitions/thoughts/beliefs and the accompanying behaviors
Virtual Reality Therapy
Using VR for trauma treatment. Often used for exposure therapy in order to maintain a safe environment
Resilience Promotion
Encouraging coping skills to prevent adverse effects of stress.
Emotional Disclosure
Emotional disclosure, particularly through written expression (known as "written emotional disclosure" or WED), has been shown to have a positive impact on reducing stress and symptoms associated with stress disorders
Challenges in Trauma Research
Difficulties in studying unpredictable events. It would be unethical to cause trauma for the purposes of research, but it is also impossible to predict trauma or the nature of it before it happens. This limits the ability to study before and after effects. Persons with trauma may also be more worry of participating in research due to the painful nature of acknowledging the disorder and its cause.
Biodot
Skin thermometer used to measure stress response.

Pulse
Heart rate measurement indicating physiological stress.

Subjective Stress Measure
Personal assessment of stress feelings.
Baseline Assessment
Initial measurement before stress exposure.
Psychophysiological Study
Research examining psychological and physiological interactions.
Causality
Relationship between stressors and psychological impacts. Correlation does not mean causation. Make sure to know the difference
Phobia
Persistent, excessive fear of specific object.
Specific Phobias
Diagnoses unique to fear triggered by specific situations or objects.
Animal Phobia
Fear of specific animals or insects.
Natural Environment Phobia
Fear of natural elements like heights or storms.
Blood-Injection-Injury Phobia
Fear of blood, injections, or injuries.
Situational Phobia
Fear of specific situations like flying or elevators.
Prevalence of Phobias
Lifetime prevalence of 12% in the population.
Gender Differences in Phobias
Phobias are more common in women.
Genetic Factors in Phobias
Monozygotic twins share phobias more than dizygotic, providing empicacal support for genetics playing a role in the development of phobias.
Behaviorally Inhibited Temperament
a tendency to be fearful and cautious in new situations; linked to higher vulnerability to developing phobias.
Exposure Therapy
Preferred treatment for specific phobias where client is exposed in some was to the trigger of their phobia. Often begins with lower stakes exposure ultimately working up to higher stakes.
Social Anxiety Disorder
severe fear of scrutiny in social situations to the point that it becomes pathological.
Lifetime Prevalence of Social Anxiety
Lifetime prevalence is also 12%.
Age of Onset for Social Anxiety
Typically begins in adolescence or early adulthood.
Comorbidity in Social Anxiety
Often co-occurs with other anxiety disorders including generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder.
Behavior Therapy for Social Phobia
Involves exposure to feared social situations.
Panic Disorder
Characterized by recurrent, unexpected panic attacks.
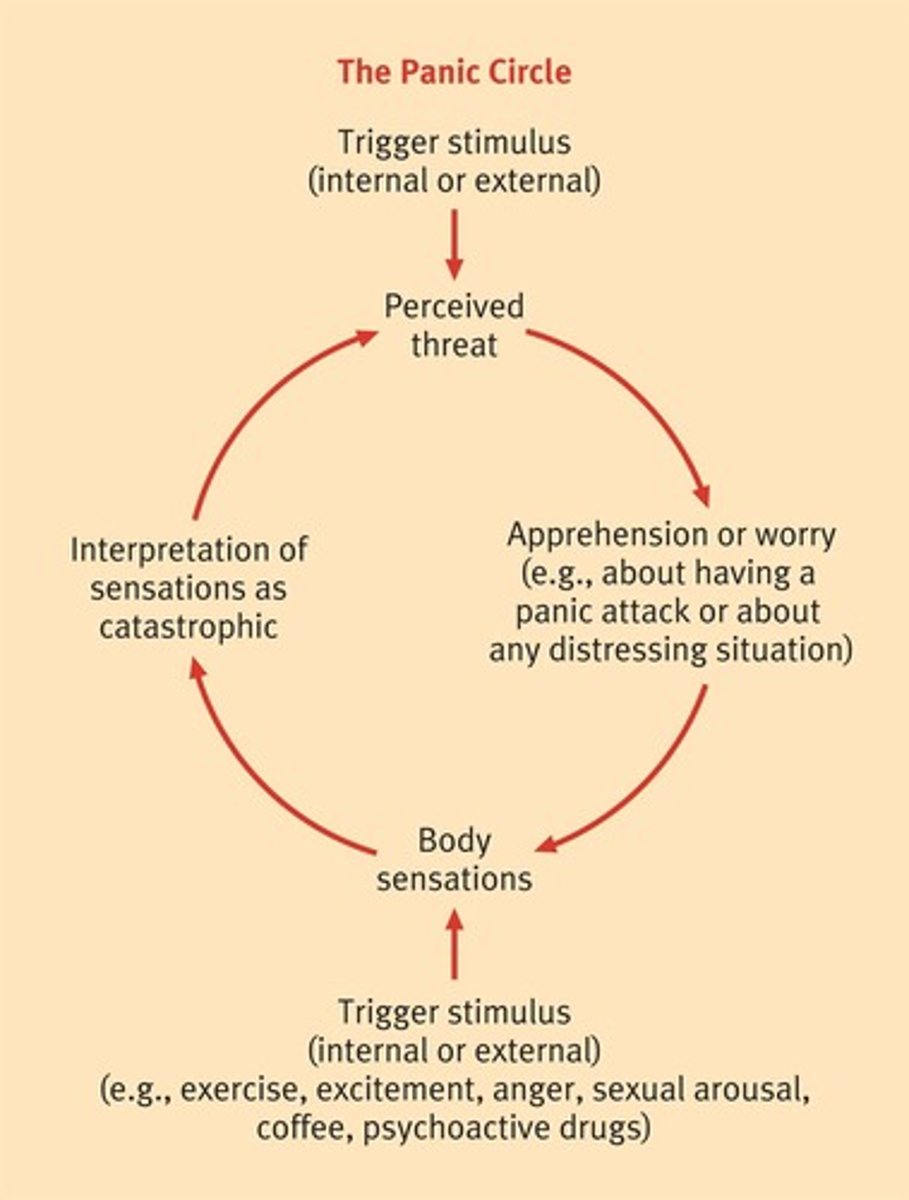
Panic Attack Symptoms
Includes 13 symptoms, mostly physical.
Agoraphobia
an anxiety disorder characterized by intense fear and avoidance of situations where escape might be difficult or help may not be available. Often results in people becoming more and more reclusive and in severe cases people may not ever leave the house or even a specific room.
Prevalence of Panic Disorder
4.7% of adults experience panic disorder.
Gender Differences in Panic Disorder
Twice as prevalent in women.
Average Onset of Panic Disorder
Typically occurs between ages 23-34.
Comorbidity in Panic Disorder
83% have at least one comorbid disorder.
Biological Factors in Panic Disorder
Moderate heritability and biochemical triggers involved.
Panic Control Treatment (PCT)
Very effective treatment for panic disorder. includes:
1.Education
2.Controlled Breathing
3.Thought errors
4.Expose to panic and build up tolerance
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Characterized by intrusive thoughts followed by compulsive behaviors to relieve the intrusive thoughts.
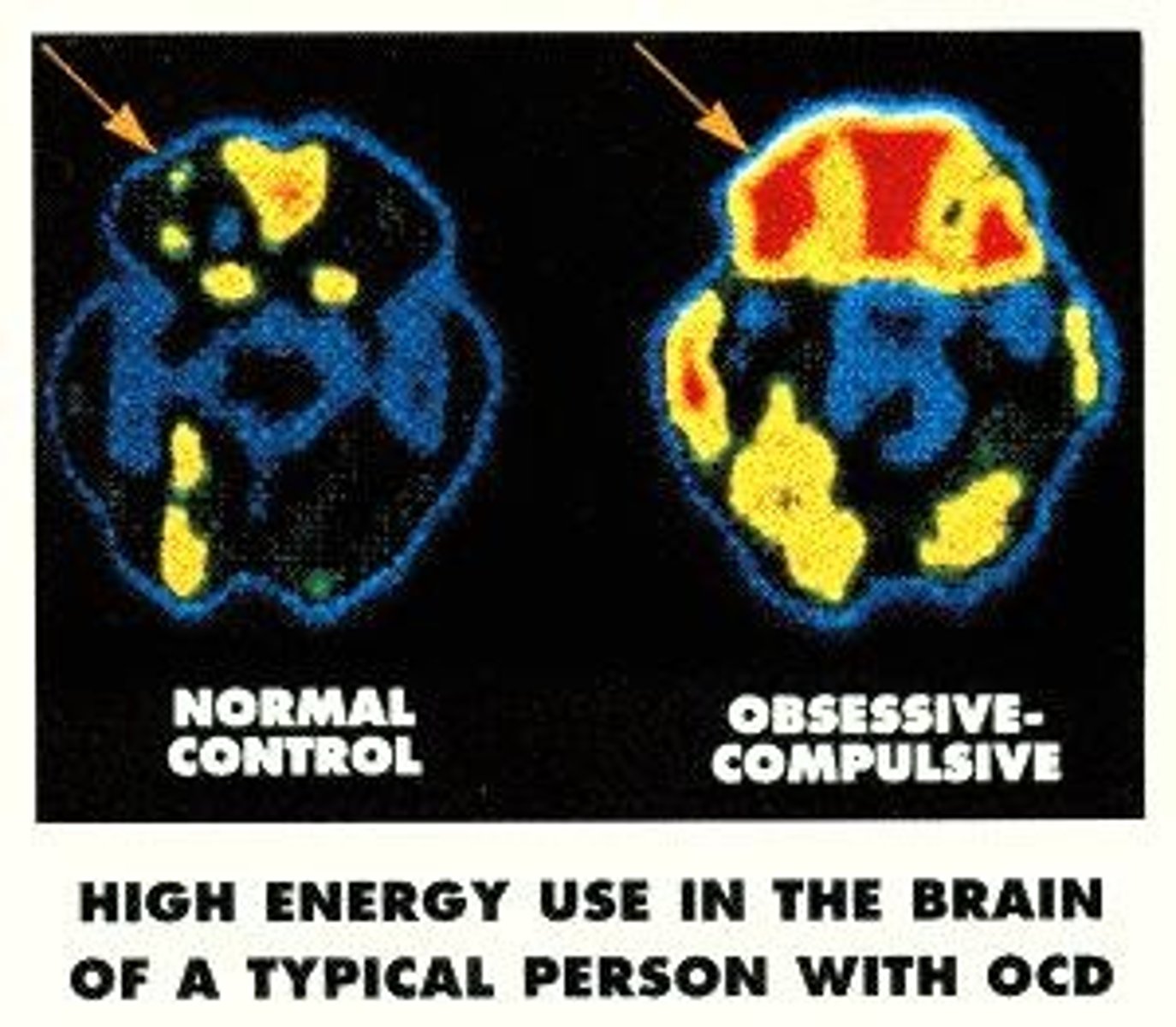
OCD Prevalence
Lifetime prevalence is 2.3%.
Age of Onset for OCD
Typically begins in adolescence or early adulthood.
Causal Factors in OCD
Includes both psychological and biological factors.
Psych:
1. two-process theory of avoidance learning
2. Attempting to suppress unwanted thoughts may increase those thoughts
Bio:
1. OCD appears moderately heritable
2. Slight structural abnormalities in the caudate nucleus and high metabolic levels in other parts of the brain
3. Serotonin is strongly implicated in OCD
Mowrer's Two-Process Theory
Neutral stimuli become associated with fearful thoughts via classical conditioning
Exposure and Response Prevention
Effective treatment for OCD. Involves exposure to the negative stimuli and source of intrusive thought and then preventing the person from performing the compulsive behavior
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Obsessive focus on perceived flaws in appearance.
Prevalence of Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Affects 1-2% of the population.
Comorbidity with Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Often co-occurs with depressive disorders.
Fear
Response to immediate threat or danger.
Anxiety
General apprehension about potential future danger and excessive worries persisting after stressor removal.
Fight or Flight Response
Evolutionary reaction that occurs within the body to perceived threats.
Panic Attack
Fear response without an actual threat present.
Three Components of Anxiety
Cognitive, physiological, and behavioral aspects.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Excessive anxiety across various situations.
Separation Anxiety Disorder
Fear of being apart from attachment figures.
Selective Mutism
Inability to speak in specific social situations.
Substance-Induced Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety caused by drug use or withdrawal.
Lifetime Prevalence of Anxiety Disorders
Estimated at 15% across populations.
Current Point Prevalence of anxiety disorders
Estimated at 7% in the population.
Global Impact of Anxiety Disorders
264 million people affected worldwide.
Mean Age of Onset for anxiety disorders
Average onset age for anxiety disorders is 21.
Cultural Differences in Anxiety
Variations in expression and diagnosis across cultures. Different cultures may not pathologize and diagnose some or all anxiety disorders
Disability Ranking of Anxiety Disorders
6th leading cause of disability in high-income countries.
Continuum of Severity
Range from non-clinical to severe anxiety.
Anxiety as an Adaptive Mechanism
Anxiety can serve a protective function when not present at debilitating levels. Some anxiety being present would have been necessary for the evolution and survival of the species
Underdiagnosis of Anxiety Disorders
Less likely to be diagnosed compared to physical disorders.
Early Onset of Anxiety
Associated with more severe anxiety expressions.
Health Anxiety
Extreme worry about illness or symptoms. Is NOT included in the DSM-V
Hypochondria
Another term for severe health anxiety. Also not in DSM-V
Comorbidity
Presence of multiple disorders simultaneously.
Risk Factors
Characteristics increasing disease likelihood of developing a disorder.
Health Psychology
Study of health and psychological interactions.
GAD Symptoms
Includes restlessness, fatigue, irritability, and sleep issues.