Cell Structure Quizes (Lecture 11-15)
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
still need lecture 15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Each round of the citric acid cycle involves the entry of two carbons, the release of two molecules of carbon dioxide, and the regeneration of _______
Pyruvate
Oxaloacetate
Hexokinase
NADH
Oxaloacetate
What happens at Complex II in the electron transport chain?
It changes FADH₂ back into NADH for the TCA cycle.
It moves electrons from NADH to oxygen and pumps protons.
It passes electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen and makes water.
It gives electrons from succinate to FAD, making FADH₂, but doesn’t pump protons.
It gives electrons from succinate to FAD, making FADH₂, but doesn’t pump protons.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE about electron transport system?
The electron transport chain is a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that occur in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Release and utilize the energy stored in NADH and FADH2
The electron transport chain operates independently of other metabolic processes.
Electrons are passed on to oxygen resulting in the formation of water
1, 2 & 4
____ and ___ ions act as poisons and disrupts the electron transport chain by blocking the Fe-S cluster.
cyanide / azide
Which of the following correctly describes the role of the δ subunit in the FoF1 ATP synthase complex?
The δ subunit synthesizes ATP directly.
The δ subunit is part of the mobile component, moving with the γ and ε subunits.
The δ subunit forms part of the ring of three αβ complexes.
The δ subunit anchors the α3β3 catalytic ring to the b2 stator stalk of Fo.
The δ subunit anchors the α3β3 catalytic ring to the b2 stator stalk of Fo.
Which of the following do you expect is not transported into the mitochondrial matrix using the TOM/TIM system?
Malate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase
NADH dehydrogenase
Which of the following statement(s) is/are FALSE about "Stop-transfer" sequences?
They are composed of a conserved consensus sequence of proline residues.
They are located at the N terminus of the protein.
They trap the nascent polypeptide in the membrane.
They are cleaved from the nascent polypeptide by signal peptidase.
1, 2, 4
Which of the following proteins would be secreted from the cell?
A protein with no signal sequence
A protein with an ER signal sequence but no retention tag
A protein with a KDEL tag
A protein with an RXR tag
A protein with an ER signal sequence but no retention tag
What is the movement of material to the cell membrane called?
Active transport
Uniport transport
Anterograde transport
Retrograde transport
Anterograde transport
Which of the following statements accurately describes the role of the signal recognition particle (SRP) in the process of ER targeting during protein synthesis?
The SRP functions exclusively in the transport of proteins to the mitochondria.
The SRP initiates the cleavage of the ER signal sequence.
The SRP binds to the ribosome and the ER signal sequence, mediating ribosome docking to the ER membrane.
The SRP directly synthesizes proteins in the rough ER.
The SRP binds to the ribosome and the ER signal sequence, mediating ribosome docking to the ER membrane.
Which of the following is not a function of smooth ER?
Calcium Storage
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Steroid Biosynthesis
Protein Glycosylation
Protein Glycosylation
What determines the incorporation of Golgi-specific proteins into different cisternae of the Golgi apparatus?
The temperature of the cellular environment.
The number of proteins attached to the Golgi.
The presence of ribosomes on the Golgi membranes.
The length of the protein's hydrophobic domain.
The length of the protein's hydrophobic domain.
SNARE proteins participate in vesicle exocytosis by
binding calcium and then forming a pore into the vesicle.
pushing vesicles from the reserve pool into the docked pool.
forming a protein complex that pulls the vesicle membrane against the plasma membrane.
forming a protein coat that maintains the vesicle's integrity.
forming a protein complex that pulls the vesicle membrane against the plasma membrane.
Match the following target organelles to their signal sequence?
Endoplasmic reticulum-
Cytoplasm-
Lysosomes-
Nucleus-
Signal Recognition Particle, Nuclear Export Sequence, Mannose-6-phosphate, Nuclear Localization Sequence
Which statement that describes processes of receptor-mediated endocytosis, exocytosis, and the changes in the membrane organization involved with each?
In receptor-mediated endocytosis, waste material is enveloped in a membrane that fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane via attachment proteins. Exocytosis involves the opsonization of the receptor and its ligand in caveolae-coated vesicles.
In receptor-mediated endocytosis, waste material is enveloped in a membrane that fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane via attachment proteins. Exocytosis involves the opsonization of the receptor and its ligand in a clathrin-coated vesicles.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves the binding of a ligand to its receptor, resulting in the formation of a clathrin-coated vesicle that enters the cell. In exocytosis, transported material is enveloped in a vesicle that fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane via attachment proteins.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves the opsonization of the receptor and its ligand in clathrin-coated vesicles. In exocytosis, waste material is enveloped in a membrane that fuses with the exterior of the plasma membrane via attachment proteins.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves the binding of a ligand to its receptor, resulting in the formation of a clathrin-coated vesicle that enters the cell. In exocytosis, transported material is enveloped in a vesicle that fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane via attachment proteins.
The Golgi apparatus has a polarity or sidedness to its structure and function. Which of the following statements correctly describes this polarity?
Proteins in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
Proteins enter the Golgi at the "trans" face and exit at the "cis" face.
Transport vesicles fuse with one side of the Golgi and leave from the opposite side.
Lipids in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
1, 3, 4
______ are found in pairs that make up _______. Both help produce and organize the MTs that connect to ________ on chromosomes during mitosis
Centrosomes, centrioles, centromeres
Centrioles, centromeres, centrosomes
Centrosomes, centromeres, centrioles
Centrioles, centrosomes, centromeres
Centrioles, centrosomes, centromeres
What is the function of Arp2/3 complex?
Protein needed for microtubules to begin to form
It is an inhibitor in actin treadmilling
Nucleates site to create new actin filaments
Binds intermediate filaments into dimers
Nucleates site to create new actin filaments
Match the following GTPases to their effect on cytoskeleton.
Cdc42 activation
Rac activation
Rho activation
formation of filopodia, extension of lamellipodia, formation of stress fibers
Choose the correct option regarding actin growth and disassembly.
ATP actin adds to + (pointed) end: slow polymerization and depolymerization
ATP actin adds to - (barbed) end: slow polymerization and depolymerization
ATP actin adds to + (barbed) end: fast polymerization and depolymerization
ATP actin adds to - (pointed) end: fast polymerization and depolymerization
ATP actin adds to + (barbed) end: fast polymerization and depolymerization
Which of the following statement(s) about microtubule growth are FALSE?
The plus (+) end of microtubules is where assembly occurs more rapidly, as demonstrated by mixing basal bodies with tubulin heterodimers.
The minus (-) end of a microtubule assembles and disassembles faster than the plus (+) end.
Tubulin dimers are added more quickly at the minus (-) end of microtubules, which is typically the faster-growing end.
Microtubules only assemble at the plus (+) end and never disassemble at the minus (-) end.
2, 3, 4
What would happen if you removed nexin from an axoneme?
All the axoneme would disassociate.
The microtubules would slide past each other, moving one MT doublet, but not bending.
No movement would occur.
Nothing would change about the movement.
The microtubules would slide past each other, moving one MT doublet, but not bending.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding kinesin movement?
Kinesin movement is independent of the microtubule's polarity.
ATP binding drives the conformational changes and forward motion of kinesin.
ADP release from the leading head allows strong binding to the microtubule.
ATP hydrolysis and Pi release from the trailing head weaken its interaction with the microtubule, preparing it for the next cycle.
1, 2, 3
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
The variation in the tail structure of myosins allows for binding to different cargos.
Tubulin subunits are shuttled to and from the growing flagellum tip by both plus- and minus-end-directed motor proteins which is known as intraflagellar transport.
The length of the microtubule doublets in cilia and flagella change constantly resulting in the localized bending motion.
Cleavage of Nexin linkages, followed by treatment with ATP, causes microtubule doublets to slide past each other.
The length of the microtubule doublets in cilia and flagella change constantly resulting in the localized bending motion.
How do kinesin and dynein move cargo molecules inside a nerve cell?
They move in random directions on microtubules.
Kinesin moves cargo molecules away from the cell body and dynein moves cargo molecules toward the cell body.
Kinesin moves cargo molecules toward the cell body and dynein moves them away.
Both move cargo molecules away from the cell body.
Kinesin moves cargo molecules away from the cell body and dynein moves cargo molecules toward the cell body.
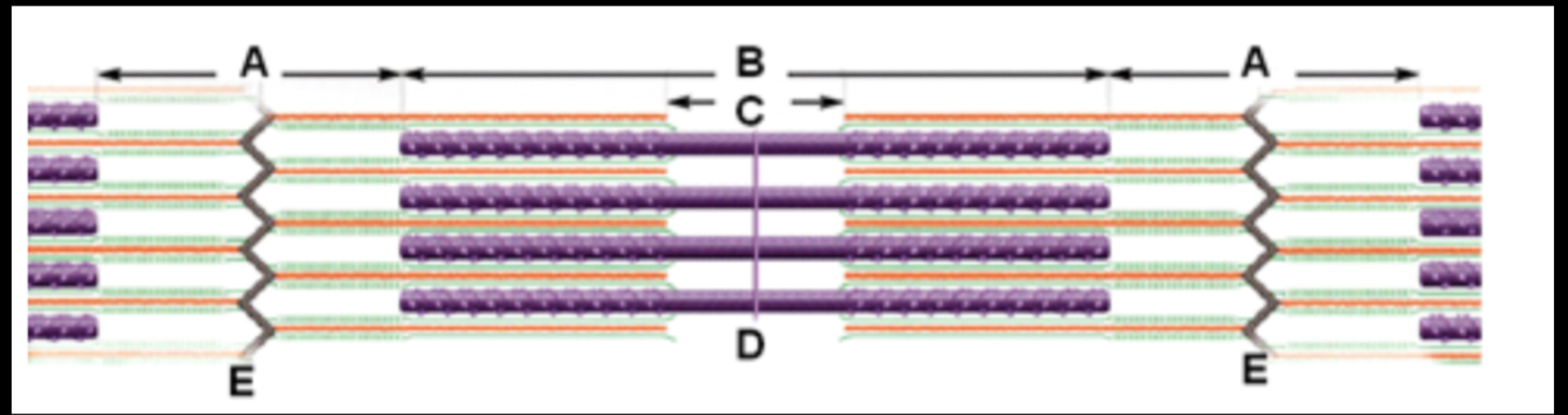
Which of the following statement(s) is/are CORRECT about the diagram?
The major protein found in the region labeled 'C' is myosin.
The image represents 2 full sarcomeres.
Region A and region C will change length during muscle contraction.
Myosin and Actin are both found in the region labeled 'A'.
Region A and region C will change length during muscle contraction.
The major protein found in the region labeled 'C' is myosin.