Truelearn basic Anesthesia exam questions
1/310
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
311 Terms
Which synthetic opioids (3) have weak serotonin reuptake inhibitor?
Meperidine, methadone, tramadol
Propofol acts primarily at which receptors?
GABAa receptors
What is the effect of adding sodium bicarbs to local anesthetics?
helps to increase the pH —> local anes becomes nonionized and able to penetrate neuronal membrane easier. Helps to shorten onset and increases density of epidural sensory block
Which lab test is best to assess liver synthetic function?
PT/INR, which most closely correlated with factor VIIa levels
Which patient would you check a preop coag studies on?
Patient with history of bleeding disorder, excessive intraop surgical bleeding, liver disease, poor nutritional or oral intake, use of anticoag.
What is acute normovolemic hemodilution?
autologous transfusion strategy that involves removals of blood from patient at higher Hct so that surgical blood loss is at lower Hct. helps to avoid needing for allogenic transfusion as patient’s blood will be transfused back in reverse order at the end of the surgery
What is the guidelines for starting beta blockers on patients?
If currently taking, continue BB. If patient are intermediate or high risk for MI or RCRI >3, preferable start BB 7-45 days prior to surgery, if not, at least 2 daysand continue on periop period.
What is the effect of citrate in pRBC?
hypocalcemia and metabolic alkalosis. citrate metaolized by the liver and convert into bicarbs.
what causes release of vasopressin?
Hyperosmolality (hyperNa) and hypovolemia (hypotension) when carotid sinus and aortic arch baroreceptor sense it. Helps to increase water absorption via V2 receptors on collecting ducts
Compared to central arterial waveform how is the peripheral wave form?
Peripheral waveform has higher systolic peak and lower diastolic, lower MAP as well. Dicrotic notch may be seen later and less prominent (or not at all) in the peripheral arteries.
How does progression of arterial waveform look?
central —> peripheral (widening of pulse pressure [increase in systolic and decrease in diastolic], decrease in MAP, blunting of dicrotic notch).
What is macroshock?
Macroshock refers to a relatively large electrical shock that can result in severe injury or death when it passes through the body. It typically involves a voltage greater than 1000 volts, capable of stimulating muscle contractions and disrupting normal heart rhythms.
What is microshock?
Microshock refers to a low-level electrical shock, direct application of very low current of electrical energy to the heart. Microshock is commonly used in therapy in cardiac pacemaker where current is delivered via pacemaker electrodes in order to stimulate myocardial contraction
What is line isolation monitor?
A line isolation monitor is a device used to detect electrical faults in isolated power systems, ensuring safety and preventing hazardous conditions in medical settings. Faults is an accidental connection between a source of electrical energy and electric ground. Line isolation monitor is only useful in monitoring for macroshock and not microshock currents
Where is Ach synthesized?
basal forebrain, laterodorsal tegmentum, pedunculopontine tegmentum
Whereis norepinephrine synthesized?
locus coeruleus in pons
Where is dopamine synthesized?
substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area
Where is serotonin synthesized?
raphe nuclei
Where is histamine synthesized?
tuberomammillary nucleus of posterior hypothalamus
What lab test is best to assess hepatic synthetic function?
PT/INR which most closely correlates with factor VIIa levels
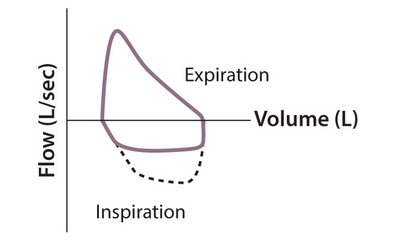
variable extrathoracic obstruction (proximal tracheal tumor, external compression from goiter)
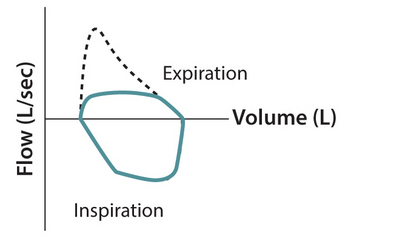
variable intrathoracic obstruction (distal tracheal tumor, mediastinal mass)
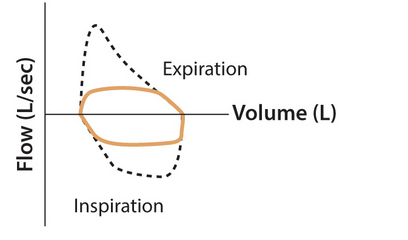
fixed upper airway obstruction (foreign body, tracheal stenosis, large airway tumor)
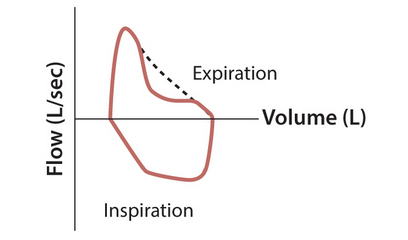
COPD
Colloid (specifically synthetic colloids) have what substance compared to crystalloid?
antithrombotic effect that results in inhibition of platelet aggregation.
How long does patient with MI have to wait before proceeding with surgery?
no coronary intervention —> 60 days
balloon angioplasty —> 14 days
bare metal stent —> 30 days
drug eluting stent —> 180 days
G-protein a1
Gq - found in postsynaptic membraine —> vascular and intestinal smooth mm and endocrine gland
Second messenger: increase IP3 —> Ca2+; increase DAG —> PKC
Smooth mm activation —> vasoconstriction, bladder/GI sphincter contraction, mydriasis.
G-protein a2
Gi - found in both pre and postsynaptic membranes (presynaptic inhibits NOR release into synaptic cleft)
decrease cAMP —> decrease Ca2+
decrease insulin secretion, plt aggregation, decrease NOR release
G protein B1
Gs
increase cAMP —> increase Ca2+
increase HR/contraction, increase renin release
G- protein B2
Gs
Increase cAMP —> decrease Ca2+
increase glycogenolysis, increase insulin secretion, vasodilation, bronchodilation
What is the Fick equation?
CO = VO2/ (CaO2- CvO2)
VO2 = total uptake of O2
Which medications are CYP-3A4 inducer?
Carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, St. John’s wort, dexamethasone, topiramate, oxcarbazepine
NPO status 2 hrs
clear liquids
NPO status 4 hrs
breast milk
NPO status 6 hrs
nonhuman milk, light meal (tea and toast)
NPO status 8hrs
full meal, fatty foods
Why does bupivicaine have the highest cardiotoxicity among local anesthetics?
causes blockade of voltage gated sodium channels in the heart —> delay conduction and repolarization and thus can lead to ventricular arrhythmias and cardiovasc collapse.
What is closing capacity?
sym of the residual volume and closing volume (volume at which small airways begin to close).
What is the benefit of adding sodium bicarbs to epidural solution?
increasing the pH —> nonionized and able to penetrate the neuronal membrane easier. Helps to shorten the onset and increase the density of the epidural sensory block
What is the effect of Dexmedetomidine in epidural solution?
intensify and prolong the effect of local anesthetics.
What is the effect of adding fentanyl into local anes?
enhances the analgesic effect
fentanyl = lipophilic (found in epidural fat)
morphine = hydrophilic (in CSF)
What does the LCx supply?
posterolateral LA and ventricle, and anterolateral papillary muscle
What does the LAD supply?
½ LA and ventricle (anterior aspect), anterior 2/3 interventricular septum, anterolateral papillary mm, cardiac apex
What does the RCA supply?
Right marginal artery: lateral RV, cardiac apex
PDA: posterior 1/3 of interventricular septum, posterior 1/3 of interventricular septum, posterior inferior aspect of heart, posteromedial papillary mm.
AV nodal artery: AV node and bundle of His
SA node artery: SA node
What the is effect of famotidine?
Histamine type 2 receptor antagonist.
Reduce gastric acidity and volume
onset 90 minutes
What is the effect of metoclopramide?
Dopamine antagonist centrally and cholingeric agonist peripherally
decrease gastric volume. no effect on aciditity.
Onset 1-3 minutes
What is the effect of omeprazole?
PPI
Decrease gastric fluid volume and increase gastric pH
onset hours to days
What is the effect of antacids (sodium citrate)?
increase gastric pH. immediate effectWhat
What perioperative finding is associated with high risk of postoperative mortality after liver transplant?
Perioperative PaO2 <50 mmHg.
What is the effect of longer expiratory time (increaes I:E) and decrease RR have on COPD pt who is mechanically ventilated?
improve dynamic pulm hyperinflation. Thus decrease end-inspiratory lung volume, elastic recoil pressure, peak airway pressure, and instrinsic PEEP (auto-PEEP).
How much fibrinogen is in a unit of cryoprecipitate?
200mg/unit.
What factors is in cryoprecipitate?
Factors VIII, XIII, fibrinogen, vWF
Pharmacokinetics vs pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics= movement of drug in the body —> how the drug is distributes, circulated, eliminated from the body
Pharmacodynamics = effect of drug itself (includes interaction w/ receptors, dose-response relationships, duration of effect, types of effect)
What is the initial fluid resuscitation goal for sepsis treatment?
30ml/kg of IVF over 3 hrs
What rhymths are shockable? (2)
pulseless VTach and Vfib
What are unshockable rhythm?
PEA/asystole
When do you administer 1mg of IV EPI in shockable rhymth?
after 2nd unsuccessful defibrillation attempt
When do you administer 300mg of IV amiodarone in shockable rhymth?
After the 3rd unsuccessful defibrillation attempt
What can cause increase in PIP?
-Increase in resistance (mucus plug, kinked tube, bronchospasm)
-decrease compliance (insufflation, bronchial intubation, pulm edema, tension PTX)
What is a shunt?
venous admixture.
Perfused but not ventilated
What is dead space?
ventilated but not perfused
What is Bachman bundle?
structure of heart that is responsible for normal conduction of cardiac impulses from right to left atria
What is the normal cardiac conduction pathway?
SA node —> LA via Bachmann bundle —> AV —> bundle of His —> fascicle —> purkinje fibers
What is the cardiovascular effect of Methohexital?
decrease CO, decrease SVR, reflex tachycardia —> BAD in pt with CAD
What is the effect of hypercalcemia on NMB?
antagonises, therefore need increase dose of NMB to get dersired effect
Myasthenia gravis and NMB
Sensitive to NONdepol NMB (roc) —> b/c needs functional Ach receptors to have an effect
Resistance to depol NMB (succinycholine) —> b/c has fewer functioning receptors to block
LEMS to NMB
Sensitive to both nondepol and depolarizing NMB.
What lab test is used to detect HIT?
antiplatelet factor 4 antibodies (high sensitivity)
Serotonin release assay (highest specificity for HIT)
What is hepatic arterial buffer response?
portal venous blood flow decreases lead to hepatic artery vasodilation resulting in increased hepatic arterial flow. Changes in arterial blood flow DOES NOT induce reciprical changes in portal venous.
key player = adenosine
Portal venous flow decrease —> accumulatioin of adenosine in hepatic vasculature —> increased [adenosine] causes vasodilation of the hepatic artery —> incraese hepatic arterial blood flow.
What % does of CO does liver get?
20-25% of cardiac output via portal vein and hepatic artery
What % of blood flow is portal vein responsible for?
75%
but still deliver 50% of O2 supply to liver
What % of blood flow is hepatic vein responsible for?
25%.
but still deliver 50% of O2 supply to liver
Improved glycemic control in T2DM reduces the risk of what complications?
microvascular complications including retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy.
Does not decrease risk of macrovascular complications like MI, CVA, PAD.
Which NMB is metabolize by Hoffman elimination?
cisatracurium
Which local anesthetics is metabolize by liver?
AMIDE local anesthetics such a lidocaine and bupivicaine
Which local anesthetics is metabolize by plasma cholinesterase?
ESTER local anesthetics such as 2-chloroprocaine
A far LATERAL disc herniation will affect what level of the exiting nerve root?
at the level of herniation (L4-L5 herniation —> affects L4 nerve roots)
A PARACENTRAL disc herniation of spinal cord will affect which nerve root level?
level BELOW the disc herniation (L4-L5 herniation —> L5 nerve root)
What is the exposure limit in parts per million for halogenated anesthetic gases ?
2 ppm
What is the exposure limit in parts per million for nitrous oxide?
25ppm
What is the exposure limit in parts per million for halogenated anesthetic gases and nitrous oxide combined?
0.5 ppm
What is the neck landmark to perform a superficial cervical plexus block?
midpoint of the posterior boarder of the sternocleidomastoid
What is the landmark to perform an interscalene block?
Between anterior and middle scalene musles
What is the vapor pressure of desflurane?
669 mmHg
What is the vapor pressure of isoflurane?
238 mmHg
What is the vapor pressure of nitrous oxide?
38770 mmHg
What is the vapor pressure of sevoflurane?
157 mmHg
What is the FRC in any healthy patient?
30ml/Kg
What is the adult oxygen consumption?
3-4ml/kg/min
Describes the content of the popliteal fossa from medial to lateral
Popliteal ARTERY —> popliteal VEIN —> Tibial nerve —> common peroneal nerve
Which inhaled anesthetic agent is asociated with fluoride production thrugh hepatic metabolism?
Sevoflurane (compound A AKA hexafluoroisopropanol)
Enflurane
What lung volume is decreased in obese patient?
Expiratory reserve volume.
FRC and total lung capacity are also decreased
D1 receptors
Gs
renal vasculature vasodilation and activate direct striatum pathway
D2 receptors
Gi
Inhibits indirect striatum pathway
H1 receptors
H2 receptors
H1: Gq —> increase vascular permeability, bronchoconstriction, pruritis
H2: Gs —> increase gastric acid secretion
M1, M2, M3 receptors
M1= Gq: increase gastric motility
M2 = Gi: decrease in HR
M3 = Gq: smooth mm contraction and increases secretions and intestinal motlity
V1 receptors
V2 receptors
V1 receptors = Gq = vasoconstriction
V2 = Gs = increase water permeability in renal collecting ducts and promotes release of vWF
Physostigmine
anticholinesterase w/ tertiary amine structure —> able to access the CNS
Treatment of choice for delirium a/w scopalamine (antidote to antimuscarinic drugs)
Neostigmine
Treatment of colonic pseudoobstruction
Does not cross BBB.
However can cross placenta (reversal agent in preggo w/ atropine)
Pyridostigmine
Quaternary amine therefore poorly absorbed in the gut and does not cross BBB.
Used in pt w/ MG and ppx against nerve agent exposure