my own notes for sciences
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
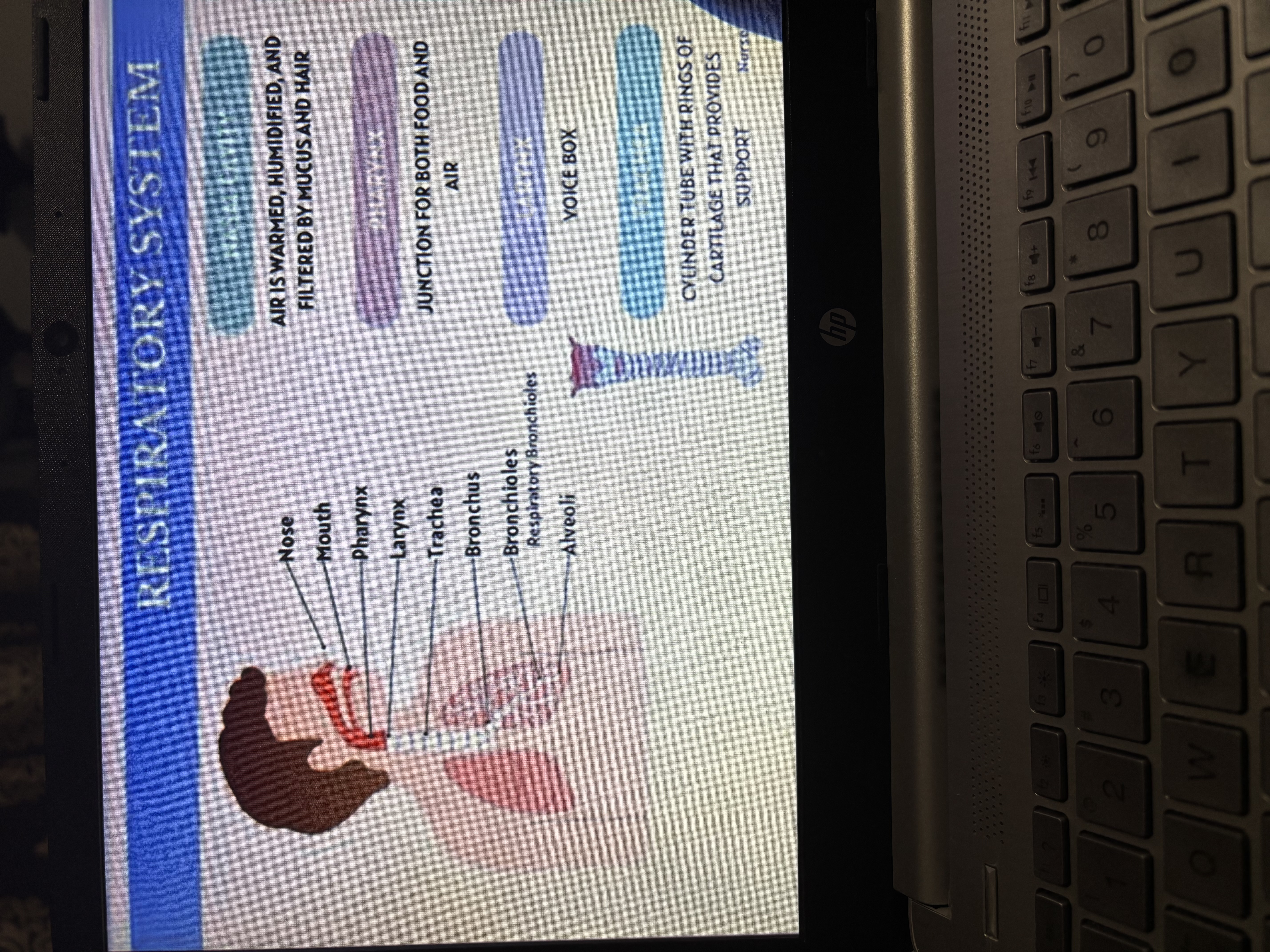
Respiratory system
Mnemonic to Remember the Order:
“Nice People Like Taking Big Big Apples” Nice – Nose
People – Pharynx
Like – Larynx
Taking – Trachea
Big – Bronchi
Big – Bronchioles
Apples – Alveoli
🫁
Air’s Journey Through the Respiratory System (Step-by-Step):
Nose/Nasal Cavity – Air enters here. It gets filtered, warmed, and moistened.
Pharynx (throat) – A shared tube for air and food.
Larynx (voice box) – Air passes through; helps with sound.
Trachea (windpipe) – Main airway going down the neck.
Primary Bronchi – Trachea splits into two main tubes:
Right Primary Bronchus → right lung
Left Primary Bronchus → left lung
Secondary Bronchi – Each primary bronchus divides into smaller branches going to each lobe of the lungs:
Right lung → 3 secondary bronchi
Left lung → 2 secondary bronchi
Bronchioles – Tiny tubes that branch from secondary bronchi like thin tree branches.
Terminal Bronchioles – The last part of the bronchioles.
They do NOT do gas exchange, but they lead into the next part that does.
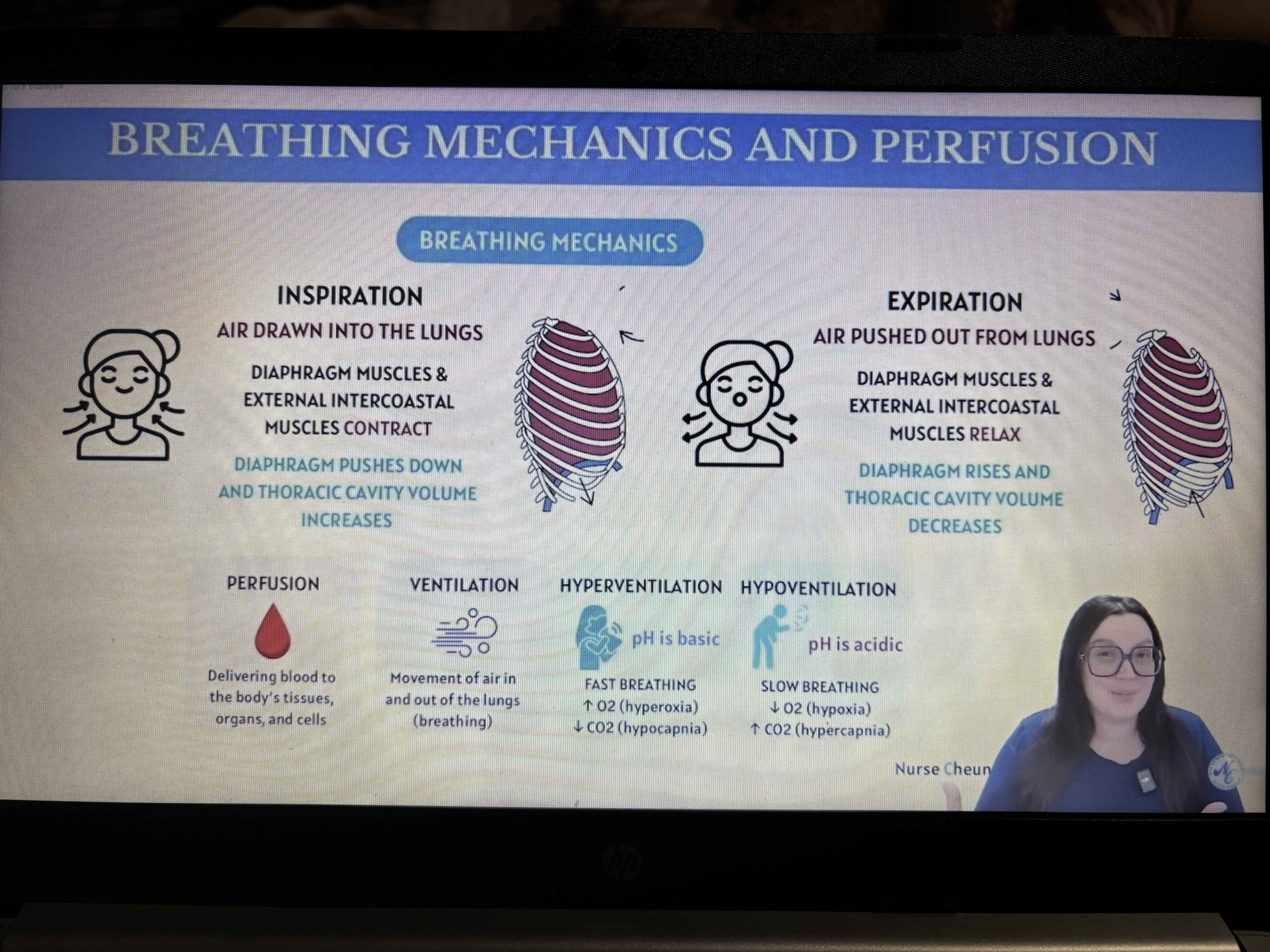
Perfusion, ventilation, hyperventilation, hypoventilation
1. VentilatioN
Definition: The process of moving air in and out of the lungs (a.k.a. breathing).
✅ Brings in oxygen
✅ Removes carbon dioxide
Controlled by:
Diaphragm & intercostal muscles
Brainstem (medulla oblongata)
2. Perfusion
Definition: The flow of blood through the lungs, especially around the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
✅ Brings CO₂-rich blood to lungs
✅ Picks up O₂ to deliver to the body
Remember:
Ventilation = AIR
Perfusion = BLOOD
🌬3. Hyperventilation
Definition: Fast, deep breathing beyond the body’s needs.
✅ CO₂ is blown off too quickly
🔻 Leads to low carbon dioxide (hypocapnia)
🔺 Blood becomes more alkaline (respiratory alkalosis)
Causes:
Anxiety or panic attacks
Pain
Fever
Brain injury
Symptoms:
Dizziness
Tingling in fingers/lips
Lightheadedness
😮💨4. Hypoventilation
Definition: Slow or shallow breathing that doesn’t meet the body’s oxygen needs.
❌ Not enough CO₂ is exhaled
🔺 Leads to high carbon dioxide (hypercapnia)
🔻 Blood becomes more acidic (respiratory acidosis)
Causes:
Drug overdose (like opioids)
Brain injury
Lung disease (e.g. COPD)
Obesity-related hypoventilation
Symptoms:
Confusion
Sleepiness
Headache
Shortness of breath
Next
Respiratory Bronchioles – These start gas exchange.
Tiny openings allow oxygen in, and carbon dioxide out.
Alveolar Ducts – Short tubes that connect respiratory bronchioles to alveoli.
Alveoli (Air Sacs) – The final destination.
Tiny balloon-like sacs
Surrounded by capillaries
This is where oxygen enters your blood, and carbon dioxide leaves your blood.
Function of the Respiratory Syste
Main job: Bring in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide
Works closely with the circulatory system (blood carries the gases)
Pathway of Air (From Nose to Alveoli)
Nose → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Primary Bronchi → Secondary Bronchi → Bronchioles → Terminal Bronchioles → Respiratory Bronchioles → Alveolar Ducts → Alveoli
Naughty = Nose
People = Pharynx
Love = Larynx
To = Trachea
Party = Primary Bronchi
So = Secondary Bronchi
Badly = Bronchioles
They = Terminal Bronchioles
Really = Respiratory Bronchioles
Are = Alveolar Ducts
Annoying = Alveoli
Zones of the Respiratory System
Conducting Zone
(Air passage only, NO gas exchange):
Nose/nasal cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi (primary & secondary)
Bronchioles
Terminal bronchioles (last part before gas exchange begins)
Respiratory Zone
(Gas exchange happens here):
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar ducts
Alveoli (where oxygen enters blood, CO₂ exits)
Lungs & Structures
Right lung = 3 lobes
Left lung = 2 lobes (because of the heart)
Pleura = double-layered membrane around the lungs
Alveoli = tiny sacs for gas exchange (surrounded by capillaries)
Diaphragm = dome-shaped muscle under the lungs that controls breathing
5 Breathing Mechanics (Ventilation)
Inhalation (Breathing in)
Diaphragm contracts (moves down)
Chest expands
Pressure in lungs decreases
Air flows in
Exhalation (Breathing out)
Diaphragm relaxes (moves up)
Chest gets smaller
Pressure increases
Air flows out
🧠 6.Gas Exchange & Transport
Happens in the alveoli
Oxygen diffuses into blood
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of blood
✅ Blood coming to the lungs = low in oxygen, high in CO₂
✅ Blood leaving the lungs = rich in oxygen
What muscle helps you breathe
Diaphragm – contracts to pull air in, relaxes to push air out.
What protects the lungs?
Rib cage and pleura (membrane