Cytogenetics 2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Whats G banding and what are its pros and cons?
It’s the old school way of looking at chromosomes
It’s good to js look over an entire genome but bad for small things cuz it has low resolution
What’s FISH and what’s its use?
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
Uses specific fluorescent probes to hybridize and visualize specific points in genome
Useful for specific situations and hypotheses
Has high resolution, wherever it binds to DNA will fluoresce
What’re microsyndromes seen by, and what’s the general idea behind them?
Can be seen by FISH
Specific features of syndrome may occur as single Mendelian disorders
Involved multiple, unrelated loci physically continuous in critical region
They are submicroscopic effects which suggests not all patients have visible deletions
Whats an example of micro syndromes?
Microdeletion and microduplication
Occurs due to unequal crossing over due to repeat regions
Explain diagram
Explain what microdeletion 22q11.2 is and related disorders
It’s the most common chromosomal disorder
Related disorders: DiGeorge syndrome, autosomal dominant Opitz, Sedlackova syndrome, Sphrintzen syndrome, VCF
Explain the idea of VCF
What was DiGeorge syndrome used to to be thought to be caused by?
Environmental factors like alcohol or retinoids acid exposure due to craniofacial defects As well as immune deficiency, brain and behavioural abnormalities
With modern techniques known to be micro deletion syndrome
What’s the most amount of genes affected by 22q11.2 deletion syndrome?
60 genes affected
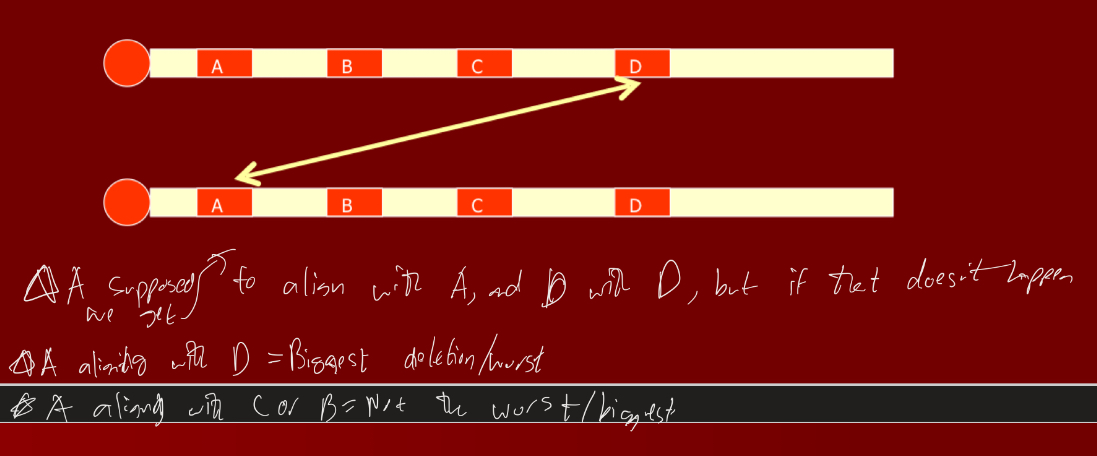
Whats the cause of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome and explain diagram that goes with it
Caused by non-allelic homologous recombination (unequal crossing over) at a series of low copy repeats
Depending on how far/ distant alleles that recombined are dictates how bad/ severe it is
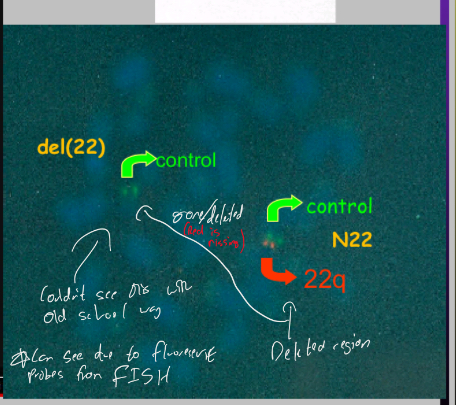
What kind of inheritance is in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome?
Autosomal dominant inheritance (Mostly on one copy, people aren’t really heterozygous for it)
Incidence of 1/4000 births
10% inherited - 90% de novo
No bias for sex of ethnicity
1/1000 fetuses carry this deletion, but most (3/4) terminate naturally
Explain the expressivity of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome
Variable expressivity depending on the size of the deletions which causes variable severities. This is due to variations in gene expression levels (epigenetics) and modifier genes
Has variable expressivity even among people with the same deletion
What genes are involved in the deleted region of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome?
Several of them are involved in facial development, covering gene dosage for a bunch of genes involved in facial development
TBX1 - Involved in neural crest cell migrations and craniofacial development
TBX1 -/- knockout mice have similar facial defects to 22q11.2 DS
CRKL and ERK2 also cause facial defects in -/- knockout mice
Combined haploinsufficiency of multiple genes causes the defect
Explain contiguous gene syndrome
When a micro deletion results in the loss of a cluster of genes on a chromosome. This results in heterozygosity for these loci
But the problems start arising when theres heterozygosity for many loci which is like an autosomal monopsony
Genes that function together often cluster together so CGS can affect multiple loci acting in one developmental pathway which is like combined haploinsuffciency (ex: facial development in 22q11.2)
Provide an example of FISH used to test a specific hypothesis
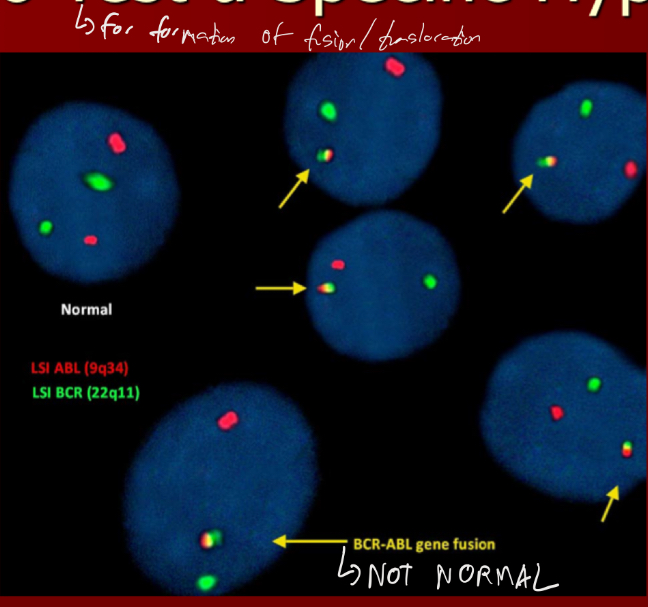
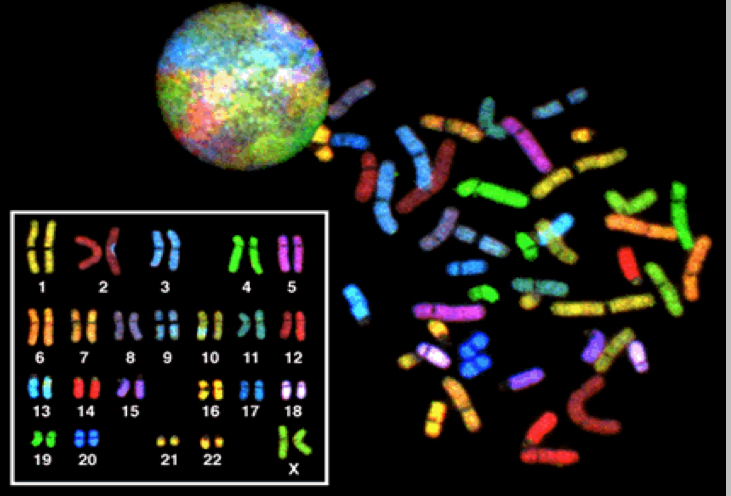
Whats an exception in FISH that looks at the entire genome?
SKY (but is rlly intensive as it requires a lot of filters)
Whats the difference between FISH and Microarrays?
FISH is for specific questions/ chromosomes and you usually have to know what you’re looking for cuz you need sequence specific probes (except for SKY which looks at entire genome)
Microarrays let you take a general look at the genome without initial bias. Like G-banding but with very high resolution
They both use high resolution
What’re the 2 types of cytogenetic microarrays?
Copy number or comparative genomic hybridization array (aCGH)
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)
What does comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) do and explain how it works?
Looks at copy number variation
Has 2 samples (patient and control) so 2 copies of everything. Compares between the patient and control to see If patient has same amount of DNA as control
If patient as a control have same amount of DNA = yellow
If not will have some spots red and/or green depending on what has more
What are microarrays packaged into?
Gene chips
Explain the 2 examples on the back
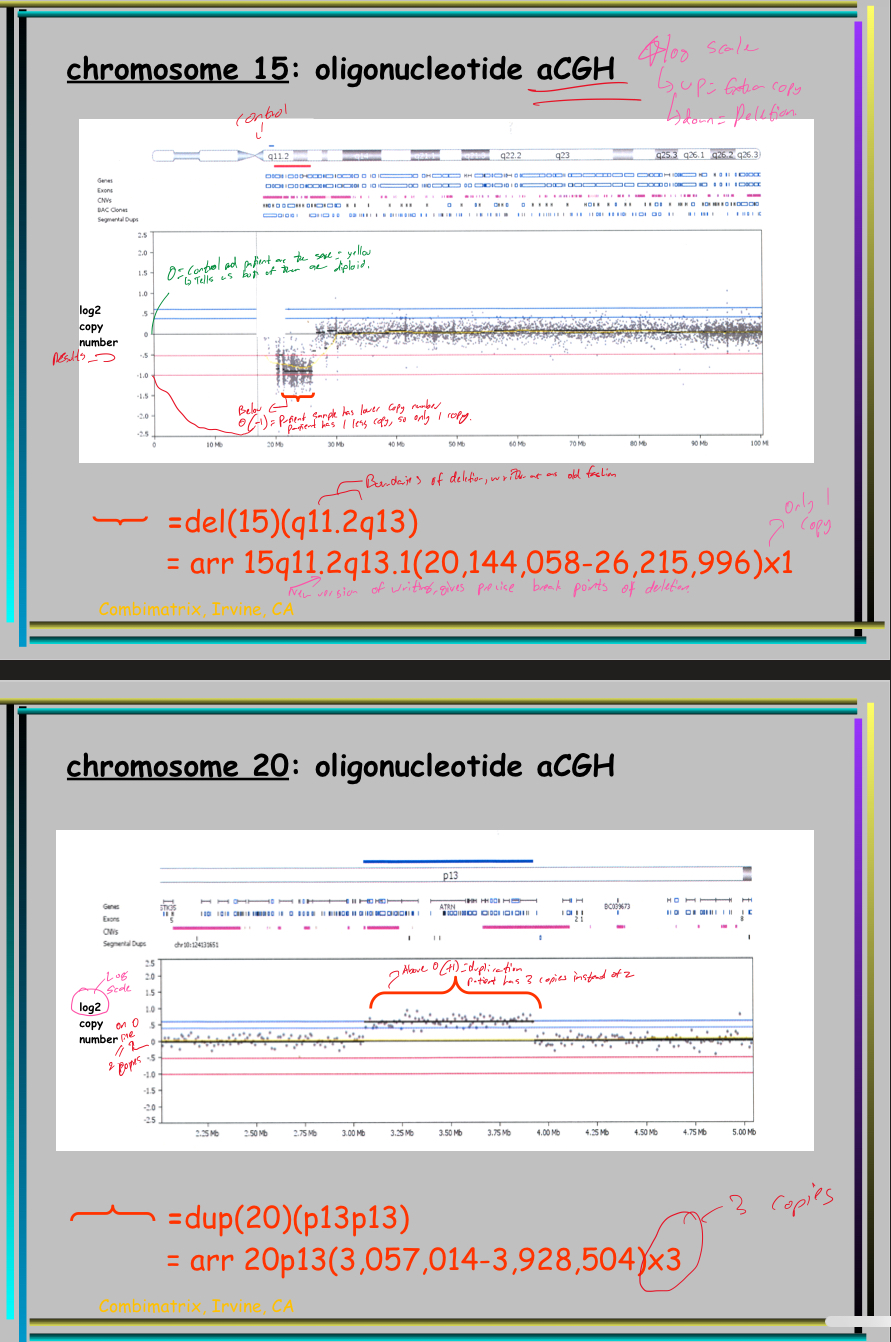
What does + and - mean on the log scale for CGH?
+/ up = Extra copy/ duplication
-/ down = Deletion
What’re Copy number variants or copy number change (CNC)?
A DNA segment with a variable copy number or copy number change compared to a reference genome
Although present in a normal person, may be associated with disease susceptibility (reduced penetrance and variable expression)
Ex: how we process drugs/ caffeine depending on copy # of enzymes
Can CGH microarrays be used to detect a reciprocal translocation or inversion and why?
No cuz the copy number in a reciprocal translocation or inversion doesnt get affected/changed cuz theres no net gain or loss of copy number
What do SNPs do?
Analyze single base pair variation between samples
Can track allelic ratios through the whole genome
Any SNP locus allele can be scored as either A or B
They don’t need a control
How many genotype possibilities at each SNP locus if disomy?
3 (AA, AB, BB)
How many genotype possibilities at each SNP locus if monopsony?
2 (A or B)
How many genotype possibilities at each SNP locus if trisomy?
4 (AAA, AAB, ABB, BBB)
Explain the following example
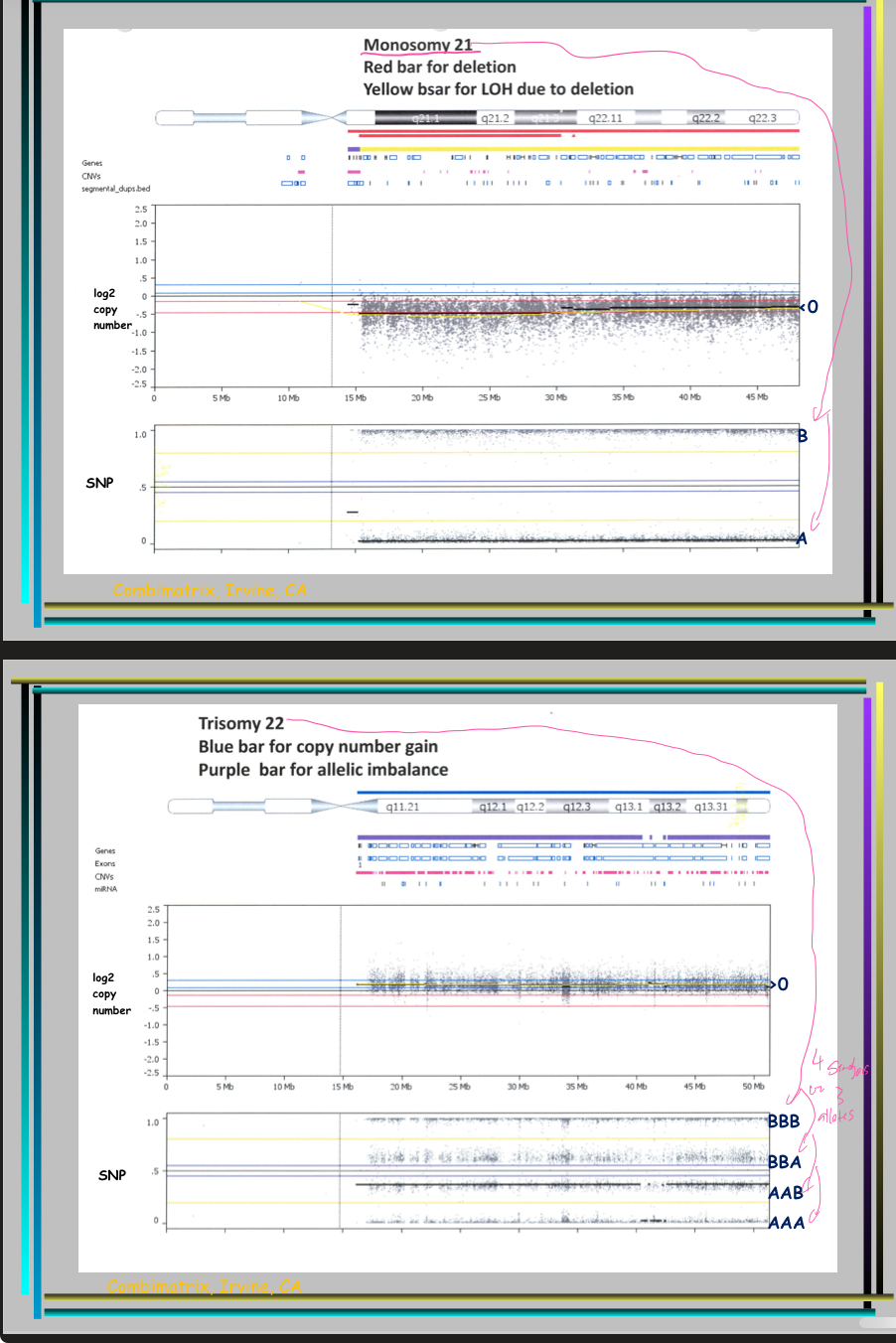
What’re the 2 ways to diagnose 22q11.2 deletion?
If the patient signs and symptoms suggest it, FISH could be used as a direct test of a deletion (ex: facial features)
CGH or SNP microarray can reveal a deletion (would show where it is and its size)
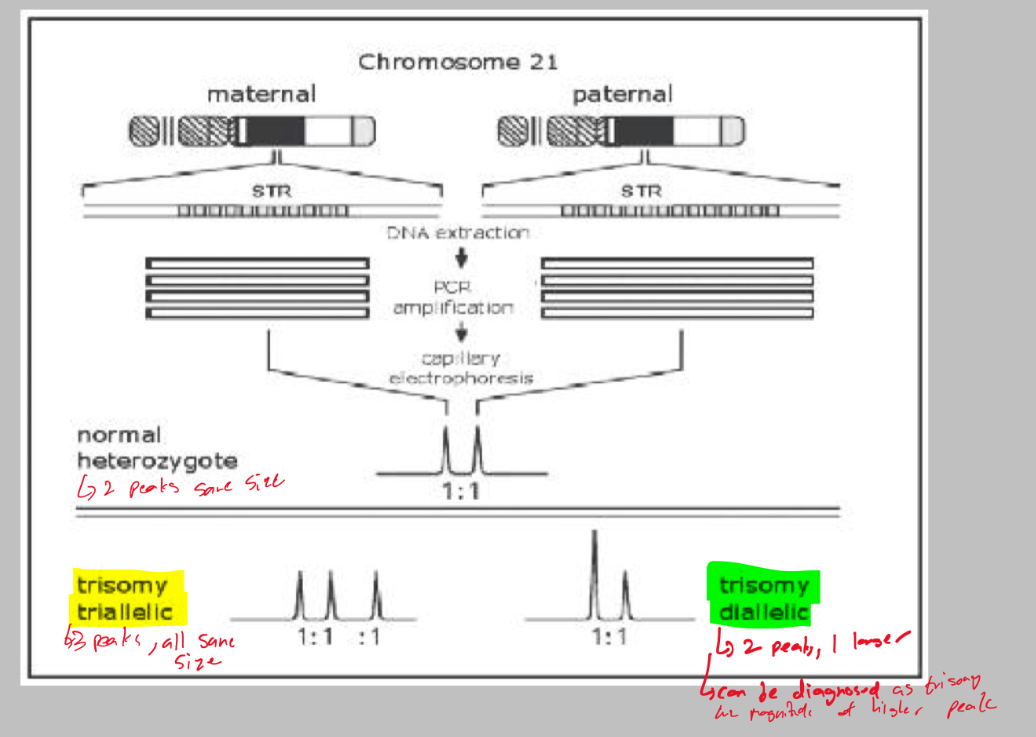
Whats QF-PCR and its function?
Quantitative Fluorescent-PCR
Amplify STR loci from the chromosomes of interest. You can separate the alleles by size and also compare relative amounts of DNA
Normally there’ll be 2 alleles with equal amounts of DNA
In a trisomy there will be 3 alleles (triallelic) or 2 alleles with one having double the amount of DNA (diallelic)
Explain trisomy triallelic and trisomy diallelic in QF-PCR
Whats imprinting?
Expression of some genes is determined by parental origin
Expression in the zygote/ offspring is mono-allelic (expressed only from the maternal or paternal chromosome)
Ex: the maternal or paternal copy of an imprinted locus is silenced through germline methylation
How is imprinting determined?
Via methylation, its determined in the maternal and paternal germlines and maintained in the somatic tissues
Explain genomic imprinting in somatic and germline tissues
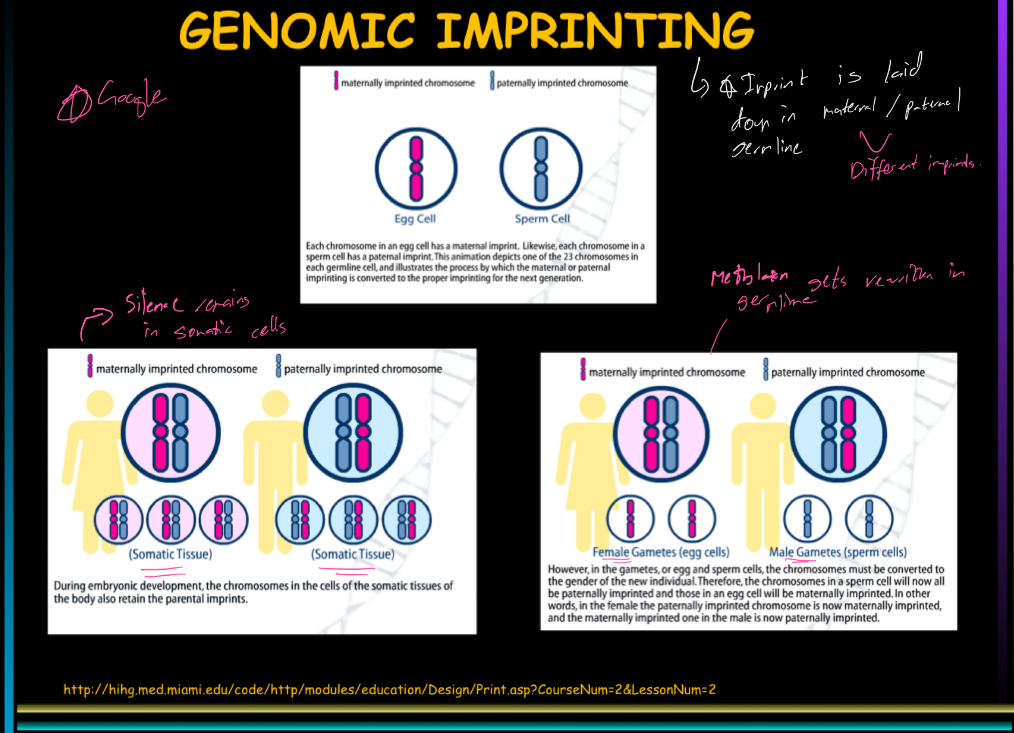
Explain the different parental origin effects if an allele is silenced
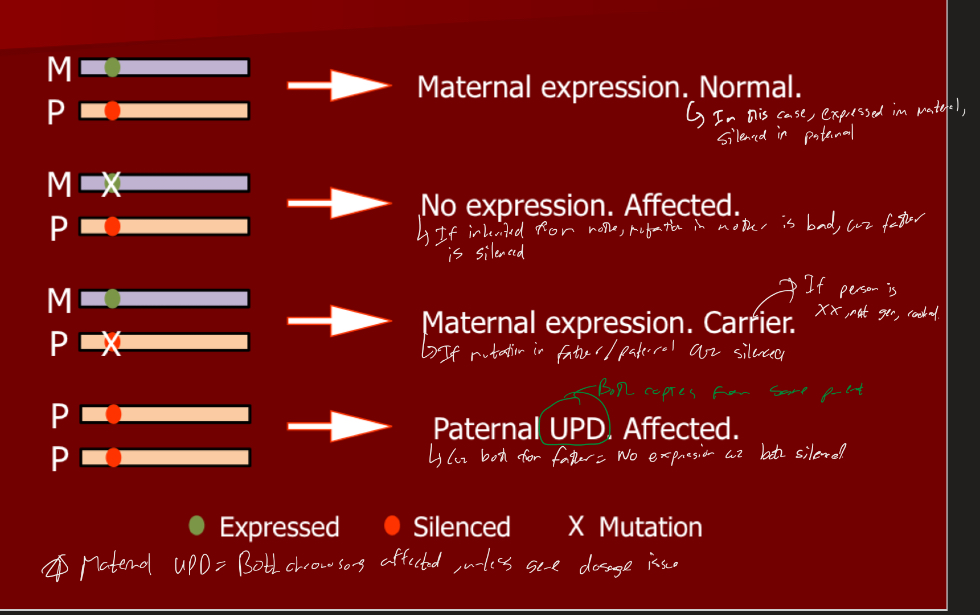
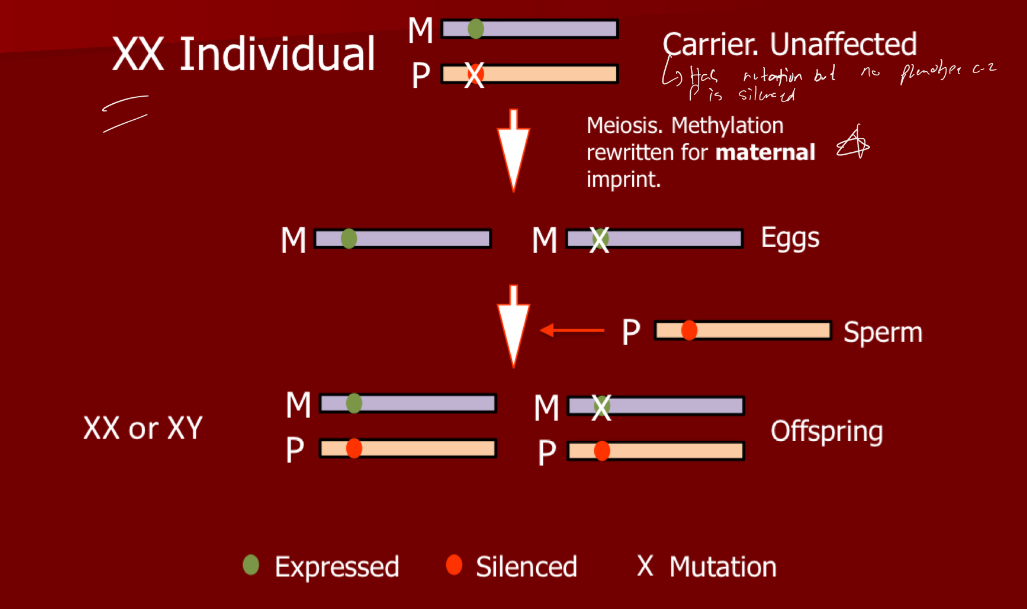
Explain what would happen from an XX individual if methylation was rewritten for maternal imprint
Explain what would happen from an XY individual if methylation was rewritten for paternal imprint
What’re some examples of imprinting disorders?
Uniparental disomy (UPD)
Monoallelic expression
Prader-Willi chr 15
Explain Prader-Willi syndrome

Whats the mechanism of silencing?
DNA methylation silences transcription, but not directly on the imprinted locus
DNA methylation can silence lncRNA loci that act to silence the imprinted loci (like Xist and X-inactivation)
So the methylated chromosome can be the one with the active allele
Whats the parental conflict hypothesis?
