CHEM 1211 Section 5.3 (Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Polarity
a situation in which there is a difference in electron density and, therefore, electrical charge between one part of the molecule and the other. Controls whether or not a covalent compound is found as a gas or liquid at room temp
polar bonds
For a molecule to be polar, it must possess _____ _____ (a bond dipole). This means there must be a significant different in electronegativity (EN) between the two atoms in the bond.
The parts of molecular geometry that determine a molecule’s polarity
Polarity of individual bonds, bond number and bond arrangement
Bond Dipole
a measure of the separation of electrical charge in a covalent bond between two atoms of different electronegativity (the greater the EN, the greater the bond dipole)
Polar Molecule
has polar bonds that do not cancel out, causing the molecule to have a permanent dipole.
Permanent Dipole
permanent separation of electrical charge in a molecule
cancel
To determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar, we must see if the bond dipoles ______ each other out.
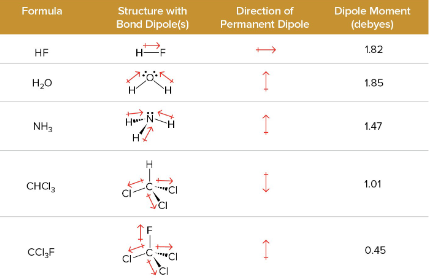
Vector Analysis
used to help add up the different pond polarities
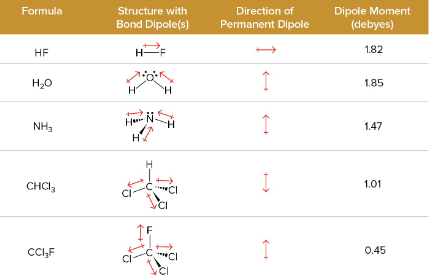
Debyes (D)
the unit of measurement for polarity in molecules, measured in dipole moment
gasses
Nonpolar compounds are most commonly found as ______ at room temperature.
liquids
Polar compounds are most commonly found as _______ at room temperature.
Cis-isomer
have two identical functional groups on the same side of a molecule
Trans-isomer
have the functional groups on opposing sides of the molecule
Stereoisomer
molecules that have the same chemical formula but different spatial arrangements of their atoms
one; other
It is possible for ___ stereo-isomer to be polar, while the _____ is nonpolar
True
VSEPR and bond polarity help determine whether a molecule has a net dipole (polar) or not (nonpolar)
net dipole
If a molecule has a ___ ______, it is polar.
no net dipole
If a molecule has __ ___ ______, it is nonpolar.
canceled out
A polar molecule has at least one polar bond that is not completely ________ ___ by the other bonds.
predisposed
Some molecular geometries are more ___________ to have polar/nonpolar molecules.
chemical properties
Even isomers with the same chemical formula may have different ________ __________, like being polar vs nonpolar.