Lecture 13: WACC, floatation costs, leverage & beta, industry beta
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the cost of capital formula? (The Wacc)
The weighted average cost of capital
ws = weight of equity
wd = weight of debt
rs = cost of equity
rd = cost of debt
Tc = corporate tax rate
interest expense is tax deductible so multiply by (1 - T) to find after tax cost of debt

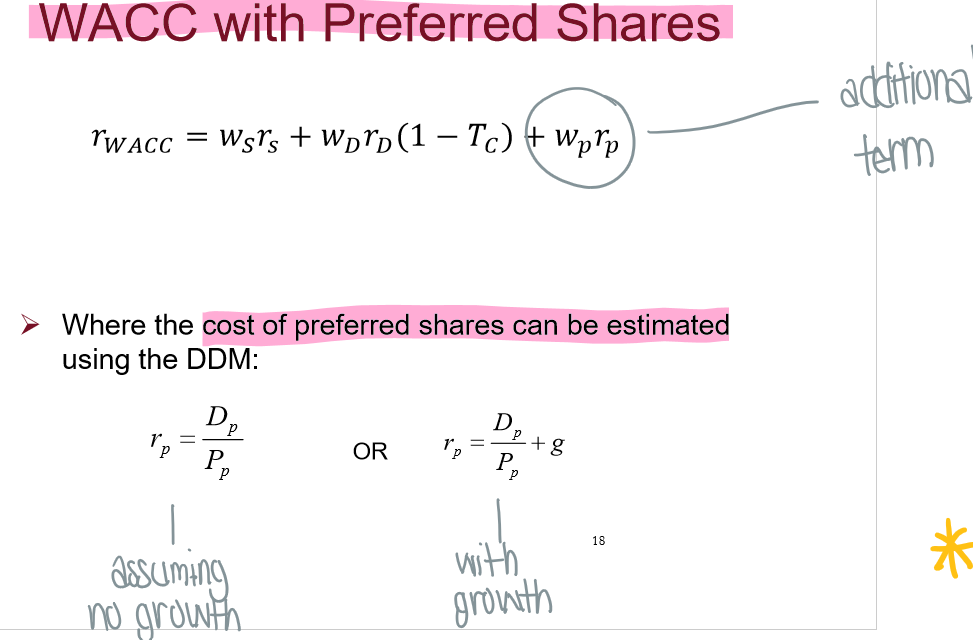
What is the WACC (cost of capital) with preferred shares formula?
wp = weight of preferred shares
rp = cost of preferred share
What is the WACC (weighted average cost of capital) from investors & firm’s perspective?
Investors: tells us the returns of investing in a firm
Firms: tells us the average cost of issuing debt
What is the WACC used for?
WACC is the discount rate used in capital budgeted & used to discount free-cash-flow to find firm’s value
used to make investing decisions between projects
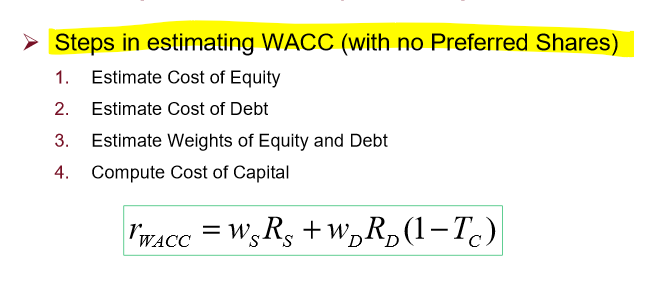
What are the 4 steps to estimating the WACC?
estimate cost of equity
estimate cost of debt
estimate weights of equity & debt
compute cost of capital
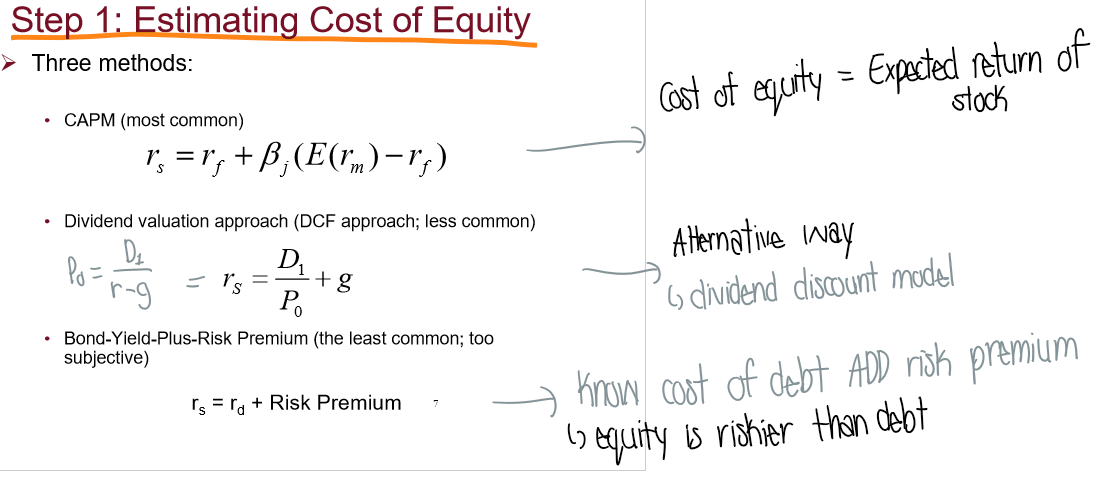
What are the 3 methods to estimating cost of equity?
CAPM
Dividend valuation (less common)
Bond yield plus risk premium (least common)
What risk free rate do you use in the CAPM equation?
It depends on what the WACC is used for
in asset pricing (investments), always use the T-bill rate as the risk-free rate!
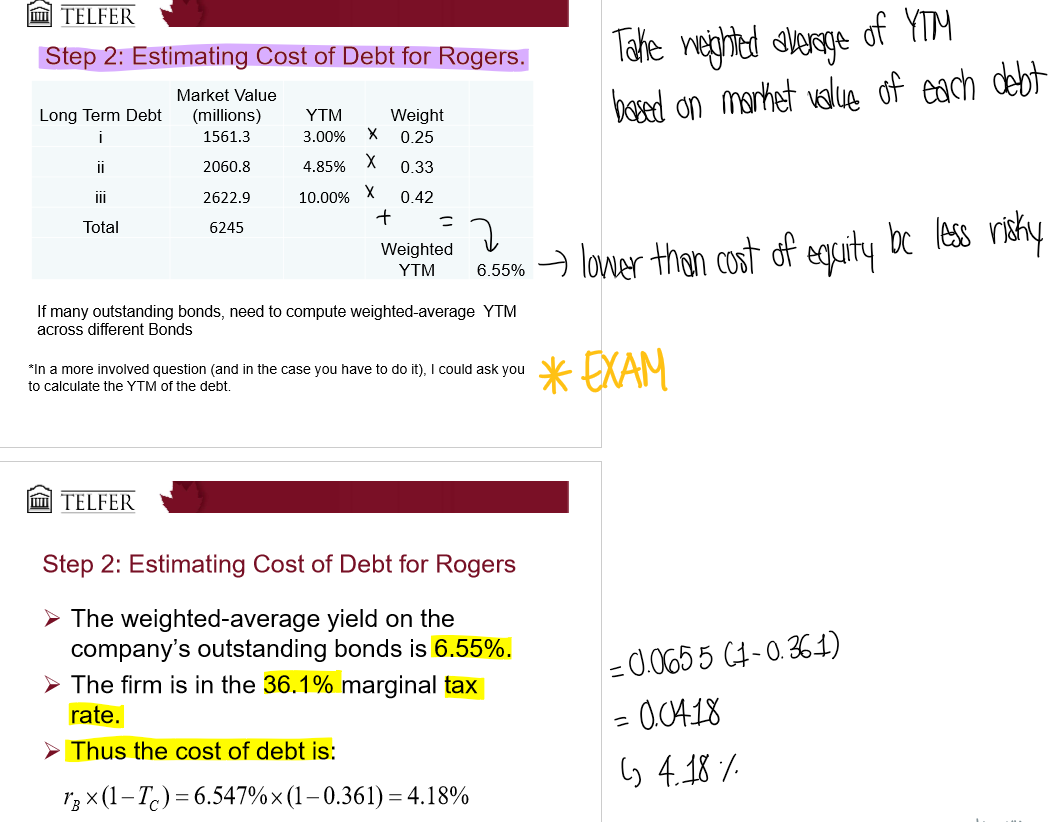
How do you estimate the cost of debt?
Use the YTM (yield to maturity) that the firm uses to pay their debts!
if firm has outstanding bonds, the weighted average of YTM on these bonds can be used as market’s required rate of return on new debt
if no outstanding bonds, bonds of similar companies/same industry can be used
Do you include short term debt in WACC calculations?
Usually not → WACC is used for capital budgeting (long-term asset decisions)
focus on long-term debt
Exclude: if short term debt is used to finance current operations
Include: if short term debt is used to finance a long-term asset (bad idea because uncertainty about new interest rates when more short-term debts are needed)
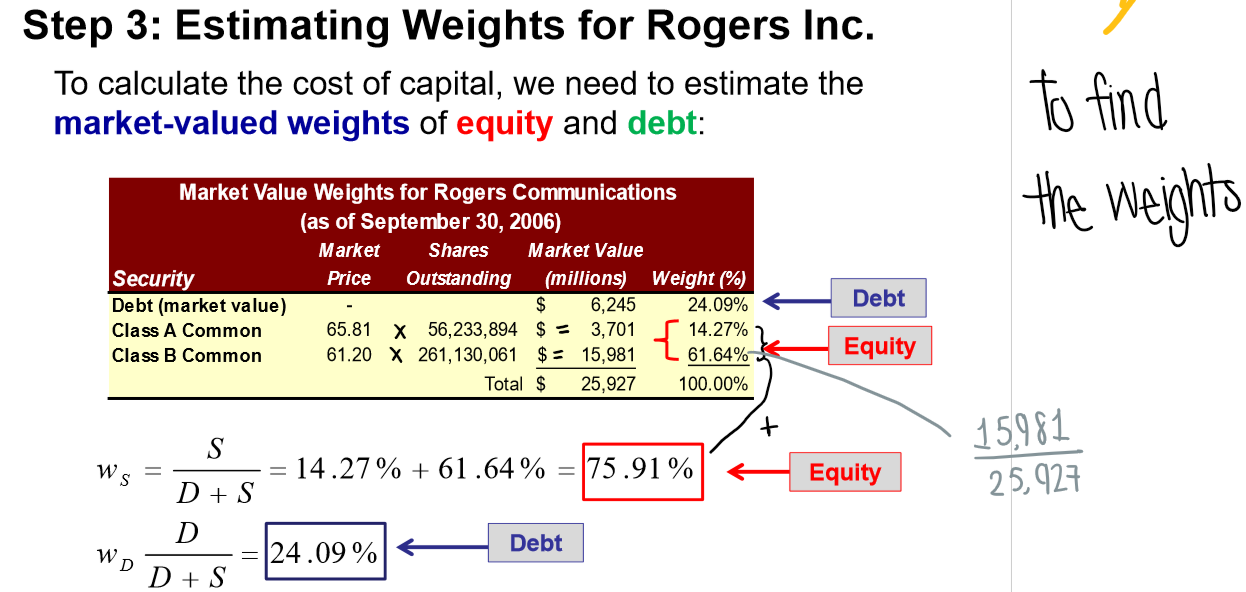
How do you estimate the weights of equity & debt?
Multiply the market price by the shares outstanding
take the sum and multiply by the total to find the weights
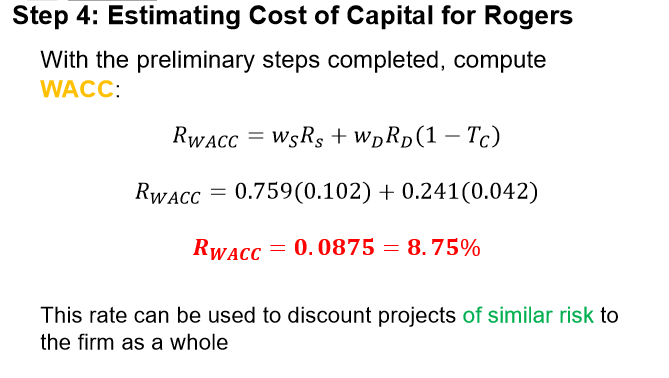
How do you estimate the cost of capital?
Use the WACC formula!
What are floatation costs?
Costs of issuing new securities → measured as a percentage of security price
to account for floatation costs, use P x (1 - F)

How much will Beta change relative to changes in leverage?
More leverage = more risk → Beta measures risk and will obviously increase, but by how much?
Assets = Debt + Equity
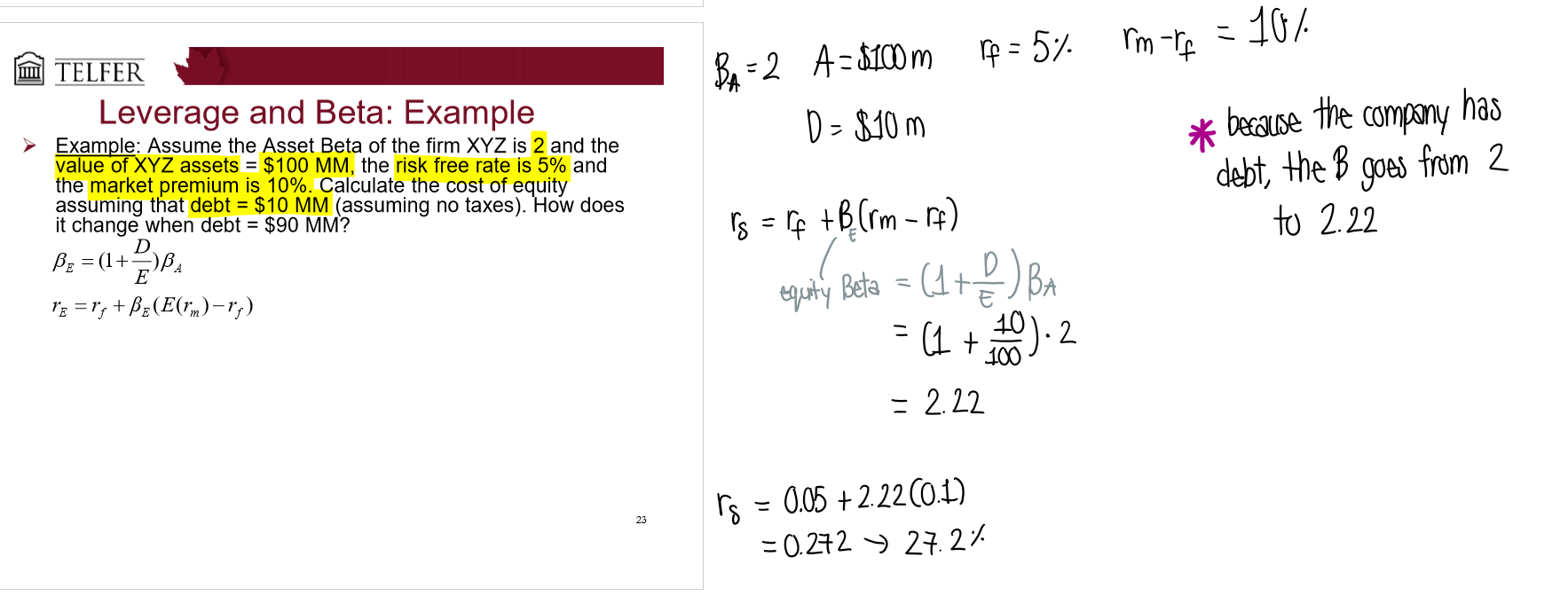
What is an asset beta and equity beta?
Asset beta (unlevered beta) - beta of a firm with no debt → no leverage
Equity beta (levered beta) - beta of a firm with debt → leverage
What are some specific issues with project WACC?
A project’s cost of capital depends on risk of the project not the risk of the firm
if risk of new project is different from existing operations, should apply a different discount rate
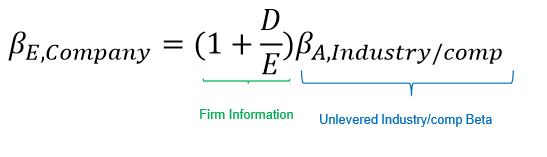
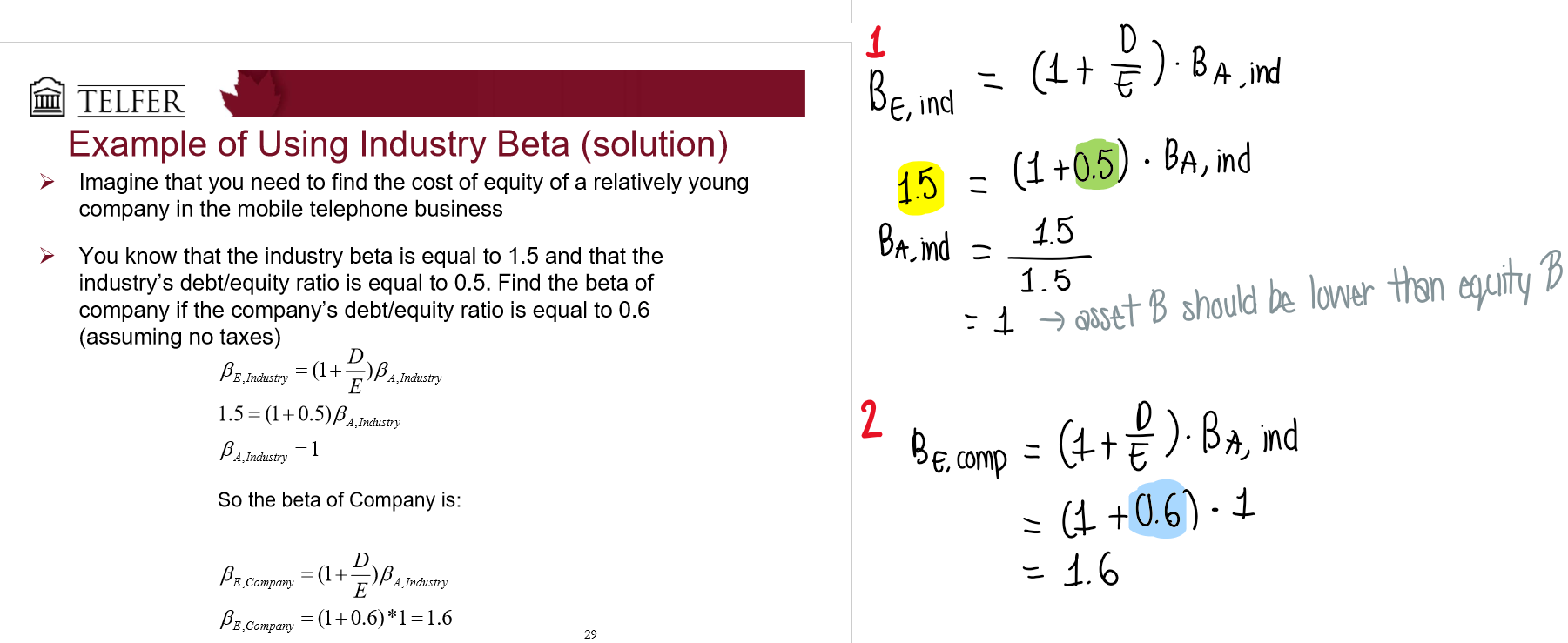
How do you use industry/comparable betas?
Find comparable companies with similar operations to estimate the WACC
Estimate the industry Beta
Un-lever the beta by finding beta without debt
Re-lever to reflect company structure & taxes