PMCY 4050 Exam 1 - Skeletal Anatomy
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Function of Bones
Support and permit movement, protection, marrow functions for formation of blood cells (hematopoiesis), storage of fat (yellow marrow) and minerals (calcium, phosphorus)
Compact Bone
Denser, covers most bones, better storage of minerals
Spongy Bone
Open network of trabeculae, lace-like appearance, trabeculae contain marrow
Osteoblasts
Bone builders; synthesize collagen and proteoglycans, function is to form new bone
Osteocytes
Osteoblasts that are entrapped in the mineralized bone matrix, maintain minerals and organic elements in matrix by coordinating with osteoblasts and osteocytes (construction men)
Osteoclasts
Bone breakers; resorb bone during growth and repair
Bone Formation
Infants’ skeleton is primarily made of cartilage, Cartilage replaced with bone, Growth occurs at epiphyseal plates, New cartilage forms, Older cartilage broken down and becomes ossified, bone remodeling
Bone Remodeling
Increased bone size = muscle hypertrophy
Decreased bone size = muscle atrophy
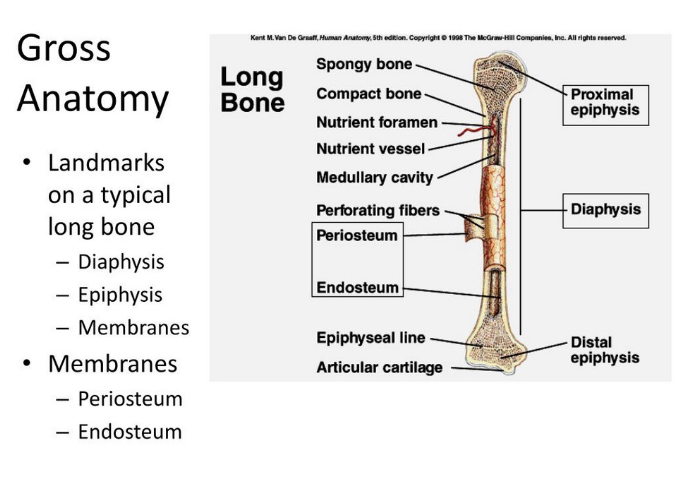
Long Bone Anatomy
Articular cartilage at ends - epiphyses (compact bone surrounding spongy bone) - diaphysis (compact bone)
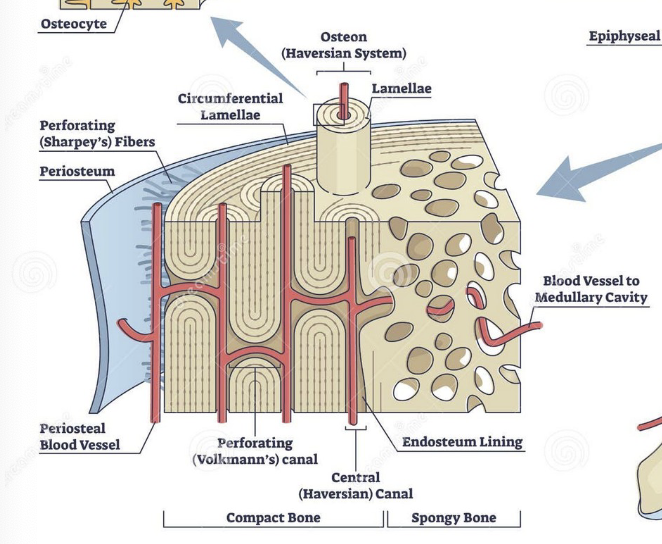
Central canal (Haversian system)
Center of osteon, conduit for blood vessels
Volkman's canal
Perpendicular to central canal, conduit for blood vessels and nerves
Lacunae
contain osteocytes, arranged concentrically
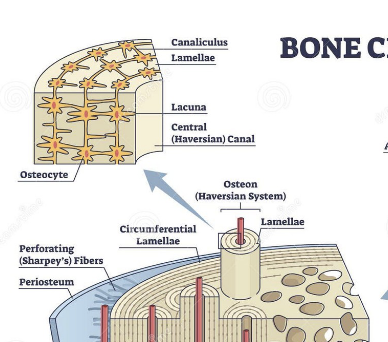
lamellae
lacunae present, circle the central canal
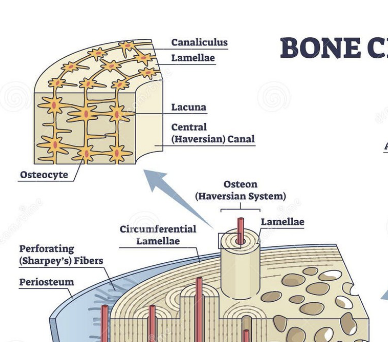
canaliculi
transport nutrients to bone cells, radiate from central canal to lacunae
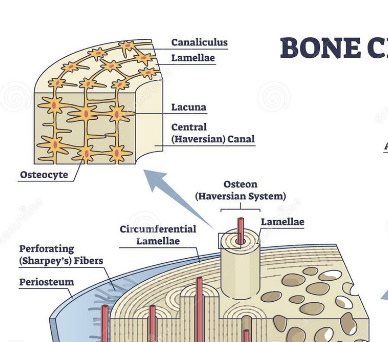
Periosteum (long bone)
Outer covering of shaft connected by Sharpey's fibers
Medullary cavity (long bone)
Contains yellow marrow (adults), red marrow (infants) for formation of blood cells
Synovial Joints
Most movable and most complex joints
-articular capsule
-synovial membrane
-synovial cavity
-synovial fluid
-articular cartilage
Synarthrosis
immovable
Amphiarthrosis
slightly movable
Diarthrosis
freely movable
Joint capsule
Connective tissue covering ends of bones, supplied with nerves, vasculature and lymphatic vessels
Synovial membrane
Smooth inner lining of joint capsule, supplied with blood and lymphatic vessels, rapid repair and regeneration
Synovial cavity
Enclosed fluid filled space between bones, allows bones to move against each other
Synovial fluid
Suprefiltrated plasma from blood vessels in synovial membrane, loss of fluid = rapid deterioration of articular cartilage
Chondrocytes
Cells that compose cartilage, along with a matrix of collagen, proteins, and water.
Axial Skeleton
Maintains upright posture and transfers weight to lower extremities (skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum)
Skull
Composed of the cranium: frontal, parietal, temporal
Facial bones: maxillary, palatine, nasal, vomer, inferior nasal conchae, zygomatics, lacrimal, mandible
Associated auditory ossicles and hyoid.
Articular cartilage
- Hyaline cartilage covering the end of each
bone
– Functions to reduce friction and to distribute
weight-bearing forces
– Composed of chondrocytes and a matrix of
collagen, proteins and water
– No blood vessels, lymph vessels or nerves
– Regenerates slowly
Sinuses
Hollow areas in the skull named based on the bone; provide resonance and amplify sounds when speaking.
Fetal Skull
Contains fontanelles (soft fibrous membranes that convert to bone at approximately 24 months); the fetal skull is large compared to body length.
Vertebral Column
C1 - Atlas
C2 - Axis
C1 - C7 = Cervical
T1 - T12 = Thoracic
L1 - L5 = Lumbar
Sacral + Coccyx
Vertebrae separated by fibrocartilage discs that absorb shock (degenerated disc disease)
Pelvic Girdle
Ilium, ischium, and pubic bone; protects the bladder/large intestine/reproductive organs, carry the weight of the upper body
Females are lighter/thinner vs male
Aging and Musculoskeletal Function
Characterized by loss of bone tissue, increased rigidity and fragility of cartilage, decreased range of motion, age-related loss in muscle mass (sarcopenia), and decreased lean body mass.
Osteoporosis
Can be generalized/regional, density or mass of bone is reduced, remaining bone normal but insufficient to maintain structural integrity and mechanical support (spongy and compact bone is lost but spongy more easily)
Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Middle-aged and older women bc decreased estrogens - sensitizes osteoclasts to parathyroid hormone actions and initiates bone resorption.a
Causes of Osteoporosis
Includes shrinkage or alterations in osteoblasts and osteoclasts, reduction in physical activity, insufficient intake or malabsorption of dietary minerals, hormonal imbalances
Pathophysiology of Osteoporosis
Bone remodeling cycle is disrupted --> imbalance between the rate of resorption and the rate of new bone formation.
Clinical Manifestations of Osteoporosis
Symptoms include pain and bone deformity, fractures being common and potential for hunchback and diminished height
Appendicular Skeleton
Shoulder girdle, arm, hand, pelvic girdle, leg, foot