ANA124: Cardiovascular Quiz (H1)
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
where does the right side of the heart begin
rib 3
where does the right side of the heart end
rib 6
where does the left side of the heart start
starts approx. between rib 2 and rib 3
where does the left side of the heart end
ends at the mid-clavicular line between rib 5 and rib 6
what is the mediastinum
space in the middle of your chest
found between the two lungs
what are the boundaries of the mediastinum
superior
inferior
anterior
middle
posterior
where is the superior boundary of the mediastinum
begins at the thoracic inlet (neck’s base)
what does the superior boundary of the mediastinum contain
contains your..
esophagus
trachea
superior vena cava (SVC)
arch of aorta
nerves
where is the inferior boundary of the mediastinum
begins under the line between the sternal angle and T4 / T5
where is the anterior boundary of the mediastinum
located at the sternum (front wall of the mediastinum)
what does the anterior boundary of the mediastinum contain
contains your..
thymus gland
fat
lymph nodes
where is the middle boundary of the mediastinum
located in the centre of the chest
surrounded by the anterior, posterior, and superior mediastinum
what does the middle boundary of the mediastinum contain
contains your..
heart
great vessels
pericardium
phrenic nerves
where is the posterior boundary of the mediastinum
thoracic vertebral column (forms the posterior wall of the mediastinum)
what does the posterior boundary of the mediastinum contain
contains your..
esophagus (inferior part)
descending aorta
inferior vena cava (IVC)
nerves
what is the pericardium
it is a double-layered sac that surrounds + protects the heart
what are the layers of the pericardium
fibrous pericardium
serous pericardium
visceral layer
parietal layer
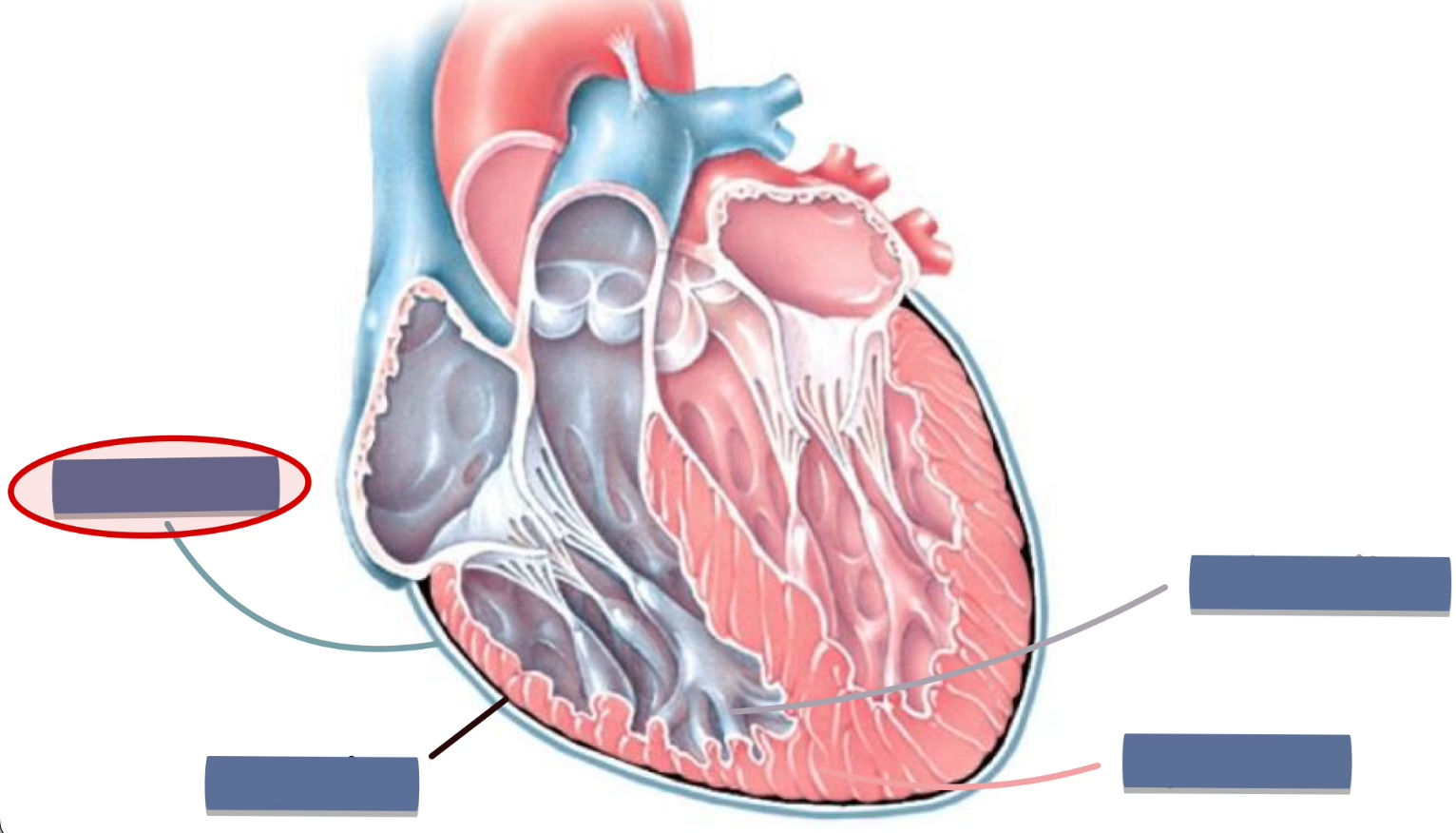
label the following
pericardium
what is the epicardium
thin, elastic layer directly on the heart’s surface
function of the epicardium
adds extra protection for the heart (prevents friction)
contains coronary vessels
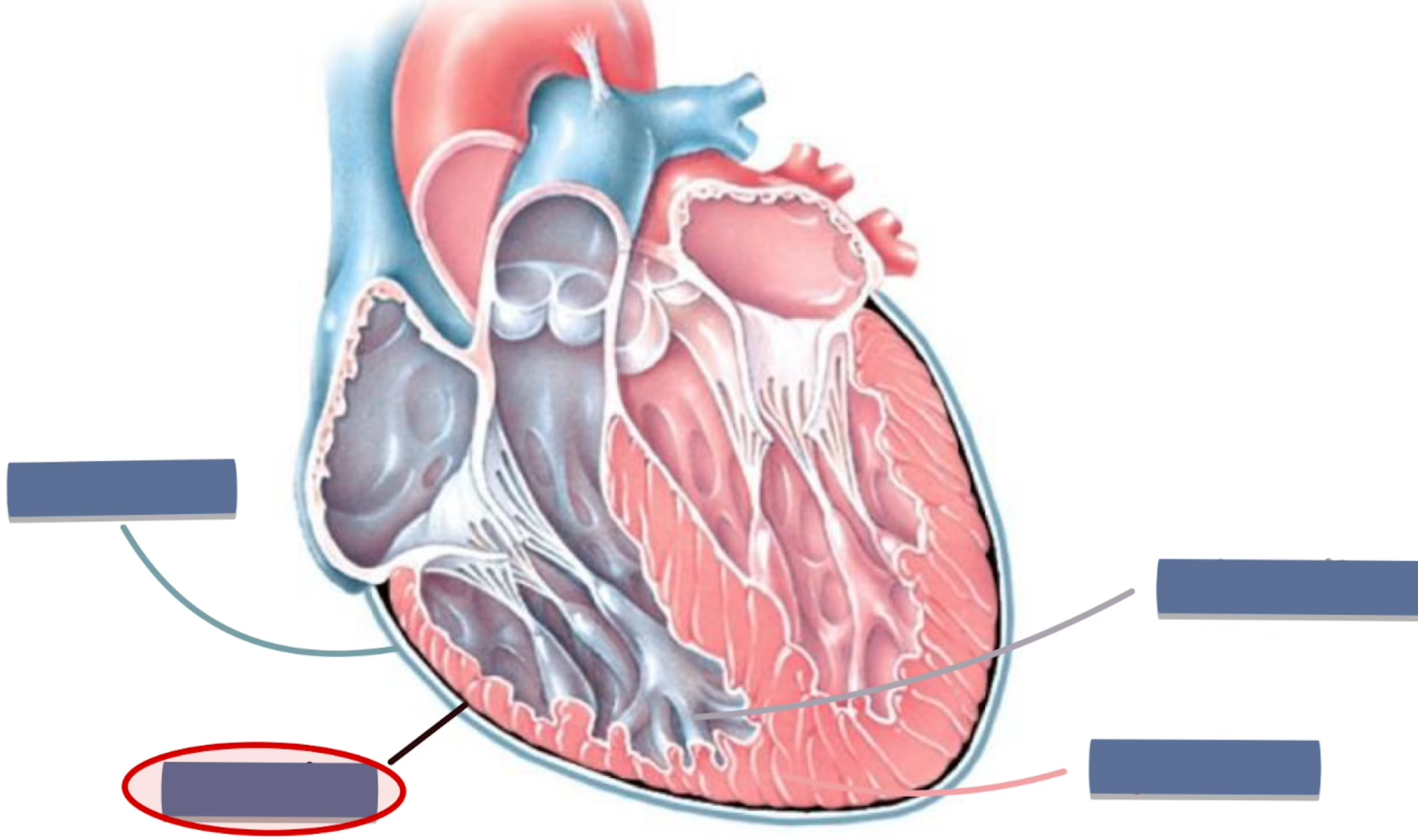
label the following
epicardium
what is the myocardium
muscle of the heart
function of the myocardium
main tissue of the heart
contracts to pump blood
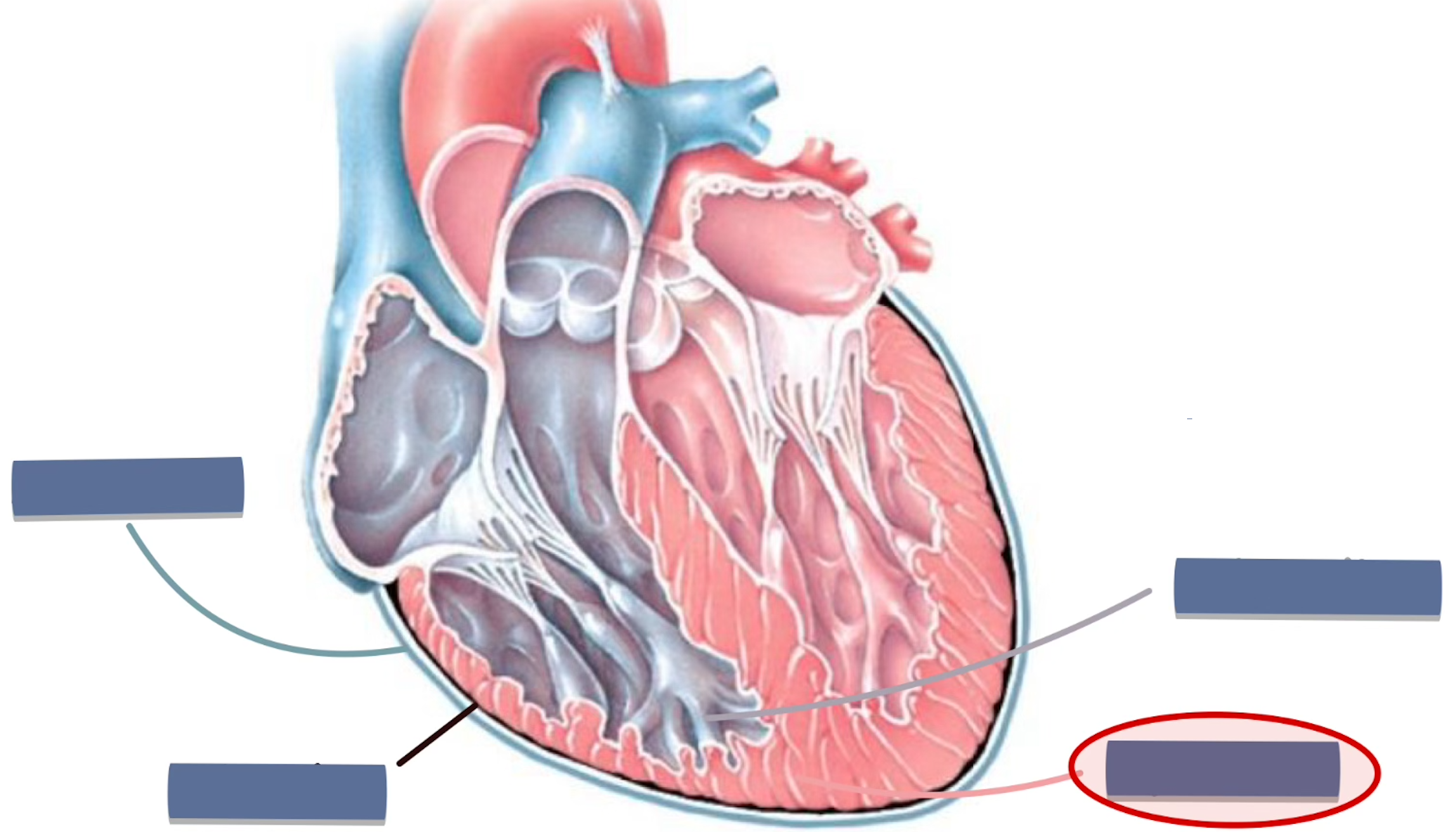
label the following
myocardium
what is the endocardium
smooth linings of the chambers of the heart
function of the endocardium
barrier between muscles + blood
reduces resistance (found in cusps)
reduces friction
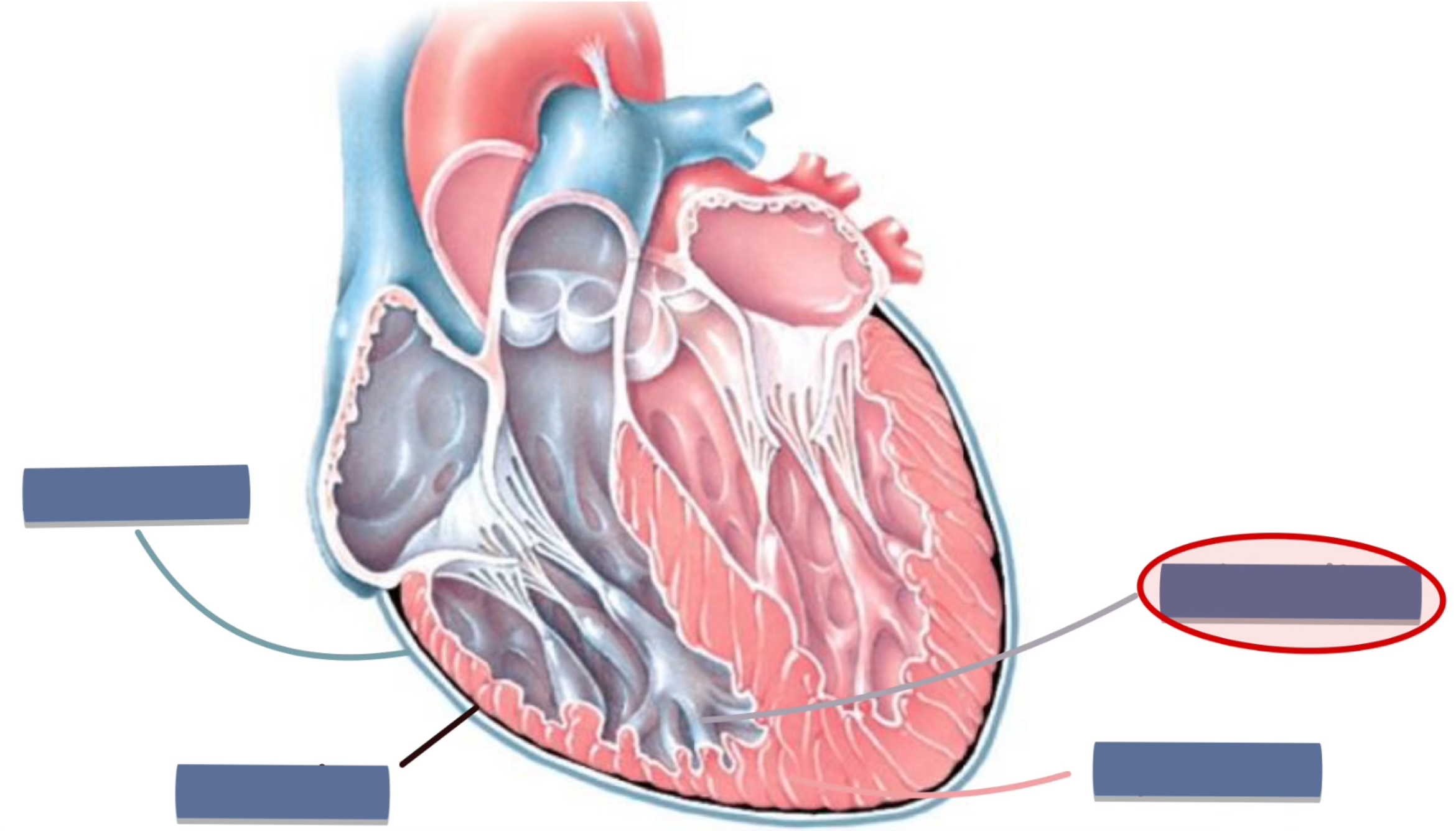
label the following
endocardium
location of the fibrous pericardium
the fibrous pericardium is the outer-most layer
function of the fibrous pericardium
anchors the heart (to diaphragm, sternum + great vessels)
prevents over-expansion of the heart when blood volume ↑
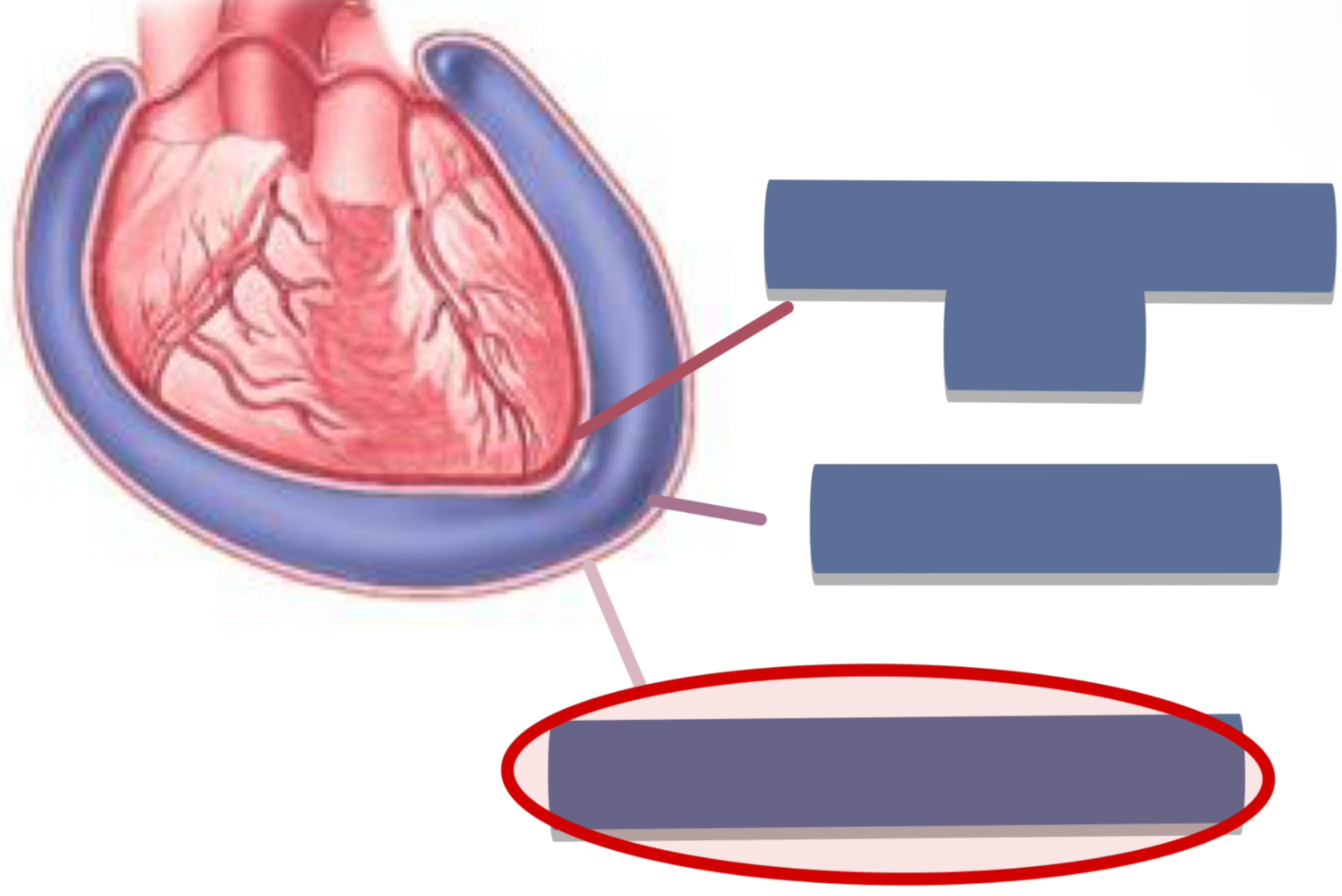
label the following
fibrous pericardium
what is the serous pericardium
double-layered, smooth inner-lining
location of the visceral layer
directly adhered to the heart’s surface (to myocardium)
function of the visceral layer
forms the pericardial cavity (w/ the parietal layer)
protects + nourishes the heart’s muscle
smooth + slippery → allows heart to move freely
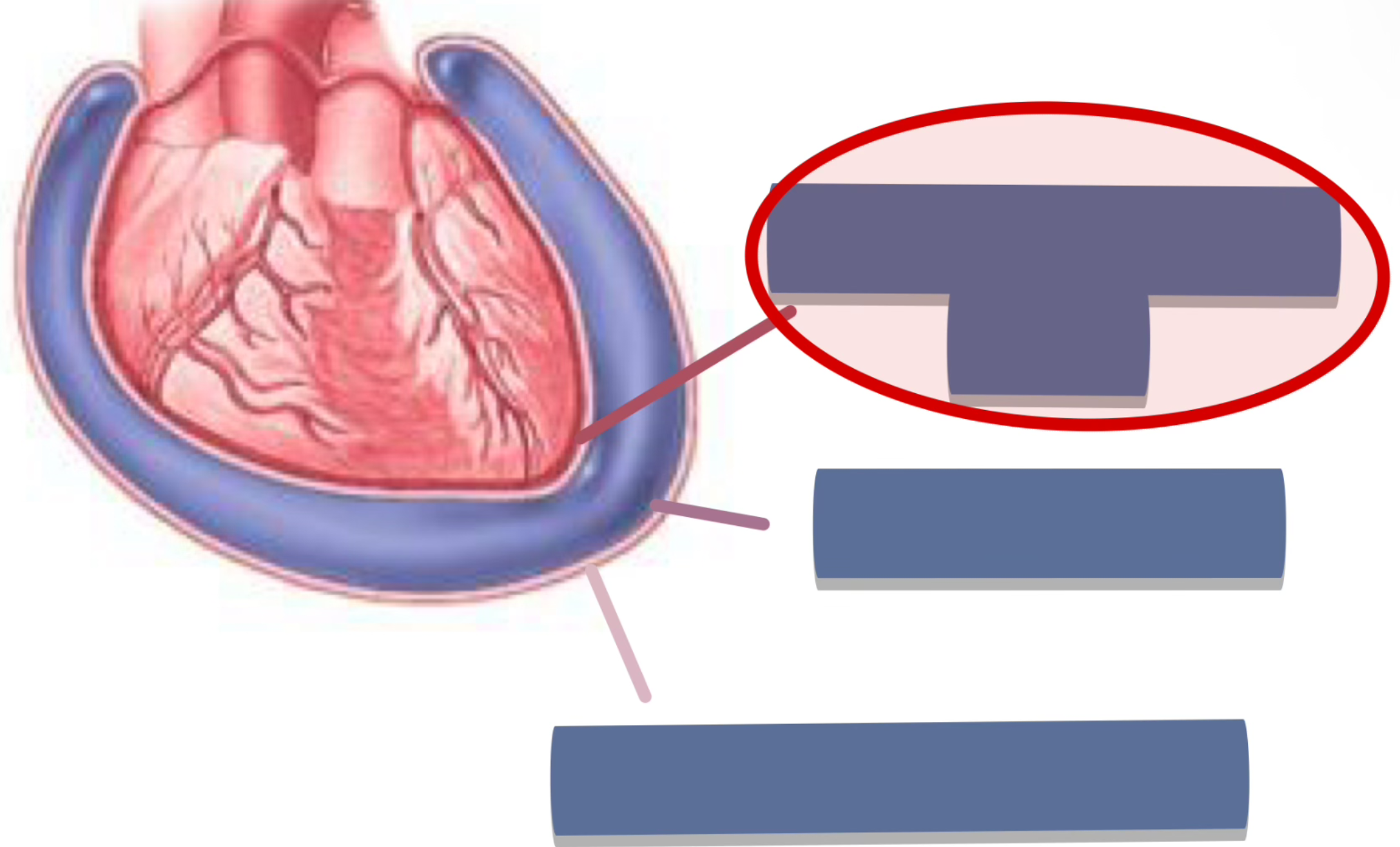
label the following
visceral layer
location of the parietal layer
lines the inside of the fibrous pericardium
function of the parietal layer
forms the pericardial cavity
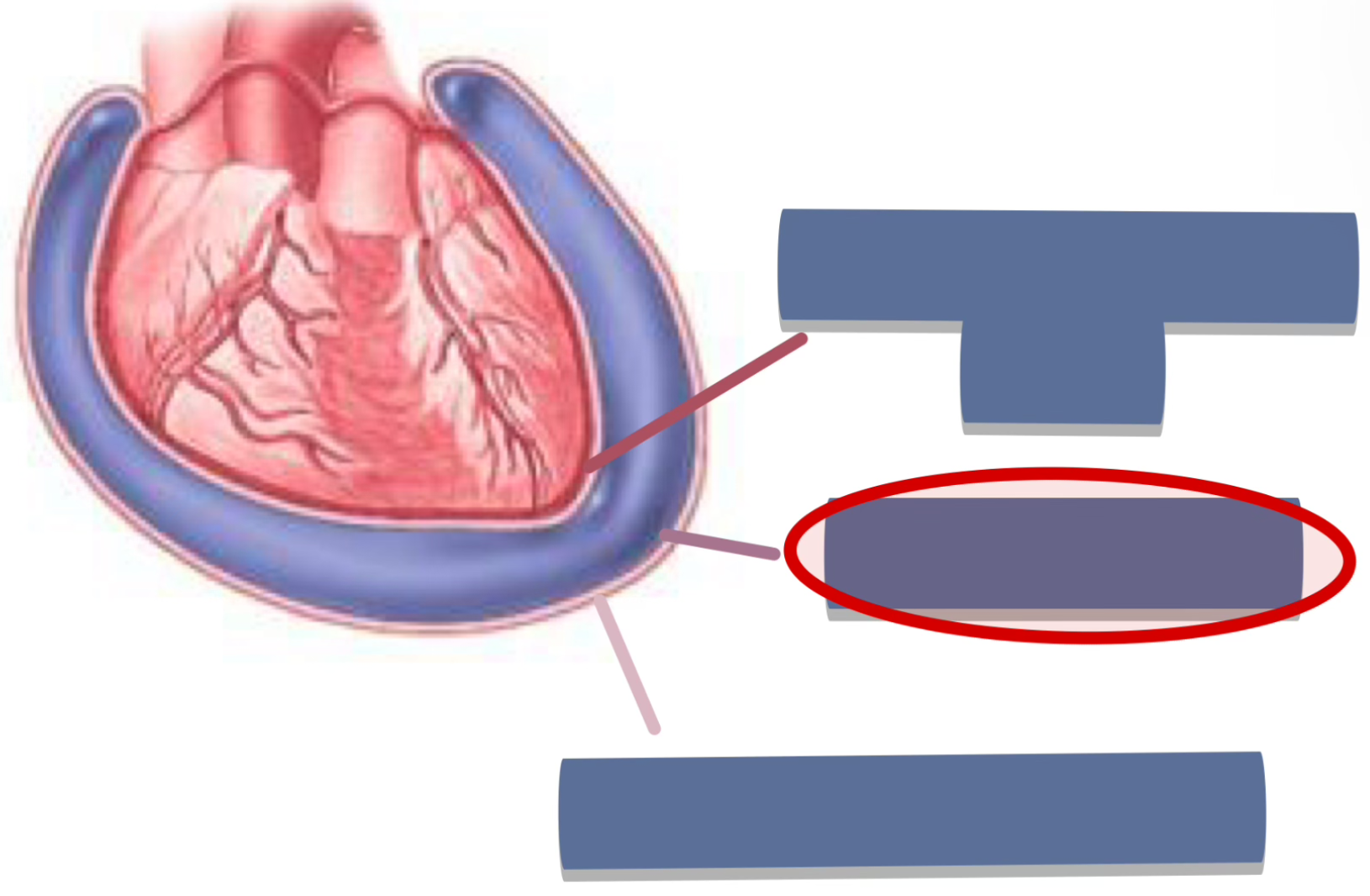
label the following
parietal layer
function of the pericardial cavity
filled w/ pericardial fluid which prevents friction of the heart
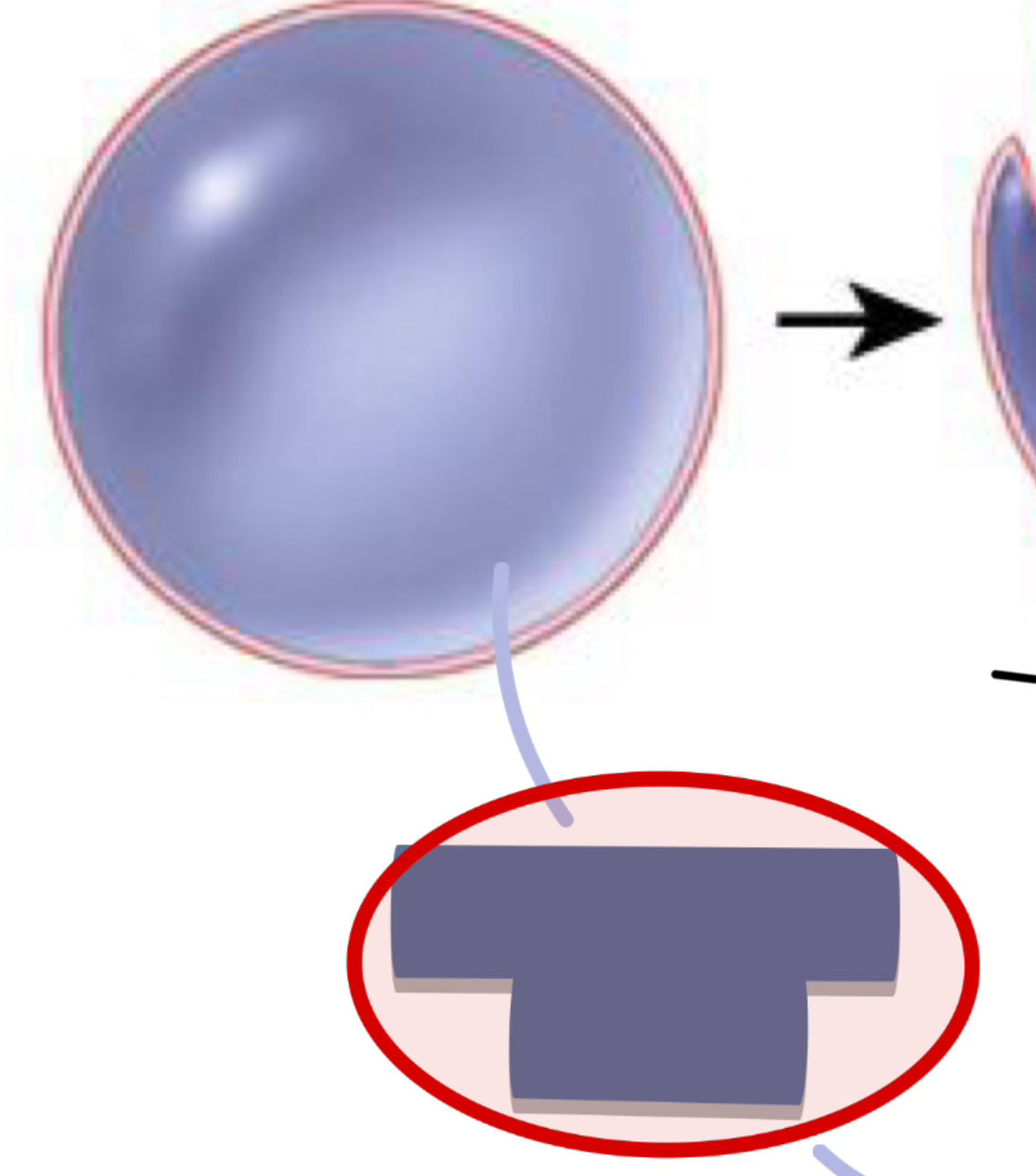
label the following
pericardial cavity
what is the anterior heart surface
surface that faces forward
where doctors listen for heart sounds
location of the anterior heart surface
behind the sternum + ribs
what is the anterior heart surface formed by
formed by the RA, RV and a bit of LV
location of the diaphragmatic heart surface
rests on the diaphragm
function of the diaphragmatic heart surface
anchors the heart → diaphragm
what is the diaphragmatic heart surface formed by
formed by the LV and RV (mainly LV)
location of the base (heart surface)
opposite to apex
posteriorly faces the vertebral column
function of the base (heart surface)
entry point for..
pulmonary veins (through LA)
SVC / IVC (through RA)
what is the base formed by
formed by the atria (both the RA and LA)
location of the right pulmonary heart surface
faces the right lung
what is the right pulmonary heart surface formed by
formed by the RA and RV (mainly RA)
location of the left pulmonary heart surface
faces the left lung
what is the left pulmonary heart surface formed by
formed by the LA and LV (mainly LV)
location of the apex of the heart
located at the tip of the heart
5th intercostal space
medial to the mid-clavicular line
function of the right atrium (RA)
collects deoxygenated blood
comes from the SVC, IVC and coronary sinus
passes the blood to the RV
function of the auricle
acts as a stretchy pouch that can expand/contract with the atria
location of the auricle
located on the atria (both the RA and LA)
function of the superior vena cava (SVC)
returns deoxygenated blood from the upper body → RA
upper body - head, neck, upper limbs + chest
location of the superior vena cava (SVC)
enters the superior part of the RA
positioned anterior to the right pulmonary artery
beside the arch of the aorta
function of the right ventricle (RV)
pumps deoxygenated blood to the pulmonary circulation (toward the lungs)
location of the right ventricle
anterior surface of the heart
function of the pulmonary trunk
carries deoxygenated blood from the RV → lungs
location of the pulmonary trunk
arises from the RV
exits the heart anteriorly
function of the left atrium (LA)
collects oxygenated blood that is returning from the lungs
location of the left atrium
lies posteriorly in the heart
forms most of the base of the heart
function of the left ventricle
pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta
location of the left ventricle
lies posteriorly and to the left in the heart
forms the apex and left border of the heart
function of the aorta
largest artery in the body
carries oxygenated blood from the LV → entire body
branches off into arteries that supply the upper + lower body
location of the aorta
arises from the LV
ascends first → descends through the thorax/abdomen
function of the brachiocephalic trunk
supplies oxygenated blood to the right side of the head, neck + upper limbs
location of the brachiocephalic trunk
first branch of the aortic arch (right side)
travels upwards
divides into the right common carotid artery + right subclavian artery
function of the left common carotid artery
supplies oxygenated blood to the left side of the head + neck
location of the left common carotid artery
second branch of the aortic arch (left side)
ascends in the neck → head
function of the left subclavian artery
supplies oxygenated blood to the left upper limb + chest structures
location of the left subclavian artery
third branch of the aortic arch (left side)
travels under the clavicle → left upper limb
function of the coronary sulcus
houses the RCA, circumflex artery, and coronary sinus
marks the boundaries between atria and ventricles
location of the coronary sulcus
in the groove between the atria and ventricles
wraps around the base of the heart
function of the anterior interventricular sulcus
separates the RV from the LV
contains..
anterior interventricular artery (LAD)
great cardiac vein
location of the anterior interventricular sulcus
groove on the anterior surface of the heart
runs between the RV and LV
from base to apex
function of the inferior vena cava (IVC)
returns deoxygenated blood from the lower body → RA
lower body - legs, pelvis, abdomen
location of the inferior vena cava (IVC)
large vein entering the inferior part of the RA
ascends through the diaphragm from the abdomen
function of the right pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood from the RV → right lung for oxygenation
location of the right pulmonary artery
branches from the pulmonary trunk
function of the left pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood from the RV → left lung for oxygenation
location of the left pulmonary artery
branches from the pulmonary trunk
function of the right pulmonary vein
carries oxygenated blood from the right lung → LA
location of the right pulmonary vein
2 veins from the right lung → right posterior side of the LA
function of the left pulmonary vein
carries oxygenated blood from the left lung → LA
location of the left pulmonary vein
2 veins from the left lung → left posterior side of the LA
function of the posterior interventricular sulcus
separates the RV from the LV
contains..
posterior interventricular artery (PDA)
middle cardiac vein
label the following
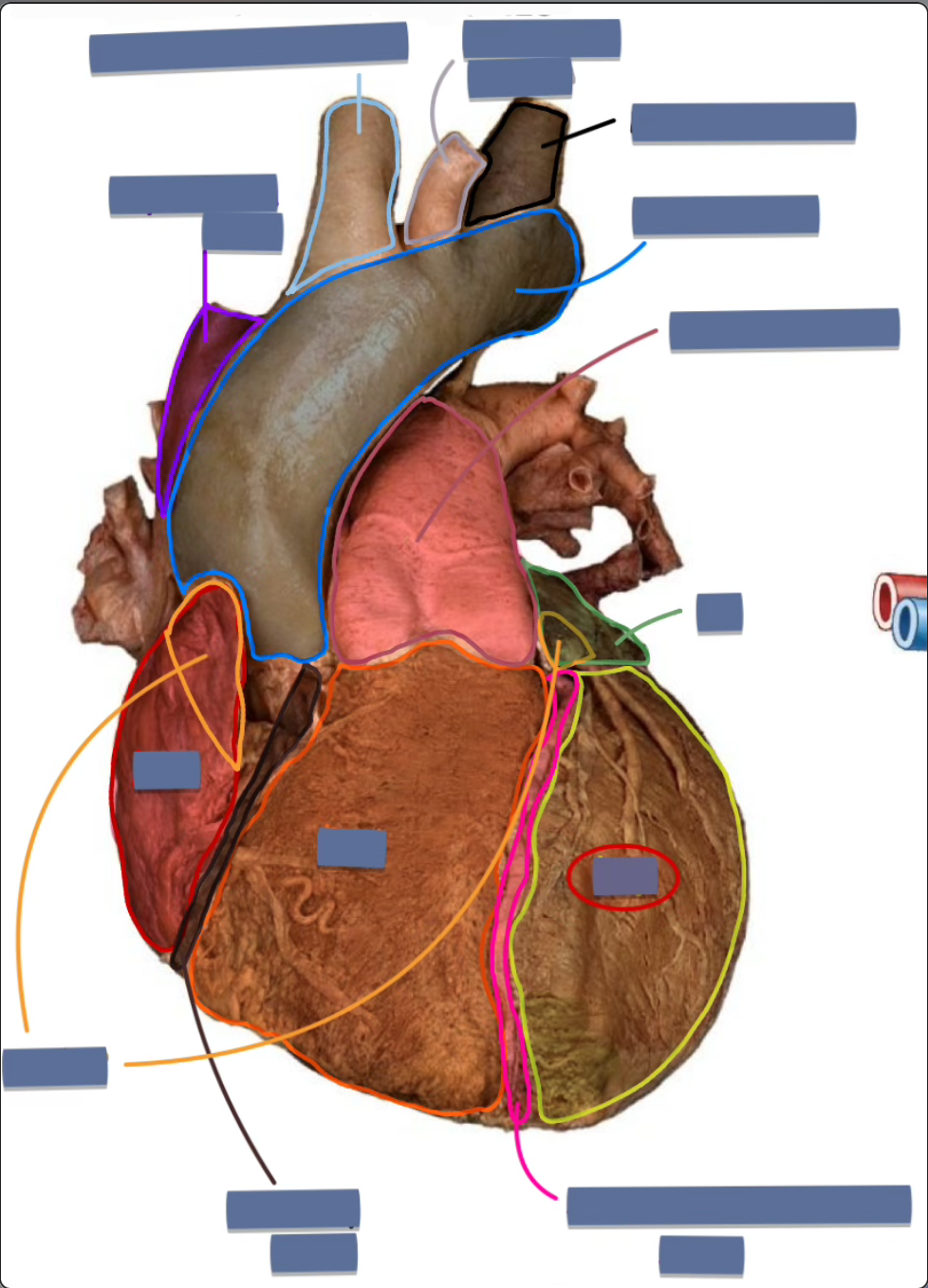
left ventricle
label the following
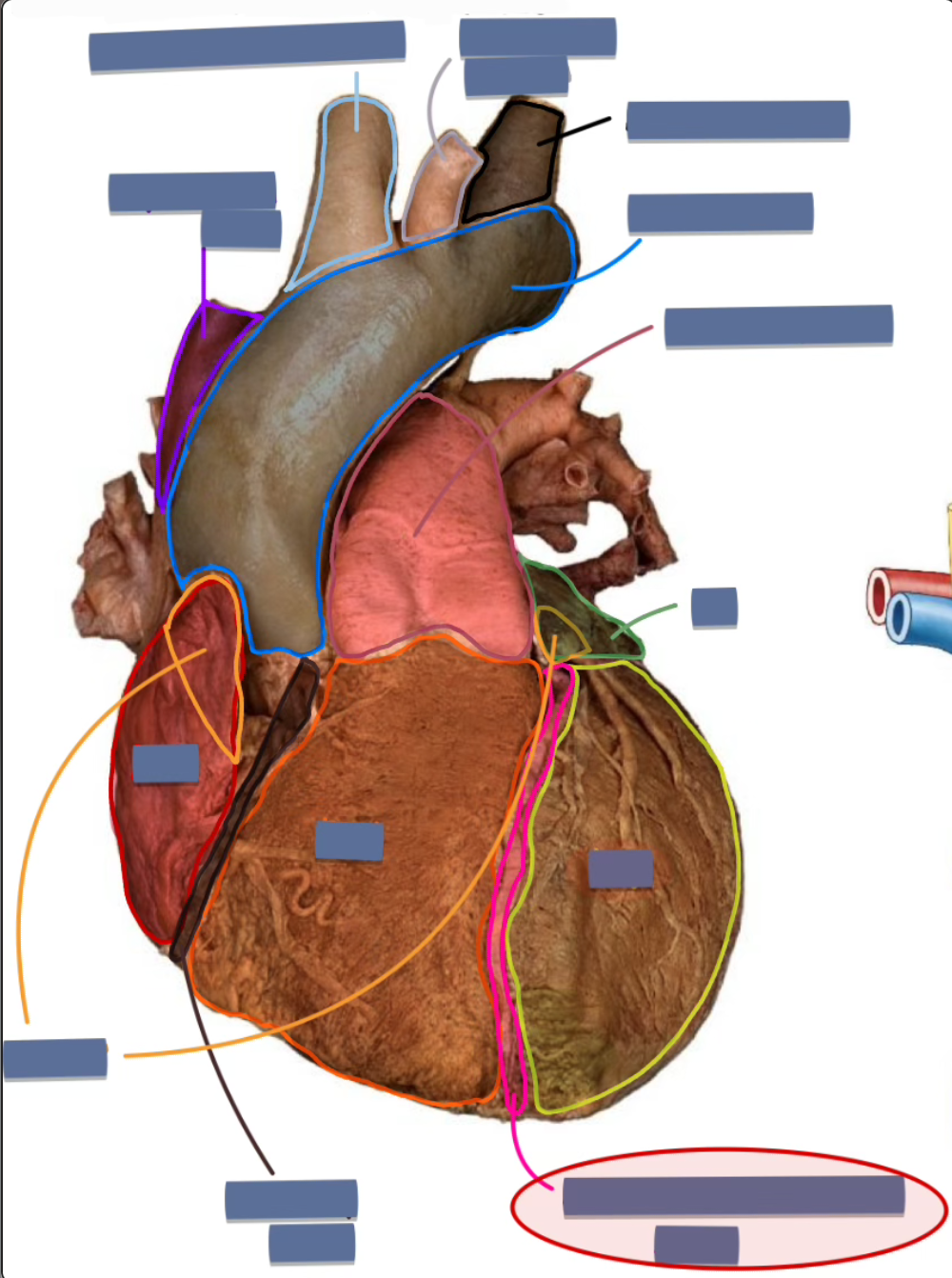
anterior interventricular sulcus
label the following
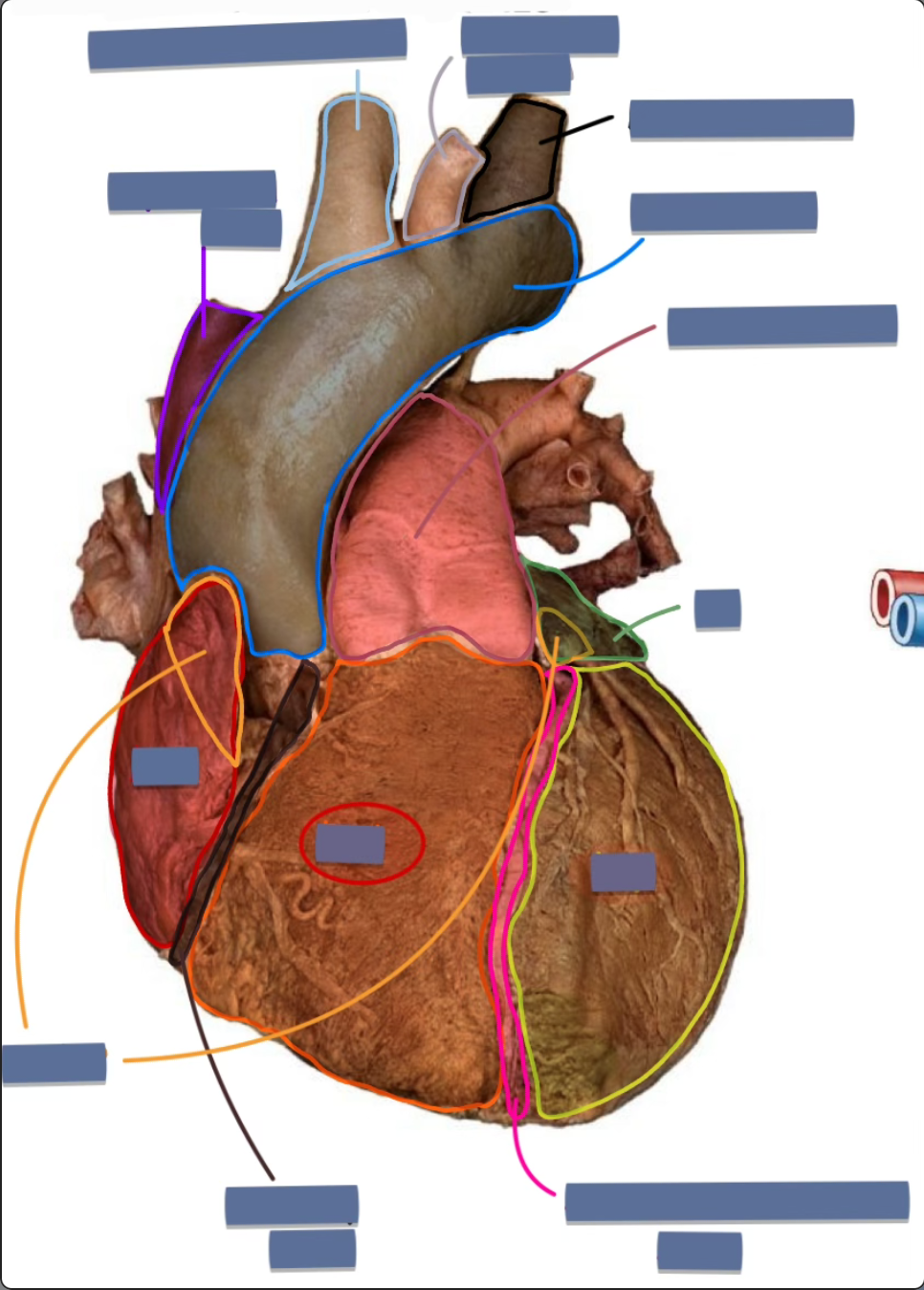
right ventricle
label the following
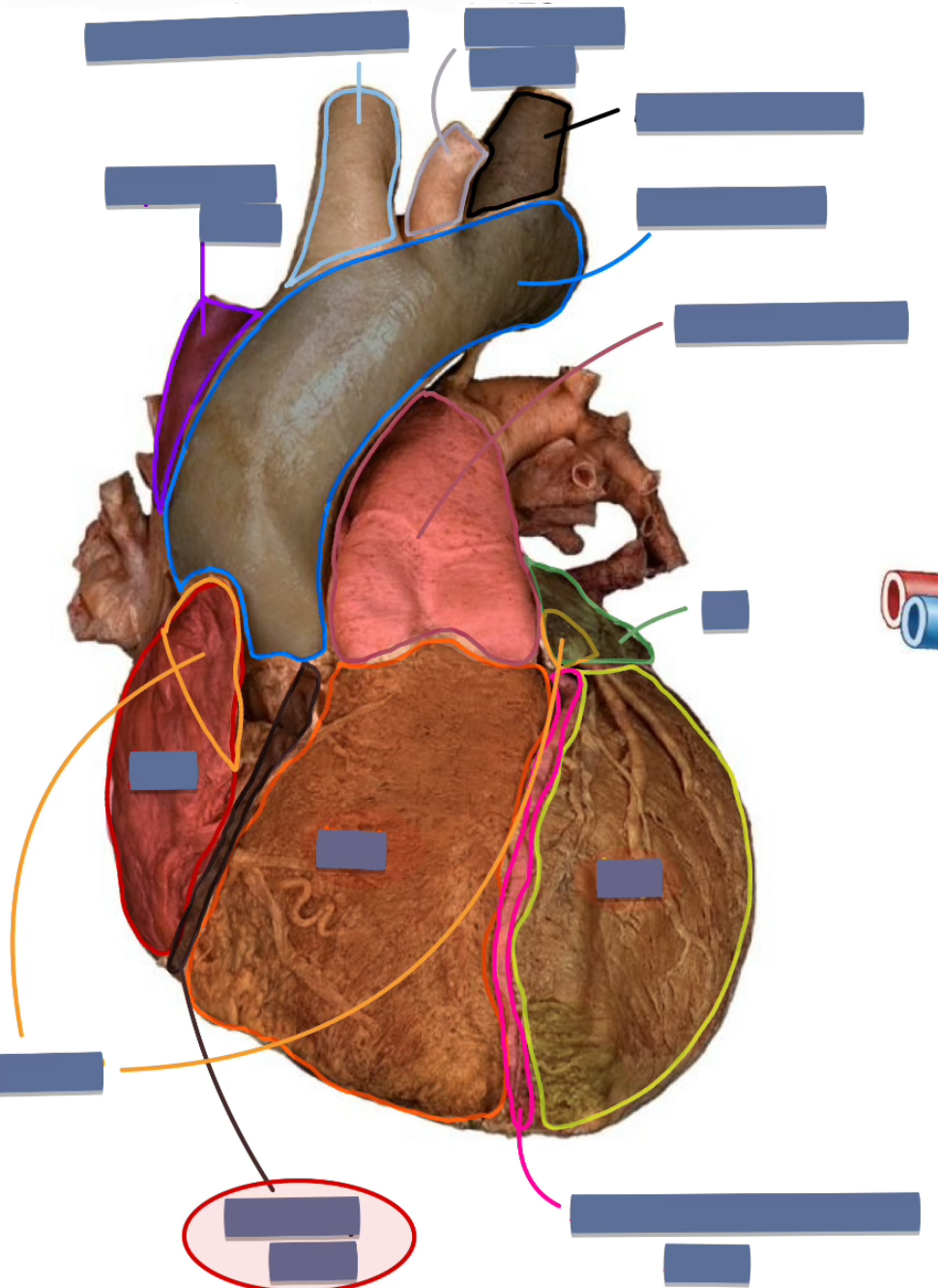
coronary sulcus (anterior)
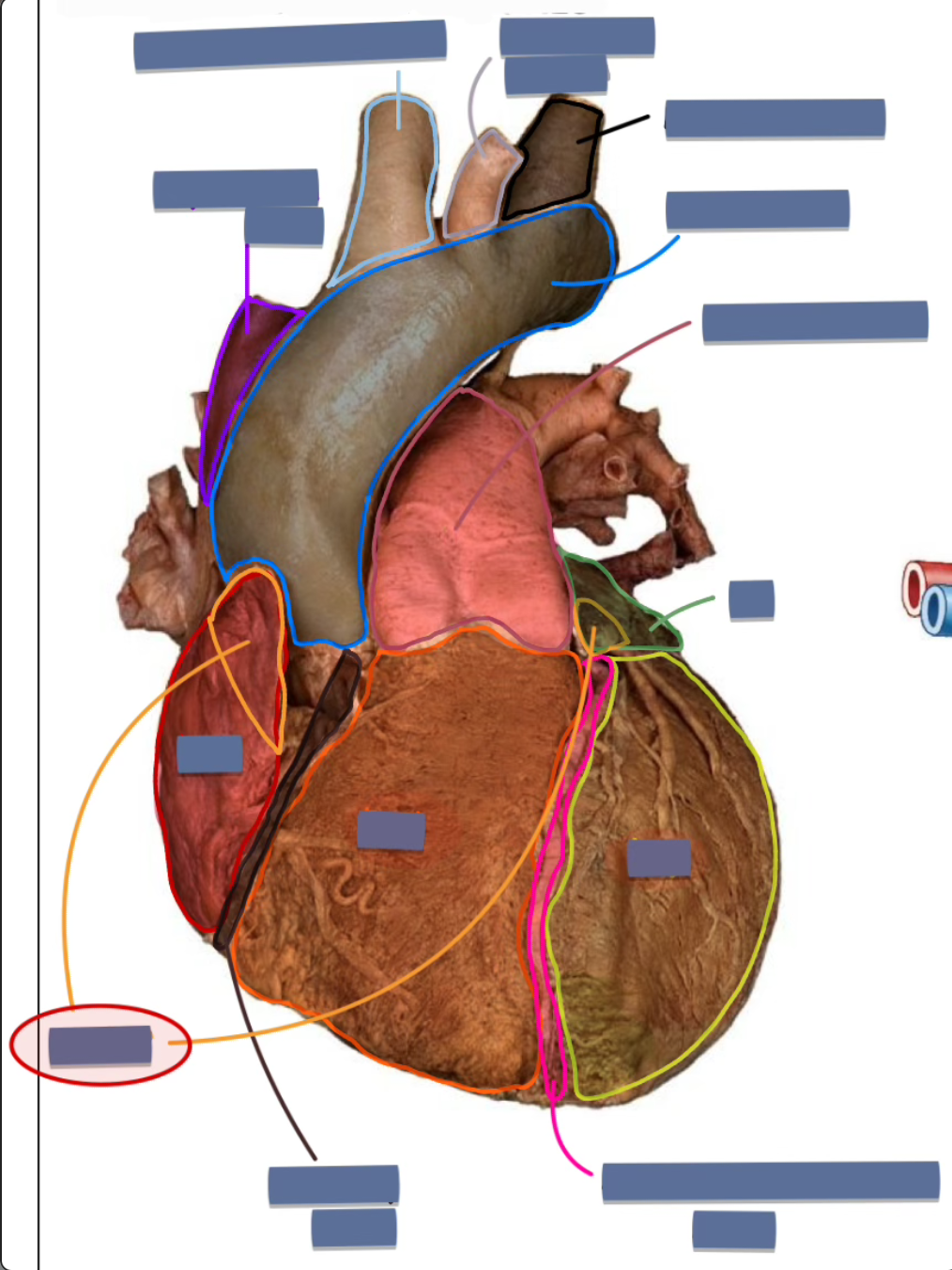
label the following
auricle
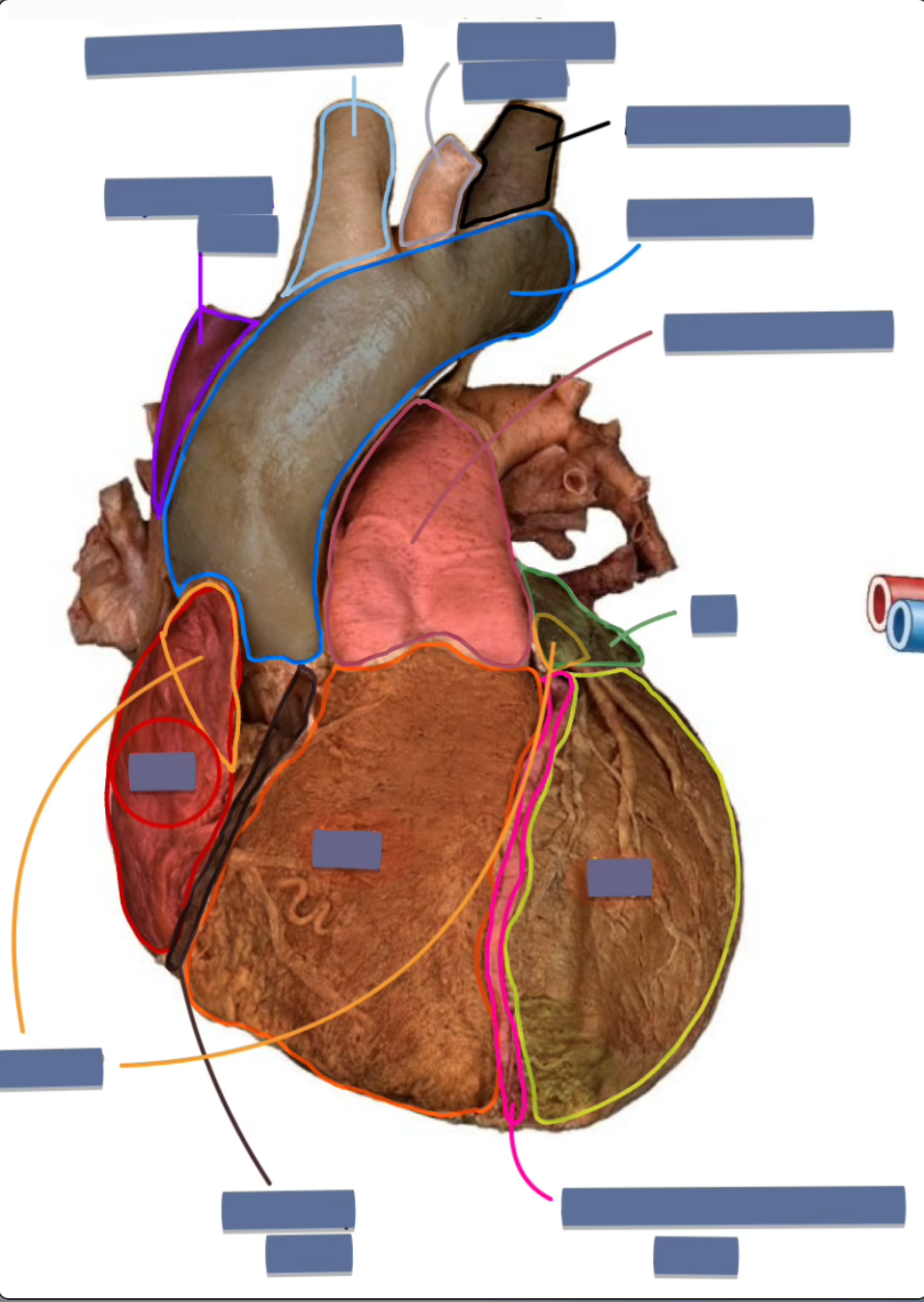
label the following
right atrium
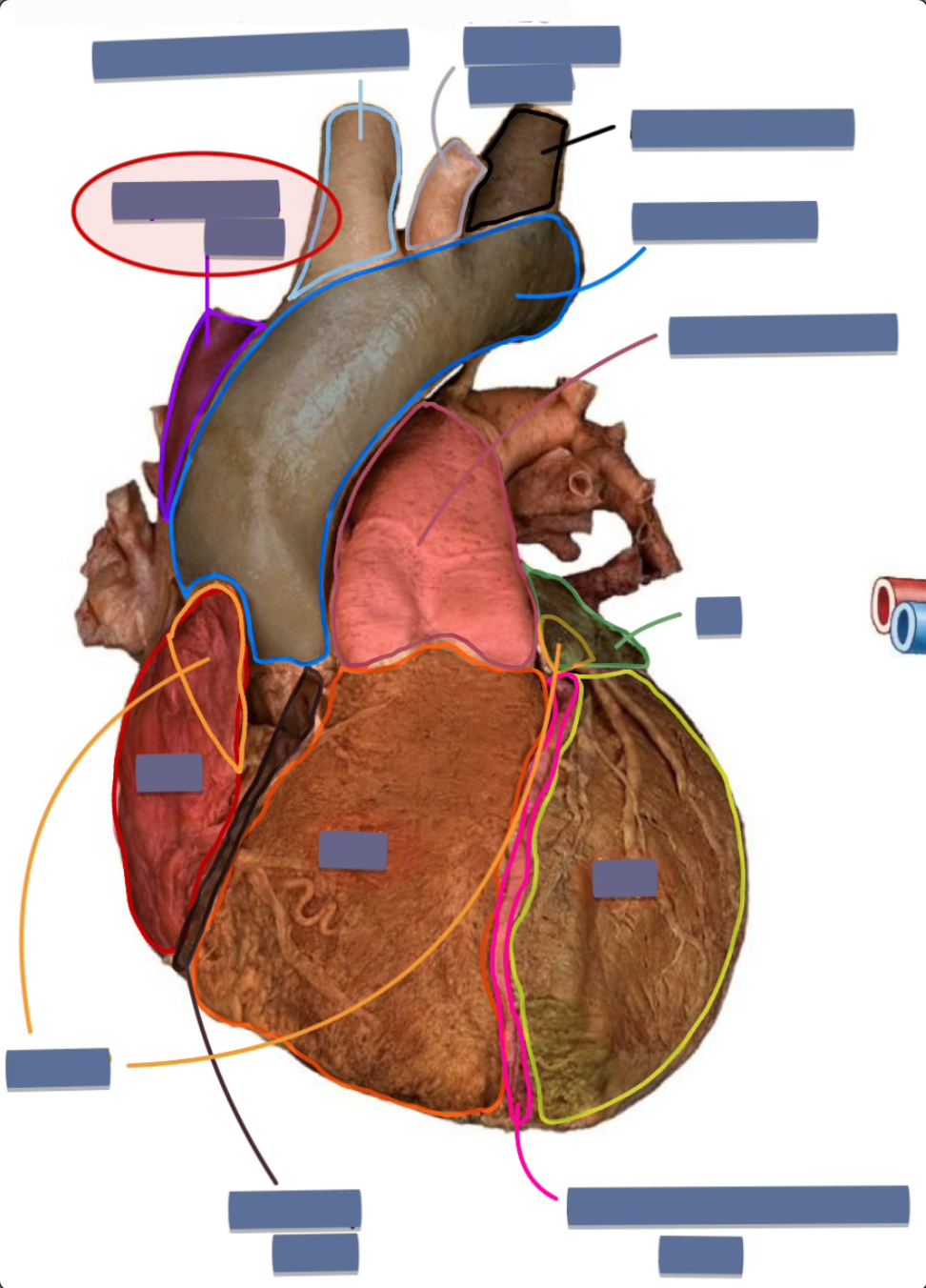
label the following
superior vena cava (anterior)
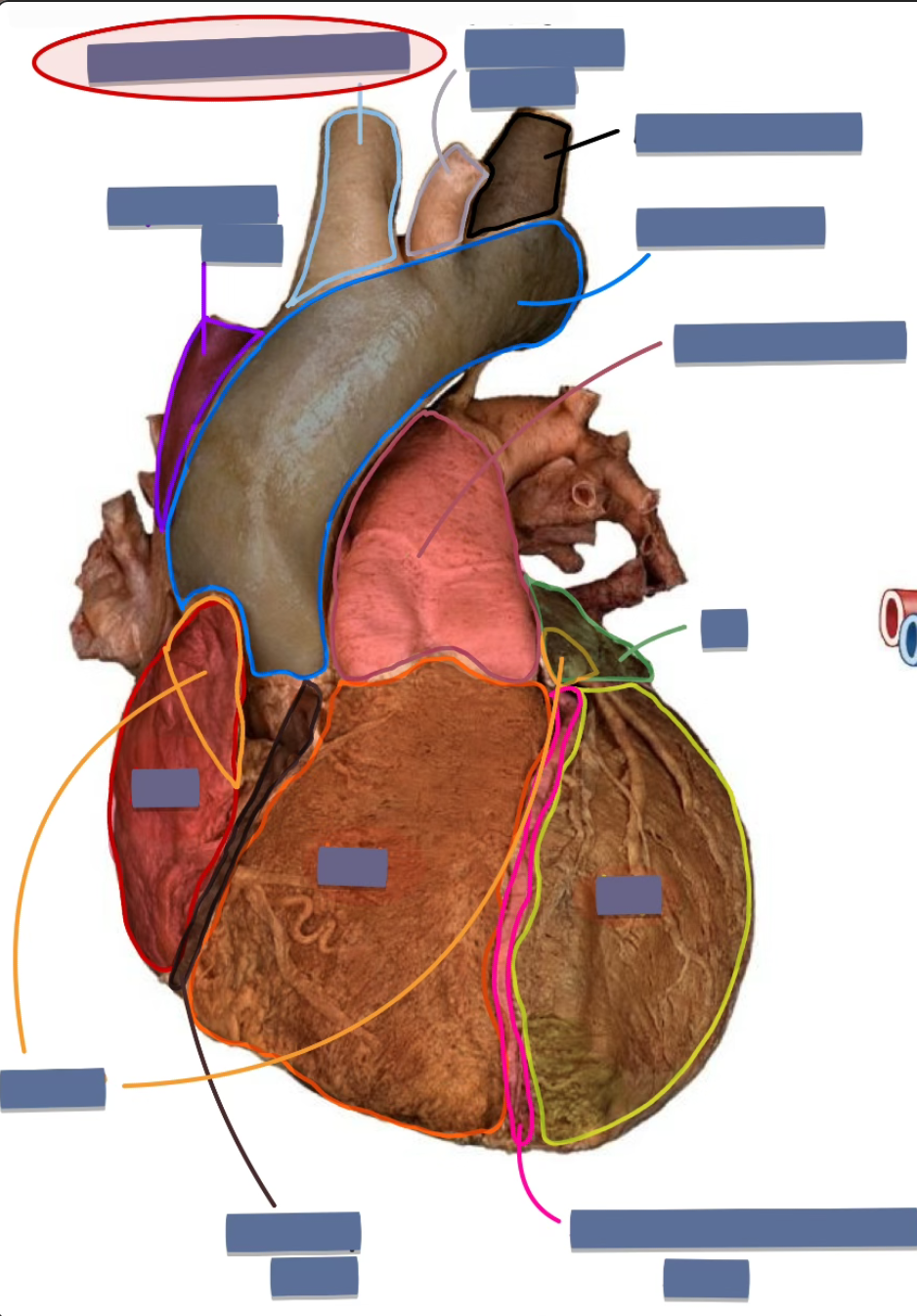
label the following
brachiocephalic trunk
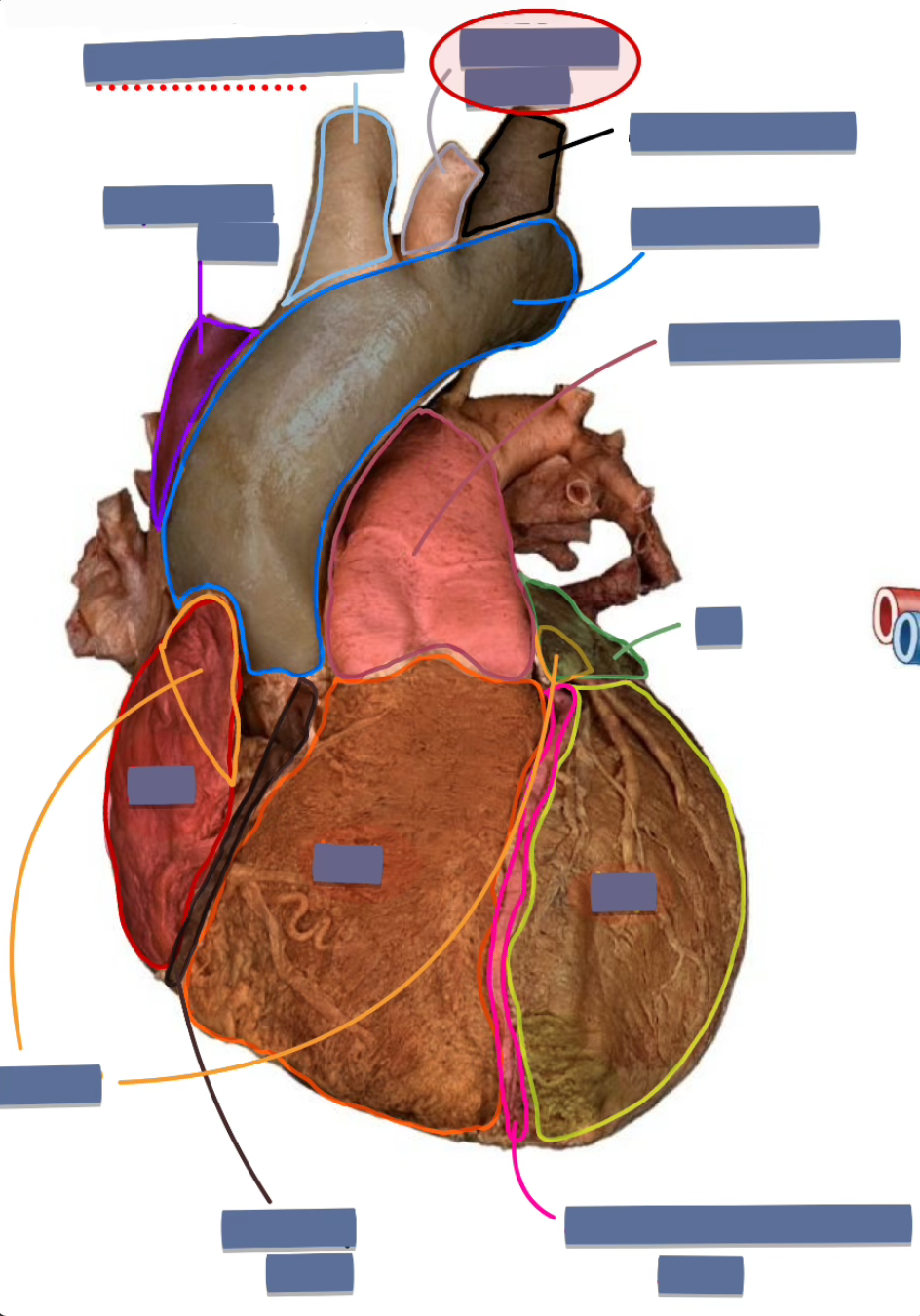
label the following
left common carotid artery
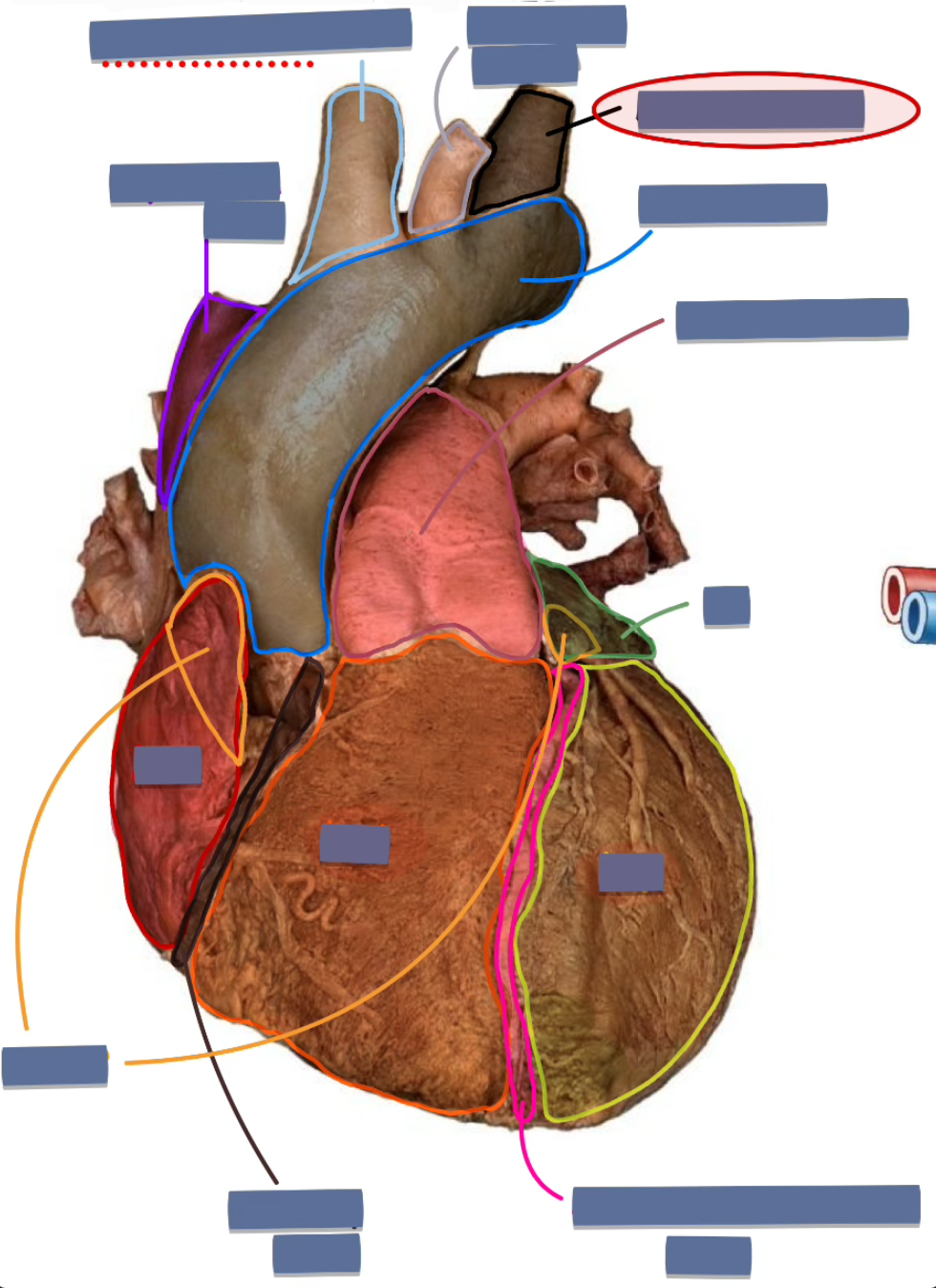
label the following
left subclavian artery
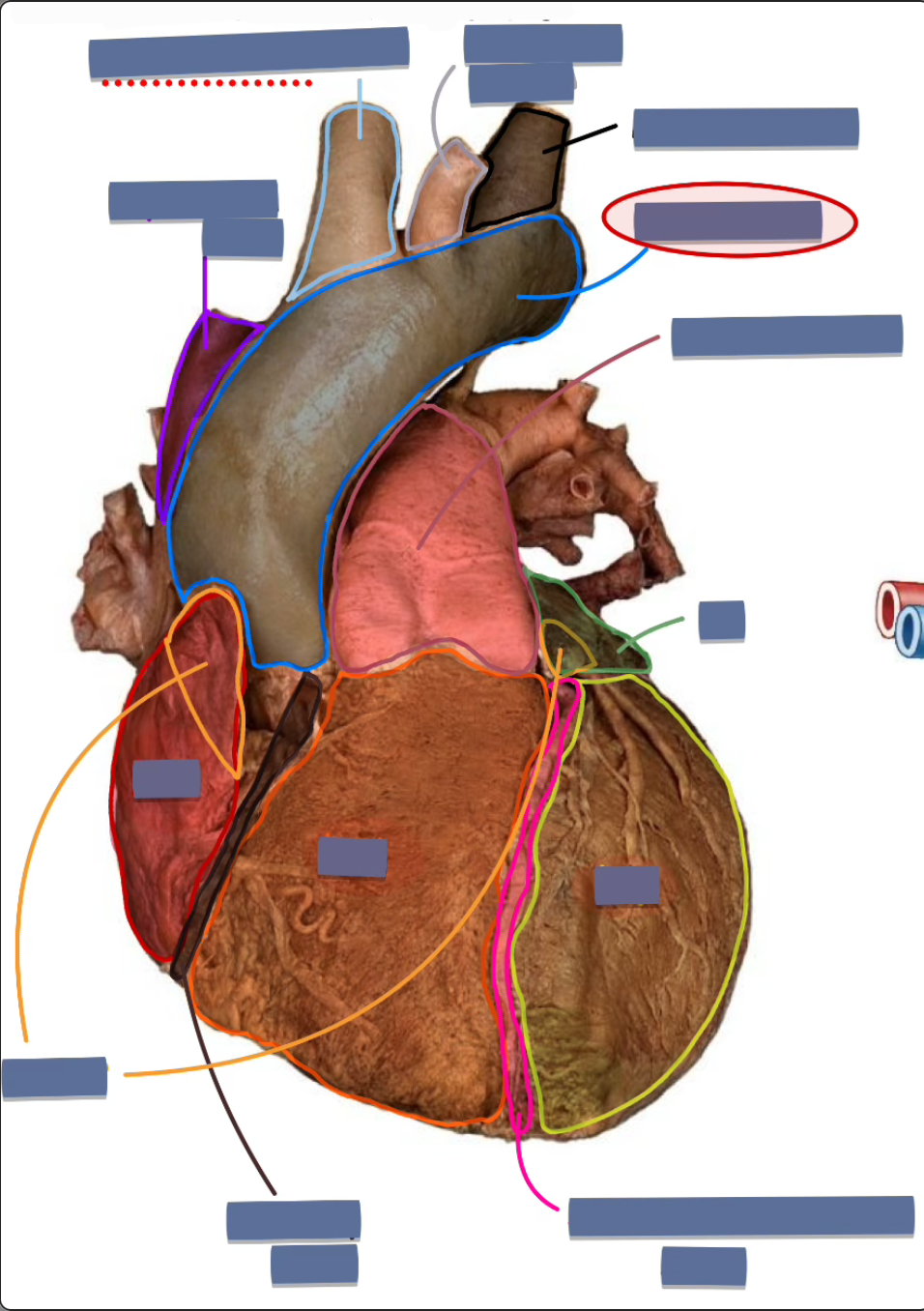
label the following
arch of aorta (ascending aorta)