Economics Exam Yr 10 Semester 2 Perth Modern
1/115
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
economics
Economics is the study of rationing systems (planned and free market economies and how scarce resources are used to fulfil the infinite wants of consumers.
Importance of economics in understanding everyday activity, personally and for society
· The study of economics helps individuals and society as a whole with decision making and resource allocation in order to best satisfy our needs and wants.
· It can help governments make the best decisions for their country.
· It can help businesses with effective resource allocation
· It can help individuals understand the fiscal and monetary policy measures that the government or central bank takes and the effects of these on their daily lives.
basic economic problem
People have unlimited wants but scarce resources, so we need to make choices based on our resource usage, leading to opportunity cost.
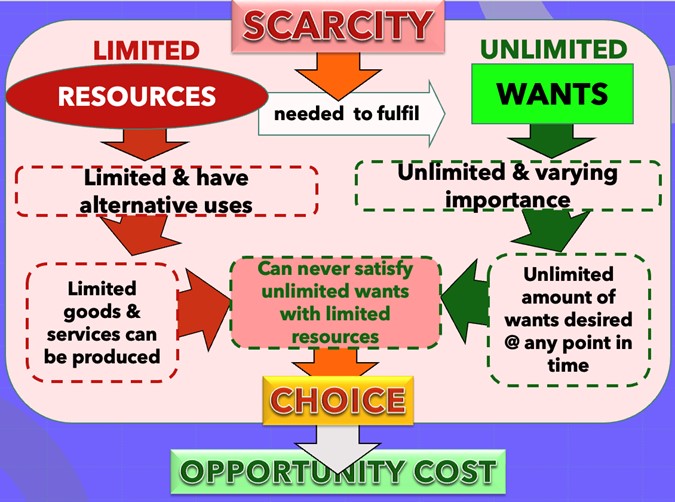
scarcity
limited resources = lack of resources to fulfil unlimited wants
choice
how we chose to use finite resources
opportunity cost
real cost of next best alternative forgone
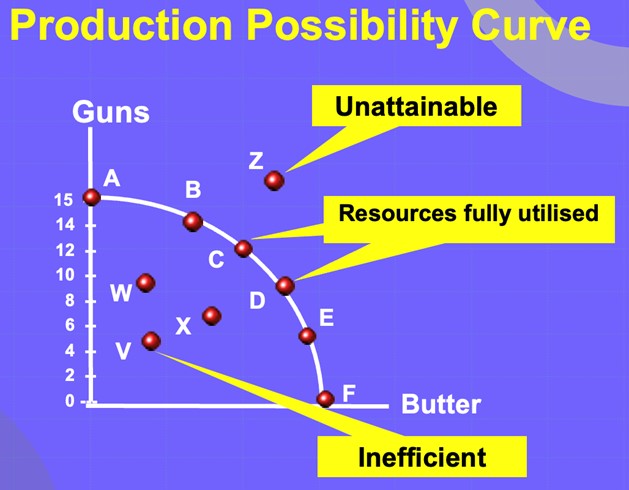
PPF + basic economic problem
PPF is combinations of 2 products given fixed resources, technology + full utilisation
The PPF represents that there is a scarce amount of resources and represents the opportunity cost when a choice is made on how to allocate the resources.
4 economic questions
what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce, how much to produce
purpose of 4 economic questions
help determine what kind of economic system is in place and help us to decide how best to allocate resources to meet our needs and wants to the best degree.
what to produce
what goods + services should an economy produce
how to produce
how should goods and services be produced- labour intensive/land intensive e.t.c.
how much to produce
amount produced based on demand + supply
factors of production
land, labour, capital, enterprise
land- def, example, + payment received
natural resources available for production- e.g minerals recieve rent
labour- def, example, + payment received
physical + mental efforts of those involved in production- e.g. construction worker receive wages
capital- def, example, + payment received
non natural/manufactured resources used in production e.g. machinery recieve interest
enterprise- def, example, + payment received
management + organization of other 3 FoP e.g entrepreneur, receive profit
economic system
way an economy organises itself to address the basic economic problem- system of production, resource allocation + distribution in society
3 main economic systems
market, mixed, planned/command
market economy
law of supply(Fop) + demand(purchases by businesses, consumers + gvt) direct the production + distribution of goods and services.
businesses sell their products at highest price consumers will pay + buyers look lowest prices in goods and services they want.
workers bid their services at highest possible wage skills will allow + employers look for the best employees at lowest possible price.
6 characteristics of a market economy
private property: most goods + services privately owned
freedom of choice: freedom to produce, sell + purchase in market
motive of self interest: everyone sells to highest bidder and negotiates lowest price for their purchases
competition: competitive pressure to keep prices low
system of markets + prices: price changes reflect demand + supply
limited government: role of government is to keep free market working
strengths of market economy
chance of wealth
goods + services being produced reflect wants of consumers
promotes innovation + efficiency
weaknesses of market economy
poor working conditions
poverty
negative externalities like pollution
planned/command economy
central govt. makes all economic decisions in accordance with a central plan + owns means of production.
govt. sets quotas + price controls
no free market forces of demand + supply
no competition
aims to allocate resources in most efficient way possible
aims to use each individuals skills to highest capacity + eliminate unemployment
strengths of planned/command economy
less inequality
resources can be efficiently and rapidly mobilised e.g for war
weakness of planned/command economy
lack of innovation
goods + services produced may not reflect needs + wants of society
mixed economy
Combines characteristics of market, command and traditional economies, having advantages and disadvantages of all.
private enterprise with strong regulatory oversight and government provision of public goods e.g roads
basic welfare
demand + supply to determine prices
strengths of a mixed economy
allows production in economy to reflect needs + wants of consumers
regulation of business ensures good working conditions
weaknesses of a mixed economy
government failure/poor planning can result in inefficient outcomes
business regulation may limit productivity
socio-political economic systems
economic systems which incorporate social and political structures and ideologies
socialism
A political and economic theory that advocates for the rights of the working class.
means of of production owned by collective
progressive taxation
Strengths of socialism
reduces relative poverty due to minimum basic income for unemployed
free healthcare results in increased labour productivity contributing towards economic growth.
a more equal society is more cohesive as socialism promotes selflessness over selfishness.
environment is protected due to limiting pollution as profits are not the highest priority but rather long term welfare
weaknesses of socialism
lack of incentives as businesses may be discentivise due to high rates of progressive taxation.
government failure can result in an inefficient allocation of resources.
an overly generous welfare state can disincentives working thus reducing the labour force
communism
state/community owns all property and means of production leading to a theoretically classless society
strengths of communism
centrally planned economy can easily mobilise resources + executive massive projects
equality on a level capitalism can never offer
employment opportunities for everyone who wants a job
weaknesses of communism
government owns everything meaning they exert significant control over citizens lives
citizens may set up a black market for goods/services not in the central plan eroding trust.
limited efficiency + productivity due to lack of incentives
poverty as the first priority is to maintain the government structure meaning people are asked to get by on the bare min.
no laws of demand/supply to set prices meaning there are often surpluses/shortages
capitalism
means of production like factories, equipment, etc are privately owned rather than controlled by the government.
believes in the lassiez faire approach:
free market will regulate itself without govt. intervention
forces of demand and supply will set prices
strengths of capitalism
spread of power meaning government is not overbearing
efficiency: firms in a capitalist society face incentives to efficiently produce goods and services that are in demand.
innovation: firms seek to develop profitable products which leads to a greater choice of goods for consumers
economic growth: firms + individuals face incentives to work hard which creates a climate of economic growth.
weaknesses of capitalism
private ownership of capital enables firms to gain monopoly power and charge higher prices.
negative externalities: negative externalities such as pollution from production ignored.
inherited wealth creates inequality in a society that is supposedly based on equal opportunity.
inequality in wealth creates resentment and social division.
classical economics
brought into mainstream by Adam Smith
no govt. intervention in the marketplace
believes in “invisible hand” - unseen forces which move the free market economy
through individual self interest and freedom of production + consumption the best interests of society are fulfilled.
market will find its equilibrium without govts forcing it into unnatural patterns
keynesian economics
school of economic thought founded by John Maynard keynes
aggregate demand by households, businesses + govt and not free market is the driving force in the economy
economy has no self balancing mechanisms leading to full employment
macroeconomy can be in recession for considerable amount of time.
advocated for govt. intervention especially during times of recession to stimulate aggregate demand
advocates for higher government deficit spending to recover from recession
shift from microeconomics to macroeconomics
supply side economics
taxes reduce incentives for work, savings + investment
accelerated economic growth without inflation can be achieved by increasing the supply of goods and services
increased production drives economic growth
supply side FP focuses on business + firms
tools are tax cuts + deregulation of businesses
companies benefit + hire more workers
resultant job growth creates more demand which further boosts job growth
monetarism
money supply is most important driver of economic growth
As the money supply increase, people demand more goods and services (increase in AD)
therefore factories produce more creating jobs
central banks play a critical role by managing monetary policy
money supply expands = lowered interest rates = consumers borrow more and buy more big ticket items
decreasing money supply raises interest rates and slows down economic growth
purpose of govt economic objectives
To ensure the economy continues growing at a sustainable rate and remains competitive.
Australian macroeconomic objectives
price stability, full employment, sustainable economic growth
sustainable economic growth
stable economic growth that can be maintained over the long term
production capacity of an economy increases over time
measured in GDP growth and has target of 3-4%
GDP
monetary value of final goods and services produced in a country in a given period of time
price stability
gradual + sustainable increase in price levels of goods and services
measured using inflation rate (CPI)
2-3%
full employment
everyone who is willing and able to work is employed
not equal to 0 unemployment (skills mismatches/moving)
<5%
economic indicators
anything that can be used to predict or ascertain financial or economic trends.
leading indicators
signal future events- not always accurate
money supply
share prices
lagging indicators
follow an event/help confirm a pattern
inflation
unemployment rate
coincident indicators
occur at same times as the events they signal
GDP growth
personal income
BTC
·The business trade cycle (BTC) represents fluctuations in the growth of real output, consisting of alternating periods of expansion (increasing real output) and contraction (decreasing real output).
real gdp on y axis time on x axis
long steady periods of expansion are desirable
large cyclical fluctuations over short periods not desirable
more steady + less rapid growth gives people more time to adapt
reducing intensity of expansion and contraction would lessen the problems of each
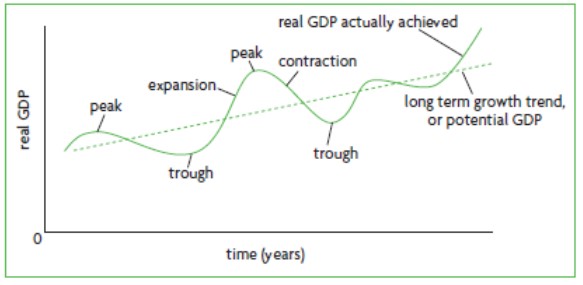
Phases of BTC
trough, expansion, peak, contraction
Expansion
sloping up = positive growth in real GDP
employment of resources increases
production increases
unemployment is decreasing
inflation is rising as households have more disposable income
Peak
max real gdp + end of expansion
employment of resources is max
unemployment is lowest + wages are high
inflation is extremely high
cost of living is high and consumers begin purchasing less leading to downswing
Contraction
falling real gdp = slope down
employment of resources decreases
unemployment increases
inflation is decreasing
production is decreasing
Trough
min level of gdp in cycle, marks beginning of new cycle
employment of resources is at all time low
unemployment is high, wages decrease
inflation is extremely low
people start buying more + labour is cheap so more people get hired redirecting into upswing
aggregate demand
measurement of the total amount of demand for all finished goods and services produced in an economy.
how aggregate demand can increase/decrease
Increased household wealth/income (from lower interest rates) generally increases aggregate demand, while decreased household wealth does the opposite.
aggregate supply
The total supply of goods and services available to a particular market from producers. It normally takes longer to respond to increased demand due to needing more workers, equipment and/or infrastructure
fiscal policy
Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and taxation to affect:
the level of macroeconomic activity
resource allocation
income distribution
instruments of fiscal policy
changing tax revenue (T)
changing government expenditure (G)
Non-Discretionary FP
automatic or built in stabilisers in place to smoothen/offset fluctuations of the economic cycle without the need for additional govt intervention
don’t regularly change
examples of non-discretionary FP
welfare benefits
tax structures including income tax
unemployment benefits
Discretionary Fiscal Policy
Deliberate use of taxes + govt spending to influence the economy when non-discretionary fp is not enough
govt makes changes to taxation/spending in sectors
examples of discretionary fp
jobkeeper during covid
what is a budget
plan for the allocation of the govts spending + taxation
it can influence the achievement of the govt macroeconomic objectives
purpose of a budget
Decide how revenue should be raised and funds allocated to areas of need.
Redistribute income from the wealthy to the less wealthy.
Influences the level of macroeconomic activity.
possible budget outcomes
neutral/balanced, surplus, deficit
neutral budget
revenue = expenditure
neutral impact on AD and economic activity
little impact on production, employment + inflation
G=T
deficit budget
expansionary
G>T
less money taken out of economy through T than poured back in through G
stimulates aggregate demand
surplus budget
contractionary
G<T
more money is withdrawn from the economy through T than poured back in through G
limits aggregate demand
government revenue
examples of government revenue
money received by a government from taxes and non-tax sources to enable it to undertake public expenditure. It is a leakage from the economy
government expenditure
is an injection into the economy involving the government spending money on items such as public services to stimulate the economy.
examples of government expenditure
welfare payments
spending for public infrastructure such as roads
What budget outcomes will the government aim for if it wants to expand the economy?
a deficit budget to create an overall injection into the economy and stimulate AD
What budget outcomes will the government aim for if it wants to contract the economy?
surplus budget to result in an overall leakage from the economy to limit production, consumption and inflationary pressure
What is monetary policy
set of actions available to a nation's central bank to control inflation and achieve sustainable economic growth by adjusting the money supply. Monetary supply is controlled through cash rate.
what is the transmission of monetary policy
how changes made by the Reserve bank to the cash rate flow through to economic activity and inflation
2 stages of transmission of monetary policy
changes made by the RBA to the cash rate influences other capital market interest rates
changes to these interest rates affect economic activity and inflation through ‘channels’
3 transmission channels
savings + investment channel
wealth + asset price channel
cash flow channel
Savings + investment channel
Interest rates influence economic activity by changing the incentives for saving and investment.
A reduction in interest rates on deposits decreases a household’s incentive to save and encourages spending.
lower interest rates encourage households + firms to increase investment + borrowing as the return on investment is now more likely to be higher than the cost of borrowing.
cash flow channel
Interest rates influence the decisions of households and businesses by change the amount of cash they have available to spend on goods and services
mainly affects those who are liquidity constrained as reduced interest rates means they have more of their income to spend on other goods + services
households who receive income from from deposits may choose to limit their spending but first effect is greater
asset price + wealth channel
Asset prices and people’s wealth influence how much they can borrow and how much they spend in the economy.
lower interest rates = increased demand for houses/assets = increase in value of assets + houses
increases equity for banks to lend against meaning people can borrow more and spend more on investments
increase in asset prices also increases household wealth
greater household spending as households generally spend some proportion of their increase in wealth
standard of living
level of welfare and prosperity citizens of a country have
Material SoL
our access to physical goods and services
e.g. car, house, food
if citizens have more goods and services to satisfy their needs and wants, life in general is better.
Non Material Standard of Living
intangible things that cannot be measured in dollar terrms but still affect our enjoyment of life.
factors affecting non material SoL
freedom of speech
low levels of crime + discrimination
preservation of the environment
adequate leisure time
life expectancy
literacy rate
indicators for material SoL
GDP per capita, housing availability
indicators for non-material SoL
OECD better life index, leisure time, low crime rates, work life balance
Concept of Poverty
state in which an individual or household is not able to fulfil minimum consumption needs
can be measured in absolute or relative terms
poverty line
estimated minimum household income threshold required to fulfil basic necessities of life
absolut epoverty
defined using the poverty line, below poverty line = poor
indicates a failure in meeting the basic necessities of life (food, water, clothing, shelter)
relative poverty
state in which a person lacks the least amount of income required to maintain the normal standard of living, in the society to which they belong.
Causes of Poverty
lack of education
geographic location
housing crisis
disability/illness
Methods to overcome poverty + improve living standards
increase minimum wage from $21.38 to something higher
fund education + training
adjust progressive taxation
funding and creating more government infrastructure
GDP- strengths
good indicator of material SoL
more goods and services to fulfil needs + wants