unit 7 bio - human nutrition
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is a balanced diet?
A diet that provides all the necessary nutrients in the correct proportions for healthy growth and function
What are the principal dietary sources of carbohydrates?
Starch from potatoes, rice, and bread, and sugars from fruits and sweets
Why are carbohydrates important?
They provide energy for the body
What are the principal dietary sources of fats and oils?
Butter, oils, nuts, and fish
Why are fats and oils important?
They provide energy, store energy, and are needed for cell membrane structure
What are the principal dietary sources of proteins?
Meat, fish, eggs, beans, and lentils
Why are proteins important?
They are essential for growth, repair of tissues, and enzymes production
What are the principal dietary sources of vitamins C and D?
Vitamin C: citrus fruits, strawberries; Vitamin D: fish, eggs, and sunlight
Why are vitamins C and D important?
Vitamin C helps with the immune system and wound healing; Vitamin D helps with calcium absorption and bone health
What are the principal dietary sources of calcium and iron?
Calcium: dairy products, leafy greens; Iron: red meat, beans, spinach
Why are calcium and iron important?
Calcium is needed for bone and teeth health; Iron is essential for forming hemoglobin in red blood cells
What is the importance of fibre (roughage)?
Fibre helps with digestion by moving food through the digestive system
What is the importance of water?
Water is needed for all metabolic reactions, maintains body temperature, and aids digestion
What causes scurvy?
A deficiency of vitamin C
What causes rickets?
A deficiency of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate
What are the main organs of the digestive system?
Mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum and ileum), large intestine (colon, rectum, anus), salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gall bladder
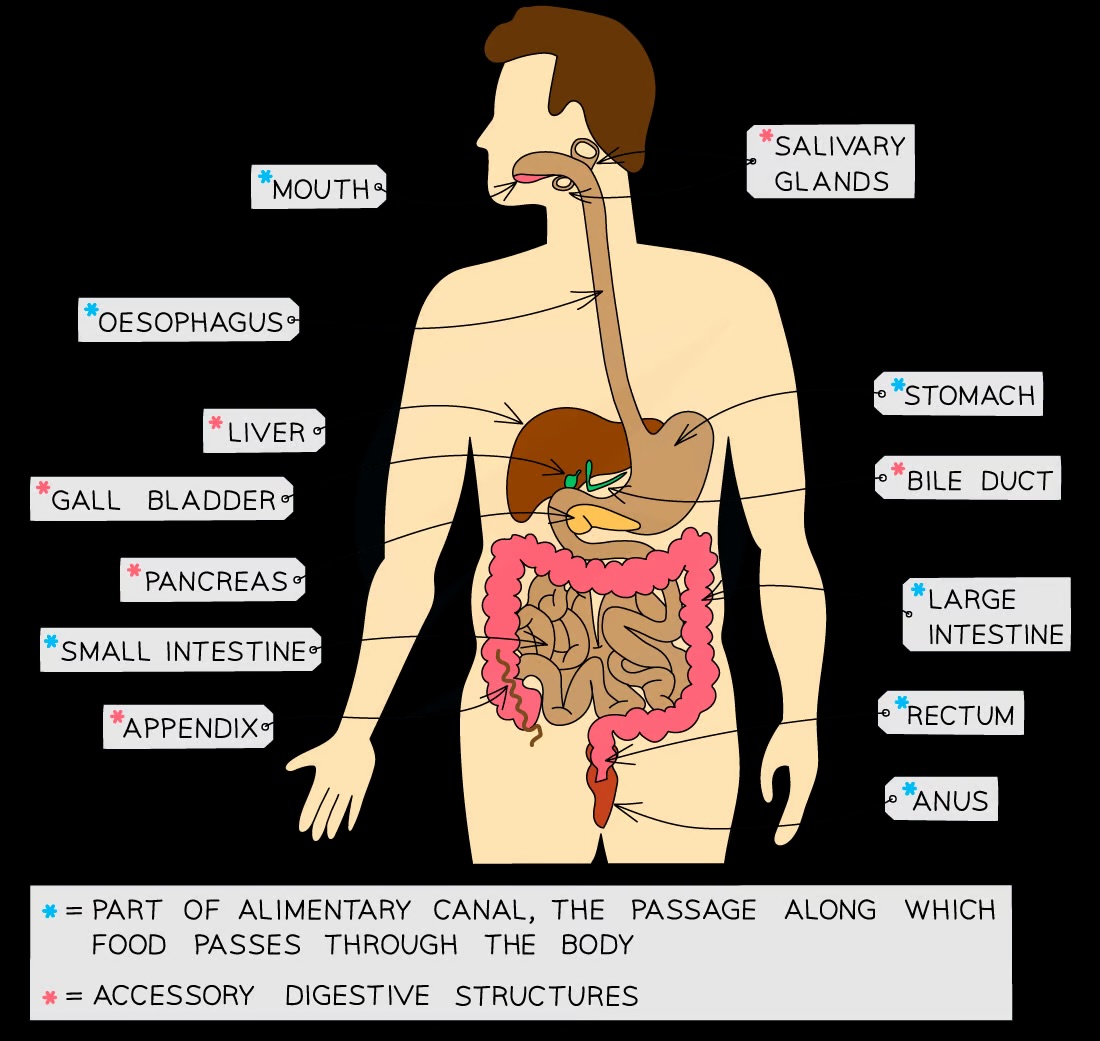
What is the function of ingestion in digestion?
The taking in of food and drink into the body
What is the function of digestion in the digestive system?
The breakdown of food into smaller molecules
What is absorption in the digestive system?
The movement of nutrients from the intestines into the blood
What is assimilation in digestion?
The uptake and use of nutrients by cells
What is egestion in digestion?
The removal of undigested food from the body as faeces
What is physical digestion?
The breakdown of food into smaller pieces without changing the chemical structure
How does physical digestion increase the surface area of food?
By breaking down food into smaller pieces, making it easier for enzymes to act on them
What are the types of human teeth?
Incisors, canines, premolars, and molars

What is the structure of human teeth?
Enamel, dentine, pulp, nerves, blood vessels, cement, and the teeth are embedded in bone and gums
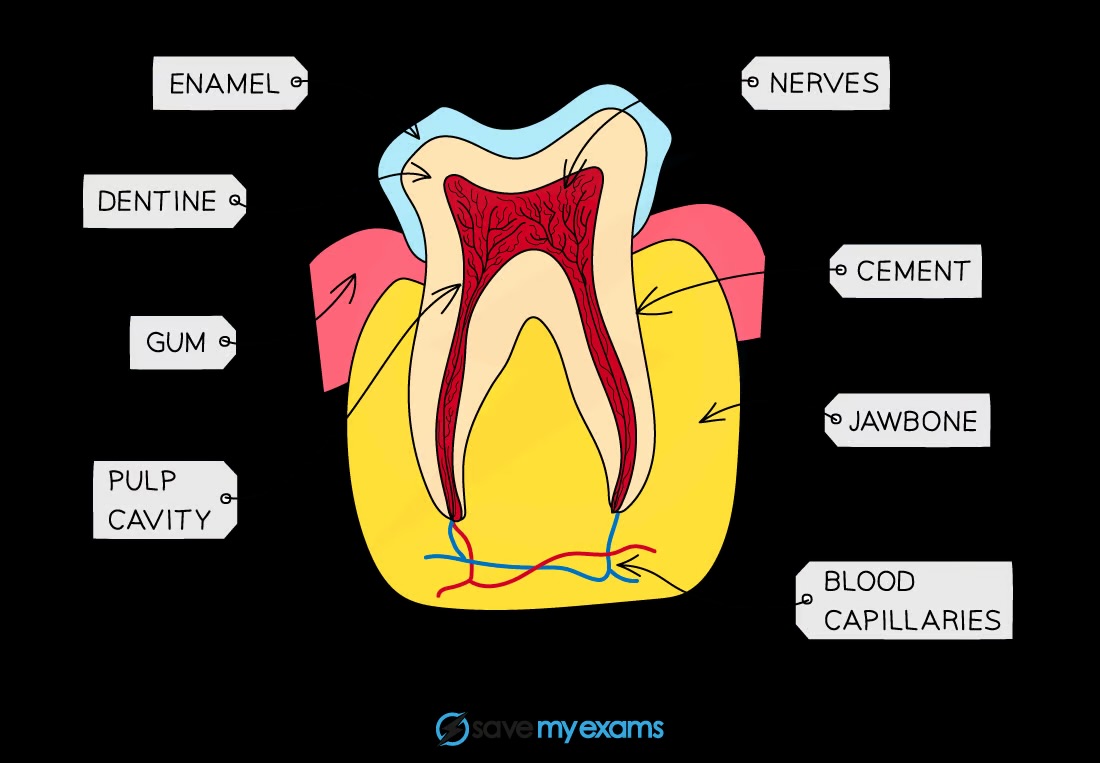
What are the functions of the types of human teeth in physical digestion?
• Incisors: cutting food
•Canines: tearing food
•Premolars and molars: grinding and crushing food
What is the role of bile in digestion?
Bile emulsifies fats and oils to increase the surface area for chemical digestion
What is chemical digestion?
The breakdown of large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules
What is the role of enzymes in chemical digestion?
Enzymes break down specific types of molecules:
• Amylase breaks down starch to simple sugars
• Proteases break down protein to amino acids
• Lipase breaks down fats and oils to fatty acids and glycerol
Where are amylase, protease, and lipase secreted and where do they act?
• Amylase is secreted by salivary glands and pancreas, acting in the mouth and small intestine
• Protease is secreted by stomach (pepsin) and pancreas (trypsin), acting in the stomach and small intestine
• Lipase is secreted by pancreas, acting in the small intestine
What is the function of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice?
To kill harmful microorganisms in food and provide an acidic pH for optimum enzyme activity
How is starch digested in the digestive system?
Amylase breaks down starch to maltose; maltase breaks down maltose to glucose in the small intestine
How is protein digested by proteases in the digestive system?
Pepsin breaks down protein in the stomach; trypsin breaks down protein in the small intestine
What is the role of bile in neutralizing gastric juices?
Bile neutralizes the acidic mixture of food and gastric juices entering the duodenum to provide a suitable pH for enzyme action
Where does absorption mainly occur in the digestive system?
In the small intestine
What is the role of villi and microvilli in absorption?
They increase the surface area of the small intestine for absorption of nutrients
What is the structure of a villus?
A villus contains capillaries and lacteals to absorb nutrients
What are the roles of capillaries and lacteals in villi?
Capillaries absorb amino acids and sugars, while lacteals absorb fatty acids and glycerol
Where is most water absorbed in the digestive system?
Most water is absorbed in the small intestine, but some is absorbed from the colon