Kinetic Model of Matter Flashcards
1/15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What happens to the particles during melting?
The speed of particles increases, become further apart, gain energy, FOA decreases
What happens to the particles during boiling?
Particles gain energy, speed increases, become further apart, FOA increases, faster evaporation with higher heat
What is the Kinetic Model of Matter/Kinetic Molecular Theory?
The idea that all substances consist of very small particles and explains the structure of the 3 States of matter and how they change.
What happens to the particles during condensation?
energy decreases, speed decreases, particles getting closer, FOA increases
What happened to the particles during freezing?
Speed decreases, energy decreases, particles become closer together, FOA increases
Describe the phase change of melting.
Solid to liquid
Describe the phase change of boiling.
Liquid to gas
Describe the phase change in condensation.
Gas to liquid
What are the four assumptions of the kinetic model of matter?
All matter is made up of very small particles. The particles are constantly moving. The freedom of movement and the arrangement of the particles differ in each state. The pressure of a gas is produced by how often the atoms collide with the walls of a container.
What are some physical properties to analyze substances?
Color, state at room temperature, melting point, boiling point, odor, density/mass/volume, solubility, conductivity
What is the freezing point in relation to the melting point?
The freezing point and melting point are the same thing
What does the heating curve look like?
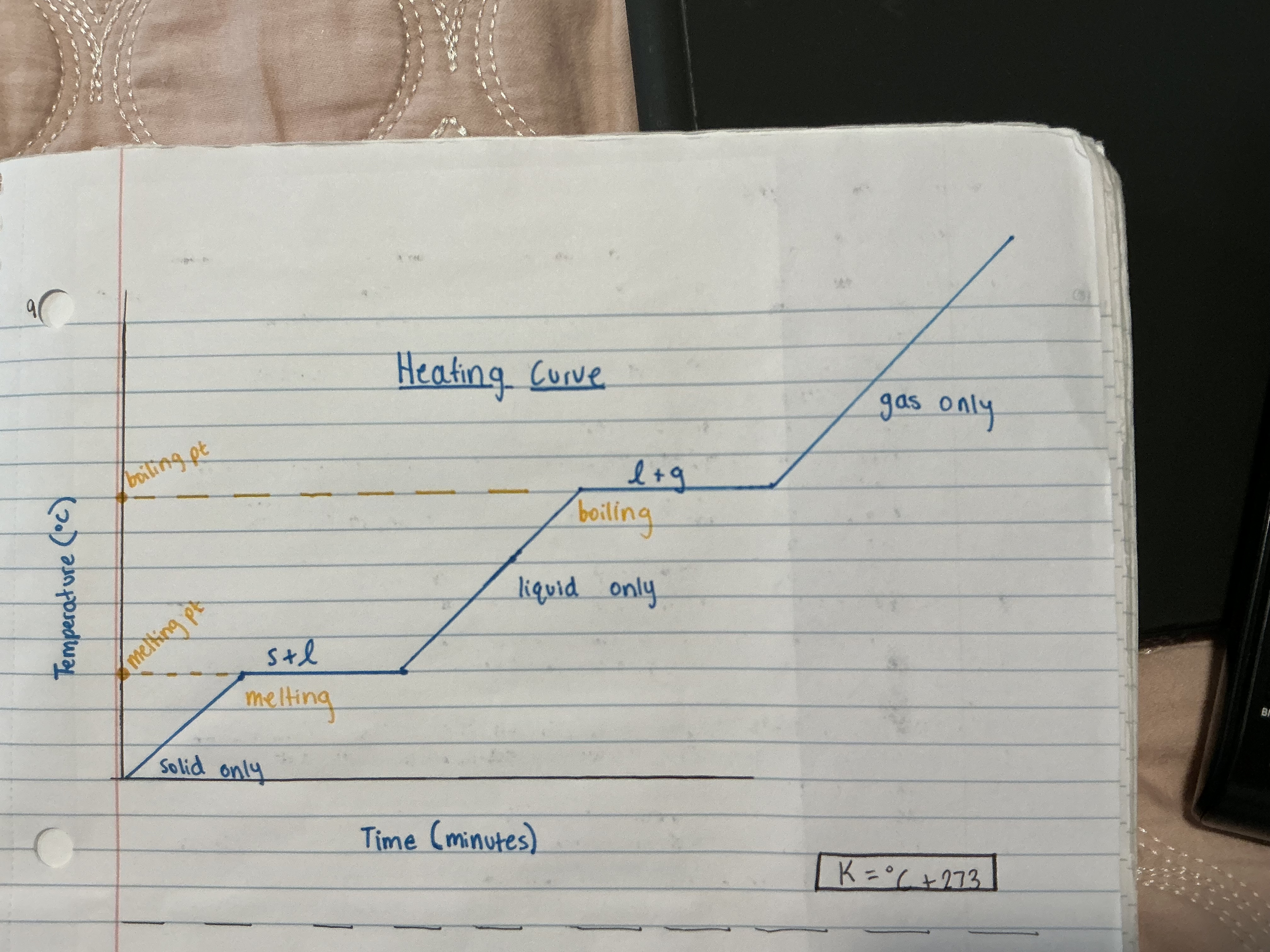
What does a cooling curve look like?
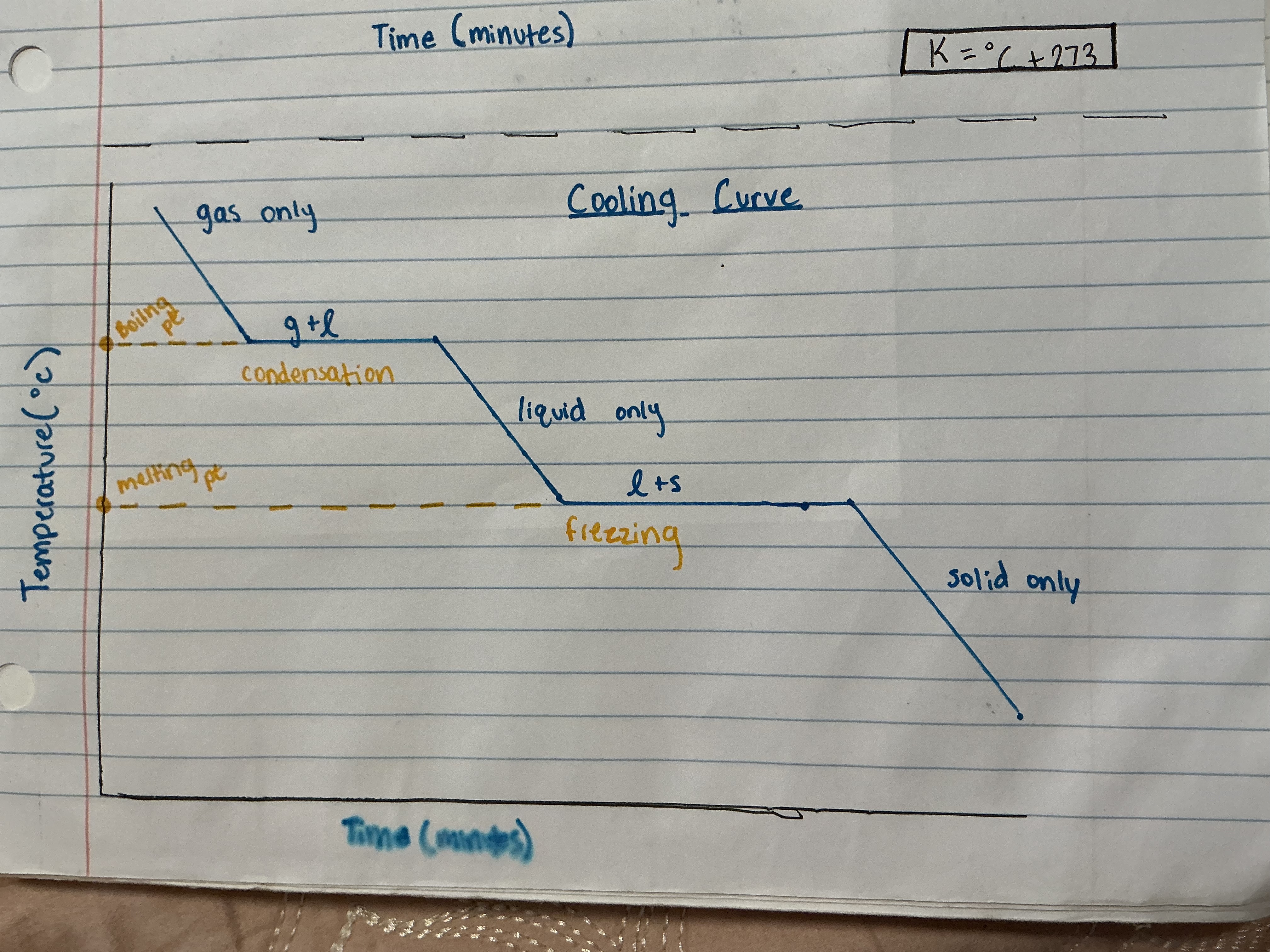
What is the conversion of kelvin?
K= C +273
How can you tell if a substance is pure by its heating curve?
There are sharp and clear, melting and boiling points