Electron Configurations - Chapter 3 Review
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
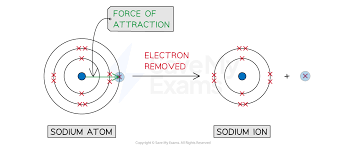
Ionization Energy
Energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons electron from 1 mole of atoms of an element.
kJ/mol
Atoms are in a gaseous state.
3 Factors of Ionization Energy
Size of nuclear charge or effective nuclear charge.
Distance of valence electron from the nucleus.
Shielding Effect.
Shielding Effect
When the full inner shells of an atom repel the outer shell, reducing the effective nuclear charge.
Nuclear Charge
The attractive force between the protons located in the nucleus and the electrons that surround it.
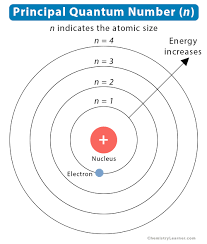
Shell
Principle Quantum Shell.
Energy Level.
Electron Shells.
Subshell
Divisions of Shells
s-subshell (2 electrons)
p-subshell (6 electrons)
d-subshell (10 electrons)
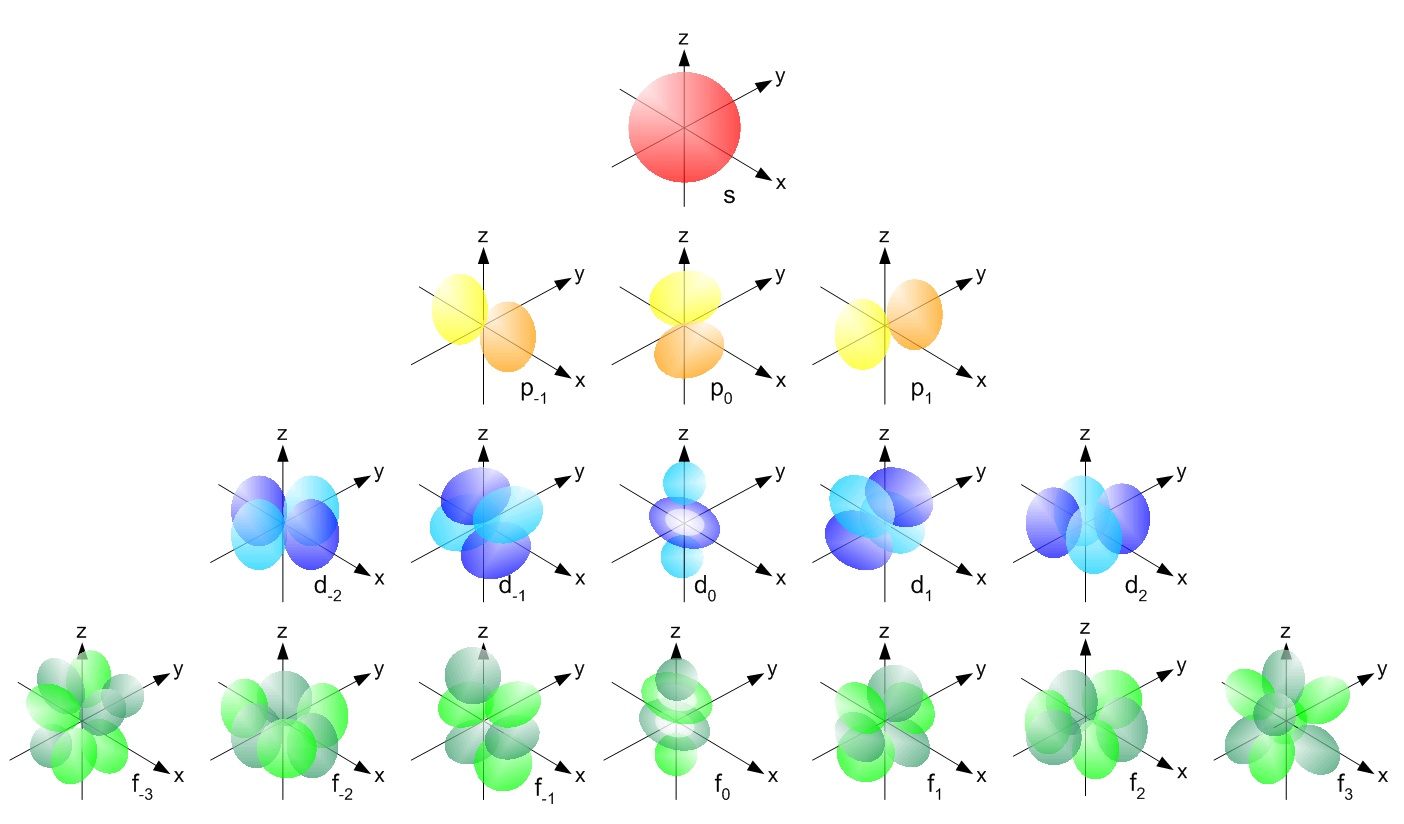
Orbitals
A region of space where an electron is most likely to be found.
Divisions of subshells.
Each holds 2 electrons.
What is the shape and number of orbitals each subshell has?
s-orbital; Spherical; 1 orbital.
p-orbital; Dumbbell; 3 orbitals.
d-orbital; A ring between 2 spheres; 5 orbitals.
Exceptions to the Electron Configuration
Chromate [Cr] 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁵ 4s¹
Copper [Cu] 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s¹
The 4s is not fully filled as the electron from the subshell moves to the 3d shell to make it more stable.
Group 6 and Group 11 elements.
![<ul><li><p>Chromate [Cr] <strong><span>1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁵ 4s¹</span></strong><span> </span></p></li><li><p>Copper [Cu] <strong><span>1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s¹</span></strong><span> </span></p></li><li><p><span>The 4s is not fully filled as the electron from the subshell moves to the 3d shell to make it more stable.</span></p></li><li><p><span>Group 6 and Group 11 elements. </span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/38792ad6-f172-46d4-8c6b-a7c5d60843bf.png)
Aufbau’s Rule
Electrons fill shells with the least energy.
Energy increases as the Principle Quantum Number increases.
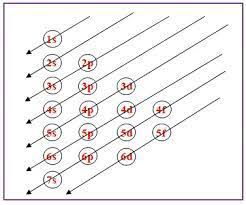
Pauli Exclusion Principle
2 electrons per orbital.
Electrons in the same orbital experience Spin-Pair Repulsion.
Hund’s Rule
Electrons will fill subshells by taking up empty orbitals first before pairing up.
Electrons that are alone spin the same direction as all other lone electrons.
How does the Ionization Energy change across a period?
Increases
Nuclear Charge increases
Distance from Nuclear Charge is constant
Shield Effect is constant

How does the Ionization Energy change down a group?
Decreases significantly
Distance from Nuclear Charge increases
Shielding Effect increases
These factors outweigh the nuclear charge increase

How does the Ionization Energy change when removing a lone electron from a subshell?
Is lower
Distance from nucleus is constant
Shielding is constant
Nuclear charge increases
Why Boron has a lower Ionization Energy than Beryllium
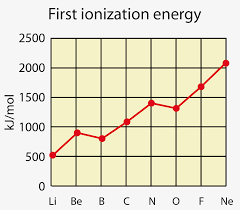
How does the Ionization Energy change when an electron is in spin-pair repulsion?
Decreases
The extra repulsion helps to remove it.
Why Oxygen has a lower Ionization Energy than Nitrogen.
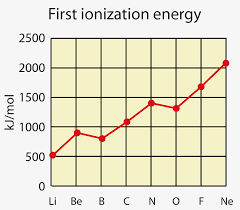
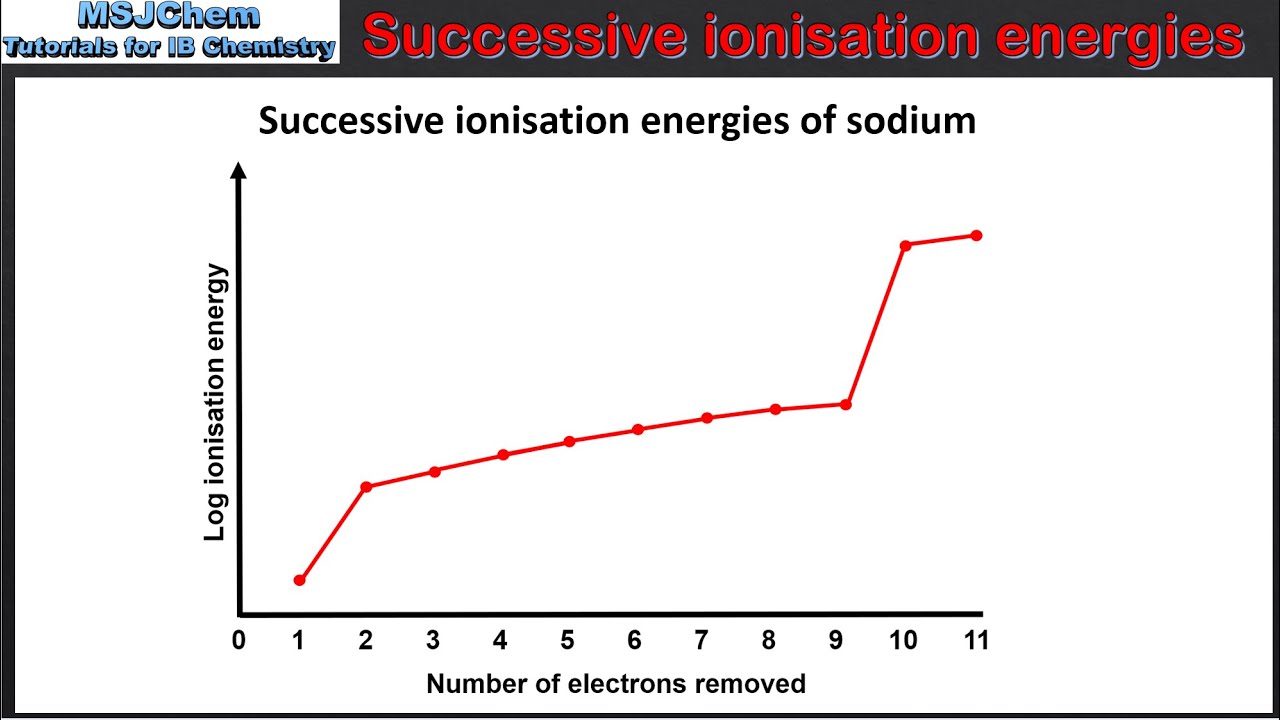
Successive Ionization Energy
Consecutive removal of 1 mole of electron from 1 mole of atoms of a particular element.
Sudden increases indicate a change in subshells
Increasing trend as effective nuclear charge increases while distance and shielding decreases.