3.4 - inflation, deflation, Philips curve
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
inflation
a sustained increase in the average prices of goods and services in the entire economy
deflation
a sustained decrease in the average prices of goods and services in the entire economy
disinflation
a decrease in the rate of inflation (eg. 10% → 7%)
consumer price index
index of prices of the costs of living for a typical household
compares the value of a basket of goods and services in one year with the value of same basket in base year
CPI for a base year is always 100
formula for CPI for a specific year
CPI for a specific year = (value of basket in specific year / value of basket in base year) x 100
real income formula in relation to CPI
real income = (nominal income / CPI) x 100
problems with CPI (overstating degree of inflation)
different rates of inflation for different income earners
CPI reflects average prices
different rates of inflation depending on regional or cultural factors
changes in consumption patterns
due to more sales and discounts
due to consumer substitution when relative price changes
new products
changes in product quality
CPI doesn’t account
core rate of inflation
excludes volatile items such as food and energy prices to provide a clearer view of long-term inflation trends.
types of inflation
demand-pull inflation
cost-push inflation
demand-pull inflation
increase in AD
real GDP>potential GDP
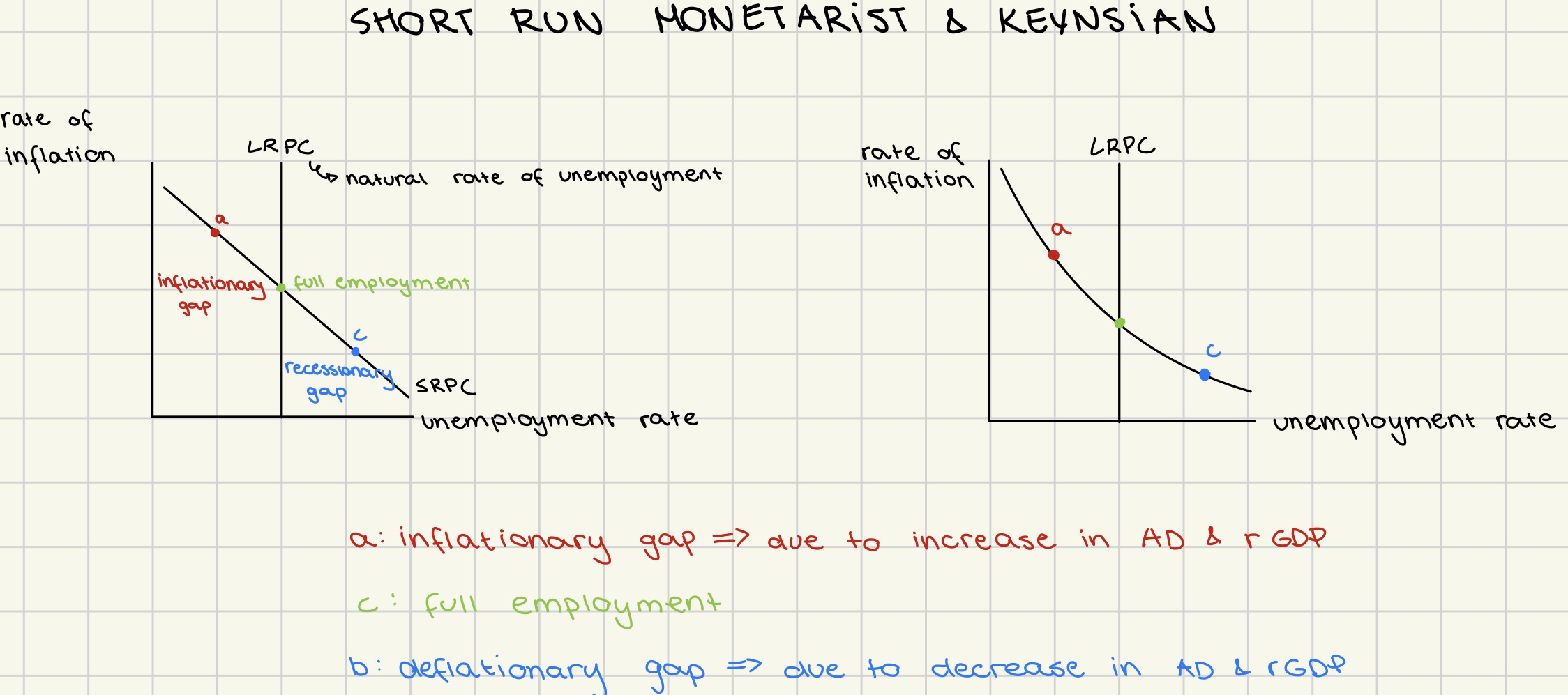
inflationary gap
unemployment <natural rate of unemployment
demand is so large the unemployment temporarily find jobs
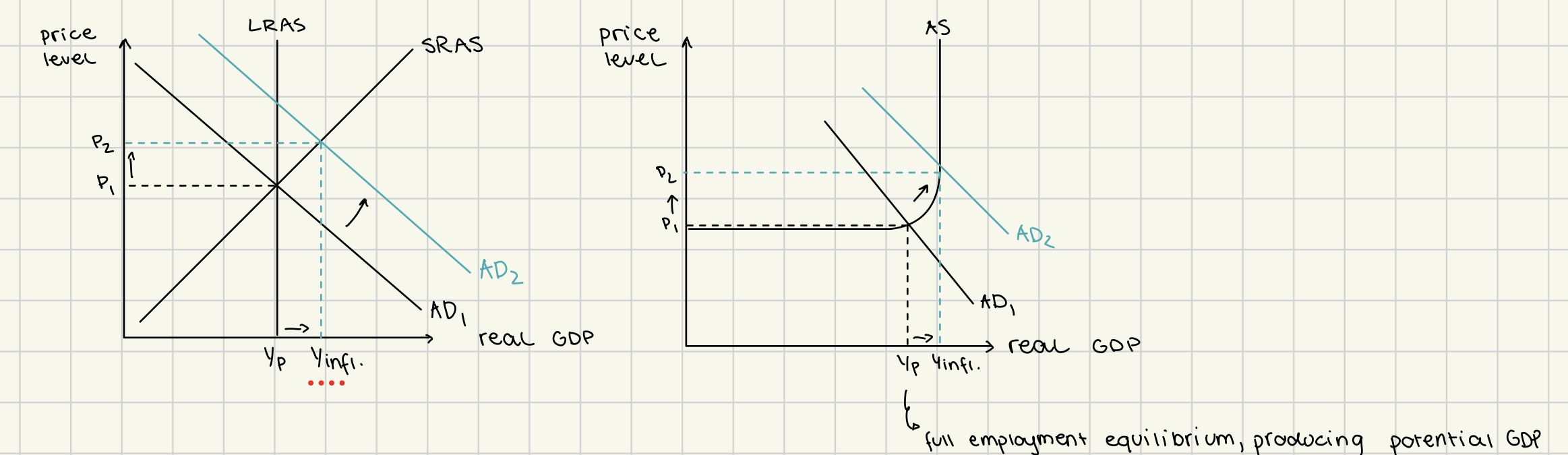
cost-push inflation
fall in SRAS, due to increased costs of production/ supply-side shocks
real GDP < potential GDP
although indicates recession, its NOT called recessionary gap
STAGFLATION
purchasing power
quantity of goods and services that can be bough with money
decreases with inflation
increases with deflation.
%change in pp = %change in nominal income - %change in price level
price level ↑ = purchasing power↓
costs of inflation
redistribution effects
uncertainty
fewer investments
effects on savings
lowered incentive to save
international export competitiveness
negative effect on economic growth
inflation = lower AD = lower economic growth
social and personal costs are unequally distributed
redistribution effect definition
inflation redistributes income away from certain groups of economy to other
redistribution effect: groups who lose from inflation (real value ↑)
people with fixed incomes/wages
people who receive incomes/ wages that increase less rapidly than rate of inflation
holders of cash
savers
creditors (when lending interest rate < rate of inflation)
redistribution effect: groups who gain from inflation (real value ↓)
borrowers (because the real value of their debt decreases)
payers of fixed incomes/ wages
payers of incomes/ wages that increase less rapidly than rate of inflation
cost of inflation: international export competitiveness
decline in international export competitiveness
as domestic goods become more expensive compared to foreign goods, potentially reducing demand for exports.
hyperinflation
a rapidly accelerating inflation rate, typically exceeding 50% per month
due to significant increases in the supply of money
governments printing money
consequences of hyperinflation
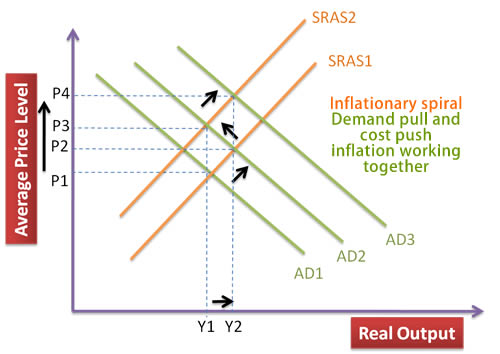
inflationary spiral
inflationary spiral
(money value ↓↓ = consumer spending ↑ = feeding AD = demand-pull inflation = worker demand for higher wages ↑= cost-push inflation = ….)
businesses stop investing
businesses withold goods from sale
creditors suffer massive losses as real value of debts falls dramatically
money loses value all together
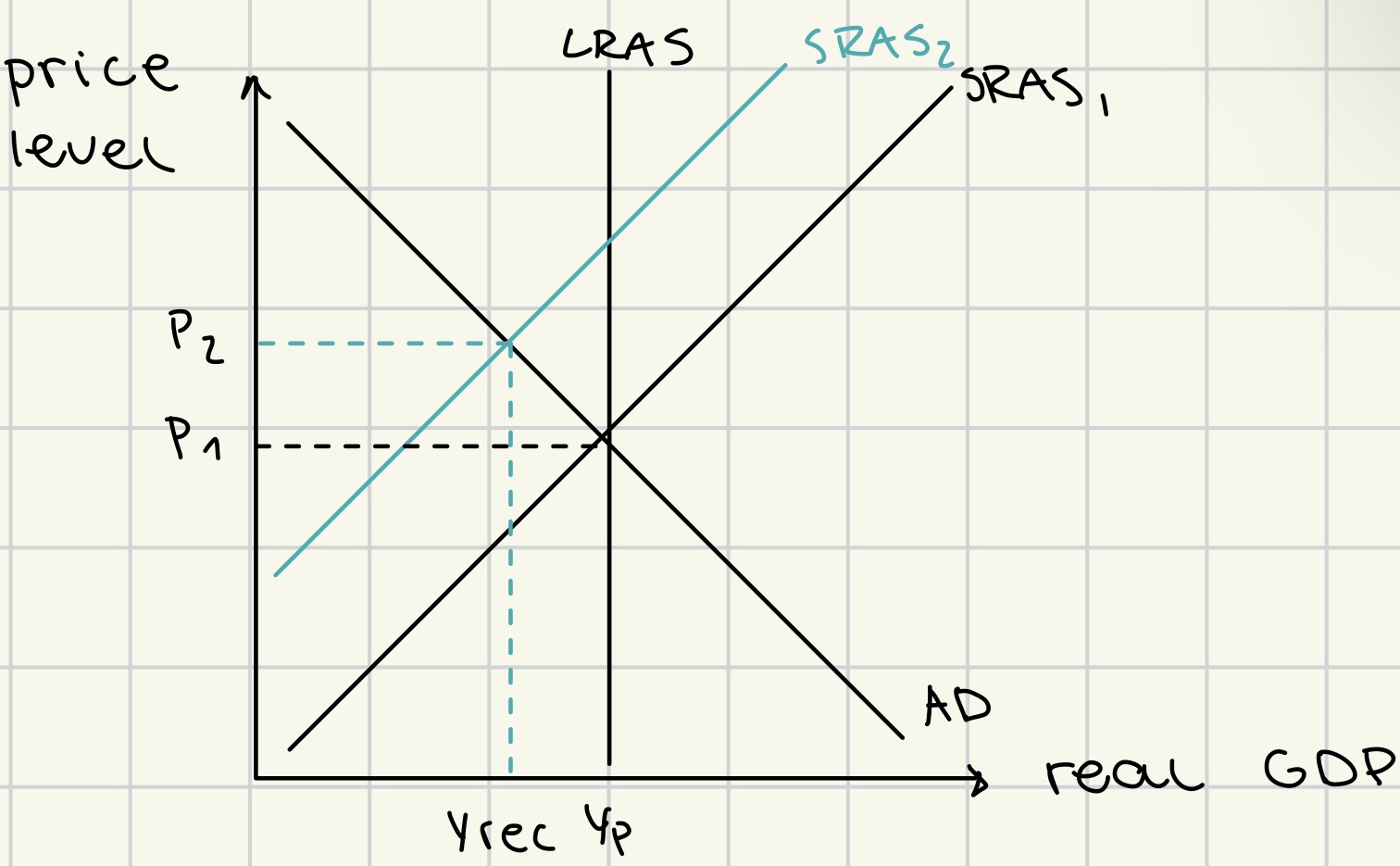
deflation
due to fall in AD
due to increase in SRAS
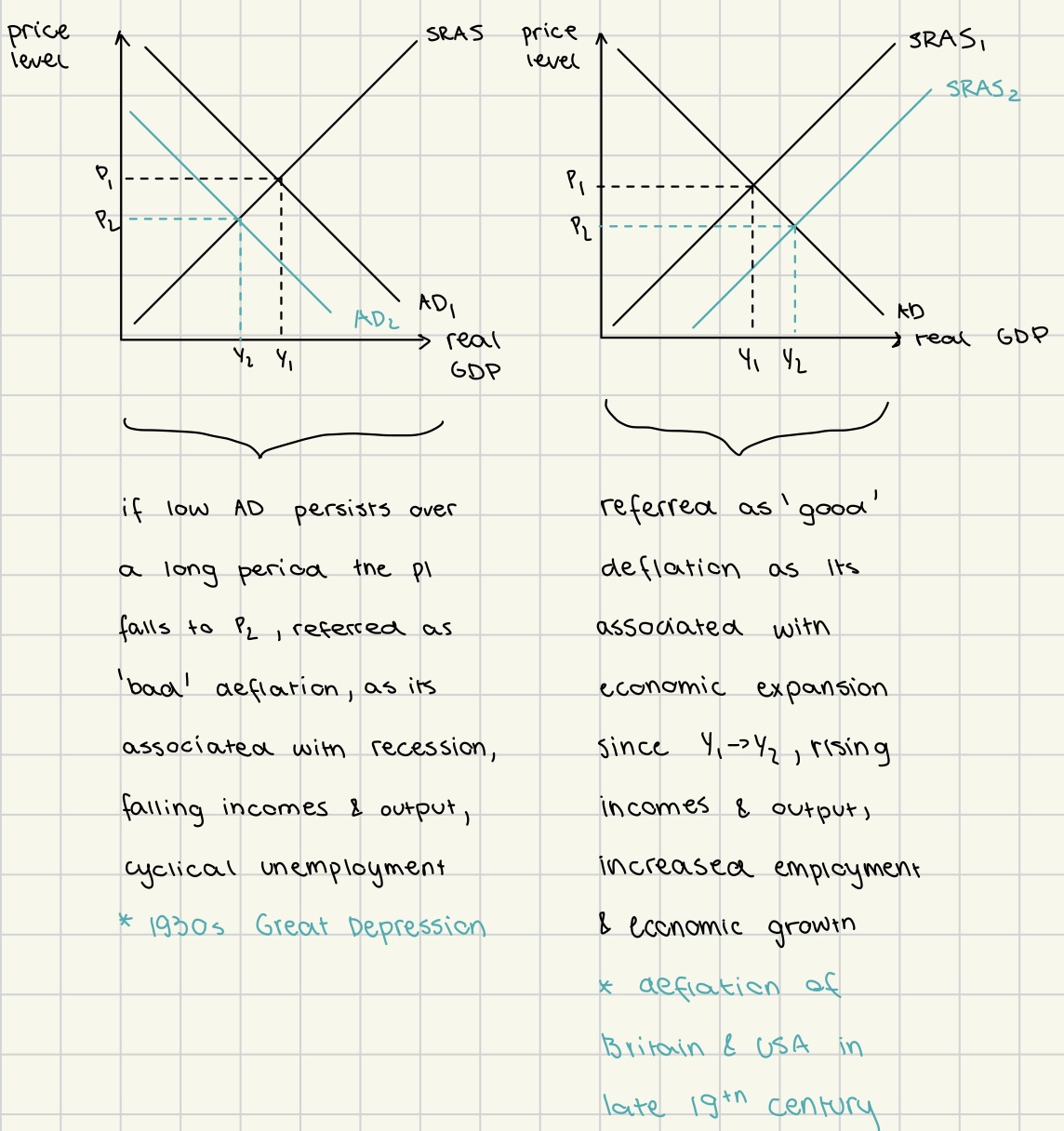
costs of deflation
redistribution effect
increase in purchasing power
deffered consumption
deflationary spiral
risk of bankruptcies
inefficient resource allocation
increased unemployment
economic stagnation
policy ineffectiveness
central banks struggle to stimulate the economy due to lower interest rates.
redistribution effect: groups who gain from deflation (real value ↑)
individuals on fixed incomes/wages
holders of cash
creditors
redistribution effect: groups who lose from deflation (real value ↓ )
borrowers
payers of fixed incomes/wages
deflationary gap
(…. real value ↓ = AD↓ = rGDP ↓= cyclical unemployment ↑ = AD ↓↓= real value ↓ ….)
consumers and businesses anticipate falling prices, leading to decreased demand for goods and services
further economic contraction
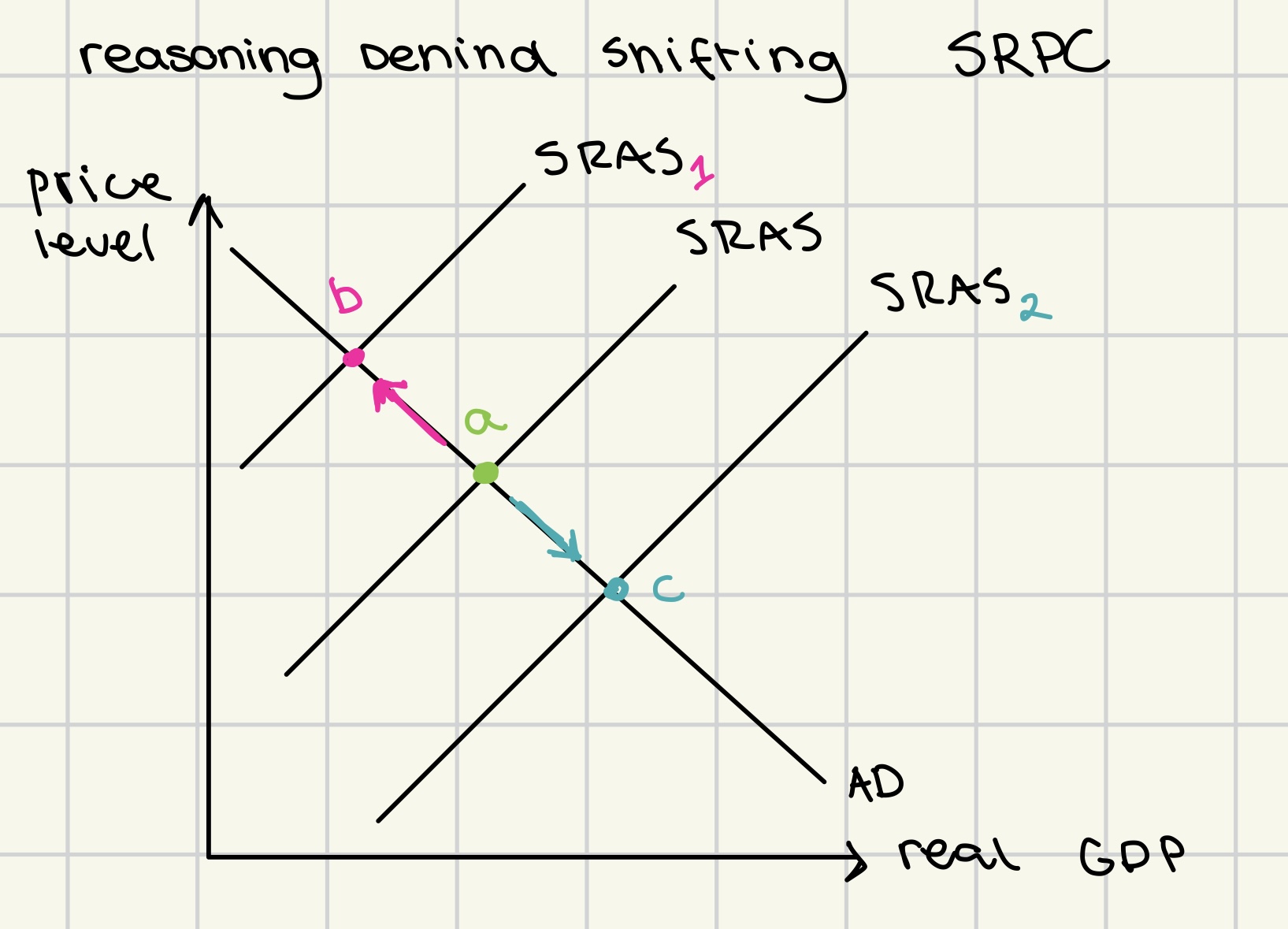
Phillips curve in short run (monetarist and keynesian)
illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment rates
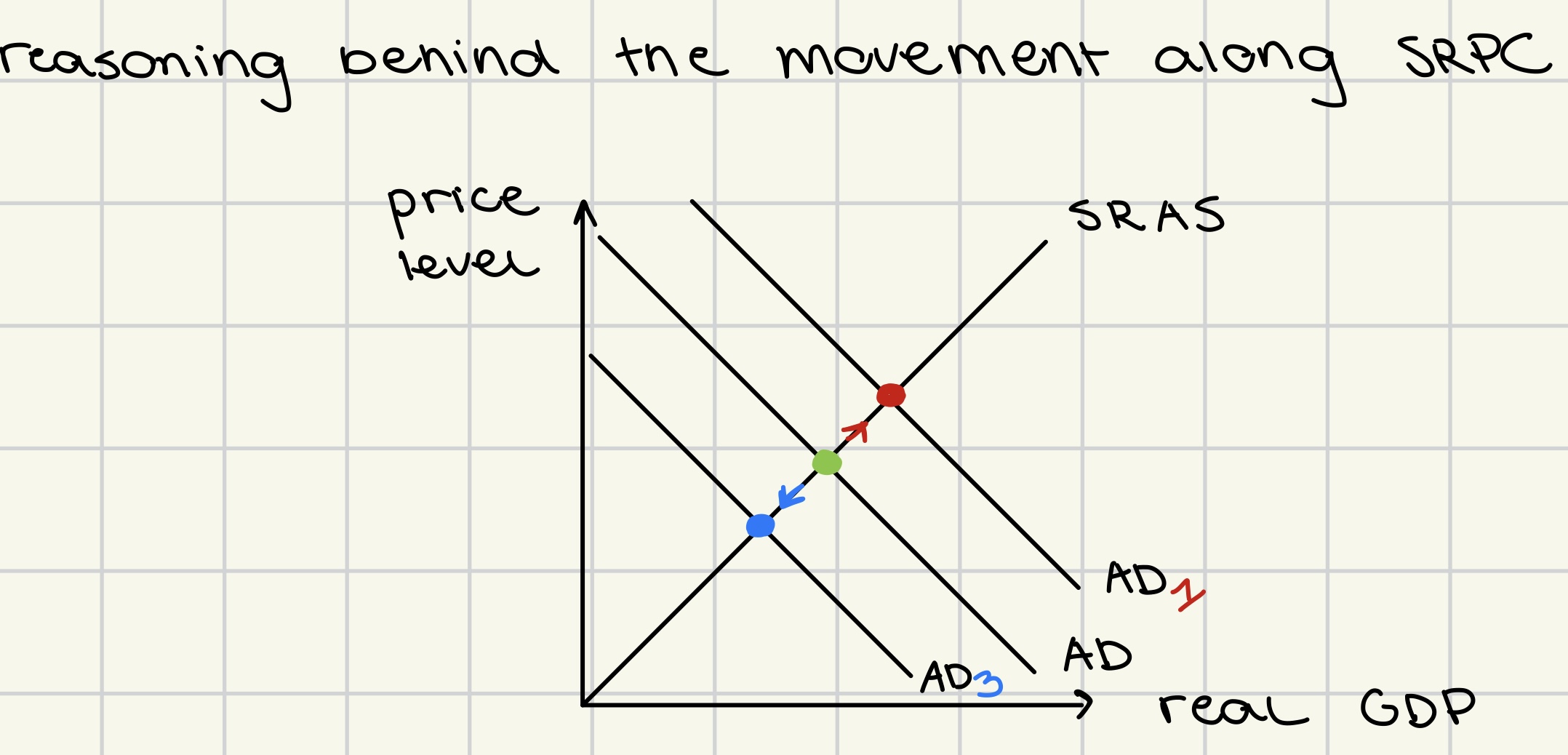
reasoning behind the movement along SRPC
Philips curve in long run Monetarist and Keynesian
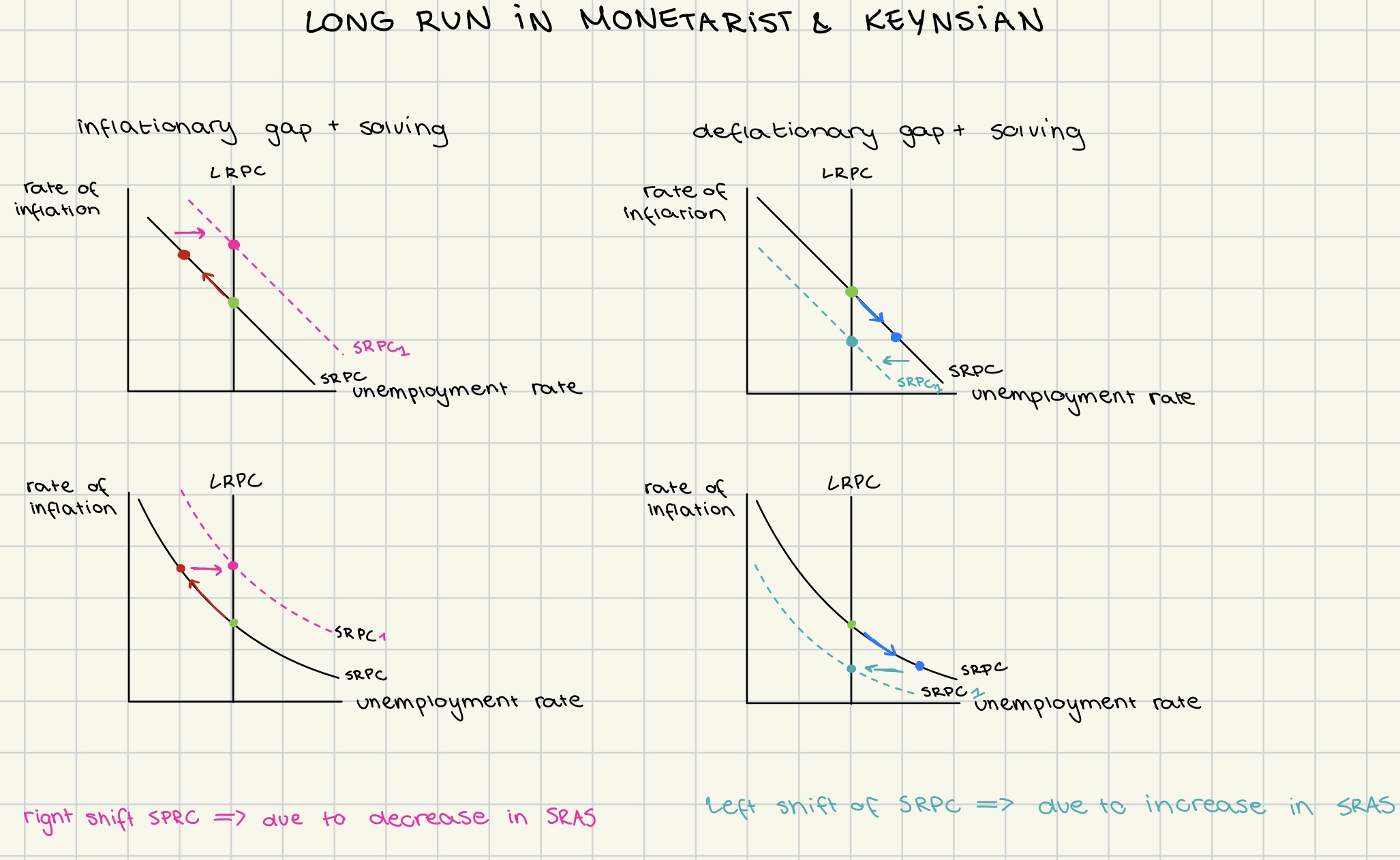
reasoning behind shifting SRPC in long term