EIA 7 (radioactivity)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
sources of radioactivity in terrestrial ecosystems
man-made
accidental release of nuclear power plants (NPP)
(test) firing of nucleat weapons¨radioactive waste deposits (NPP, medical use)
uranium and oil shale mines
routine release of nuclear power plants
Natural
bedrock geology (granite)
radon gas release by weathering
pathways to human exposure
inhalation (radon indoors)
ingestion (food - cow milk, game meat, mushrooms, cereal)
external exposure
radiation safety
Swedish Radiation Safety Authority (SSM) responsible for handling crisis and preparedness together with several agencies and authorities Radiation protection act (Strålskyddslagen) 2018:396
international organisations
-International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)Stakeholders such as:
Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Co. (SKB Co.)
farmers
reducing radioactivity in agricultural products in case of radioactive atmospheric deposition
1) improve shield (move animals indoors → cover)
2) wait (mix in Cs fixator, K-fertilization → slaghter timing, rinsing, cooking
3) remove, deep-ploughing and new sowing
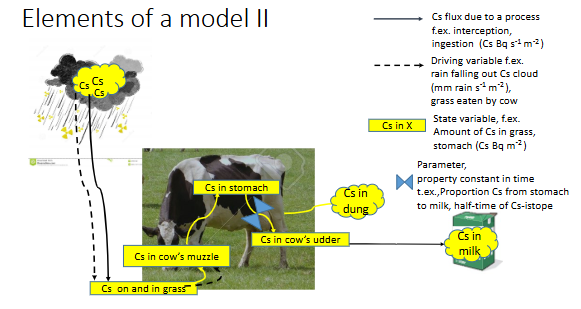
elements of process-oriented dynamic process-based model I
1) Define your system and boundaries:
Atmosphere-plant-animal-milk for
consumption
2) Source / Sinks
(Amount per unit time and area)
Cs Deposited /Cs in milk (Cs= Cesium)
elements of a model
tracey model
the trace element cycling in terestrial ecosystem
identification of low and high accumulating ecosystems and their regulating factors
the bioavalibility in the alder system is much higher because of larger amounts are stored close to soil surface(= rooting zone of many plants) and humus will decompose and thereb release trace eleme
scenarios of water contamination
Scenarios, combinations of:
- 2 initial groundwater levels (deep and shallow)
- 2 root uptake (passive with water uptake and
active due to growth),
- 3 rooting depths (shallow, medium and deep)
the soil profile of pine-spruce (up hill, low accumulation, adsorbtion higher) is partly contaminated, while the one of alder (low land, active uptake, high contamination) is totally contaminated
grain storage
TE intercepted flux (Yellow rings) is the TE flux that is adsorbed or stays on grain, leaves and stem and depends on rainwater interception (driving variable, blue dashed arrows).
→ TE can be fixated, TE Fixated, purple arrow,
that is internal stored (state variable) that depends on the parameter TE grain fixation,
If not fixated, TE stays intercepted or be can wash-offed next rain event.
→ TE wash-off flux is the TE flux that is washed-off grain, leaves and stem and depends water throughfall flux, a driving variable (blue dashed arrow).
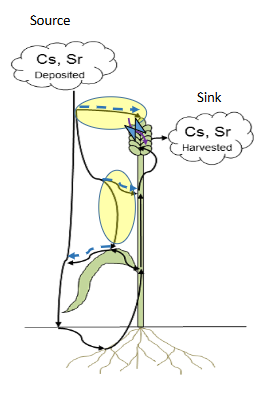
grain cs storage
Grain’s Cs storage increased when deposition was close to harvest
Governing plant properties of grain storage of Cs and Sr depend on growth stage at time of deposition
The grain interception capacity can be used to predict grain storage at
most riskiest period, i.e. deposition shortly before harvest.