Understanding Emotional Intelligence and Its Components
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is emotion?
A complex psychophysiological experience involving physiological arousal, expressive behaviors, and conscious understanding.
What are the five components of emotion?
1) Subjective feelings (experience), 2) Physiological response (bodily reactions), 3) Motor expression (facial expression, body language, gestures), 4) Action tendency (motivational component), 5) Evaluation or appraisal.
How do emotions typically arise?
In response to an event, either internal or external, that has a positively or negatively valenced meaning for the individual.
What is mood?
A pervasive and sustained feeling tone that influences virtually all aspects of a person's behavior and perception of the world.
What is the role of the sympathetic nervous system in emotions?
It prepares the body to act or react following an emotion-evoking event, triggering fight or flight responses.
What physiological changes occur due to sympathetic nervous system activation?
Increase in heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, slower digestive processes, and pupil dilation.
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
It keeps the body from expending energy, promoting rest and digestion.
What is the limbic system's role in emotion?
It is involved in emotional responses, including the regulation of motivated behaviors and categorizing experiences as pleasant or unpleasant.
What is the amygdala's association with emotions?
It is linked to emotions such as fear and pleasure and is involved in facial expressions of human emotions.
What happens when the amygdala is damaged in rats?
They cannot be classically conditioned to fear new objects and appear unable to remember to be afraid.
What effects are associated with amygdala damage in humans?
Impairment in determining emotions from facial expressions of others.
What are the four Fs of motivation regulated by the limbic system?
Fleeing, feeding, fighting, and sexual behavior.
How do emotions find expression behaviorally?
Through facial expressions, bodily movements/actions, posture, and gestures.
How do facial expressions communicate emotions?
They convey our emotions and intentions to others and allow quick judgments of hostility or friendliness.
Are facial expressions universal?
Yes, but they can also be misleading, exaggerated, or minimized.
What are macro-expressions?
Facial expressions that typically last between 0.5 to 4 seconds and involve the whole face.
What are micro-expressions?
Expressions that go on and off the face in a fraction of a second, as fast as 1/30 of a second, often trying to conceal emotions.
What is the cognitive component of emotion?
Labeling or interpreting the subjective feeling, which involves retrieving memories of previous experiences and perceiving the context of the emotion to come up with a solution.
What is primary appraisal in emotional response?
It determines whether and how a subject's goals are affected by an event, such as how two individuals react differently to not making a sports team.
What is secondary appraisal in emotional response?
It determines how best to cope with an event once it has been classified as furthering or thwarting the subject's goals.
What is one purpose of emotions?
Emotions guide us in facing predicaments and tasks, contributing to survival and reproductive success.
How do emotions prepare us for action?
Emotions link events in our environment to our responses, activating physiological reactions like the 'fight-or-flight' response.
In what way do emotions shape our future behavior?
Emotions promote learning that helps us make appropriate responses to similar situations in the future.
How do emotions help regulate social interaction?
We communicate our emotions through verbal and nonverbal behaviors, signaling to others what we are experiencing and helping them predict our future behavior.
What is the affiliation function of emotions?
It involves seeking harmony, closeness, and love with others, illustrating the importance of social bonds for health and well-being.
What is the distancing function of emotions?
It involves avoiding others who may pose a threat, competing for social status or power, and differentiating oneself or one's group from others.
What physiological response is associated with fear when encountering a threat?
The activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, leading to the 'fight-or-flight' response.
What role does labeling play in the cognitive component of emotion?
Labeling involves interpreting feelings and explaining experiences to oneself, which influences emotional understanding.
How can two individuals react differently to the same event in terms of primary appraisal?
One may view the event as unimportant while the other perceives it as very stressful, affecting their emotional response.
What does the secondary appraisal process involve after an event is classified?
It involves determining the best coping strategy for the situation, influencing future actions.
What is one example of how emotions promote learning?
An emotional response to an unpleasant event teaches individuals to avoid similar circumstances in the future.
How do emotions signal to observers in social contexts?
Emotions are communicated through behaviors that allow others to understand our experiences and predict our actions.
What impact does social isolation have on individuals according to research?
It leads to poorer health and well-being and inhibits the development of social, emotional, and cognitive skills.
What is the significance of social bonds in emotional contexts?
Emotions help establish or maintain cooperative and harmonious relations with others.
How do emotions differentiate or distance individuals from others?
Emotions can serve to compete for social status or power and to avoid those perceived as threats.
What is the relationship between emotions and survival?
Emotions guide actions that are crucial for survival, helping individuals respond effectively to challenges.
What is the role of emotions in reproductive success?
Emotions influence behaviors that enhance reproductive success by guiding social interactions and bonding.
What is an example of a physiological reaction associated with fear?
The activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which prepares the body for immediate action.
What is social dysfunctionality in relation to emotions?
Social dysfunctionality is likely to occur if the social impact of one's emotions is ignored or if inappropriate appraisals of the social context are made.
What does Robert Plutchik's Wheel of Emotion illustrate about the intensity of emotions?
The intensity of emotion decreases as you move outward from the center of the wheel and increases as you move toward the center, with darker shades indicating more intense emotions.
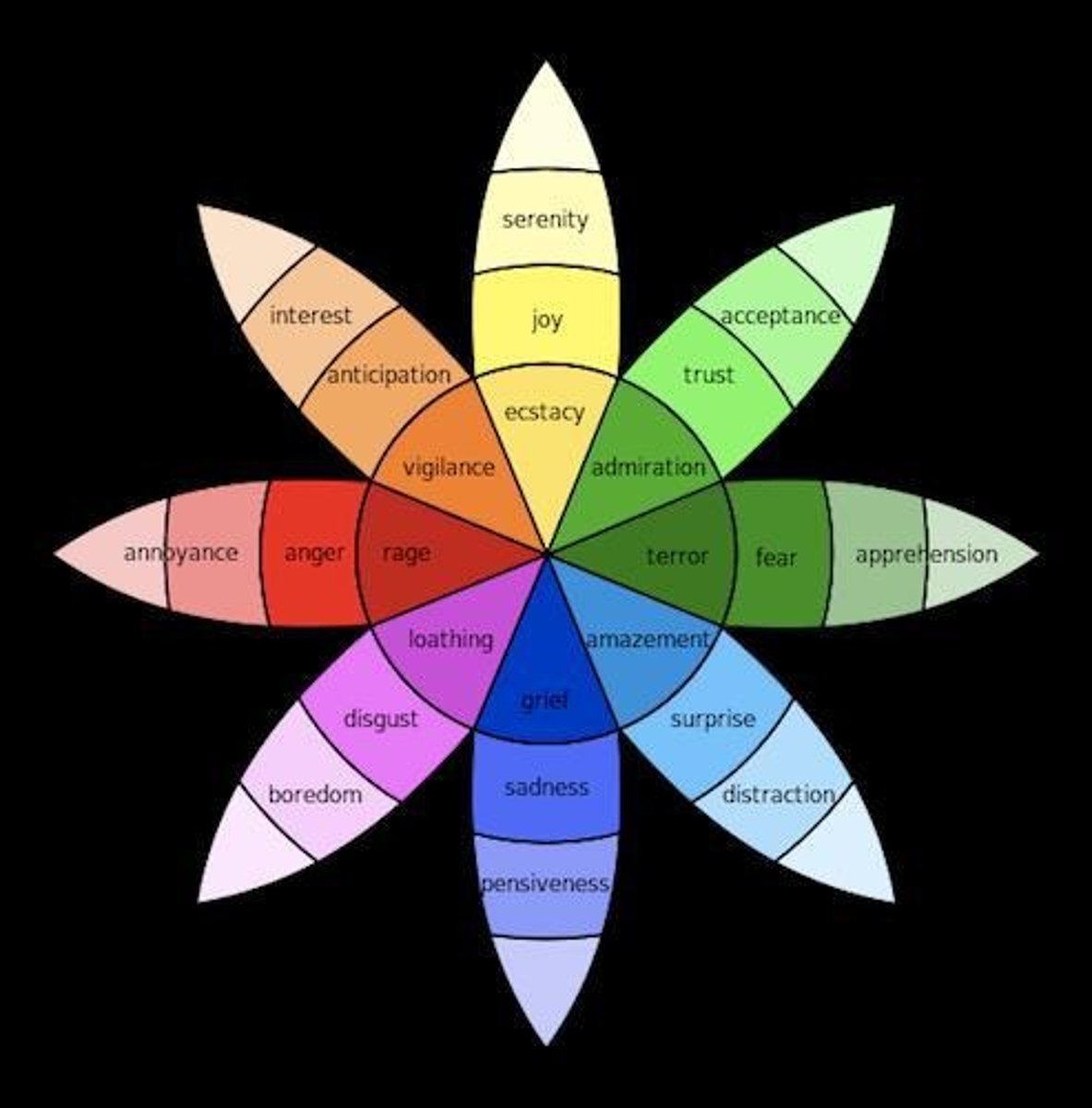
What are the polar opposites of joy, fear, and anticipation according to Plutchik's Wheel of Emotion?
Joy is opposite to sadness, fear is opposite to anger, and anticipation is opposite to surprise.
Why is recognizing combinations of emotions important?
Recognizing when a feeling is a combination of two or more distinct feelings is a helpful skill.
What is the flow of the Biological/Physiological Component of Emotion theory?
Stimulus > Emotion > Arousal (e.g., 'I am shaking because I am afraid.').
Describe the Common Sense Theory of emotion.
It posits that feeling a particular emotion leads to a physical reaction and then to a behavioral response.
What does the James-Lange Theory state about the relationship between physiological reactions and emotions?
It states that a physiological reaction leads to the labeling of an emotion (Stimulus > Arousal > Emotion).
What is the Cannon-Bard Theory of emotion?
This theory asserts that physiological reactions and emotions occur simultaneously (Stimulus > Brain Activity > Arousal > Emotion).
Explain the Two Factor Theory (Schachter-Singer Theory) of emotion.
This theory states that both physical arousal and the labeling of that arousal based on environmental cues must occur before the emotion is experienced (Stimulus > Arousal > Cognition > Emotion).
What is the Facial Feedback Theory?
It suggests that facial expressions provide feedback to the brain about the emotion being expressed, which can enhance the emotion (Stimulus > Arousal > Facial Expression > Cognition > Emotion).
What is the Cognitive-Mediational Theory (Lazarus Theory) of emotion?
This theory posits that a stimulus must be appraised by a person to result in a physical response and an emotional reaction (Stimulus > Appraisal > Emotion > Arousal).
Who first studied Emotional Intelligence (EQ)?
Emotional Intelligence was first studied by Mayer and Salovey and popularized by Daniel Goleman.
What are the four abilities associated with Emotional Intelligence according to Goleman?
1. Ability to perceive, appraise, and express emotion accurately. 2. Ability to access and generate feelings that facilitate thought. 3. Ability to understand emotion and emotional knowledge. 4. Ability to regulate emotions to promote growth.
What skills are encompassed within Emotional Intelligence (EQ)?
EQ includes skills for accurate assessment, evaluation, expression, and regulation of emotions.
What is the significance of being aware of and managing one's own emotions in EQ?
It facilitates thinking and helps attain goals, as well as understand emotions in others.
What benefit is associated with perceiving and using emotions in leadership?
Being able to perceive and use emotions has been linked with leadership effectiveness.
What is the impact of emotions on behavior?
Emotions can drive behavior and impact people positively and negatively. Managing emotions, especially under pressure, can help build stronger relationships, make good decisions, and deal with difficult situations.
How are emotional intelligence (EQ) and intelligence quotient (IQ) related?
EQ and IQ share the same brain areas and functions, are interdependent, and general intelligence is related to EQ in terms of comprehension and speed.
What are the characteristics of adolescents with low emotional awareness?
Adolescents who are low in emotional awareness are least likely to seek help from nonprofessional sources and have the highest intention of refusing help from everyone.
What is self-awareness in emotional intelligence?
Self-awareness involves recognizing one's emotions and their effects on others, accepting one's feelings, and accurately labeling everyday feelings.
What does self-regulation entail in emotional intelligence?
Self-regulation involves controlling disruptive impulses caused by negative emotions, managing reactions, and includes trustworthiness, conscientiousness, adaptability, and innovation.
What is the role of motivation in emotional intelligence?
Motivation involves self-motivation to work, setting goals, reframing negative thoughts, choosing moods, and countering automatic negative thoughts.
How does empathy contribute to emotional intelligence?
Empathy helps recognize and understand how others feel, discerns feelings behind needs and wants, and involves imagining how others might feel in certain situations.
What are social skills in the context of emotional intelligence?
Social skills, or 'people skills,' involve working well with others through collaboration and cooperation, being a good team player, and adapting responses based on situational and cultural factors.
What defines a passive response in emotional situations?
A passive response is not expressing one's needs and feelings, or expressing them so weakly that they are not addressed.
What characterizes an aggressive response?
An aggressive response involves asking for what you want or expressing feelings in a threatening, sarcastic, or humiliating way that may offend others.
What is an assertive response?
An assertive response involves asking for what you want or expressing feelings honestly and respectfully, without infringing on another person's rights.
What is the importance of emotional intelligence in decision-making?
Emotional intelligence helps in making good decisions by managing emotions effectively, especially in difficult situations.
What are the components of emotional intelligence?
The components of emotional intelligence include self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills.
How does self-regulation relate to trustworthiness?
Self-regulation involves maintaining standards of honesty and integrity, which is a key aspect of trustworthiness.
What does conscientiousness mean in the context of emotional intelligence?
Conscientiousness refers to taking responsibility for one's work and actions.
What is adaptability in emotional intelligence?
Adaptability is the ability to be flexible in handling change.
What does innovation mean in emotional intelligence?
Innovation refers to being open to new ideas and approaches.
How can motivation influence task performance?
Choosing the right mood can help someone get motivated, concentrate on a task, or try again instead of giving up.
What is the significance of listening in empathy?
Taking time to listen is crucial in empathy as it helps understand others' emotions and perspectives.
What factors should be considered when responding to others?
Responses should consider situational factors (like heat and room density) and cultural factors (such as age, sex, and race).
How can emotional intelligence help in building relationships?
By managing one's own and others' emotions, emotional intelligence fosters stronger relationships through better understanding and communication.