AQA GCSE Homeostasis and Response
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is homeostatis?
The regulation of the conditions in our body maintaining stable internal environment
What does homeostasis do?
Responds to any change in internal or external conditions.
What is a stimulus?
A change in your environment than requires a response
Give some examples of stimuli?
Light, sound, touch, pressure, pain, chemical or temperature.
What do the receptors do?
Detect the stimulus or change in environment.
What happens after the receptors?
Receptors send messages to the CNS via the sensory neurone.
What makes up the central nervous system?
The brain or spinal cord
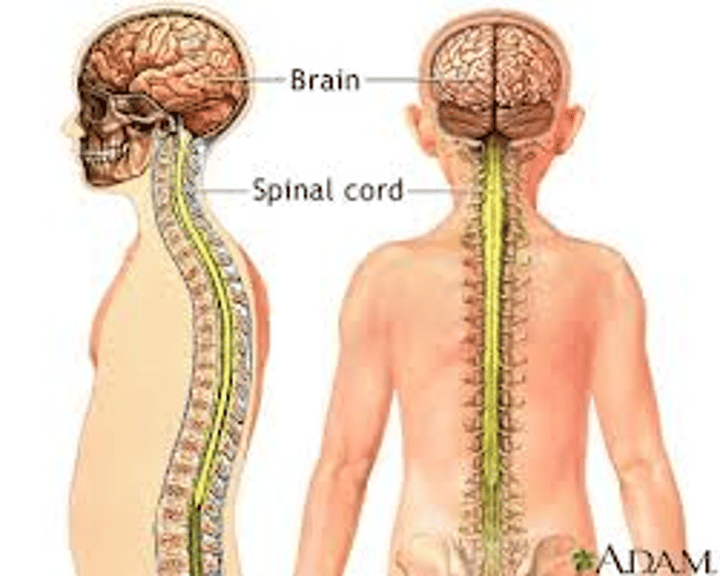
What is an effector?
Muscles or glands that bring about a response.
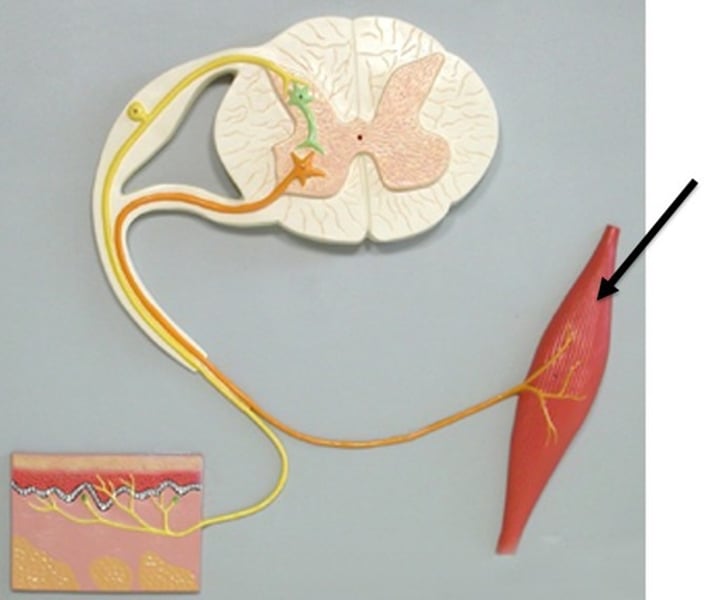
What do the muscles and glands do in response to stimuli?
Muscles contract and glands secrete chemical substances(hormones).
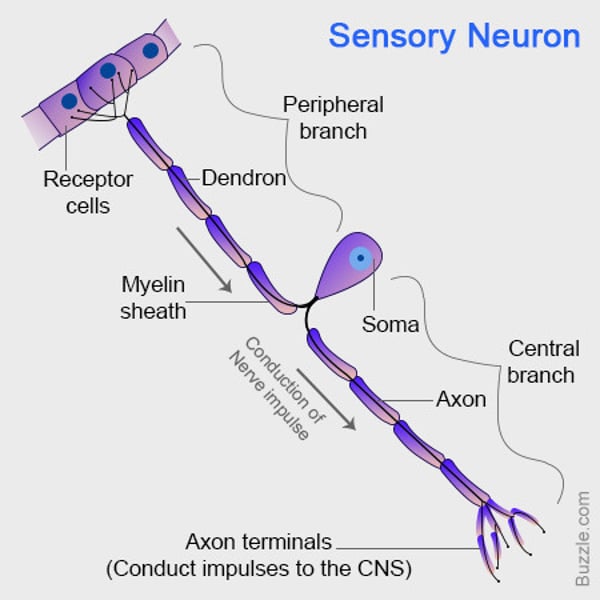
What is a sensory neurone?
A neurone that carry information from the receptors to the CNS.
What is a relay neurone?
Neurones that carry impulses from the sensory neurone to the motor neurone.
What is a motor neurone?
Neurones that carry information from the CNS to the effectors.
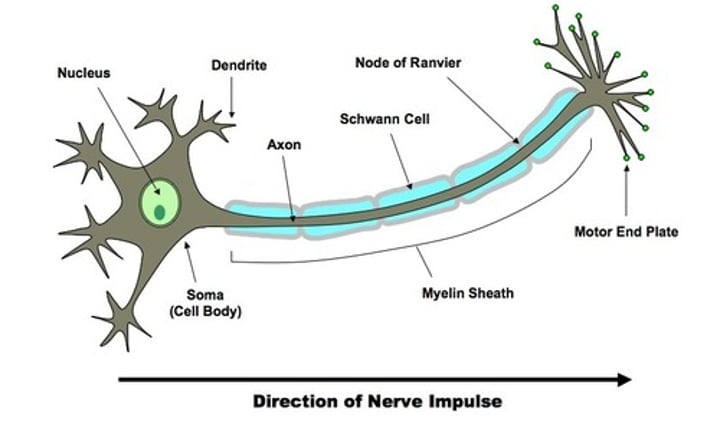
What is the nervous system?
It is a system that allows you to react to your surroundings.
How do signals travel across a synapse?
The chemical or neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse and binds to a complementary receptor on the neurone (postsynaptic). This causes an electrical impulse to travel down the next neurone.
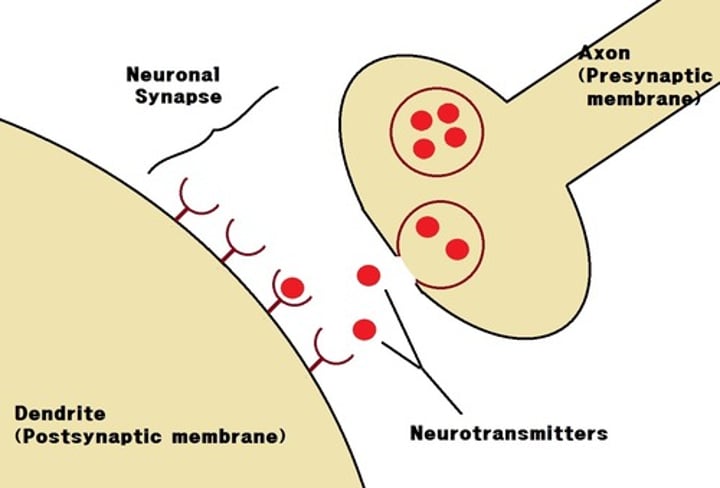
What is a synapse?
A gap between two neurones.
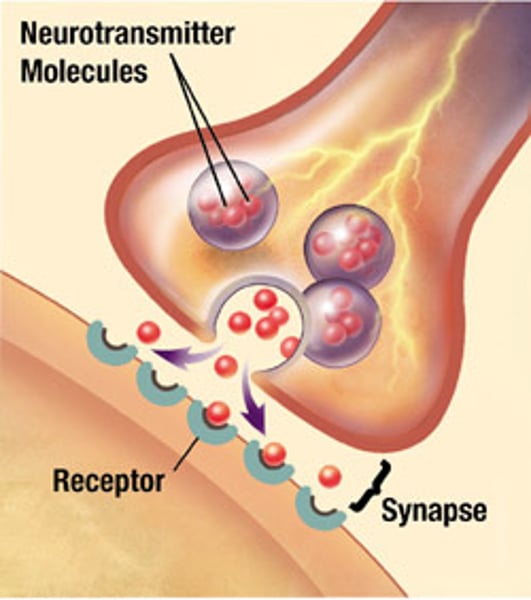
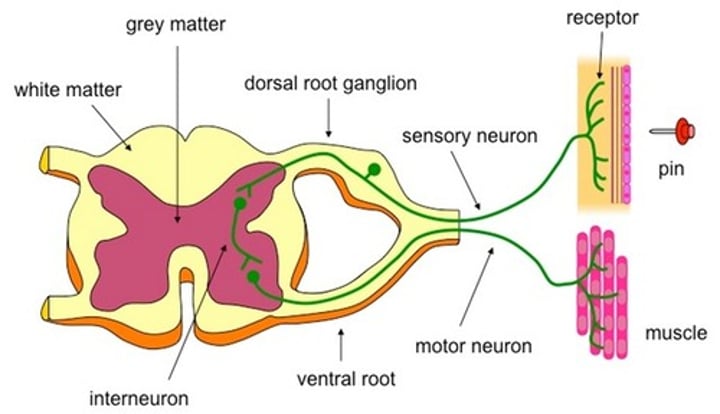
Describe the stages in a reflex arc.
Stimulus->Receptor->sensory neurone->CNS (relay neurone) -> motor neurone -> effector -> response
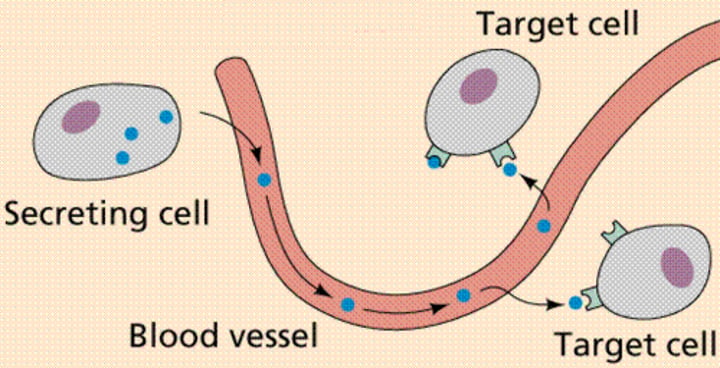
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers that travel in the blood to target organs.
Compare and Contrast the endocrine (hormone) system and the nervous system.
Nervous is faster acting than the endocrine system.
Hormones have longer lasting effects compared to electrical impulses. Nerves act on a very specific area whereas hormones act more general.
What does the thyroid gland do?
Produces thyroxine which is involved in regulating metabolism.
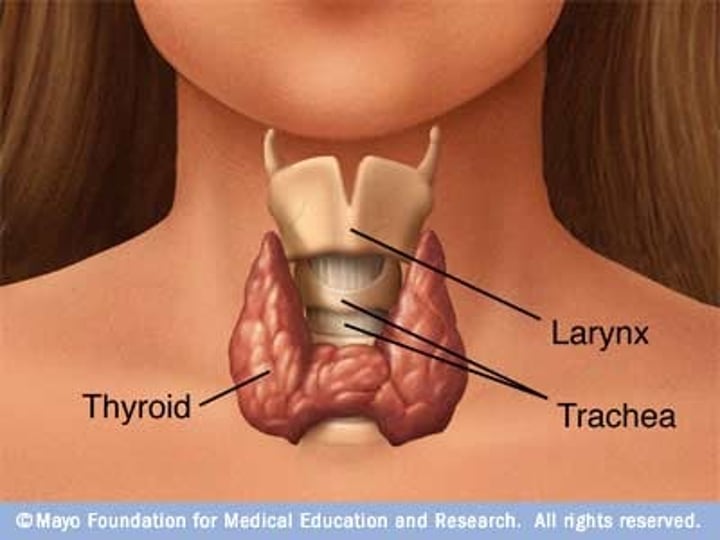
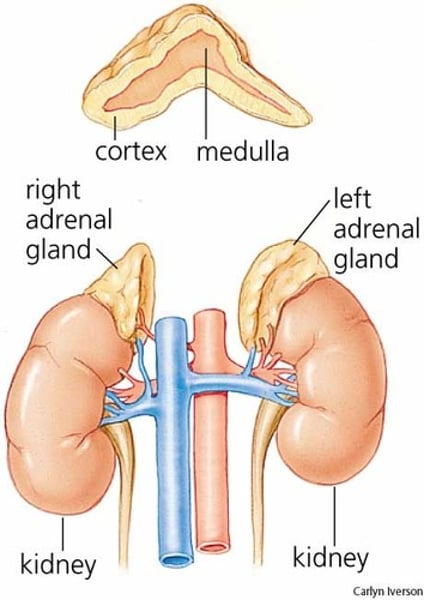
What do the adrenal glands do?
Produce adrenaline which is used to prepare the body for fight or flight.
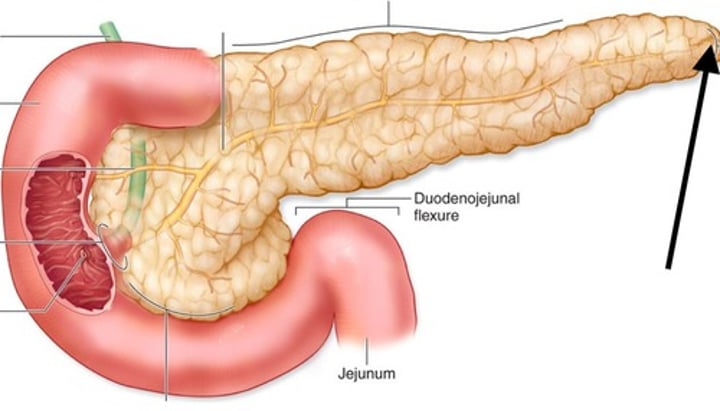
What is the role of the pancreas?
Produces glucagon and insulin which are involved in regulating glucose levels in the blood.
Name the hormone that is released if blood sugar is too high.
Insulin
What does insulin do?
It makes the liver convert glucose into glycogen. This causes blood glucose levels to decrease.
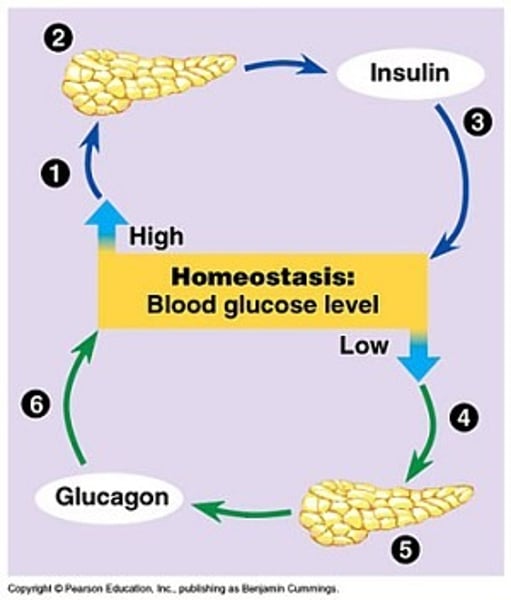
Name the hormone that is released if blood sugar is too low.
Glucagon
What does glucagon do? HINT GLU-COSE-GONE
It makes the liver convert glycogen to glucose. This causes the blood glucose level to increase.
What is type I diabetes?
When the pancreas produces little or no insulin.

What is type II diabetes?
When a person becomes resistant to their own insulin. Being overweight can increase your chances of type II diabetes.
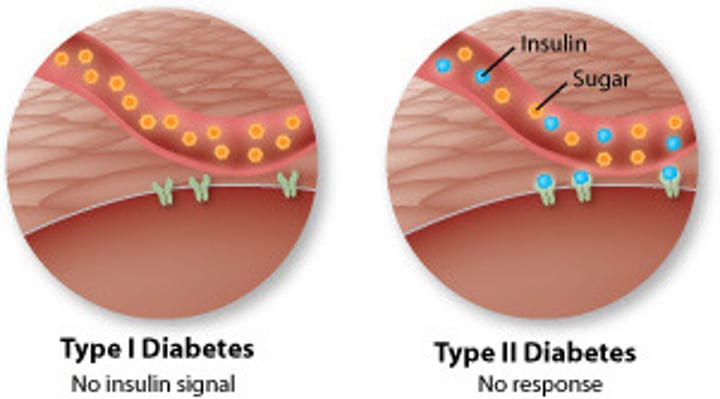
How can type I diabetes be treated?
Insulin injections, limiting intake of foods rich is simple carbohydrates e.g. sugars and regular exercise.
How can type II diabetes be treated?
It can be controlled by eating a carbohydrate controlled diet and getting regular exercise.
What are the four stages of the menstrual cycle?
1) Menstruation-the uterus lining breaks down
2) The uterus lining builds up again
3) Ovulation-Around day 14 a egg is released from an ovary.
4) The wall is maintained for about 14 days until day 28. If the egg has not been fertilised and implanted into the uterus lining it breaks down.
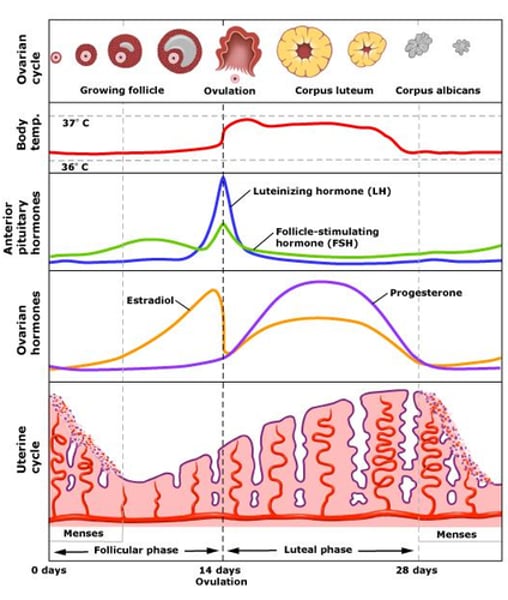
What is the role of FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) in the menstrual cycle?
Made in the pituitary gland.
Causes a egg to mature in one of the ovaries in a structure called a follicle.
Stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen.
What is the role of oestrogen in the menstrual cycle?
Produced by the ovaries. Causes the lining of the uterus to grow. Stimulates the release of LH (which causes ovulation) and inhibits the release of FSH.
What is the role of LH (Luteinising hormone) in the menstrual cycle?
Produced in the pituitary gland.
Stimulates the release of an egg (ovulation) at day 14.
What is the role of progesterone in the menstrual cycle?
Produced by the ovary by the remains of the follicle. Maintains the lining of the uterus. When the level of progesterone falls the lining of the uterus breaks down. Inhibits the release of LH and FSH.
Where is testosterone produced?
In the testes.
How does the contraception pill work?
Contains oestrogen and progesterone. Taking oestrogen every day prevents the release of an egg by inhibiting FSH. Progesterone reduces fertility by stimulating the production of thick sticky mucus at the cervix preventing the sperm getting to the egg.
What are the side effects of the pill?
Headaches and nausea. Still contract STIs.
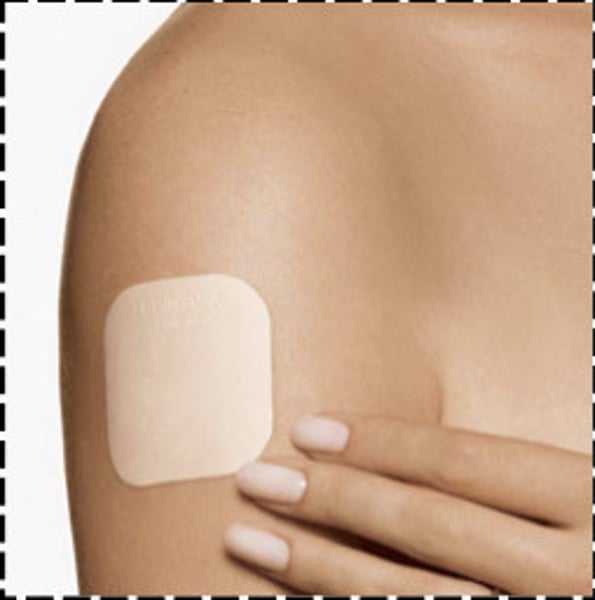
What is the contraceptive patch?
Contains same hormones as the pill. Patch is stuck under the skin (5cm x 5cm). Each patch lasts a week.
What is the contraceptive implant/injection?
Implant is inserted under the skin. Releases progesterone. Can last for 3 years. Injection lasts less time 2-3 months.
What is an intrauterine device?
Is a T shaped device that is inserted into the uterus to kill sperm and prevent implantation of the fertilised egg.
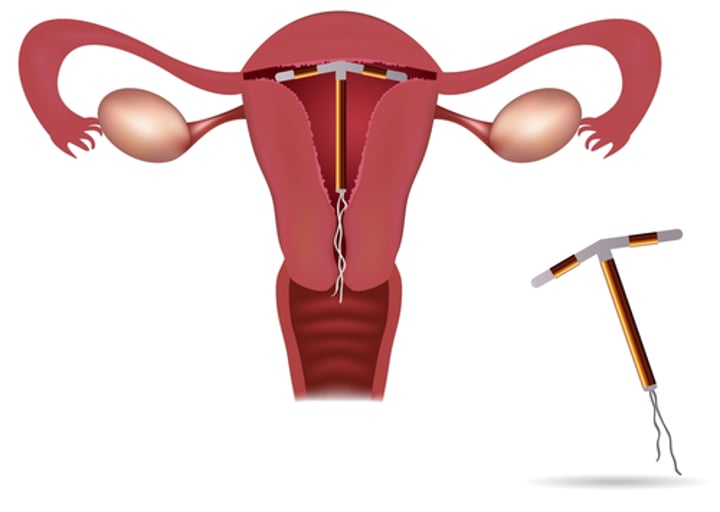
Name three barrier methods, non hormonal methods of contraception.
Male and female condom, diaphragm, spermicide
What is the diaphragm?
A plastic cup that fits over the cervix (opening to the womb) to form a barrier.
How does spermicide work?
It kills or disables the sperm.
Name a permanent ways to avoid pregnancy.
Abstinence (not having sex), sterilisation which is having Fallopian tubes or sperm duct cut.
How does IVF work to help infertile couples?
FSH and LH are given to a woman to help eggs mature and release. Eggs are then collected from a woman's ovaries. The eggs are fertilised in a lab with the man's sperm. The fertilised eggs are grown into embryos in an incubator. The 1-2 embryos are then transferred to the woman's uterus to increase chance of pregancy.
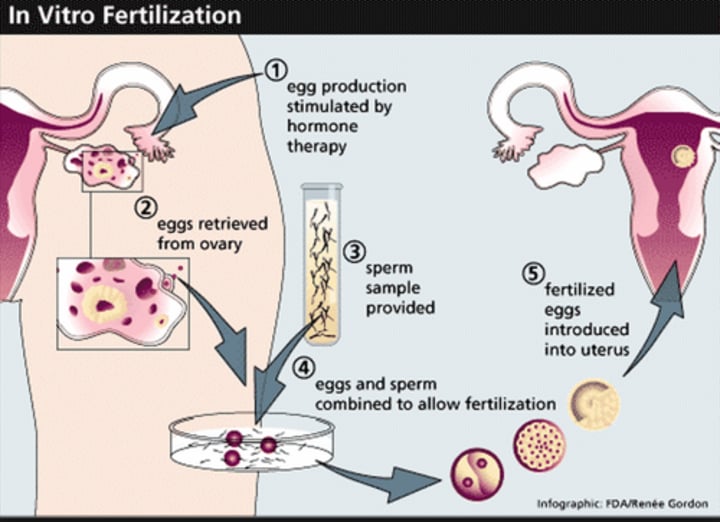
What are the pros and cons of IVF?
PRO: Gives an infertile couple a child.
CON: Multiple births, these are risky, more chance of still birth and miscarriage.
CON: Success rate is low
CON: Emotionally and physically stressful
CON: Side effects of hormones e.g. abdominal pain
What are the ethical concerns linked to IVF?
IVF leads to unused embryos which are destroyed or used for medical research. (Potential life).
Genetic testing could be carried out on the embryo which could lead to designed babies.
What is reaction time?
The time it takes to respond to a stimulus
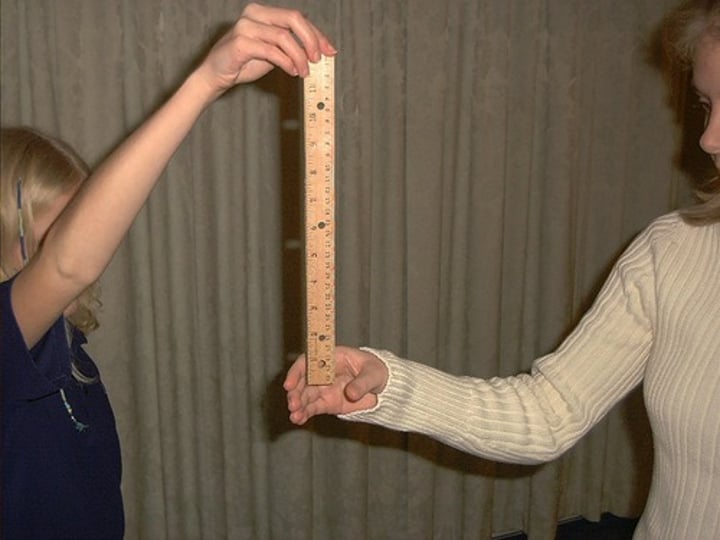

What is reaction time affected by?
Age, drugs e.g. caffeine or gender
Why are computers a better way of measuring reaction time than the ruler test?
Computers can give a more precise reaction time because they remove human error.
Computers can record the reaction time to a millisecond so more accurate.
Computers remove the possibility that a person can predict when to respond by using a persons body language.