Research Methods 2 Midterm
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
variance
much each score in a given set of responses varies on average from the mean
standard variance
the square root of variance; a measure of how spread out the data is in relation to the mean
Steps to find variance
Step 1: calculate mean
Step 2: subtract mean from each score deviation Step 3: square each deviation score
Step 4: add the squared deviation scores
Step 5: divide by degrees pf freedom: N – 1
total variance = _______+__________
systematic + error
types of error variance
Phenomena are multiply determined, Individual differences, Transient states, Environmental factors, Differential treatment, Measurement error
a good experiment (that can predict causality) can:
Vary (manipulate) at least one independent variable (IV)
Control extraneous variables (eliminate confounds!)
Have the power to assign participants to conditions
Systematic variance
portion of total variance that reflects differences among the experimental groups
Treatment variance
portion of systematic variance due to the IV
Confound variance
portion of systematic variance due to error variance that differs systematically between conditions
types of experiment manipulation
Environmental manipulations, Instructional manipulations, Invasive manipulations, Real world interventions
Environmental manipulations
Vary participants’ physical or social environment
Instructional manipulations
Vary participants’ verbal instructions
Invasive manipulations
Create physical changes through surgery or drugs
Real world interventions
Programs, policy changes, practice changes
Control condition
Participants receive zero level of IV
Experimental condition
Participants receive a nonzero level of the IV
Between subjects (between-groups) design
Each participant participates in only one condition in the experiment
Within subjects (repeated measures) design
Each participant participates in every condition in the experiment
Random assignment is essential to experiments because…?
Biased assignment to conditions
Miscellaneous design confounds
Problems with the design, History effects, Pre-test sensitization, Differential attrition, Maturation
order effects
Effects of an experimental condition are contaminated by the order they occurred in
ex: Practice effects, Fatigue effects, Sensitization effects, Carry-over effects
Can fix this through conterbalancing
counterbalancing
presenting the conditions in different orders to different participants
researcher’s dilemma
as internal validity increases, external validity decreases
Inferential statistics
Can estimate how much the means would differ just by chance if the IV has no effect
statistically significant
it exceeds our estimate of how much the means would differ due to chance
t-test
used to test difference in means between 2 conditions
ANOVA
variance of analysis; used to test differences in means across multiple conditions
If T ______ critical value (p < .001) Its unlikely to be due to chance. This means that we ____ the null hypothesis
exceeds; reject
Problem Definition
What is psychology’s central bias when it comes to researching social problems? What is the researcher’s approach?
Person-centered problem definition
focuses on the individual rather than the whole problem; can often person-blame
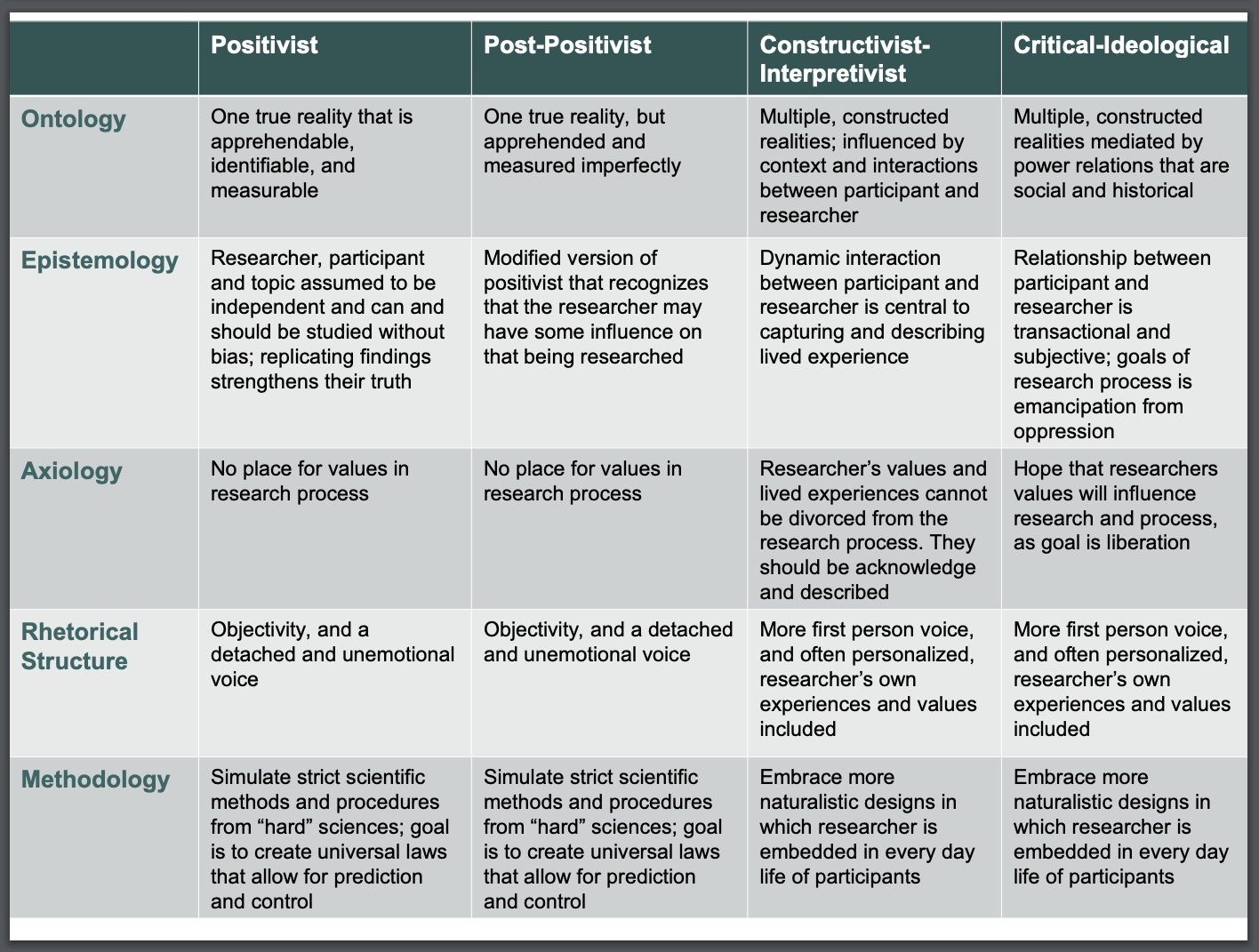
Philosophy of science
the conceptual roots or fundamental beliefs of a researcher on how to properly answer their research question
ontology
Concerns the nature of reality and being; What is the form and nature of reality and what can be known about that reality
epistemology
Concerned with the relationship between the “knower” (participant) and “would be knower” (researcher)'; Are the participant and researcher and topic independent of each other? and Can the participant and topic be studied without bias?
axiology
Concerns the role of researcher values in the scientific process; Is there a place for values in research?
rhetorical structure
Concerns the role of researcher values in the scientific process; Is there a place for values in research?
Methodology
Refers to the processes and procedures of research; What kinds of designs are preferred? Ones that resemble the “hard” sciences or more naturalistic ones?
philosophy of science
Quantitative approaches to operationalization
Observational approaches, Archival data Physiological / neuroscientific approaches, Standardized assessments, and Self-report questions and scales
validity
is this measure an accurate representation of our construct? Is it measuring what we think it is?
reliability
How consistently does it represent our results over time?
multiple item scale
Consists of a set of items all thought to measure the underlying dimension in slightly different ways; average or sum across multiple items better captures the full dimensionality of the construct
Inter-item reliability
the degree of consistency among items thought to make up a scale; Commonly assessed by Cronbach’s alpha (α)
factor analysis
Statistical method that looks at the correlations among a set of items and determines how many constructs could most simply account for the patterns seen
Exploratory factor analysis
when you don’t have any expectations about how many factors there are or what items might represent which factor
Confirmatory factor analysis
when you expect from theory or research that items will represent constructs in a specific way
Orthogonal rotation
used in factor analysis when factors are uncorrelated
Oblique rotation
used in factor analysis when factors are correlated
higher eigenvalues correspond to _____ variance explained by each factor. A “good” eigenvalue should be ___ or higher
more; 1.0
In a factor analysis you should keep items above the ______ on a scree plot
elbow
Factor structure matrix
an output used to interpret the nature of underlying factors in a factor analysis
Factor loadings
the correlations between each item and the factor on a factor structure matrix
For a “high loading” item, it should be at/above _____ to keep the item on the construct.
0.4
One-way design
Only one IV (factor) is manipulated and there are 2 + levels
ANOVA
Test whether means from 3 or more conditions are statistically different from each other
One-way ANOVA
Use for 1 IV with 3+ conditions
Two-way ANOVA
has 2 IVs, each with 2+ conditions
To use an ANOVA, you must….
the DV must be continuous (interval or ratio) and normally distributed
If, and only if, the F-test is significant, then you determine which means are different from each other with ____________
post-hoc comparisons
F-test
finds whether the means from more than 2 conditions (groups) are significantly different, using a single test; divides the average variance between groups by the average variance within groups
Factorial Experimental Design
More than one (IV) (factor) is manipulated and each IV can have 2 or more levels (e.g. conditions)
interaction effects
the effect of one IV differs across the levels of other IVs
Randomized groups factorial design
Participants are randomly assigned to each of the possible combinations of the factors
Within subjects (repeated measures) factorial design
Each participant participates in every condition
Mixed factorial design
One factor is between groups randomly assigned, and the other factor is within-subjects
Independent variable
the variable(s) manipulated in a study
Subject variable
a personal characteristic of participants
There is no interaction in a design if the lines on a graph are ______
parallel
There is no interaction in a design if the bars on a graph __________
show the same pattern in each condition
Factorial nomenclature examples
•A “2 x 2 factorial” (read “2-by-2”) is a design with two independent variables (factors), eachwith two levels
A “3 x 3 factorial” has two independent variables, and each IV has three levels
A “2 x 2 x 4 factorial” has three independent variables, the first and second IVs have two levels, the third IV has four levels
Number of numbers = number of factors Value of each number = number of levels in each factor
Analyzing factorial design
In a factorial ANOVA, the average variance between groups (SSbg) is broken into components representing the main effects and interactions
Each main effect and interaction are compared to the same estimate of error, MSwg
Each main effect and interaction gets its own F-ratio
Median-split procedure
divide participants into groups based on 50th percentile (to create high vs. low motivation groups)
Extreme groups procedure
pretest a large number of potential participants and then select those with extreme scores (top and bottom 25%) for the study
quasi-experimental design
a study which it’s goal is also to see if one variable is causing change in another, but can not be as sure about the cause-and-effect relationship
Weaknesses in quasi-experimental designs
Less or no control over the independent variable
No control over participant assignment to conditions (no random assignment)
More difficult to eliminate confounds
Reasons to use quasi-experimental design
Answer real-world questions
Policy and legislation
External validity of a laboratory finding
Intervention in a natural setting was effective
When random assignment not practical or ethical
More cost-efficient
one group pretest-posttest design
Tests a group before and after an intervention
Because there are so many threats to validity, it is often rejected as a quasiexperimental design and considered a “preexperimental” or correlational design
Nonequivalent control group designs
Researcher includes one or more groups of participants who are similar to the group that receives the intervention, but do not get it
Nonequivalent control group posttest only
a nonequivalent control groups design that only records results after an intervention
can have selection bias and Local history effect
Nonequivalent control group pretestposttest
a nonequivalent control groups design that records results before and after an intervention
Can have local history effect