Meiosis, Oogenesis, Spermatogenesis (Practical 4)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
meiosis
a specialized type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, producing gametes (sperm and egg cells)
two cell divisions (Meiosis I and II), reducing chromosome number and amount of DNA by half during Meiosis I. Meiosis II is similar to mitosis I
what is the process of meiosis?
DNA replicated (in interphase)
what happens prior to Meiosis I?
1. prophase I
2. metaphase I
3. anaphase I
4. telophase I
5. cytokinesis
what are the 5 steps in meiosis I?
reduces the chromosome number from 46 (diploid or 2n) to 23 (haploid or n) in human gametogenic cells (those destined to become viable germ cells - sperm and eggs
what does Meiosis I do?
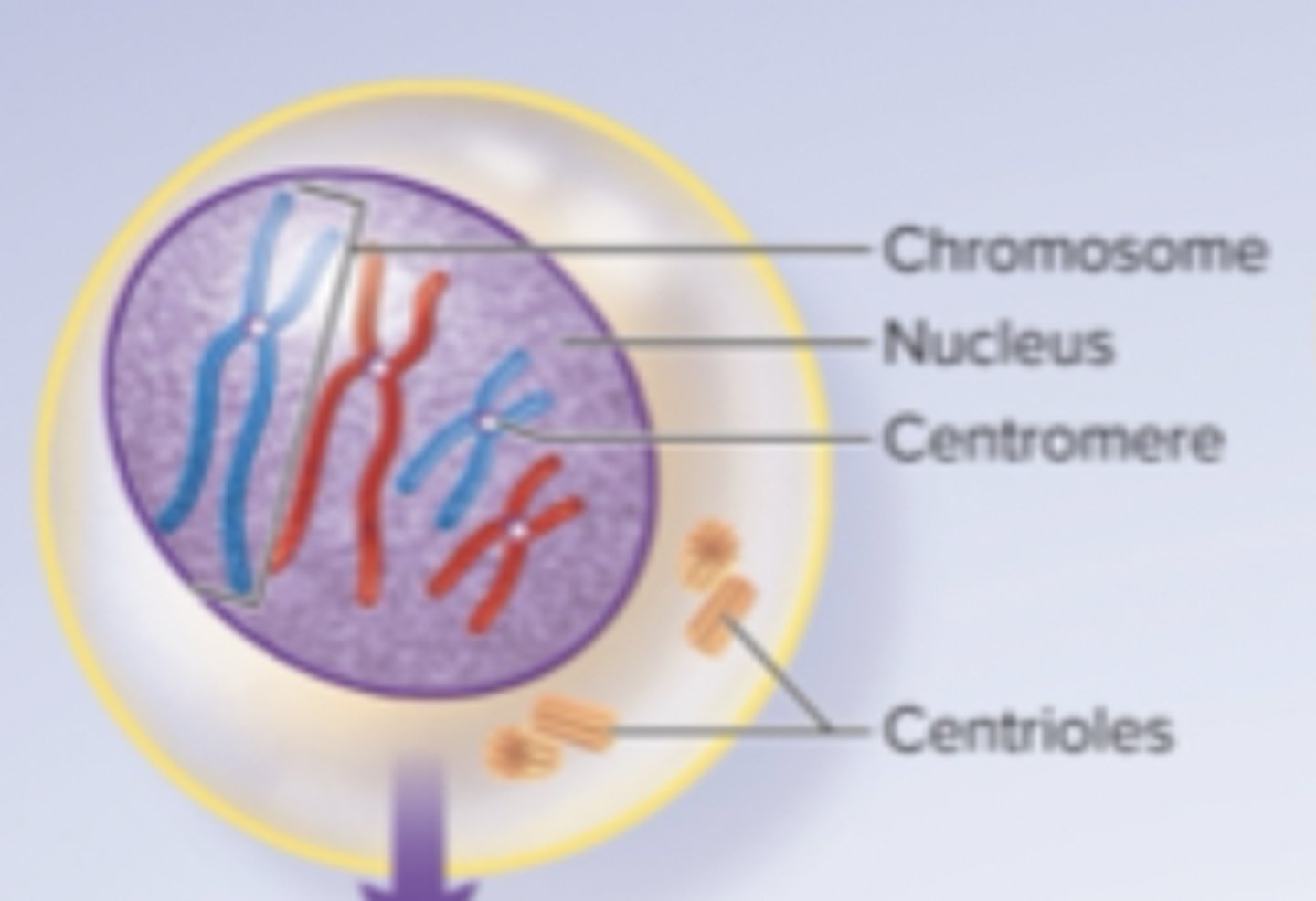
early prophase I
chromatin condenses to form visible chromosomes
-each chromosome has two chromatids joined by a centromere
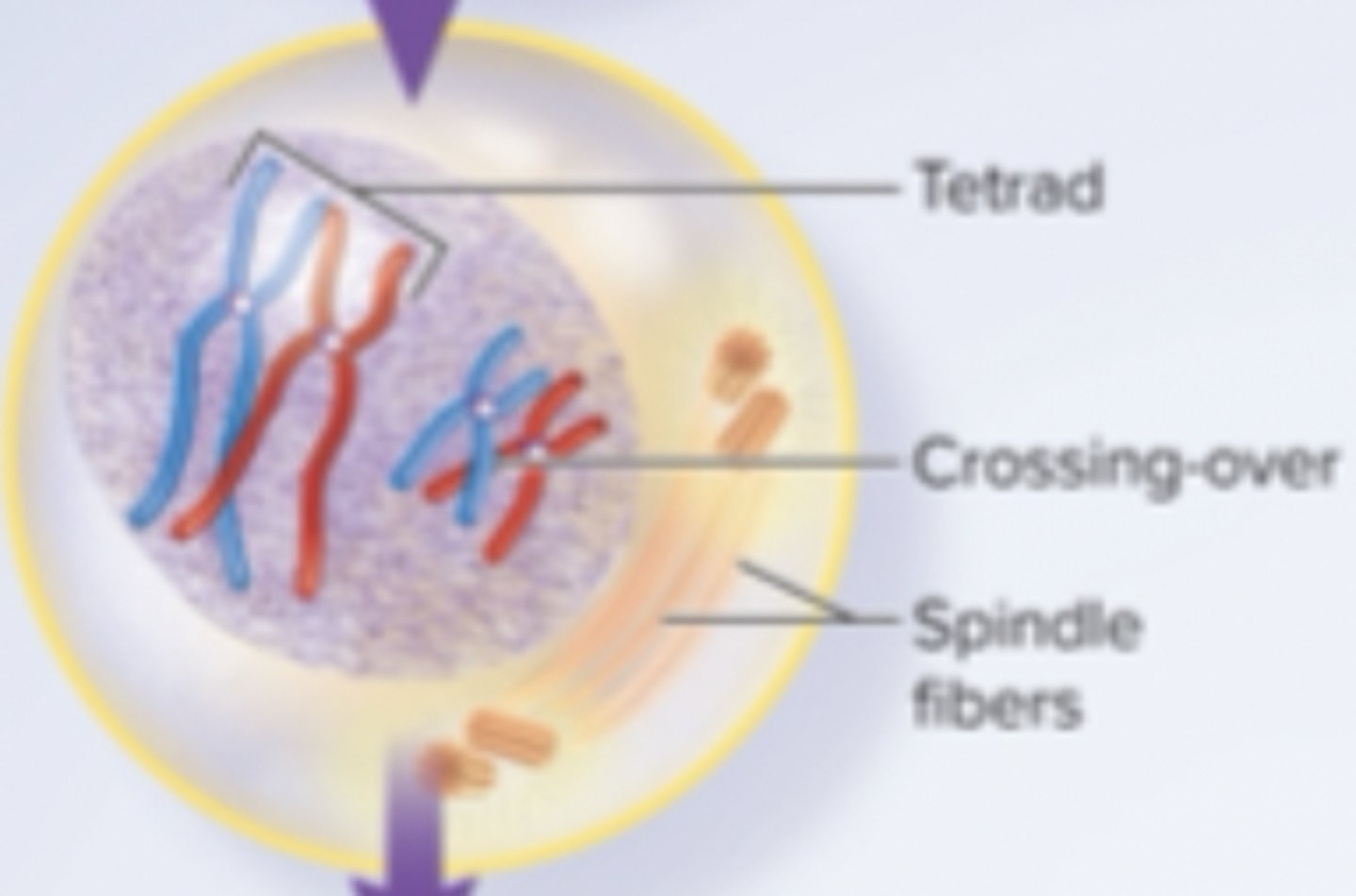
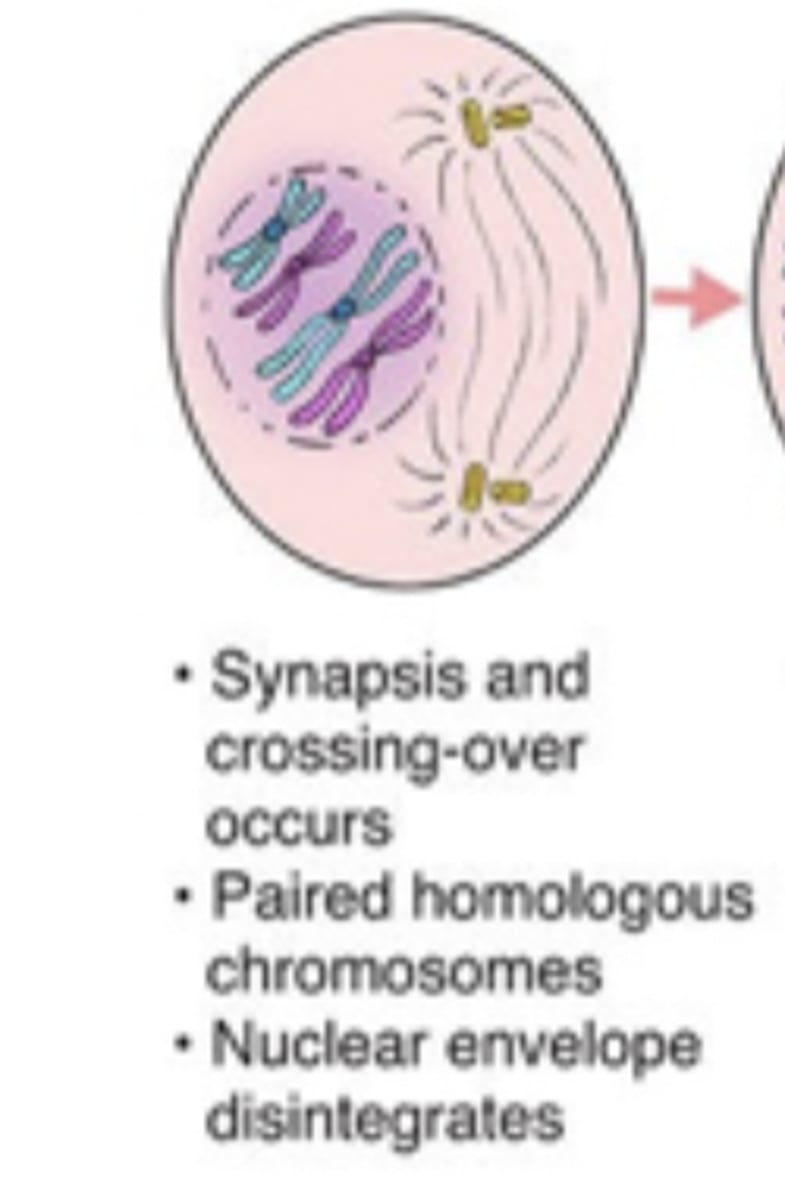
mid-to late prophase I
-homologous chromosomes form pairs called tetrads
-chromatids often break and exchange segments (crossing-over)
-centrioles produce spindle fibers
-nuclear envelope disintigrates
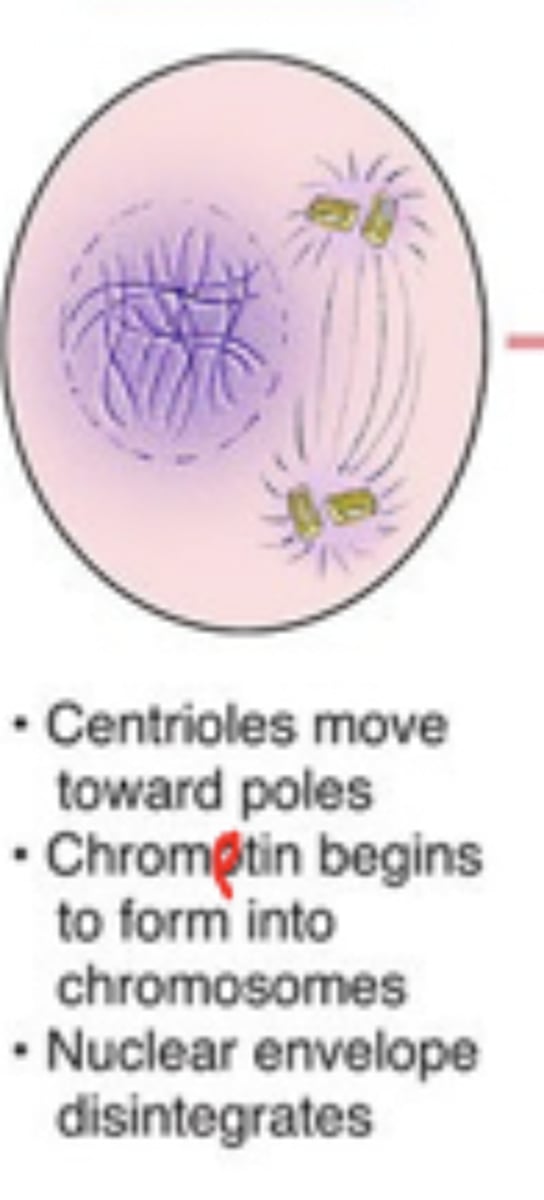
prophase 1
chromatin condenses, nuclear envelope disappears, homologous chromosomes synapse and crossing over between homologous chromosomes occurs
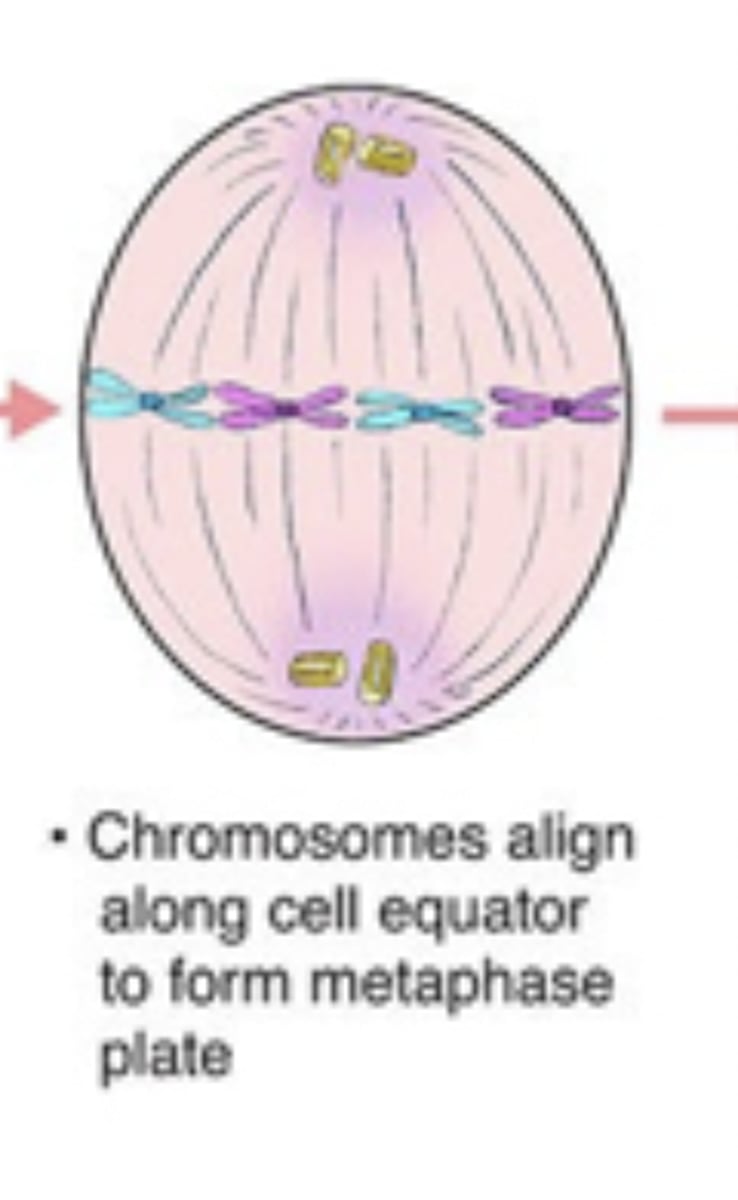
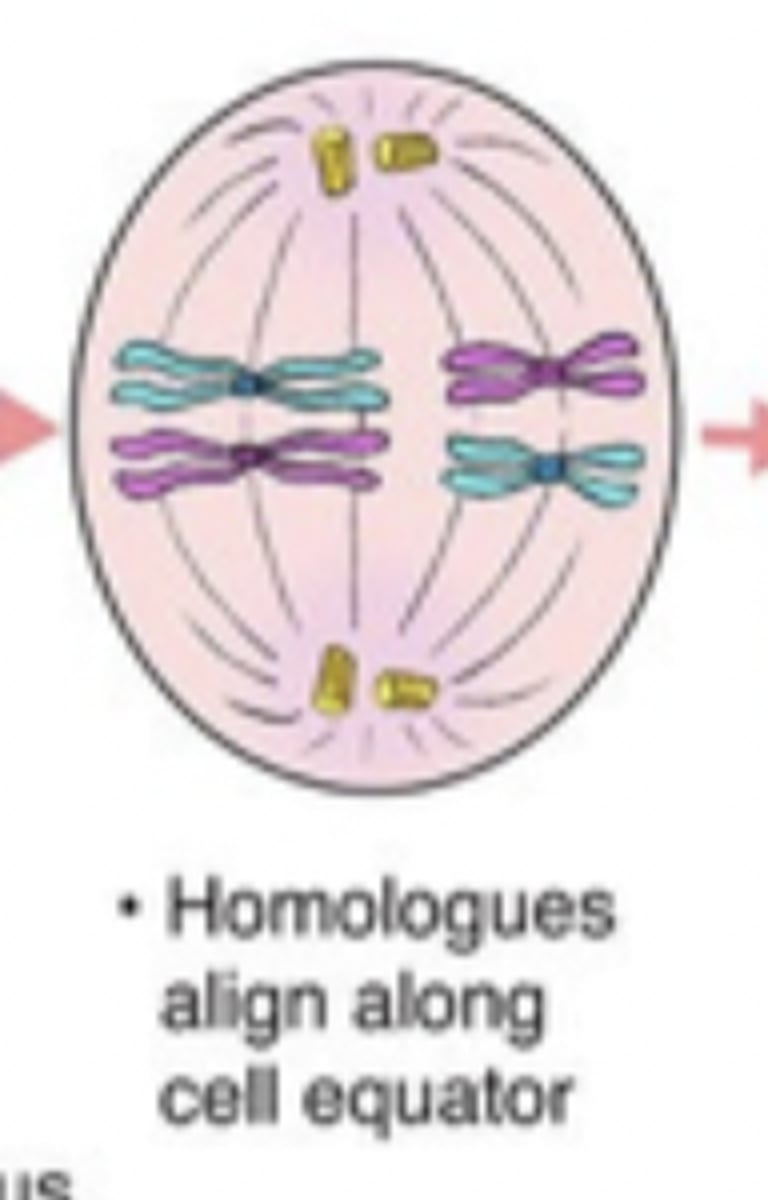
metaphase I
homologous chromosomes align at metaphase plate
anaphase I
homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles
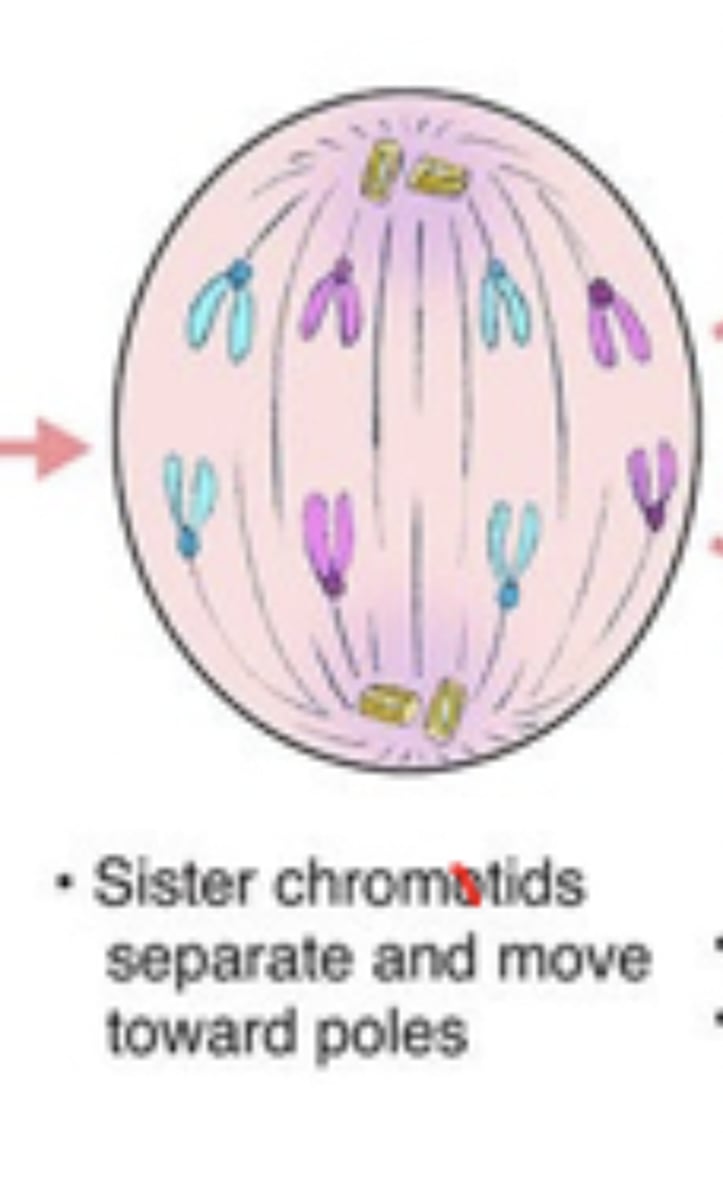
telophase I
chromosomes uncoil, nuclear envelope reforms
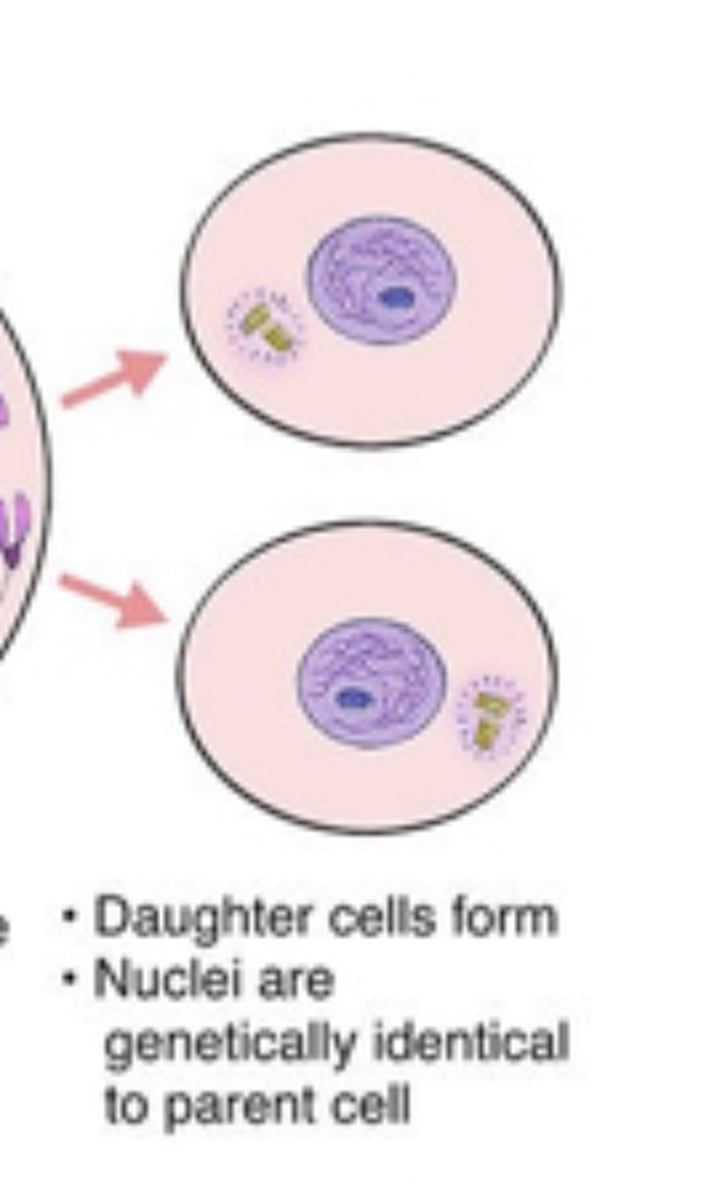
cytokinesis
cytoplasmic division produces two haploid daughter cells
1. prophase II
2. metaphase II
3. anaphase II
4. telophase II
what are the 4 stages of meiosis II?
prophase II
The duplicated chromosomes and spindle fibers reappear in each new cell
metaphase II
Chromosomes line up at the equator
anaphase II
sister chromatids of duplicated chromosomes separate
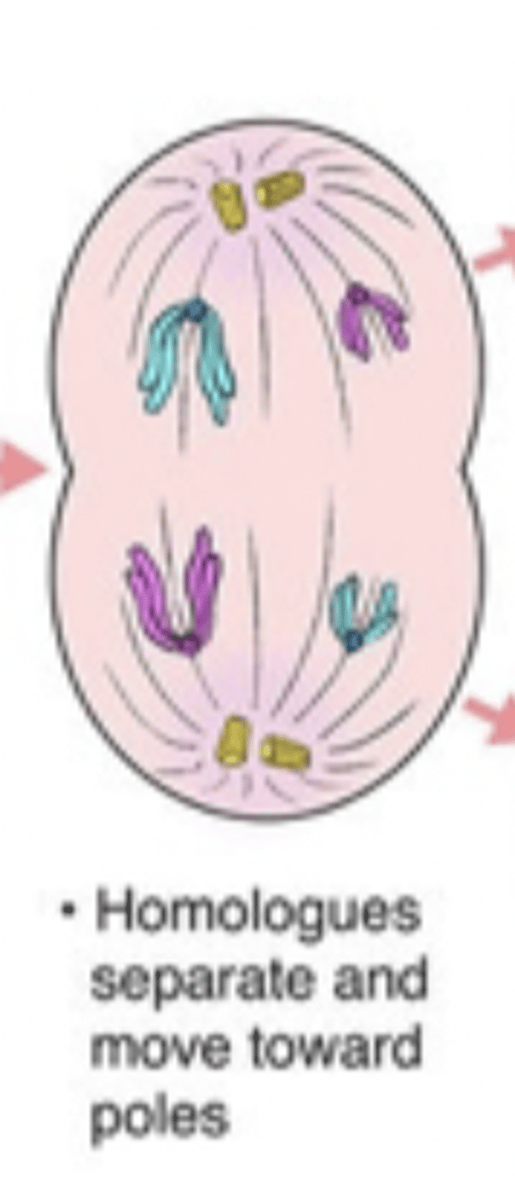
telophase II
nuclei have half the amount of DNA the parent cell had
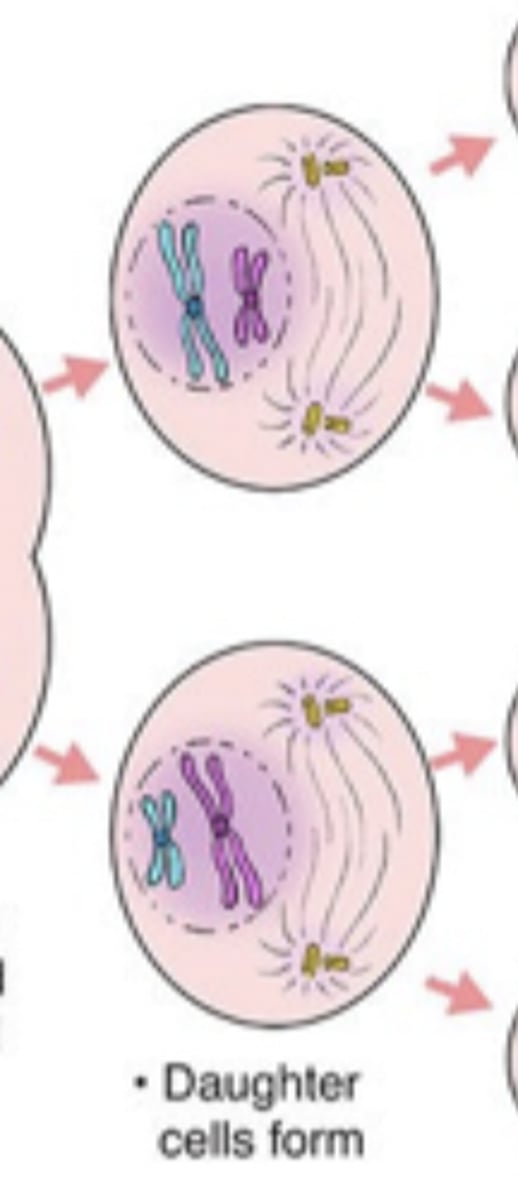
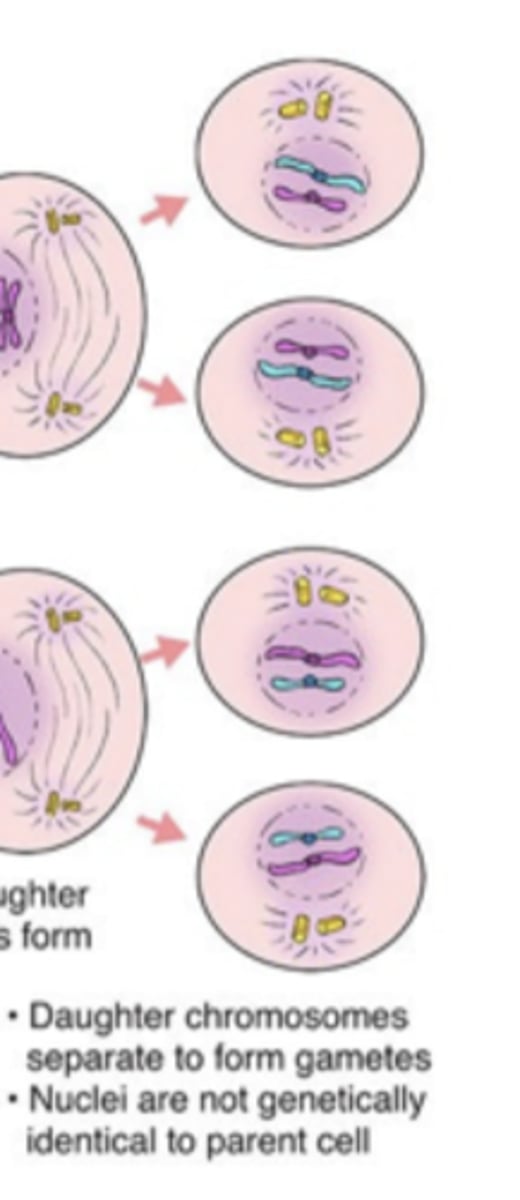
meiosis II
-phases look the same as mitosis, but with half the number of chromosomes
-since each daughter cell from meiosis I undergoes meiosis II, a total of 4 daughter cells are produced
2 haploid daughter cells
what is the end result of meiosis 1?
secondary oocyte
what is the end result of meiosis 1 for oogenesis?
secondary spermatocyte
what is the end result of meiosis 1 for spermatocytes?
23 chromosomes
how many chromosomes does each secondary spermatocyte and oocyte have after meiosis 1?
4 haploid daughter cells
what is the end result of meiosis 2?
spermatids with 23 chromosomes
what is the end result for meiosis 2 for spermatocytes?
fertilized zygote (diploid)
what is the end result for meiosis 2 for oogenesis?
spermatogenesis
occurs within seminiferous tubules of testes
1. spermatogenia
2. meiosis I
3. meiosis II
4. spermatids
spermatogenic cells give rise to sperm in what 4 series of events?
spermatogonia
(diploid, 2n = 46 chromosomes) divide by mitosis to become primary spermatocytes
meiosis I
primary spermatocyte (diploid, 2n = 46 chromosomes) undergo meiosis I to become a secondary spermatocyte (haploid, n = 23 chromosomes)
meiosis II
secondary spermatocytes become spermatids (both secondary spermatocytes and spermatids are haploid, n = 23 chromosomes)
spermatids
undergo spermiogenesis to form mature sperm (spermatozoa)
1. spermatogonia
2. primary spermatocytes
3. secondary spermocytes
4. spermatids
5. mature sperm cells
what are the 5 stages of spermatogenesis?
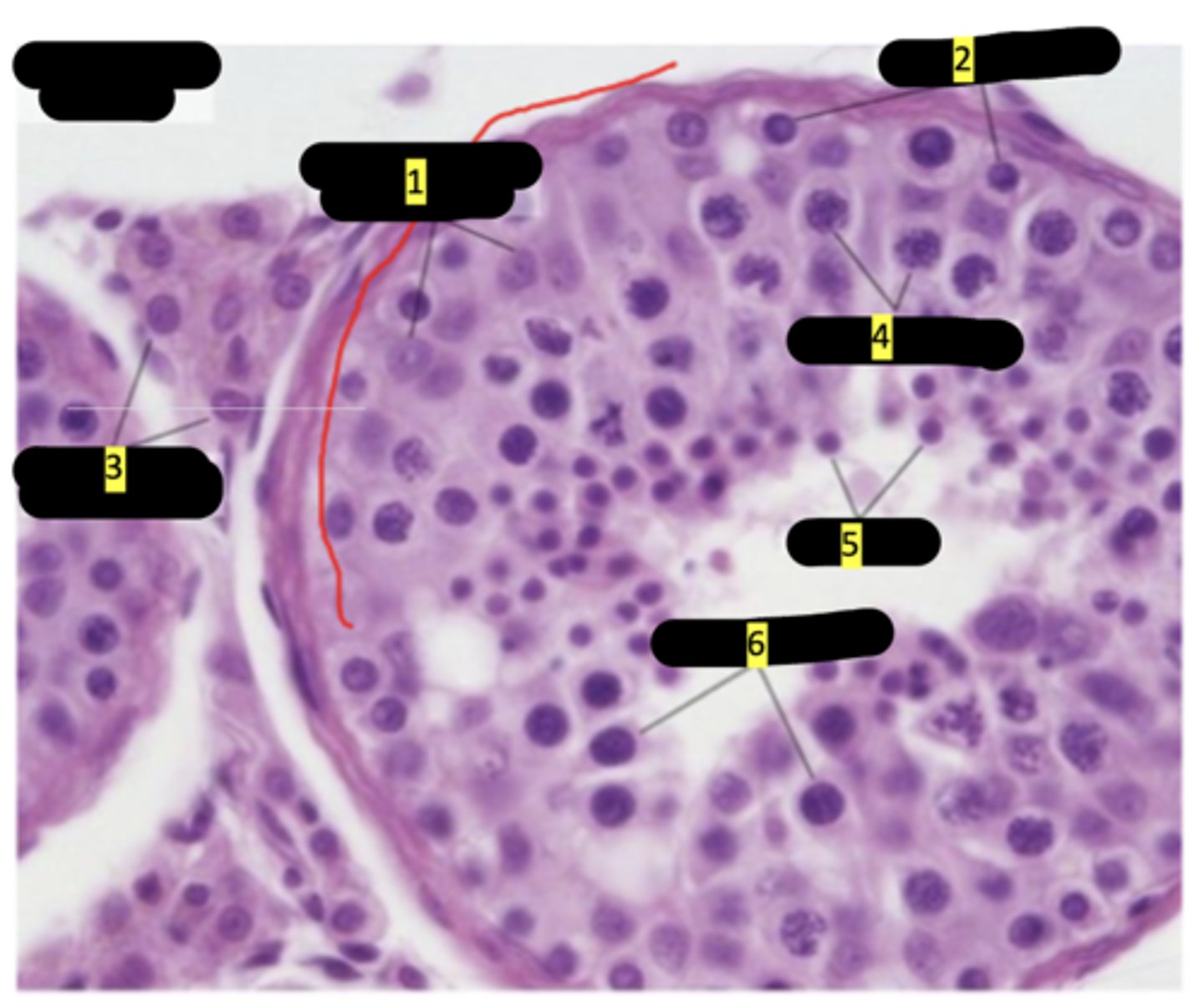
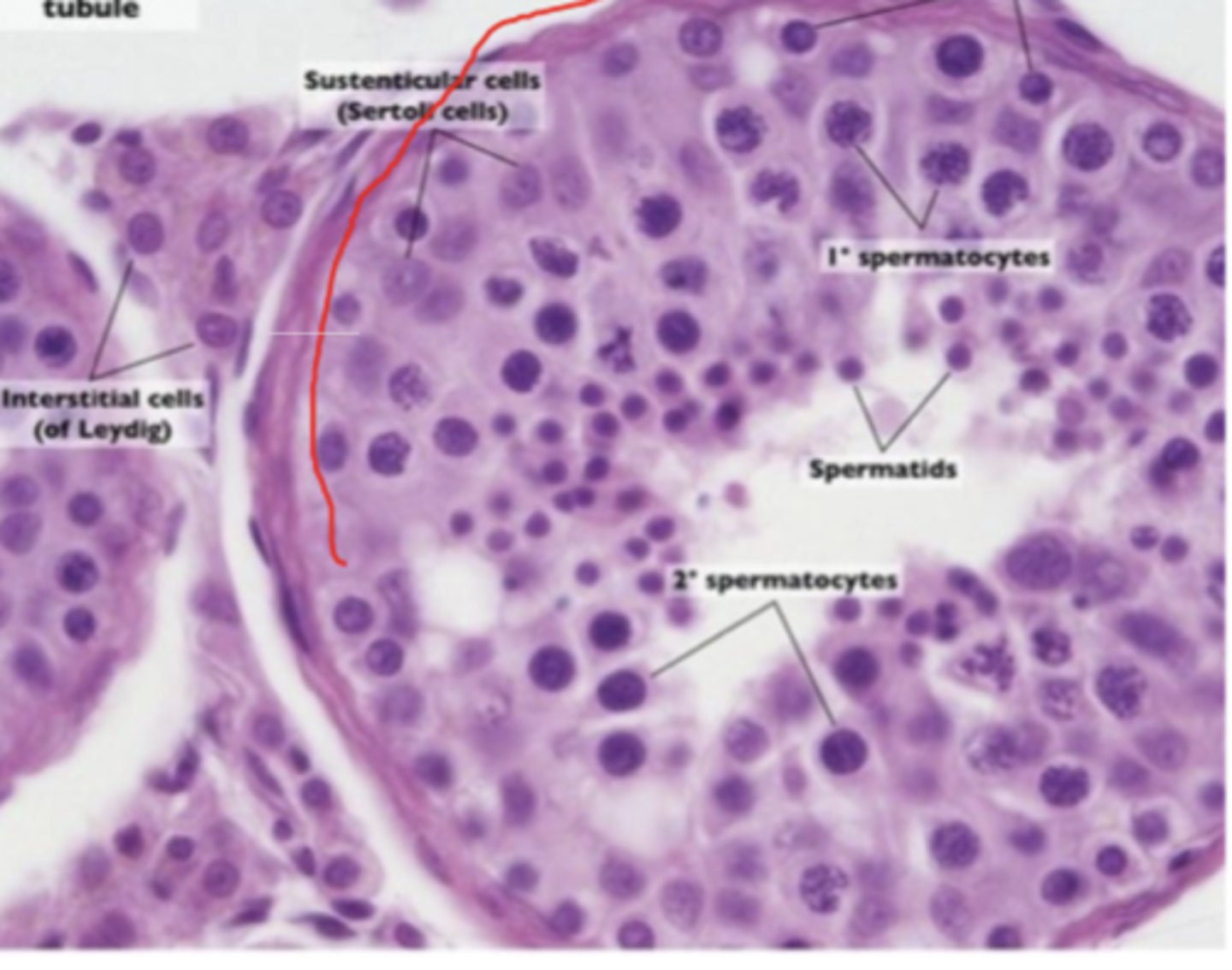
seminiferous tubule of testes
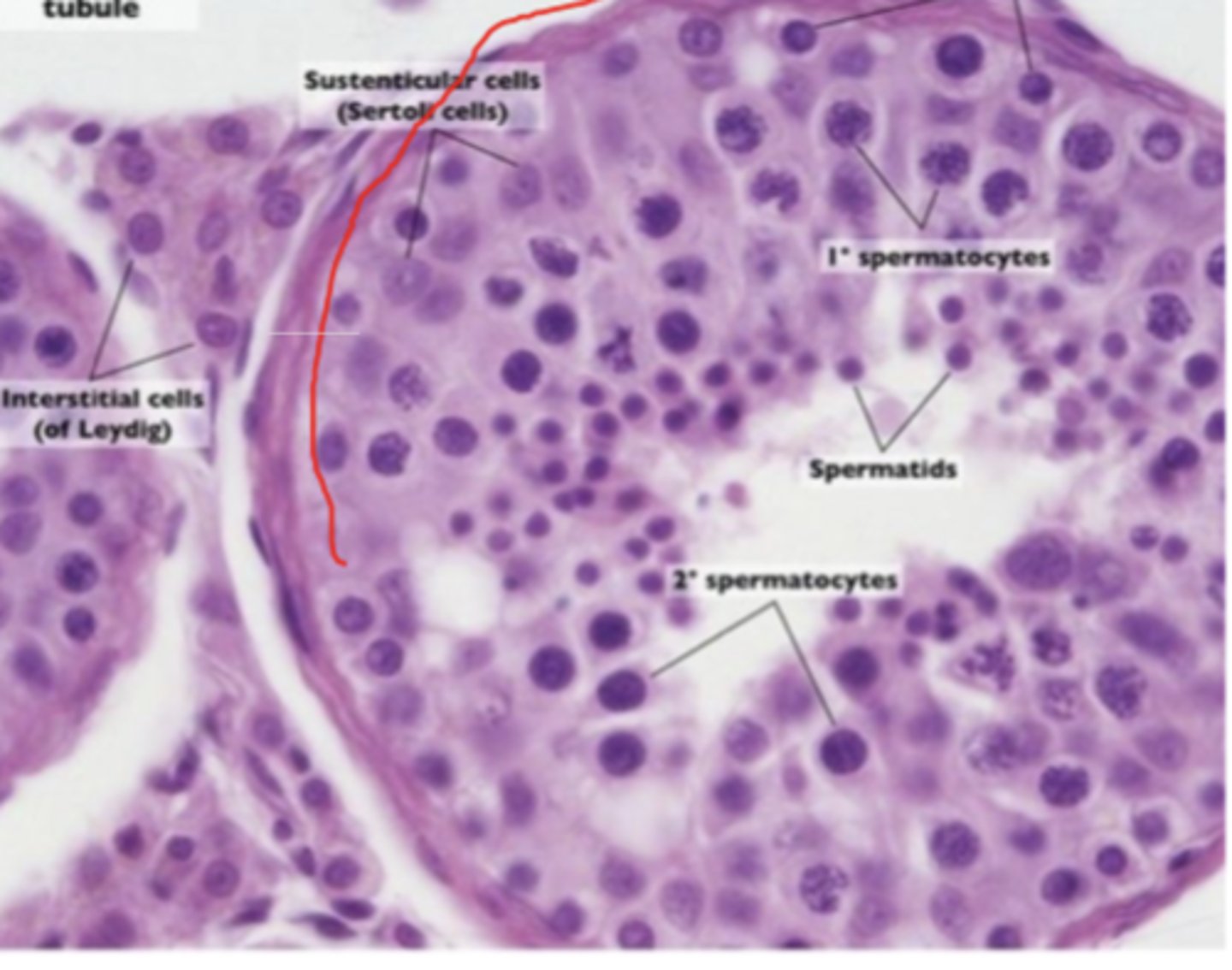
Sustenticular cells (sertoli cells)
#1
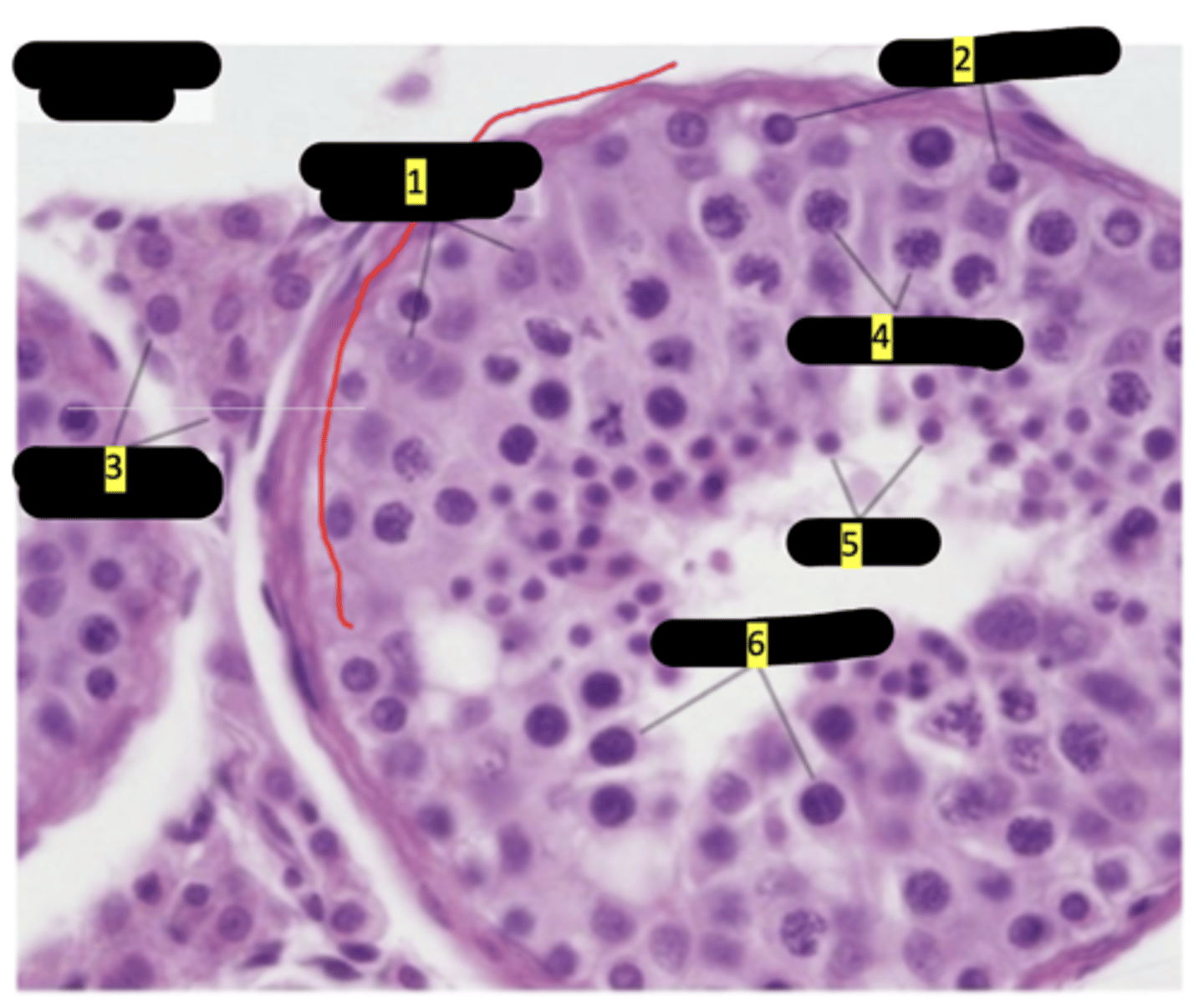
spermatogenesis
#2
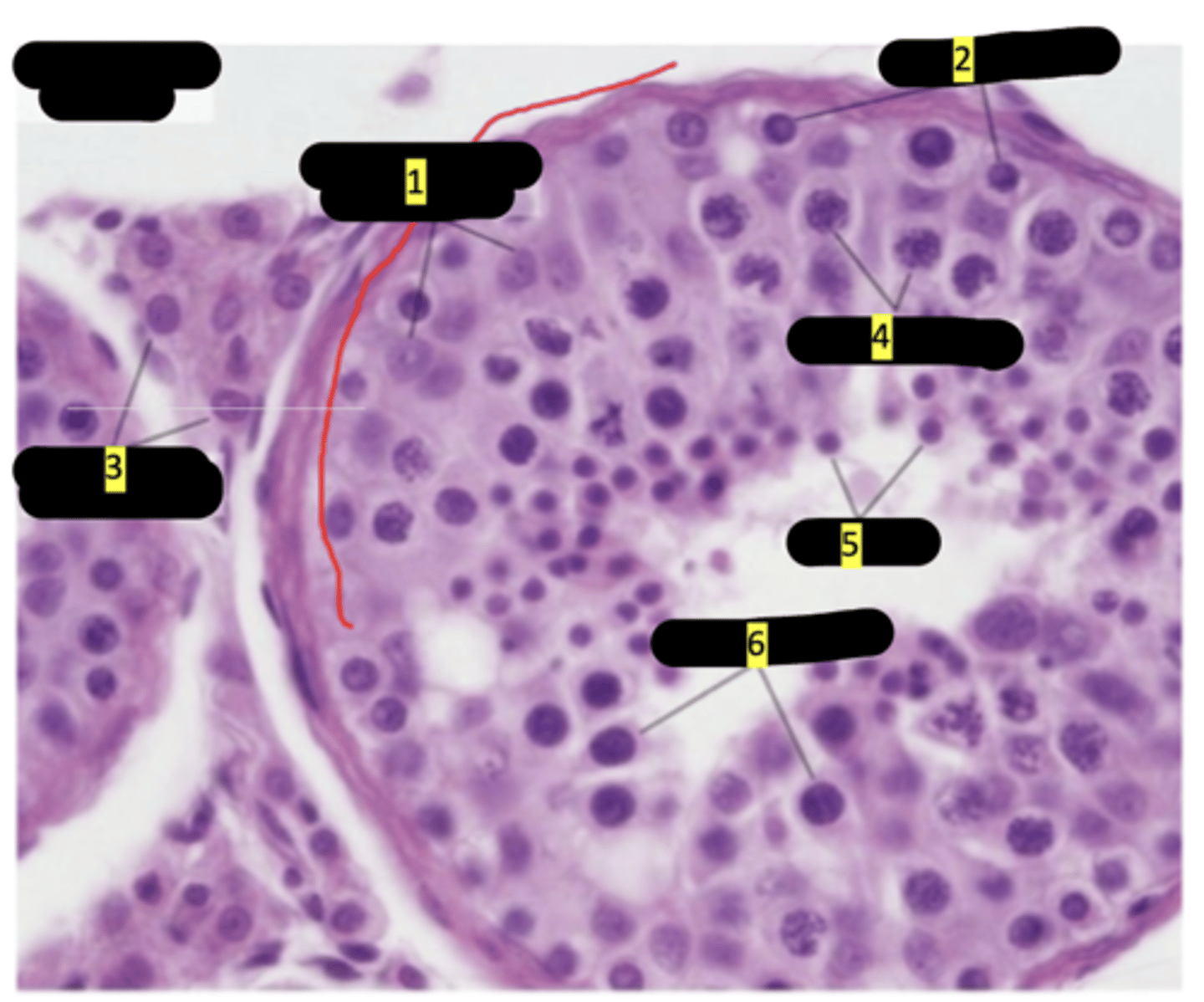
interstitial cells (of leydig)
#3
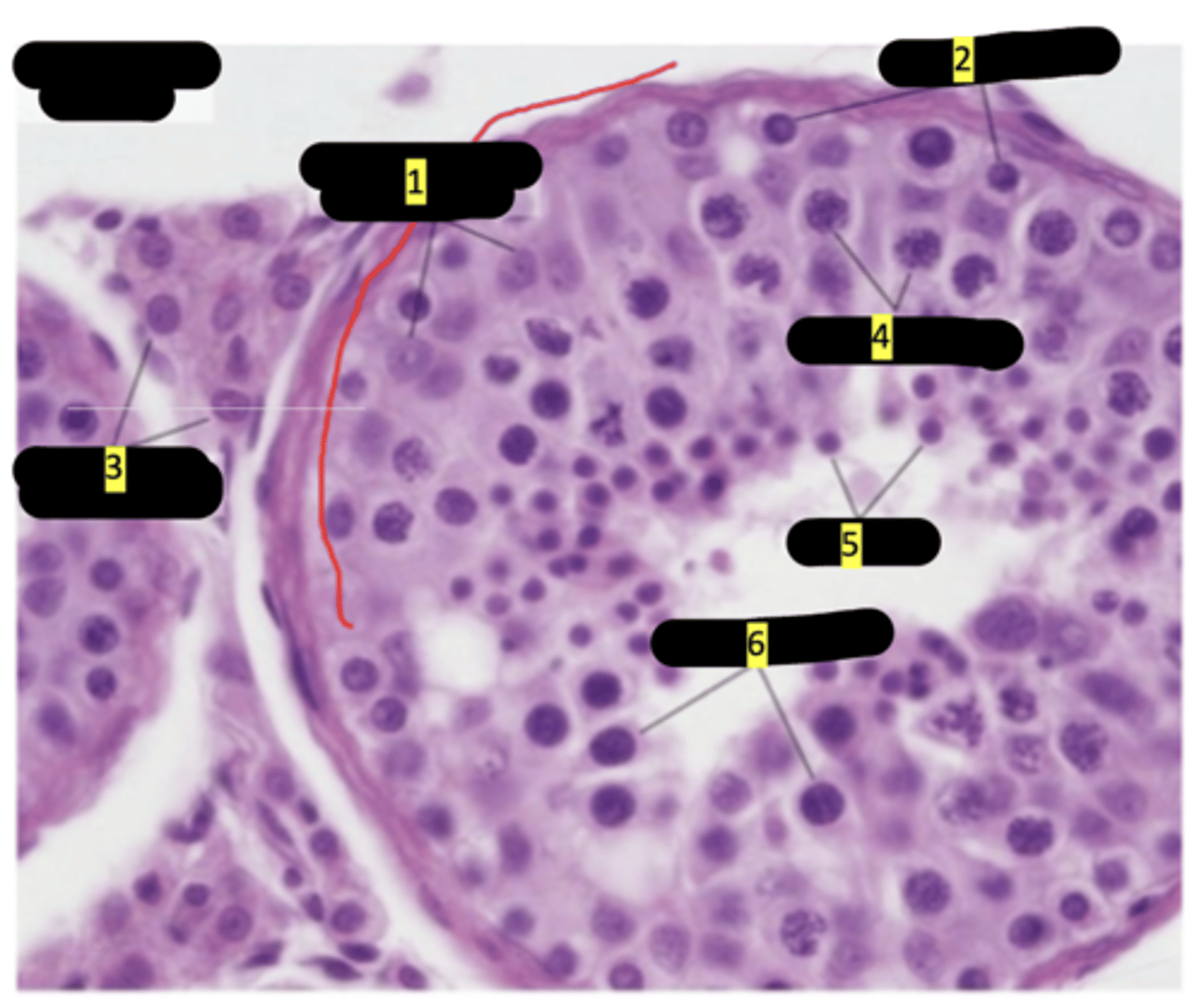
primary spermatocytes
#4
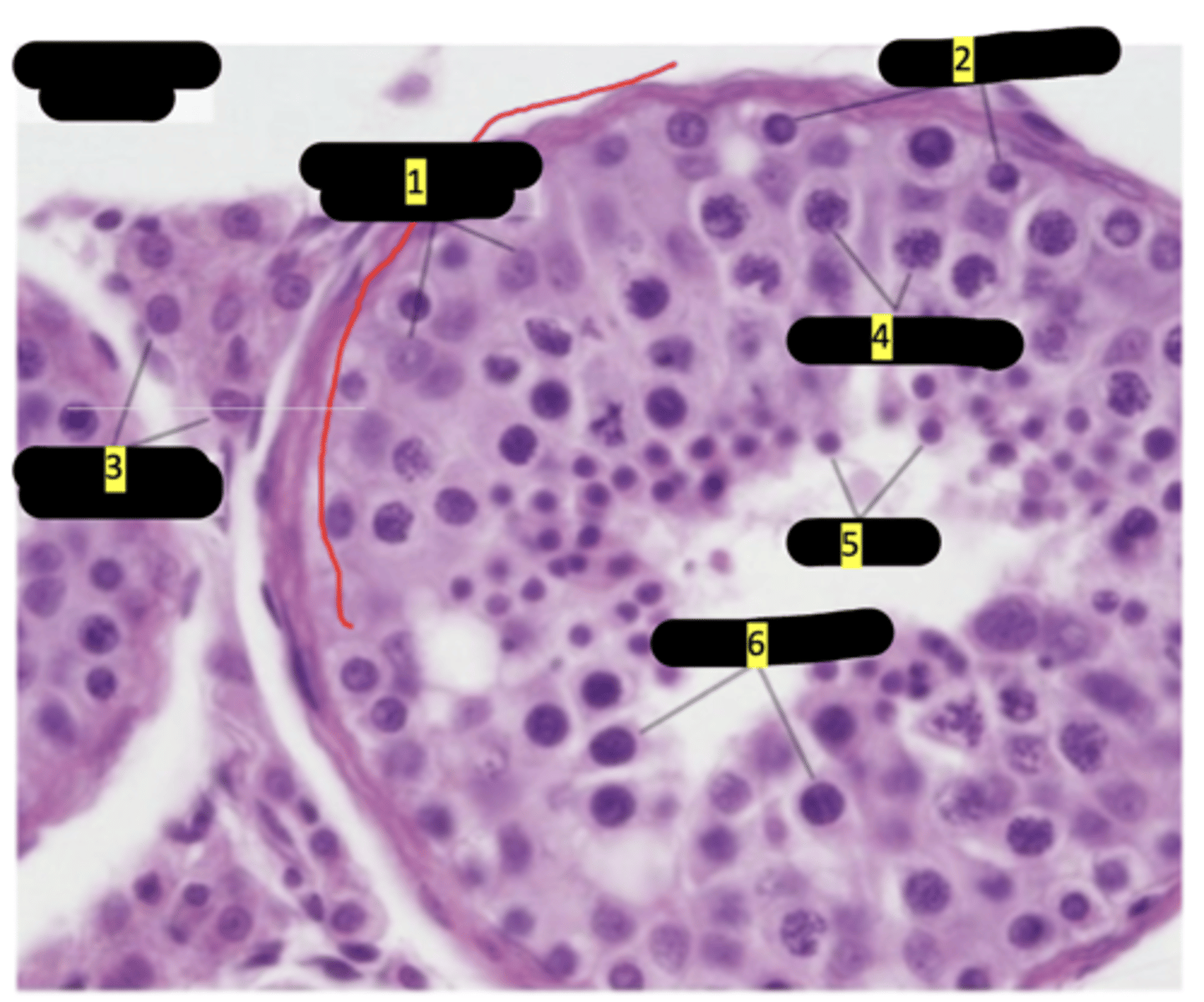
spermatids
#5
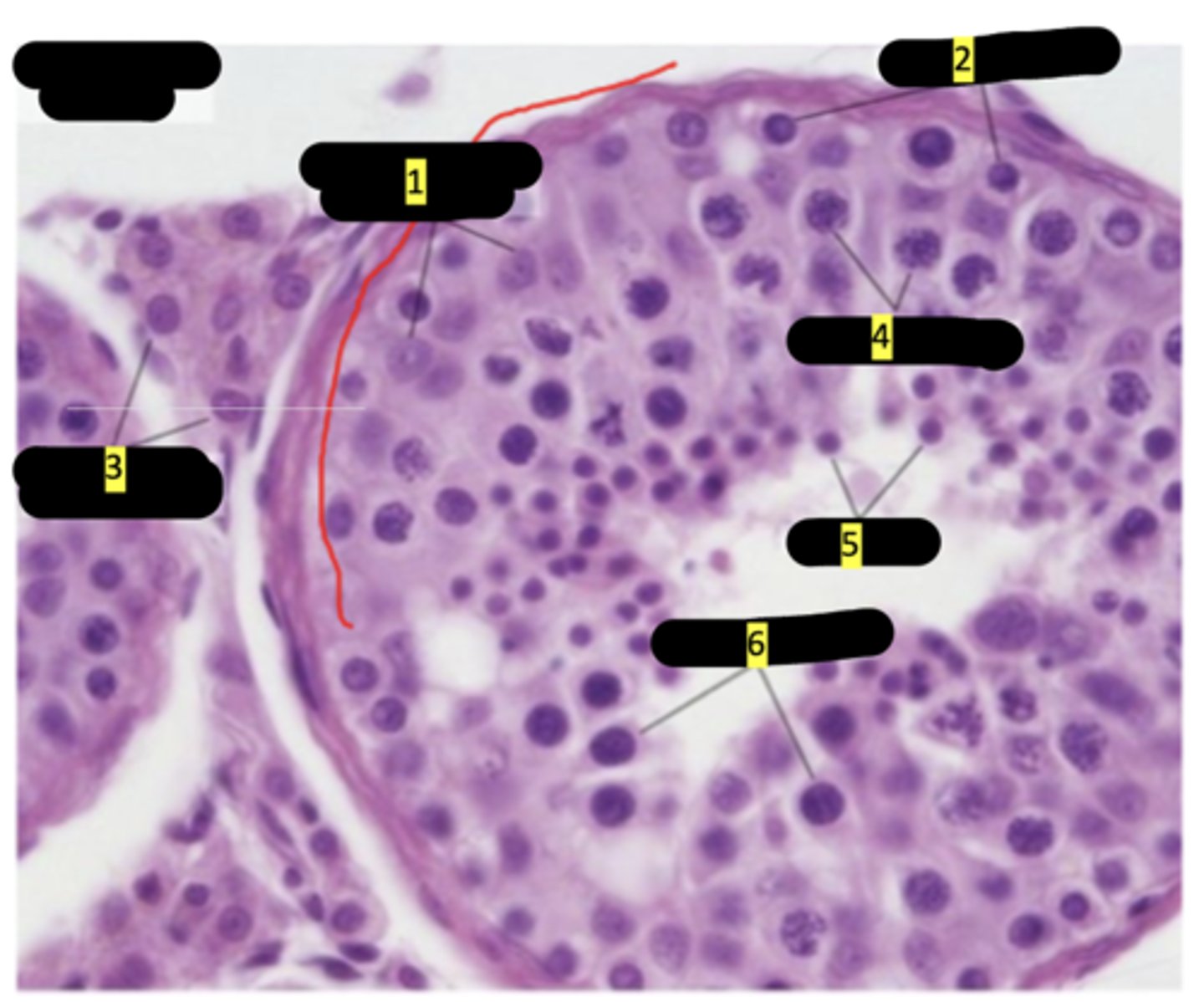
secondary spermatocytes
#6
seminiferous tubule showing stages of spermatogenesis
primary spermatocytes
#1
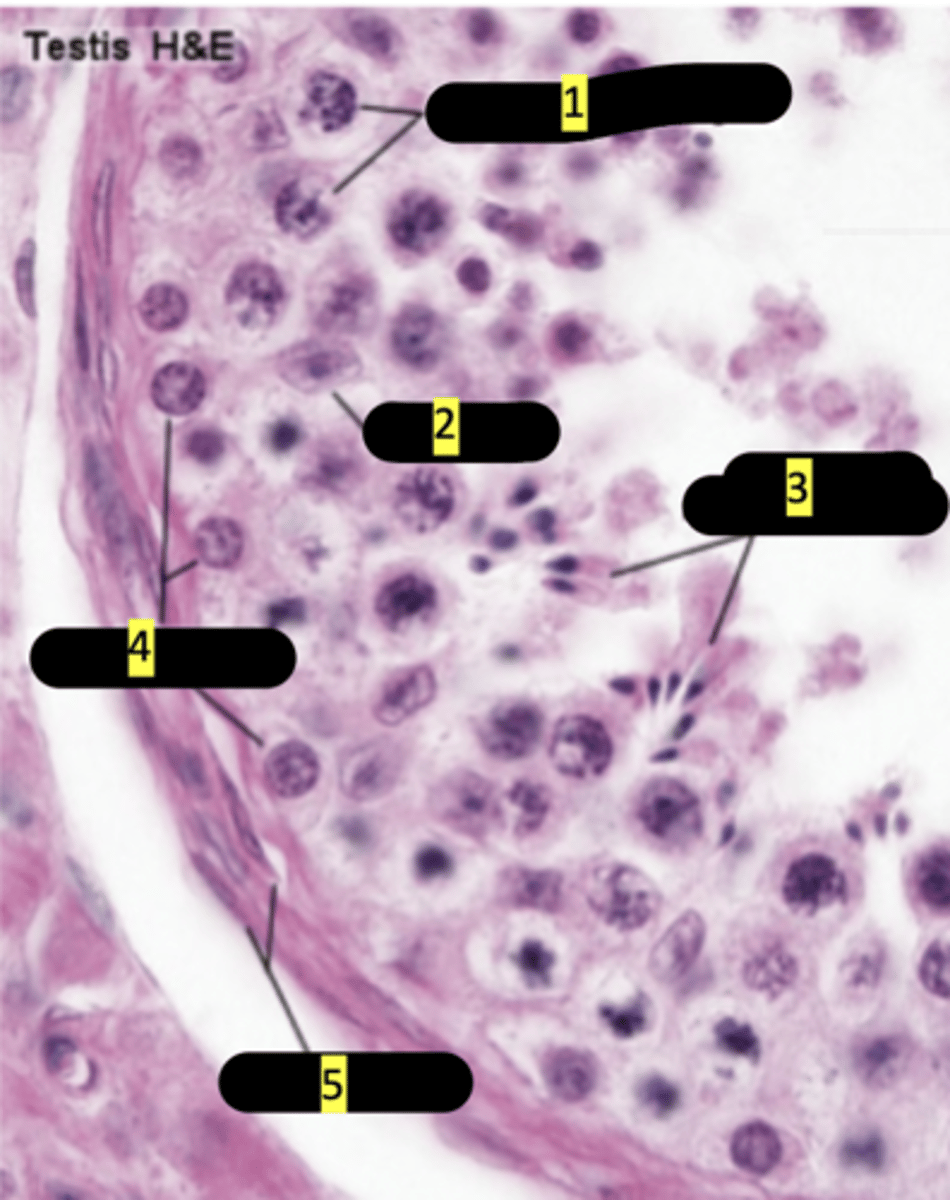
sertoli cells
#2
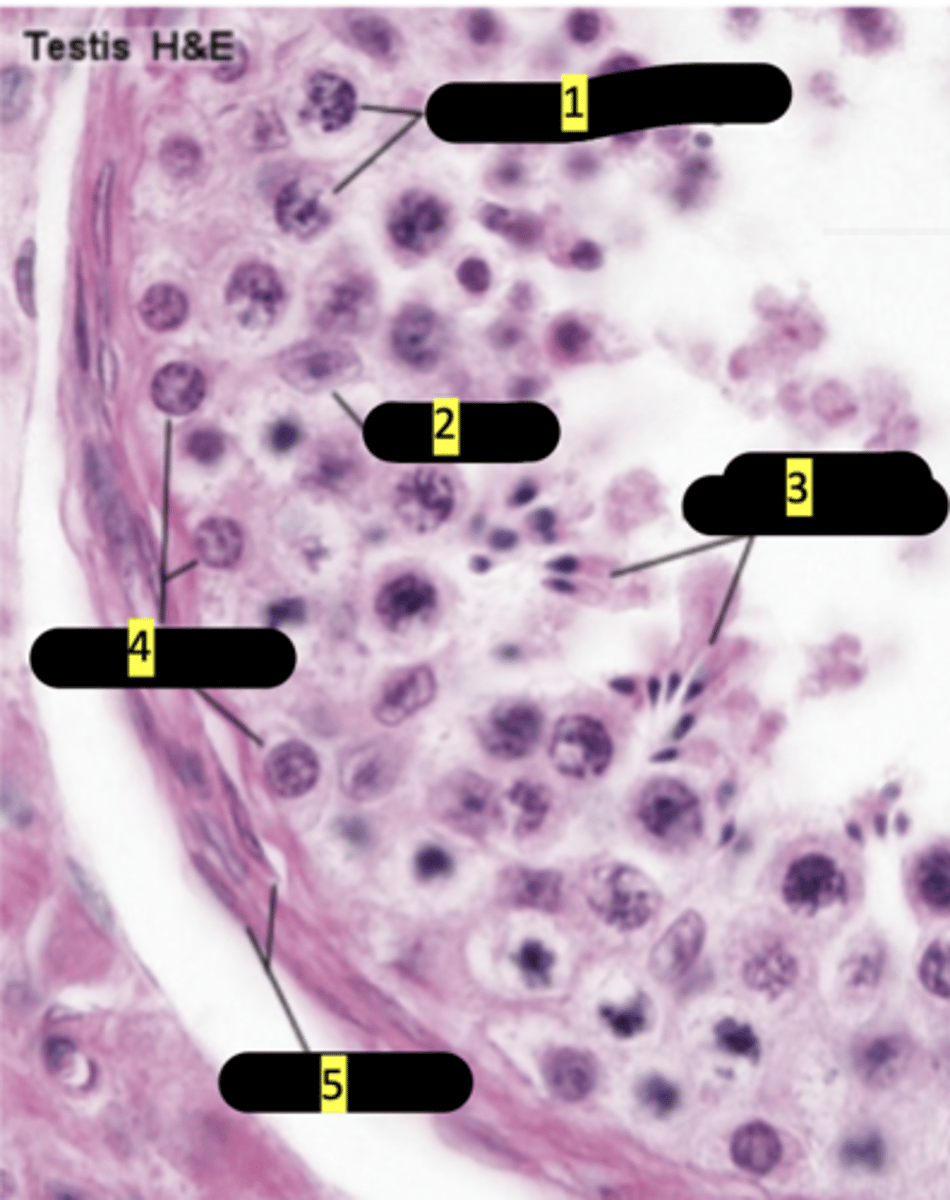
spermatids maturation phase
#3
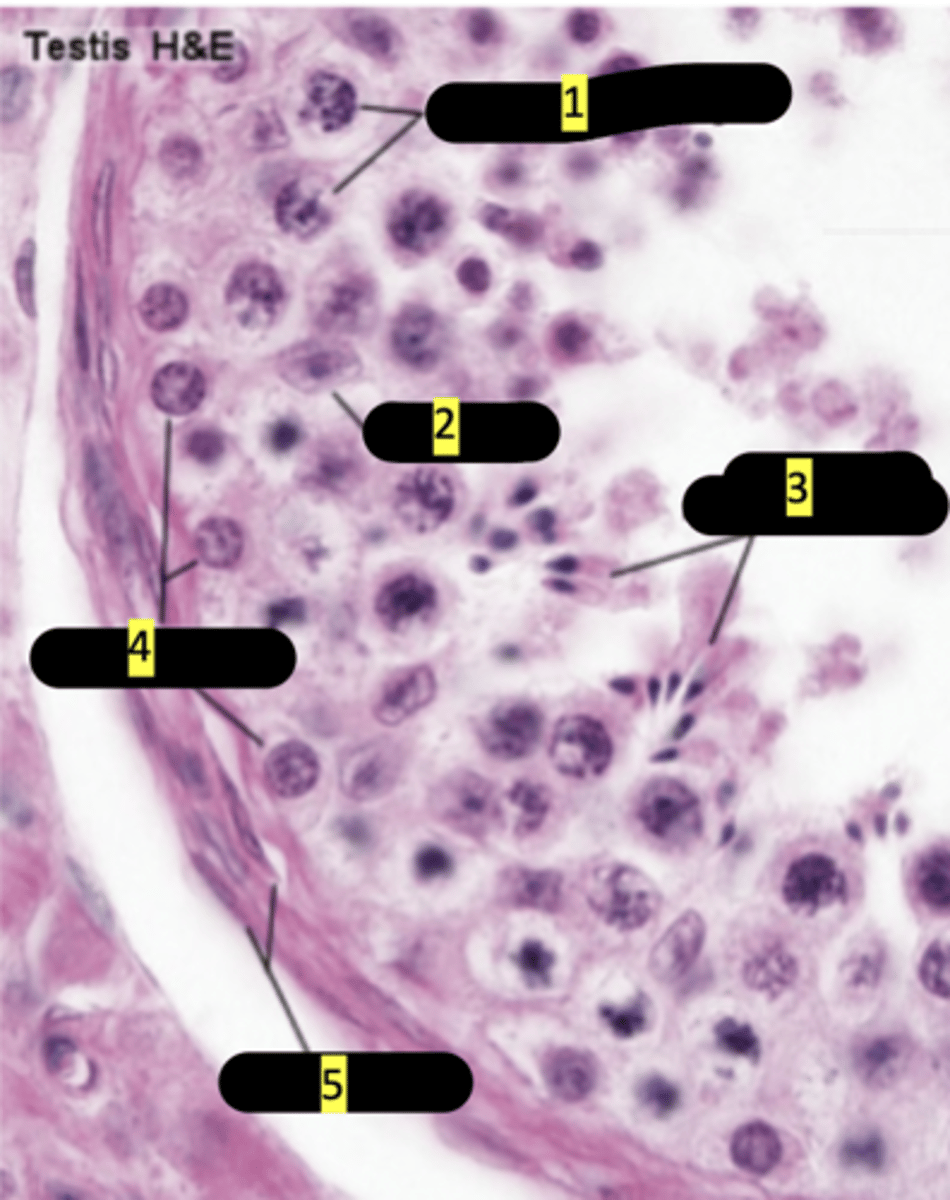
spermatogonia
#4
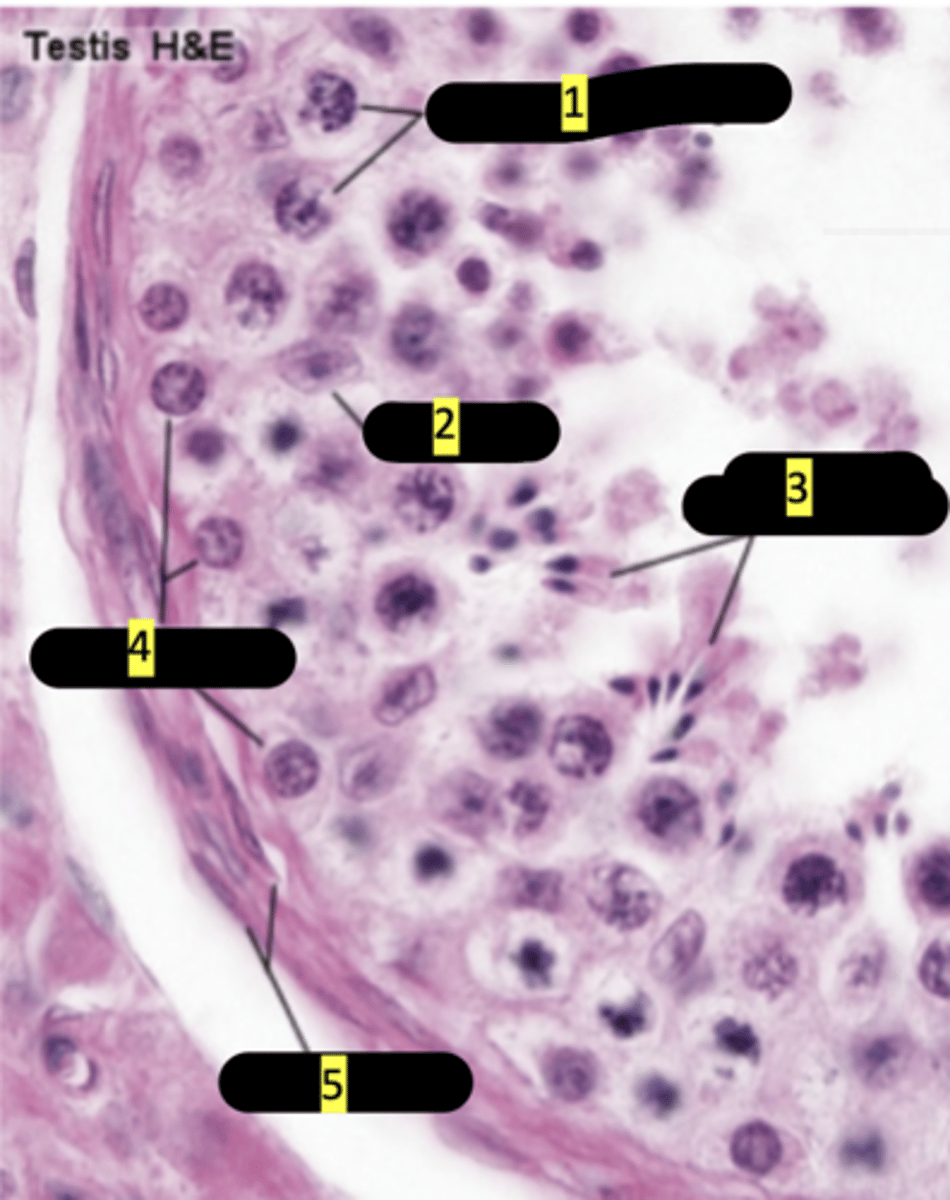
smooth muscle
#5
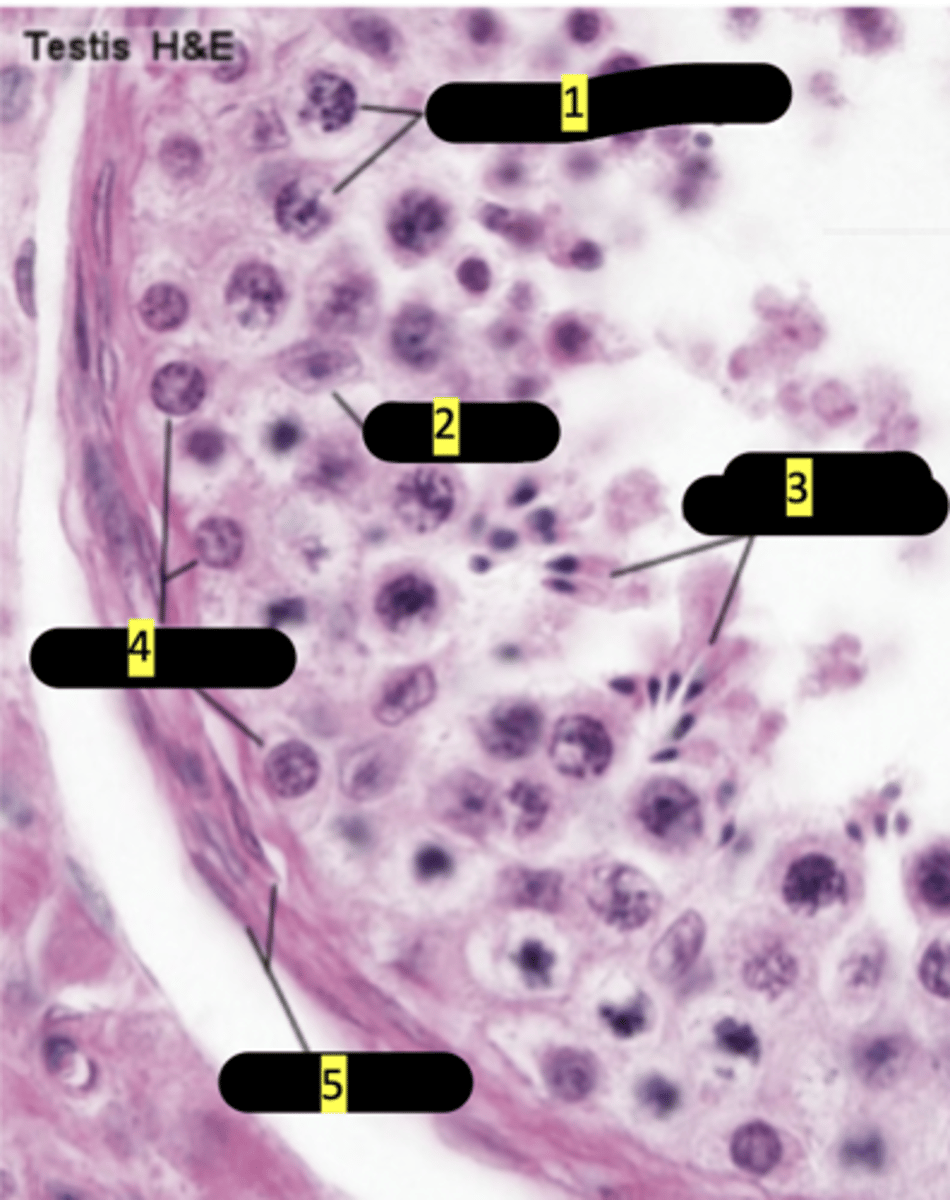
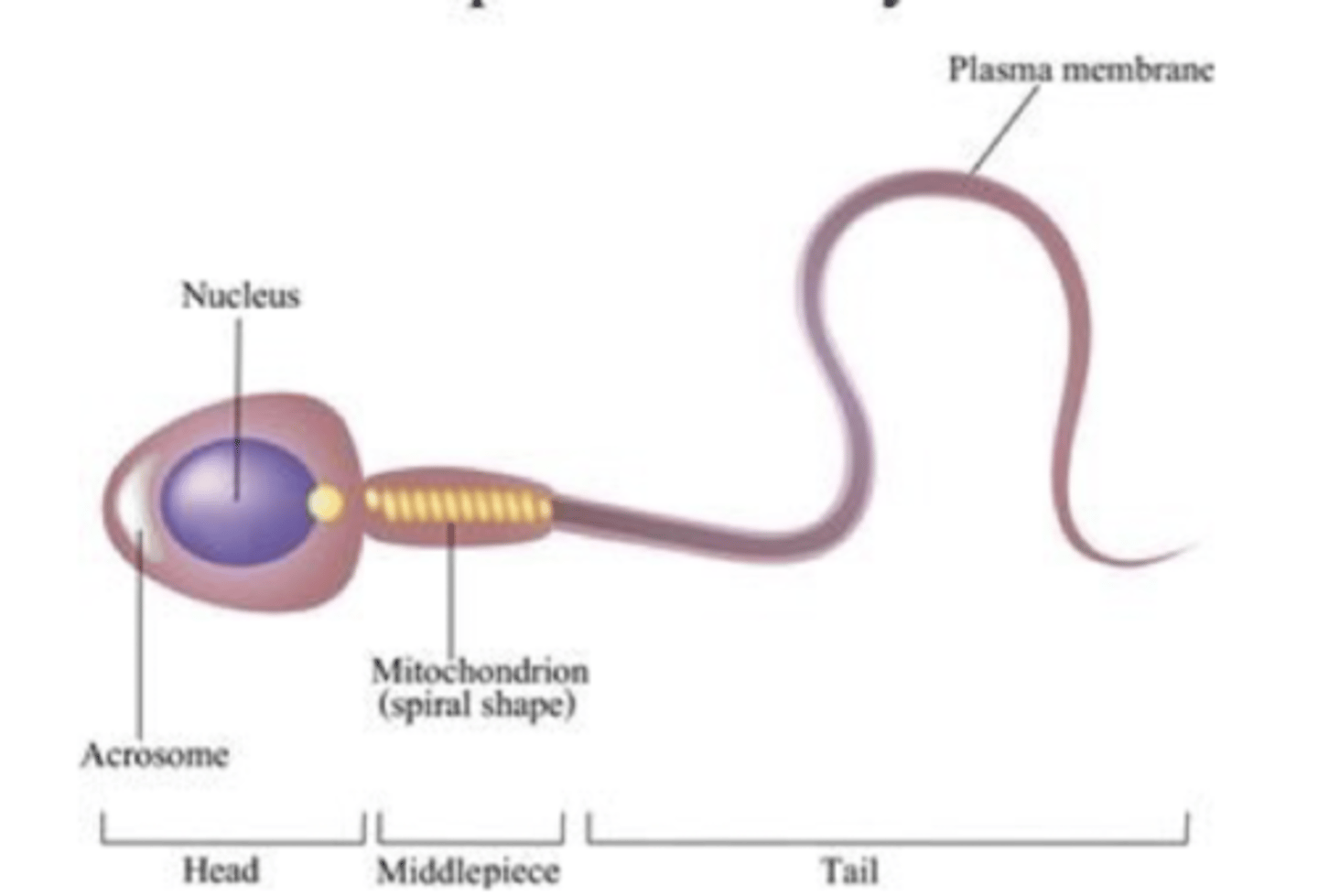
plasma membrane
#1
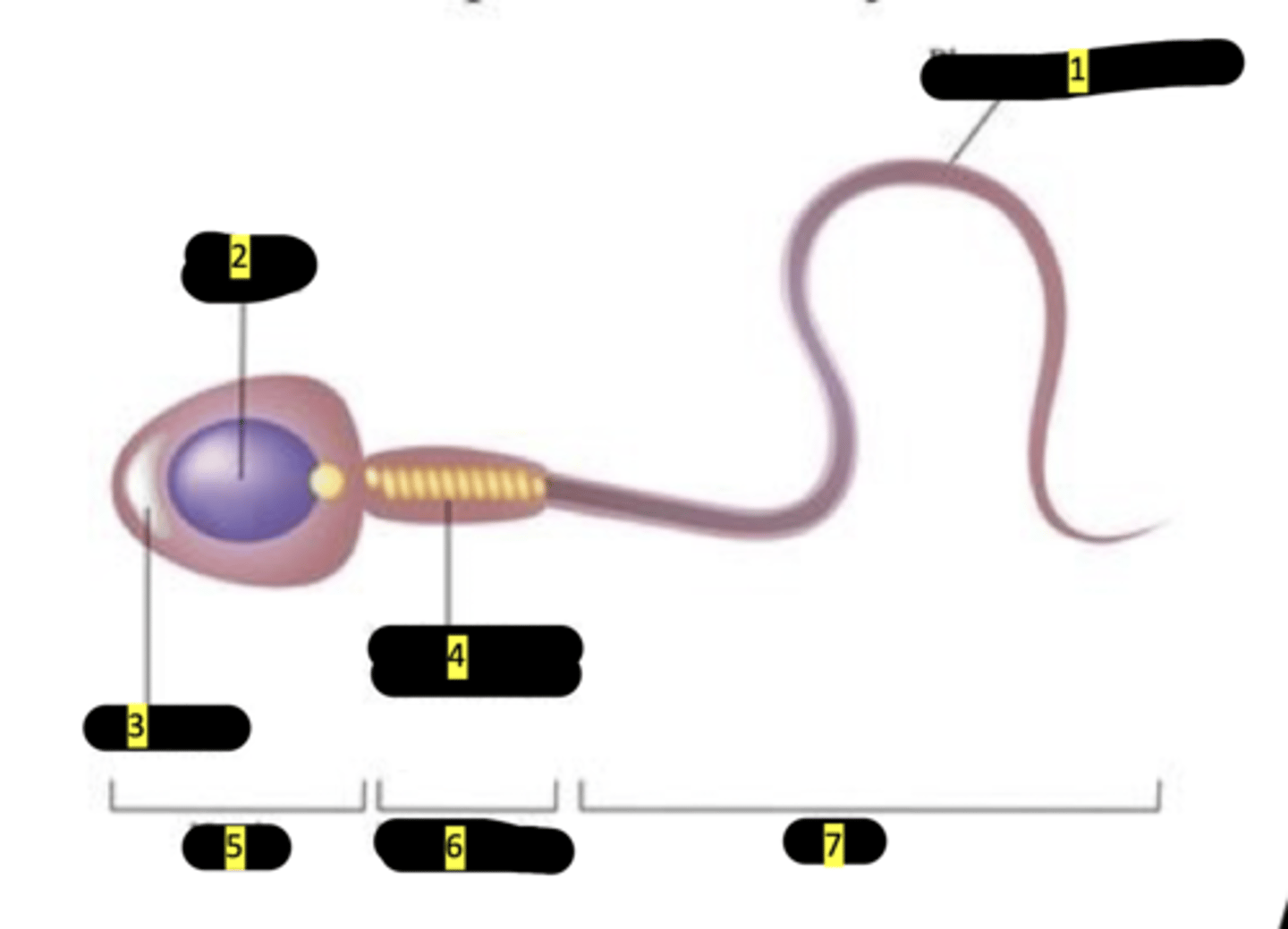
nucleus
#2
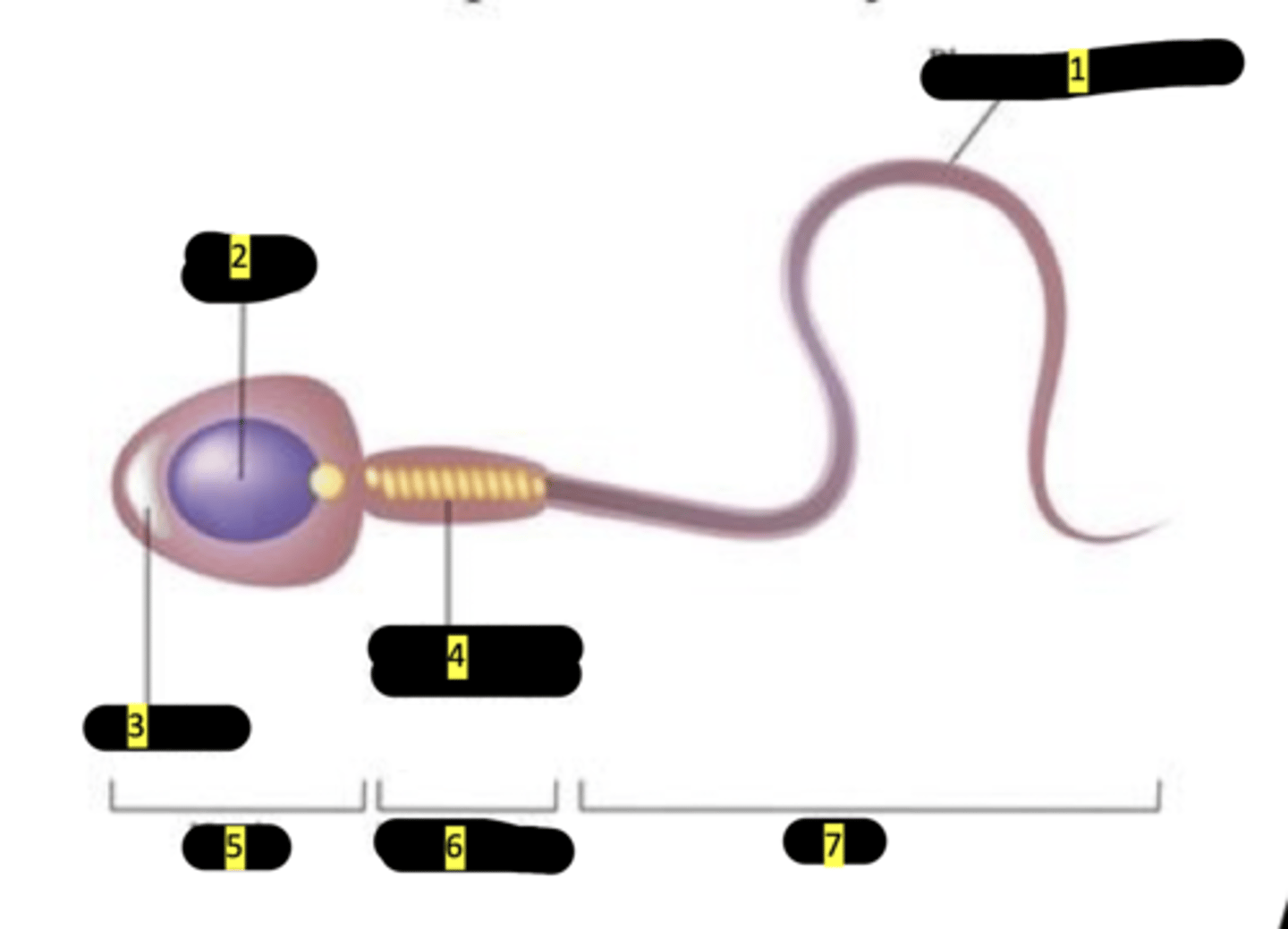
acrosome
#3
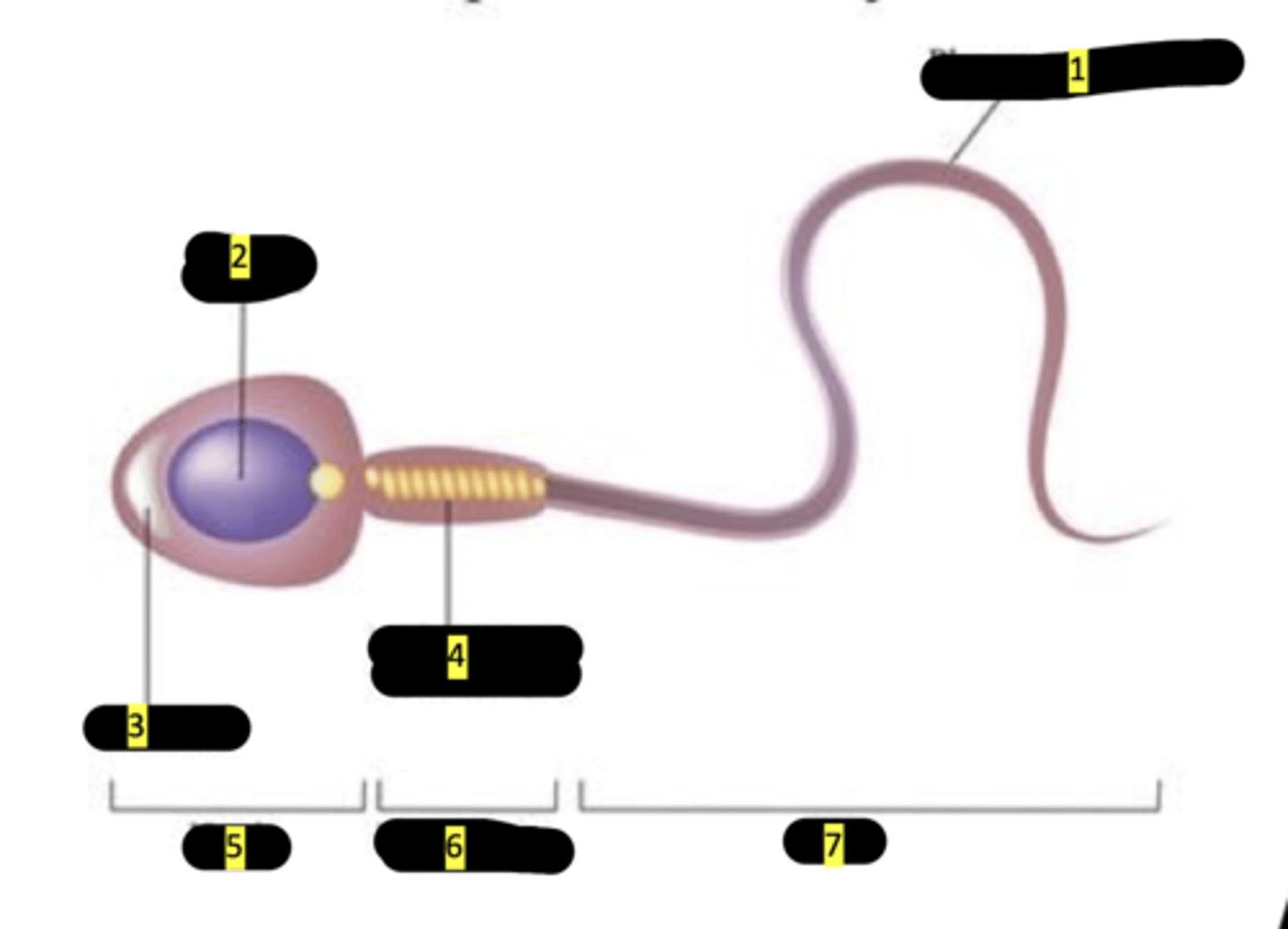
mitochondrion (spiral shape)
#4
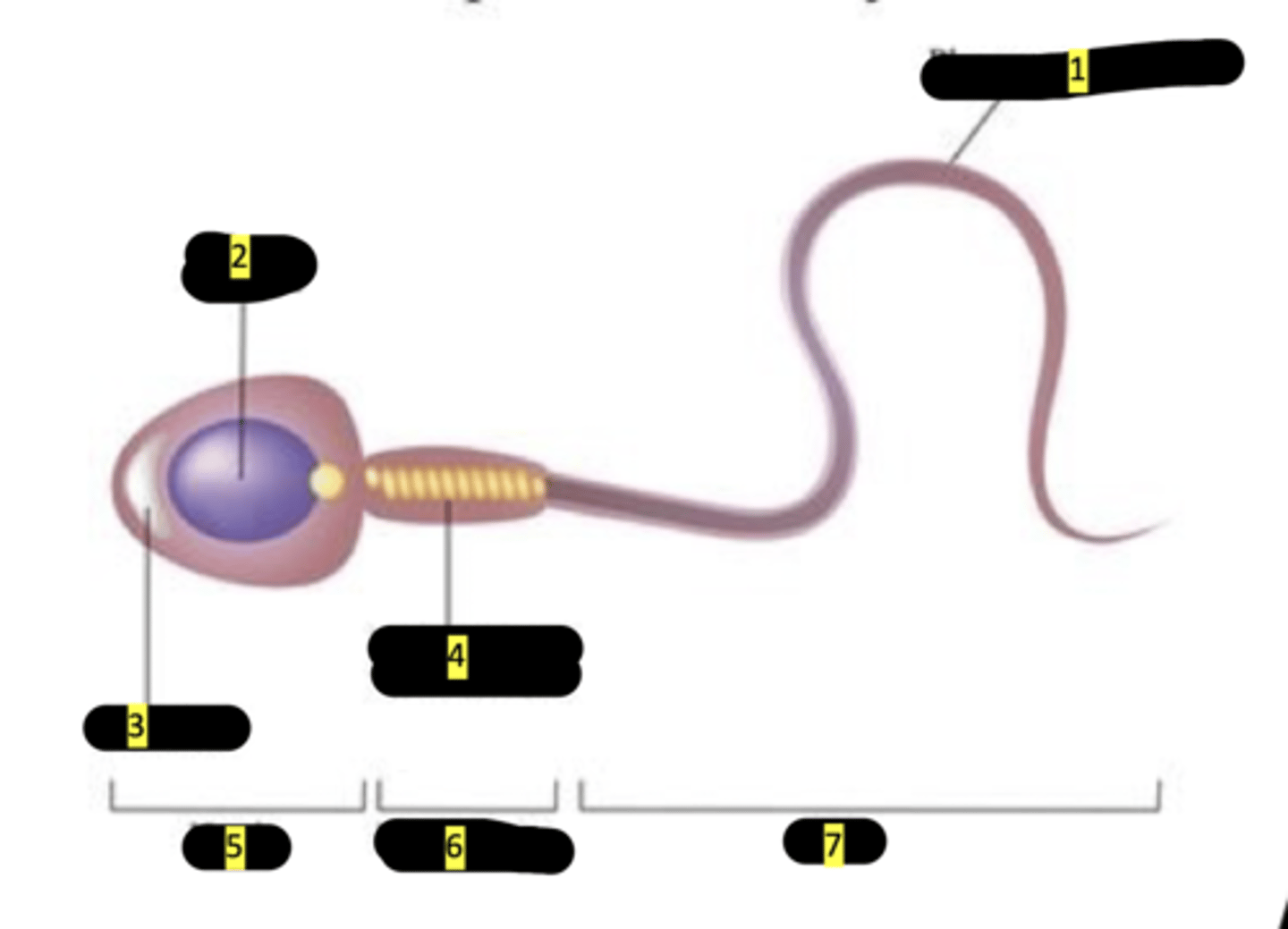
head
#5
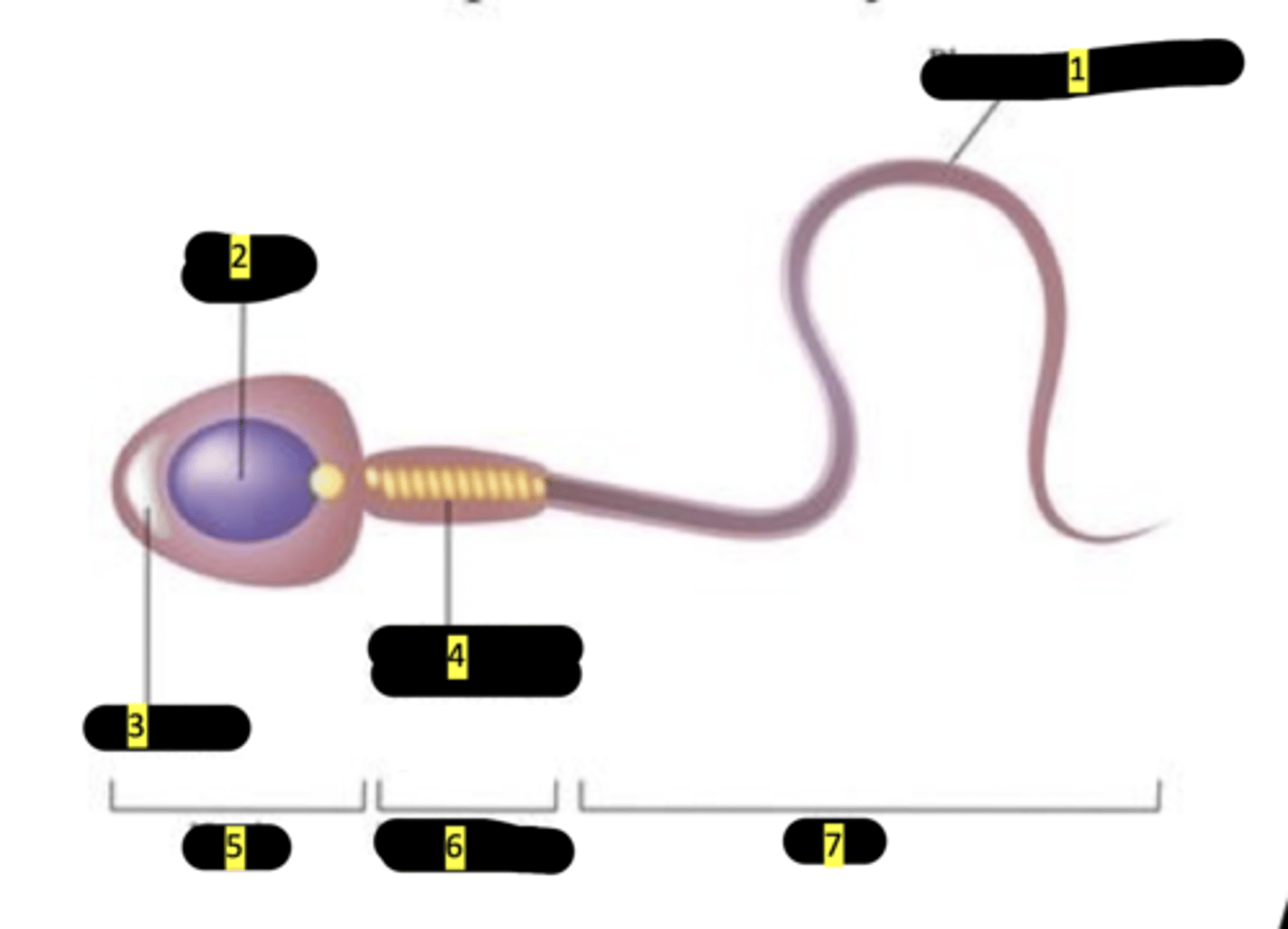
middlepiece
#6
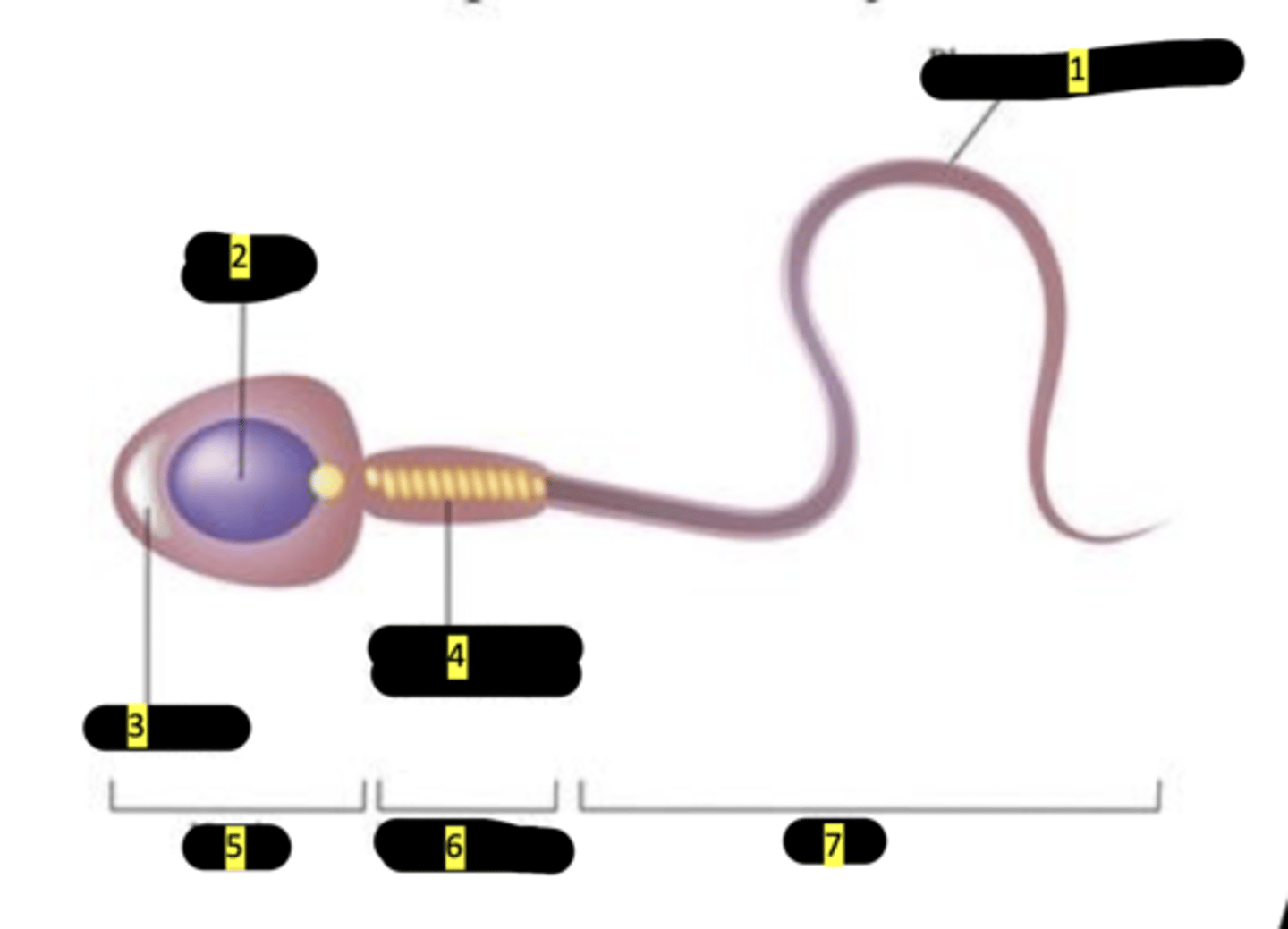
tail
#7
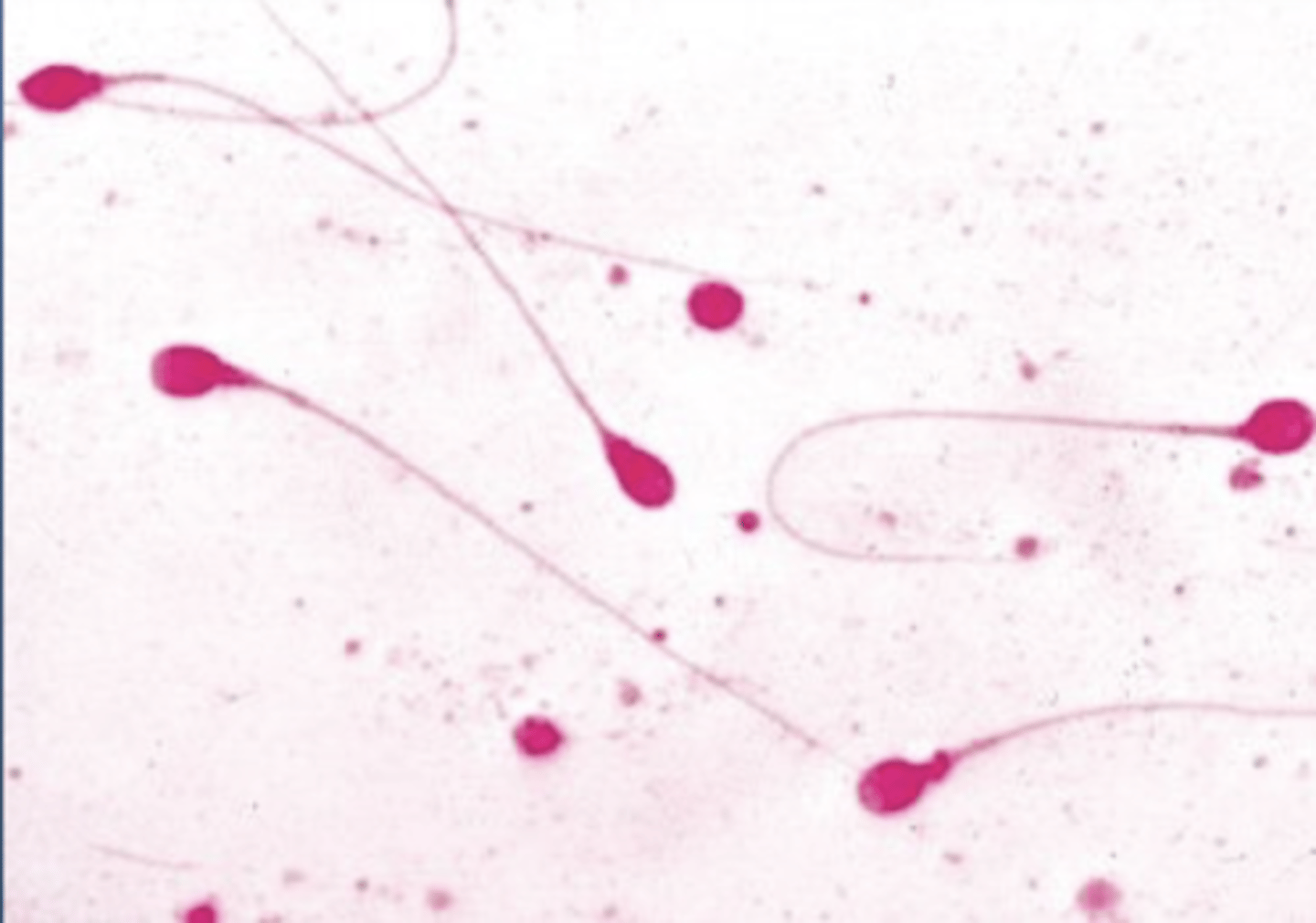
sperm
sperm
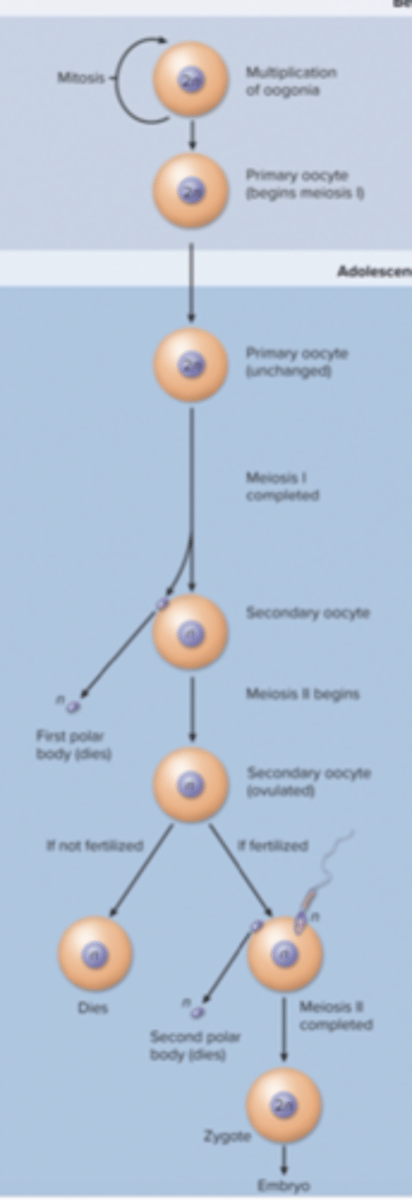
oogenesis
the production of female sex cells by meiosis
-between puberty and menopause, occurs monthly as part of the ovarian cycle
-primary oocytes (are diploid, 2n = complete meiosis I until (after) puberty
-meiosis I yields a polar body and a secondary oocyte (these are haploid, n = 23 chromosomes)
-if penetrated by sperm the secondary oocyte completes meiosis II
1. one large ovum (the functional gamete)
2. a tiny second polar body
if penetrated by sperm the secondary oocyte completes meiosis II yields what two things?
fetal period of oognesis
-oogonia (diploid, 2n ovarian stem cells) multiply by mitosis and store nutrients
-primordial follicles form once oogonia prepare to begin meiosis I
meiosis I of oogenesis
primary oocyte
prophase I and stay at this stage until puberty
when does meiosis stop in oogenesis and how long does it stay at that stage?
development of egg (oogenesis)
-light blue = before birth
-dark blue = adolescence to menopause
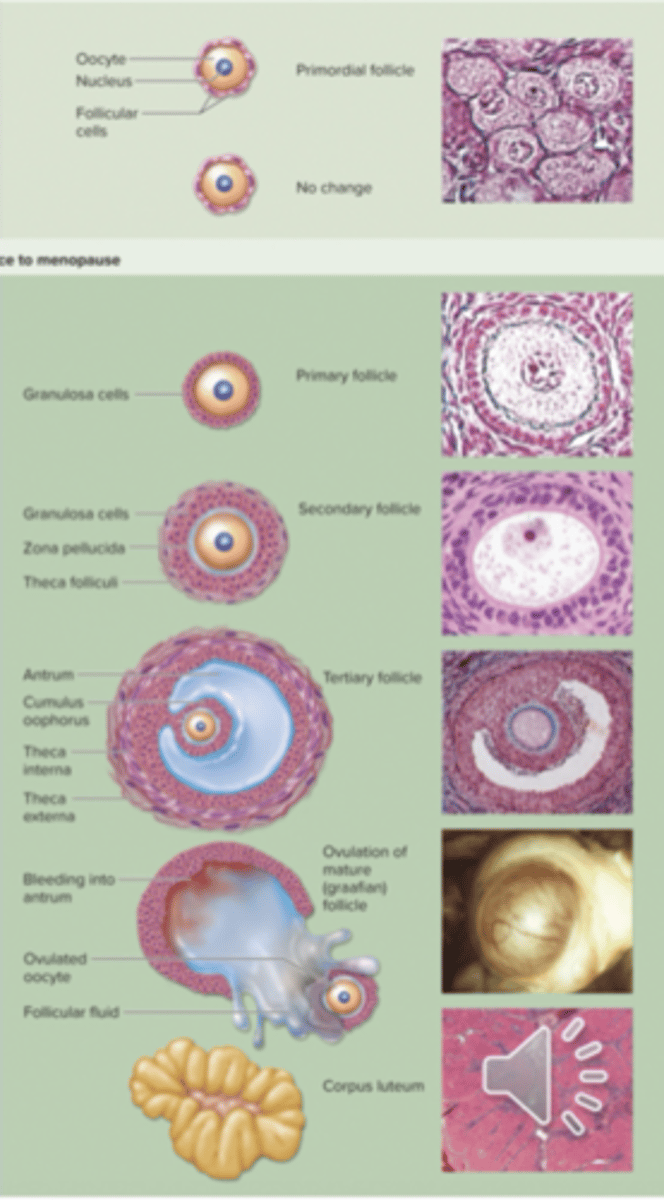
development of follicle (folliculogenesis)
-light green = before birth
-dark green = adolescence to menopause
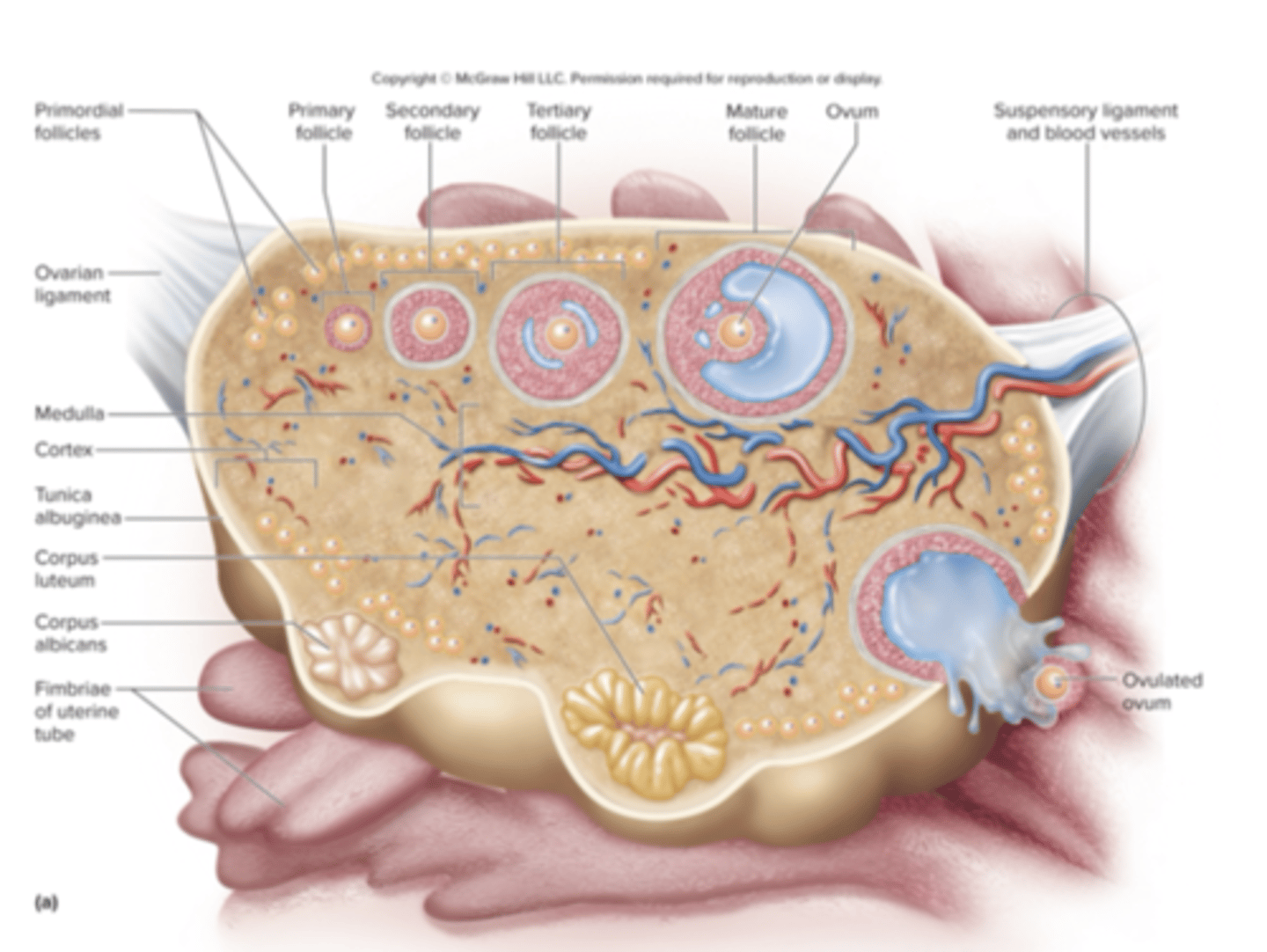
structure of an ovary
ovary with follicles
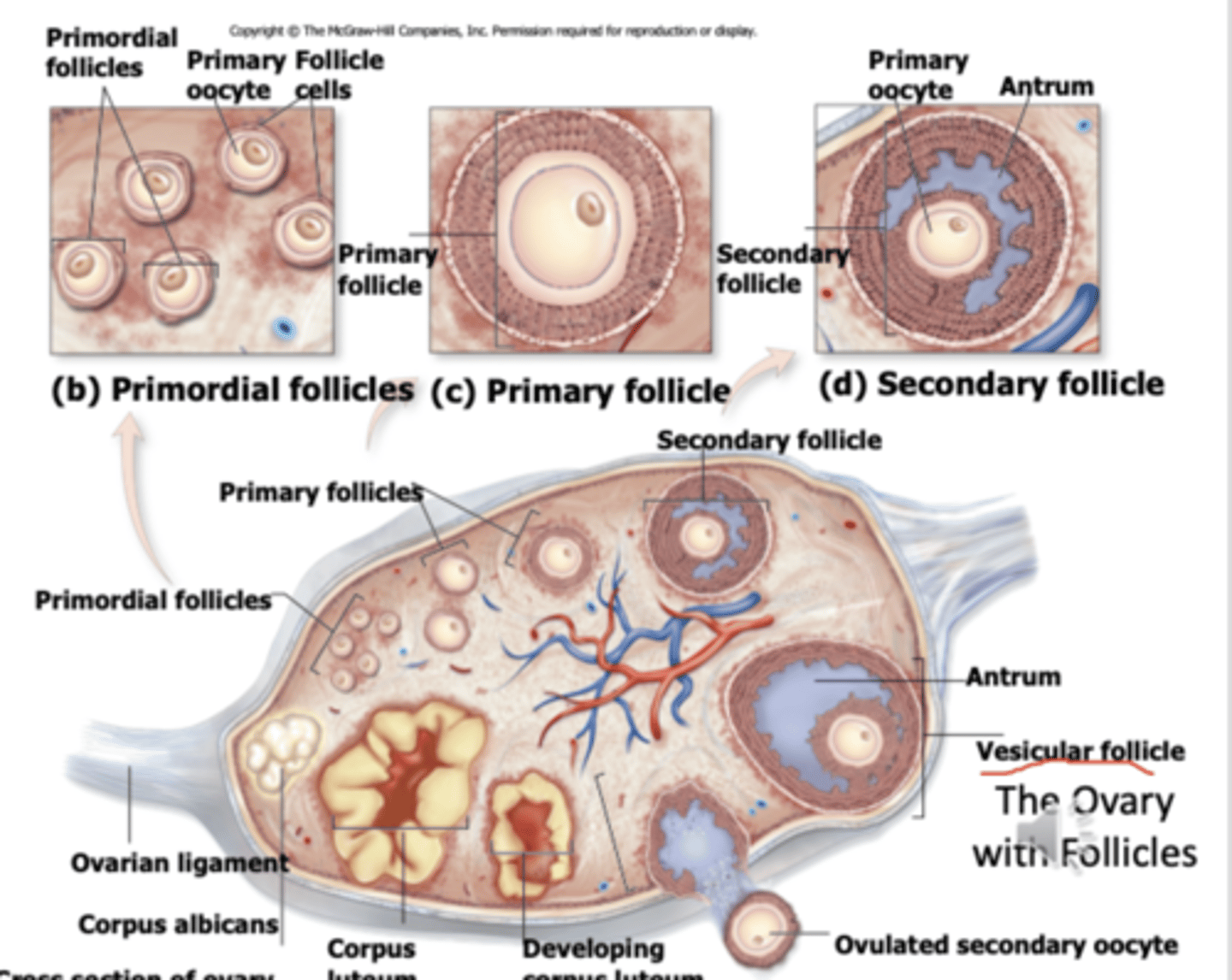
histology of ovary
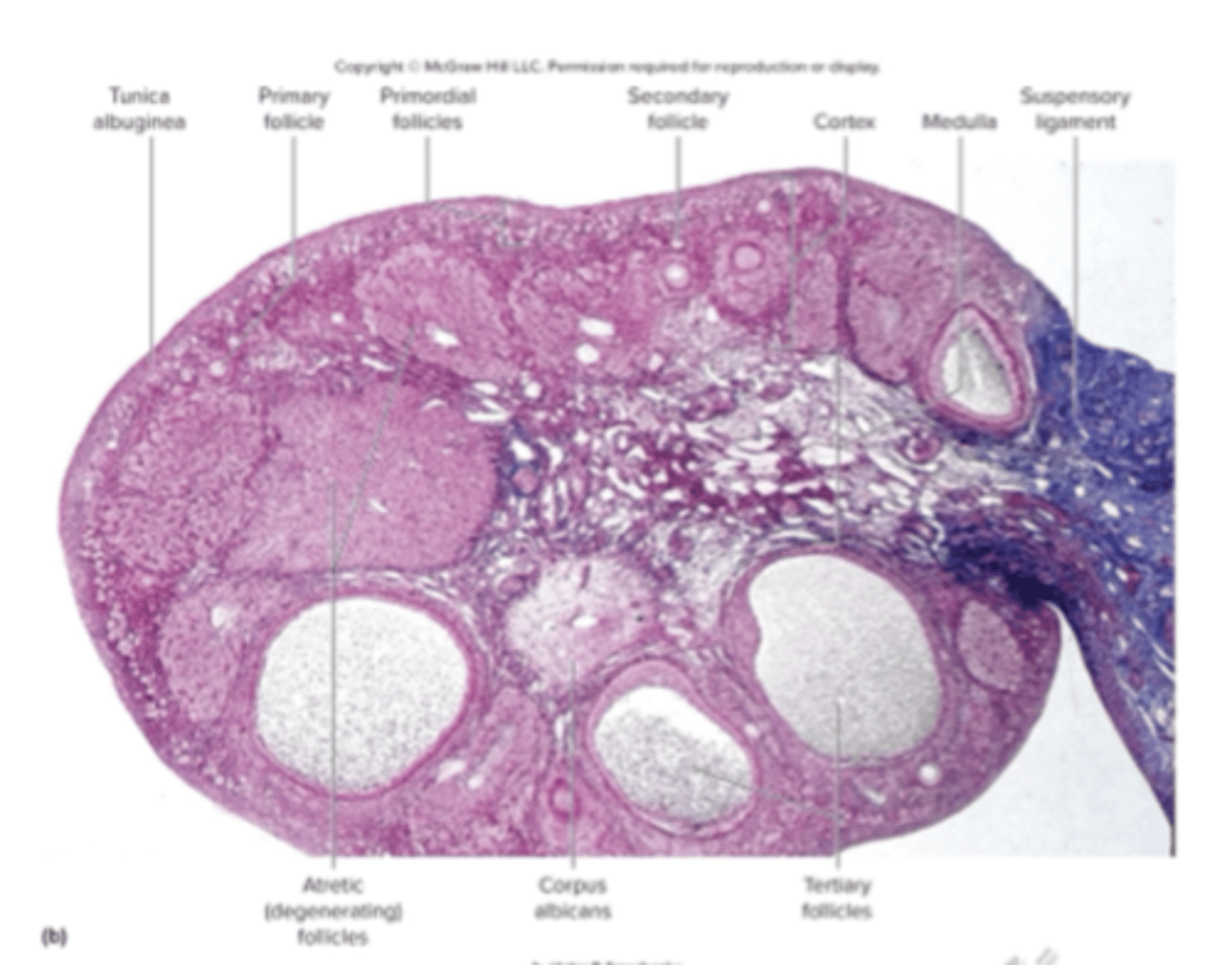
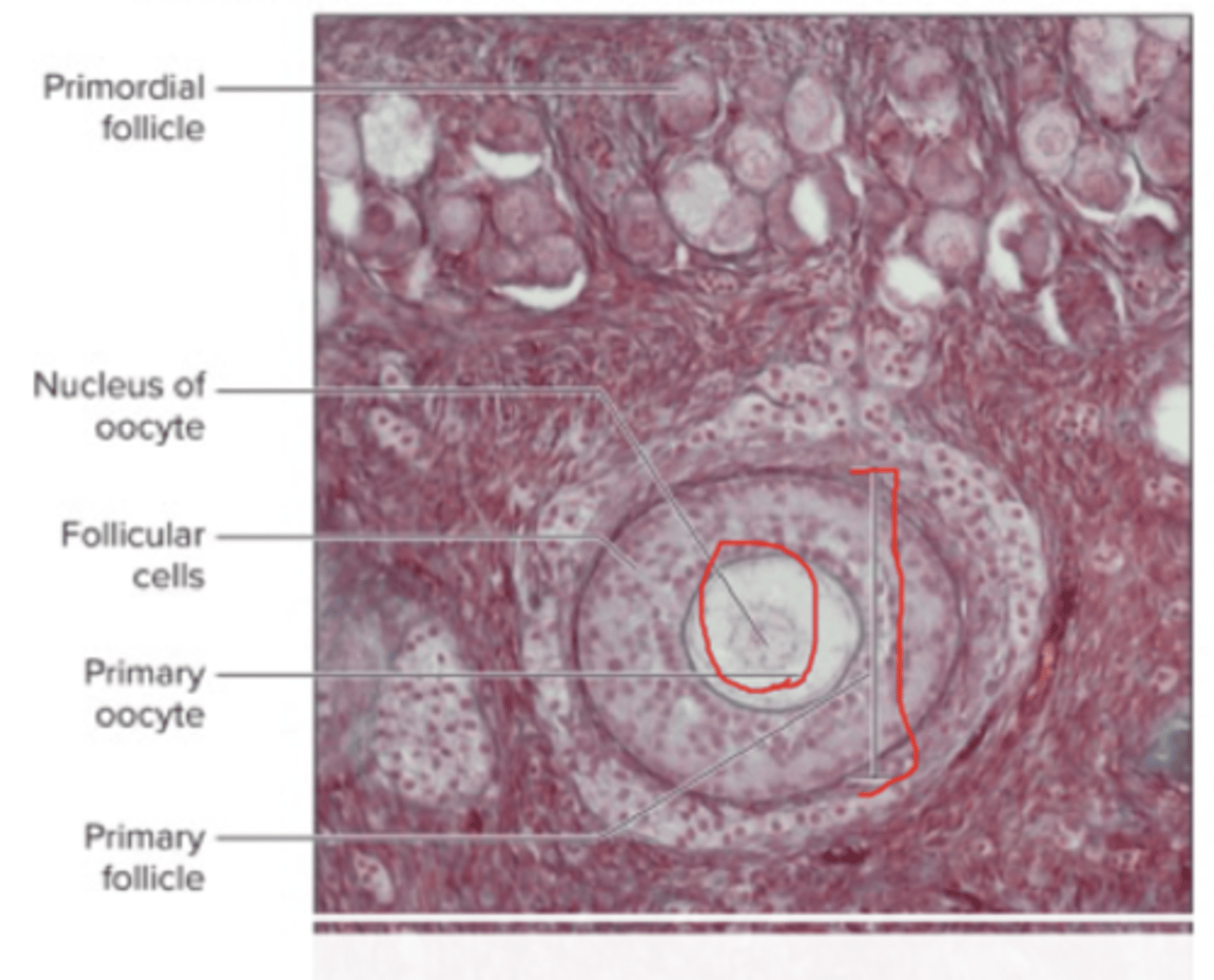
histology of ovary
gametogenesis
the biological process where sex cells, or gametes, are produced
haploid (n)
a cell or organism that has one set of chromosomes (n)
diploid (2n)
a cell or organism that has two complete sets of chromosomes
homologous chromosomes
pairs of chromosomes that contain the same genes, but may have different alleles, one comes from each parent
zygote
a single cell that results when a sperm and egg join during fertilization. It contains a full set of chromosomes, with 23 from the egg and 23 from the sperm
-aka fertilized egg
mitosis
a process of cell duplication, in which one cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells
prophase 1
when does crossing over occur in meiosis?