Protein Synthesis and the Central Dogma of Biology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Central Dogma of Biology
The process by which DNA is transcribed to RNA and then translated to protein.
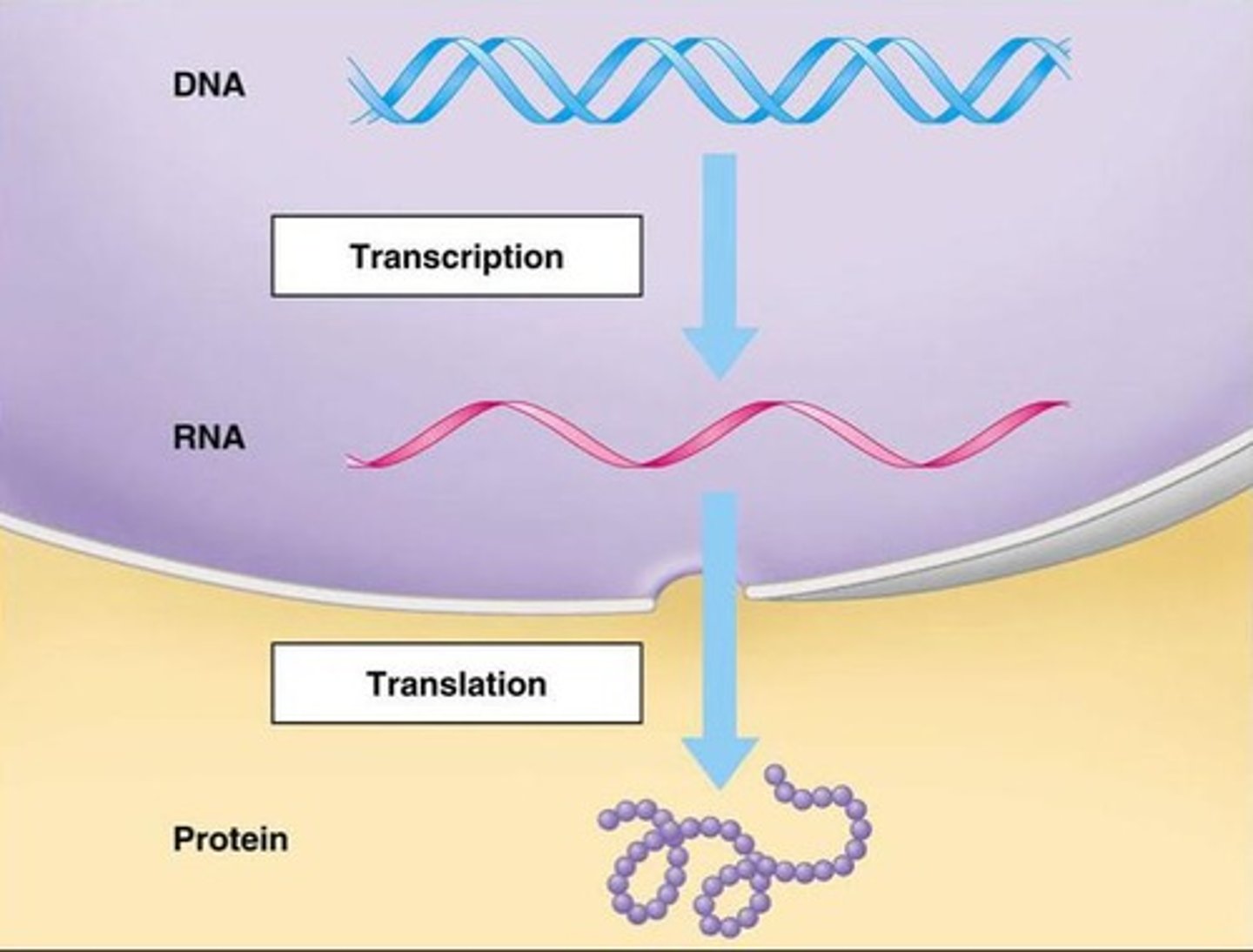
Instructions for building proteins
DNA provides the instructions for building proteins.
Location of DNA in eukaryotic cells
DNA is located in the nucleus.
Location of DNA in prokaryotic cells
DNA is located in the cytoplasm (free-floating).
Ribosomes
Cellular structures that build proteins, located in the cytoplasm.
RNA
A nucleic acid polymer composed of nucleotides, similar but not identical to DNA.
Sugar in RNA
RNA contains ribose sugar.
Nitrogen base in RNA
RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
Size comparison of DNA and RNA
DNA is a longer molecule while RNA is a shorter molecule.
Transcription
The process that uses DNA as a template to make mRNA.
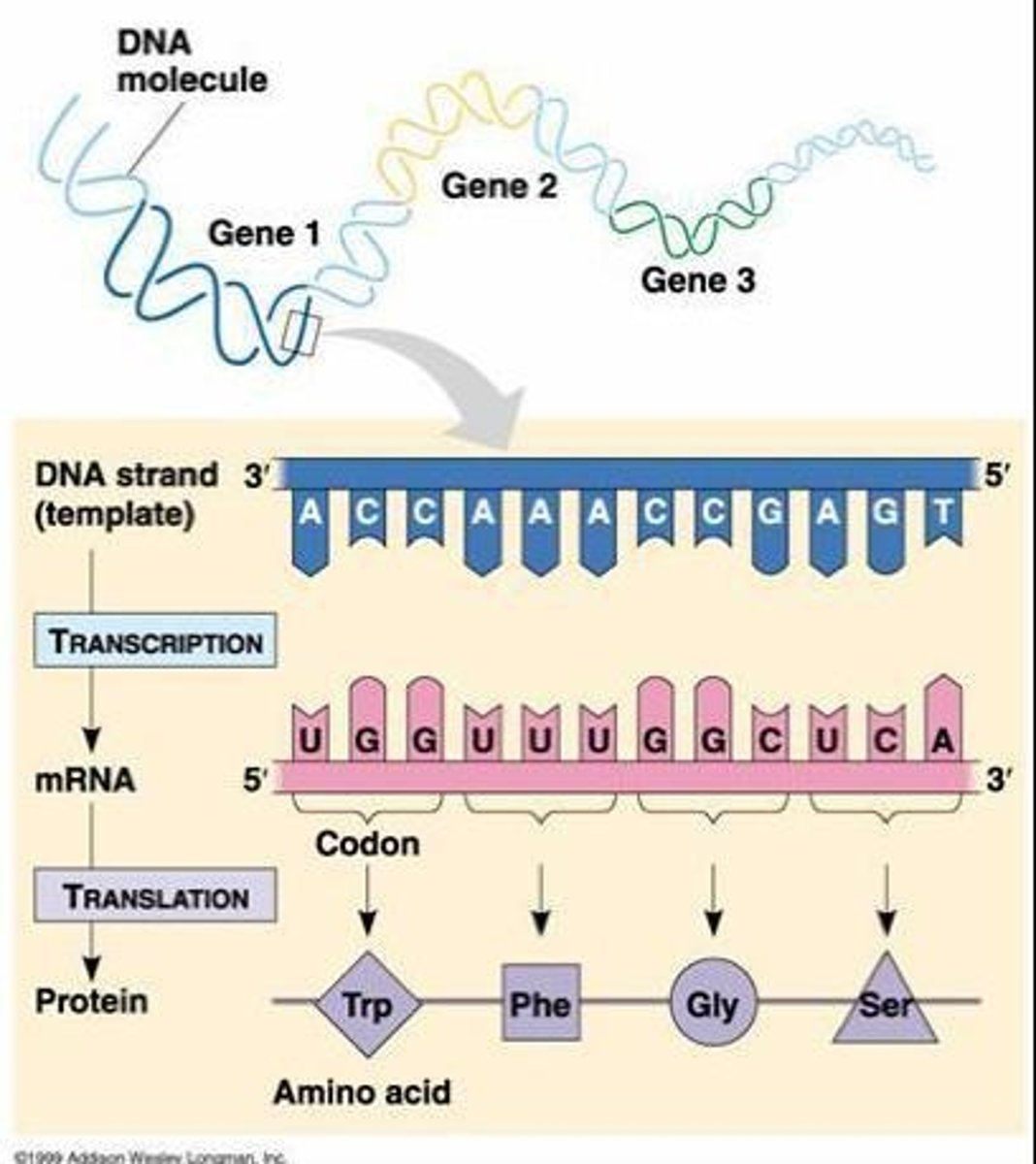
Base pairing in RNA
In RNA, uracil (U) pairs with adenine (A).
Base pairing in DNA
In DNA, adenine (A) usually pairs with thymine (T).
Process using mRNA to make a protein
Translation.
Flow of information in eukaryotic cells
Information flows from DNA to RNA in the nucleus and then to proteins in the cytoplasm.
Difference between DNA and RNA
DNA has deoxyribose sugar, while RNA has ribose sugar.
Difference between DNA and RNA
DNA contains thymine (T), while RNA contains uracil (U) instead.
Difference between DNA and RNA
DNA is a longer molecule, while RNA is a shorter molecule.
Function of RNA
RNA serves as a copy of the genetic instructions from DNA that can leave the nucleus.
Location of ribosomes
Ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm.
Template for mRNA
DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of mRNA.
Complementary base pairing
In RNA, U pairs with A, which differs from DNA where A pairs with T.
mRNA
Messenger RNA: the instructions for making a protein are encoded within its sequence of nucleotides.
tRNA
Transfer RNA: attaches to amino acids and then transfers them to the ribosome during translation.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA: combines with ribosomal proteins to make up the actual ribosome.
Transcription
The process of making an RNA copy of a piece of DNA sequence.
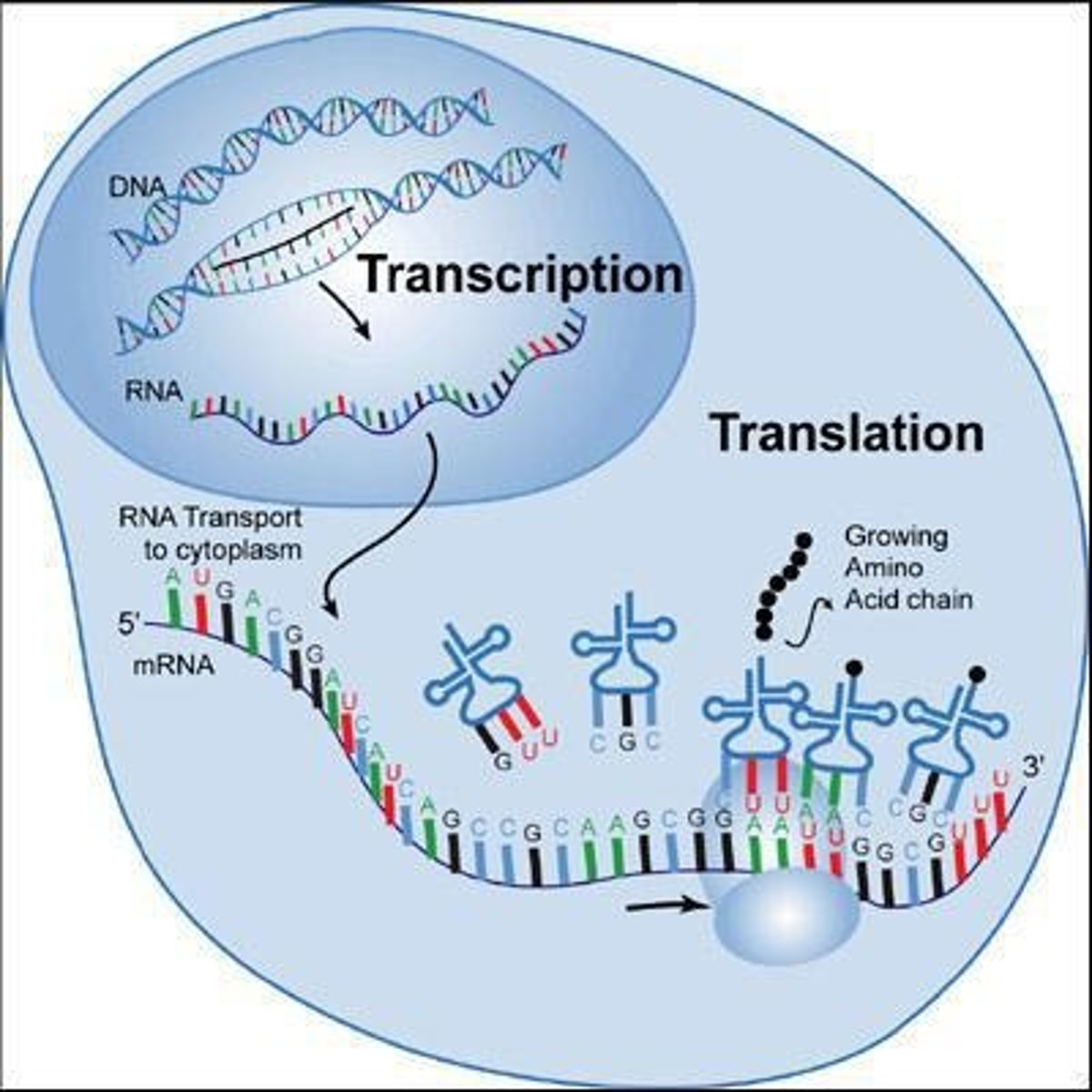
Translation
The process of assembling amino acids according to the RNA sequence to eventually make a protein.
Amino Acid Coding
Each group of THREE letters (three bases) codes for ONE amino acid.
Location of Transcription
Occurs inside the nucleus.
Location of Translation
Occurs in the cytoplasm.
Gene Expression
A gene would be expressed if it coded for a protein that is needed inside that particular cell.
Non-expressed Genes
If a cell doesn't need certain proteins, then the associated genes won't be expressed.
Types of RNA
There are three main types of RNA: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
Purpose of Transcription
To make an RNA copy of a piece of DNA sequence.
Purpose of Translation
To assemble amino acids according to the RNA sequence.
DNA Template to mRNA
Transcription of DNA A T C G G A T A C results in mRNA U A G C C U A U G.
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule.
Nucleus
The organelle where transcription occurs.
Cytoplasm
The location where translation occurs.
Protein Synthesis
The process of creating proteins based on the instructions carried by mRNA.
Ribosome
The molecular machine that assembles amino acids into proteins during translation.
Gene Regulation
The process by which cells control the expression of genes.