Life Processes – Class 10 Vocabulary Review
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and concepts from the Class 10 ‘Life Processes’ lecture notes, including digestion, respiration, circulation, excretion, photosynthesis and associated structures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Universal energy currency of all cells; stores and supplies energy for metabolic reactions.
Explain types of respiration.
RESPIRATION is the process of break down of food molecules to release energy. There are two main types:
1] Aerobic respiration-
The type of respiration that occurs in presence of oxygen IN MITOCONDRIA. The products formed are more energy, carbon dioxide and water.
2] Anaerobic respiration-
The type of respiration that occurs in lack or absence of oxygen IN CYTOPLASM. The types of it are;
a] Lactic acid fermentation
The process of anaerobic respiration producing energy IN LACK oxygen, resulting in byproducts such as lactic acid. MUSCLE CELLS
b] Alcoholic fermentation
The process of anaerobic respiration producing energy in ABSENCE of oxygen, resulting in byproducts like ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Anaerobic respiration
Energy-releasing breakdown of glucose without oxygen, producing less ATP and end-products such as lactic acid or ethanol.
Mitochondria
Cell organelles where aerobic respiration and most ATP synthesis occur.
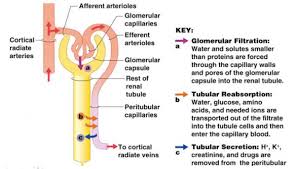
GIVE THE PROCESS OF URINE FORMATON.
TELL ABOUT;
the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion that take place in the kidneys to form urine.
Lactic acid
Organic acid produced during anaerobic respiration in muscle cells; accumulation causes cramps.
Photosynthesis
Process by which green plants make glucose from carbon dioxide and water using sunlight and chlorophyll, releasing oxygen.
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in chloroplasts that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
Light-dependent reactions
First stage of photosynthesis that converts light energy to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) and splits water.
Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions)
Set of photosynthetic reactions that fix CO₂ into glucose using ATP and NADPH.
Stomata
Microscopic leaf pores that regulate gas exchange and water loss.
Transpiration
Evaporation of water vapour from aerial parts of plants, mainly through stomata.
Root pressure
Osmotic pressure in roots that pushes water upward in xylem, prominent at night.
Transpiration pull
Tension created by water evaporation from leaves that draws water upward through xylem during the day.
Xylem
Vascular tissue transporting water and minerals from roots to shoots.
Phloem
Vascular tissue that transports sugars and other organic nutrients throughout the plant.
Resins and gums
Waste products stored in old xylem tissue of plants.
Emulsification
Process in which bile salts break large fat globules into tiny droplets, increasing surface area for lipase action.
Bile juice
Alkaline liver secretion (stored in gall bladder) that neutralises chyme and emulsifies fats.
Gall bladder
Small sac under the liver that stores and concentrates bile.
Pancreas
Gland that secretes digestive enzymes (amylase, trypsin, lipase) into the small intestine and hormones into blood.
Trypsin
Pancreatic enzyme that digests proteins in the alkaline small intestine.
Pepsin
Gastric enzyme that digests proteins in acidic stomach conditions.
Lipase
Enzyme that hydrolyses emulsified fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Salivary amylase (ptyalin)
Enzyme in saliva that begins starch digestion, converting it to maltose.
Villi
Finger-like projections lining the small intestine that greatly increase surface area for absorption.
Lymph
Clear fluid derived from tissue fluid; transports fats, drains excess fluid and houses immune cells.
Lymphedema
Swelling caused by blockage of lymphatic vessels and impaired fluid drainage.
Nephron
Structural and functional unit of the kidney responsible for urine formation.
Glomerulus
Tuft of capillaries in a nephron that filters blood under pressure.
Bowman’s capsule
Cup-shaped nephron structure that collects filtrate from the glomerulus.
Tubular reabsorption
Process by which useful substances move from nephron filtrate back into the blood.
Tubular secretion
Active transport of additional wastes and ions from blood into nephron tubule.
Osmoregulation
This pathway involves detecting changes in blood osmolarity, triggering hormonal responses to influence water and salt reabsorption in the kidneys, and controlling thirst to regulate water intake.
ADH [antidiuretic hormone] playing crucial roles in maintaining the body's water and electrolyte balance through mechanisms such as filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
![<p><span>This pathway involves detecting changes in blood osmolarity, triggering hormonal responses to influence water and salt reabsorption in the kidneys, and controlling thirst to regulate water intake.</span></p><p><strong><mark data-color="#NaNNaNNaN" style="background-color: #NaNNaNNaN; color: inherit">ADH [antidiuretic hormone]</mark></strong> playing crucial roles in maintaining the body's water and electrolyte balance through mechanisms such as filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9f4737a0-7bdf-4978-95ec-da97a25f1184.png)
Ureter
Tube that carries urine from each kidney to the urinary bladder.
Urinary bladder
Muscular sac that temporarily stores urine before excretion.
Epiglottis
Cartilaginous flap that closes the trachea during swallowing to prevent food entry into airways.
Trachea
Windpipe; air passage supported by C-shaped cartilaginous rings.
Bronchi
Two main branches of the trachea that lead into the lungs.
Alveoli
Thin-walled sac-like structures in lungs where gaseous exchange occurs.
Diaphragm
Dome-shaped muscle separating thoracic and abdominal cavities; its contraction drives inhalation.
Double circulation
Circulatory pattern in which blood passes through the heart twice per body circuit (pulmonary and systemic loops).
Pulmonary artery
Blood vessel carrying deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs.
Pulmonary vein
Blood vessel carrying oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium.
Aorta
Largest artery; carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to the body.
Vena cava
Large vein (superior and inferior) returning deoxygenated blood from body to right atrium.
Arteries
Thick-walled elastic vessels that carry blood away from the heart under high pressure.
Veins
Thin-walled vessels with valves that return blood to the heart at low pressure.
Capillaries
Microscopic one-cell-thick vessels where exchange of gases, nutrients and wastes occurs between blood and tissues.
Countercurrent exchange
Mechanism in fish gills where blood and water flow in opposite directions, maximising oxygen uptake.
Amphibian heart
Three-chambered heart (two atria, one ventricle) that allows partial mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Warm-blooded (endothermic) animals
Organisms that maintain a constant internal body temperature through high metabolic activity.
Cold-blooded (ectothermic) animals
Organisms whose body temperature varies with environmental conditions.
Muscular cramps
Painful contractions caused by lactic acid accumulation after anaerobic respiration in muscles.
Root pressure vs. transpiration pull
Root pressure pushes water upward at night; transpiration pull draws water upward during daytime evaporation.