Vertebrates
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Hormones are
chemical signals or messengers (excite)
Hyposecretion
Abnormally reduced output
Hypersecretion
-Abnormally increased output
-Some cases, hormones secretes, but receptors do not respond
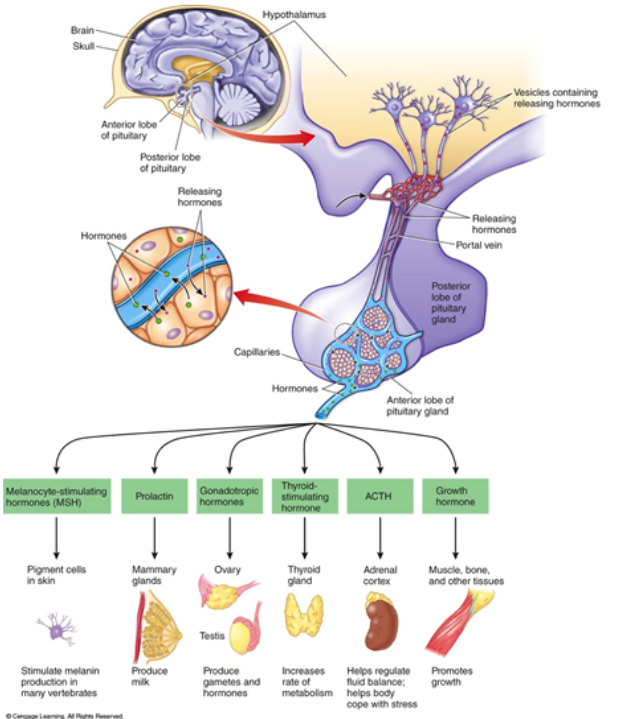
Hypothalamus Function
link nervous and endocrine systems anatomically and physiologically control most endocrine activity (directly or indirectly)
Pituitary gland: Location
connect to hypothalamus
Pituitary gland: Function
secretions control several other endocrine glands and tissues
Pituitary gland Structure
human pituitary gland has two lobes: anterior and posterior
Posterior pituitary Structures
(connection with hypothalamus)
-axons from neurons in hypothalamus extend into pituitary
Posterior pituitary: Hormones released:
neurohormones (peptide hormones) from hypothalamus
Hormone ADH: function and origin
antidiuretic hormone: Posterior Pituitary Gland
-kidney: water conservation
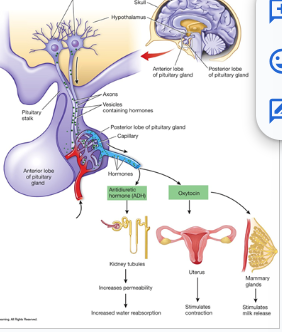
Hormone: Oxytocin: function and origin
Posterior Pituitary Gland
-stimulates uterine contraction, social behaviors (facilitates bonding with mother and infant), and facial recognition and trust
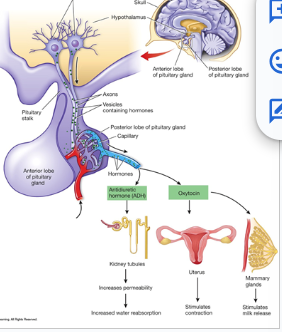
Explain the portal system
Anterior pituitary (A.P.):
hormones enter capillaries in hypothalamus, travel via portal vein to capillary bed in AP, from AP capillary bed diffuses out and contact cells
Anterior Pituitary Products (6)
-MSH; Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
-Prolactin
-Gonadotropic Hormones
-Thyroid-stimulating Hormone
-ACTH
-Growth Hormone
Hormone: MSH
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone: Anterior Pituitary
-stimulate melanin production in many vertebrates
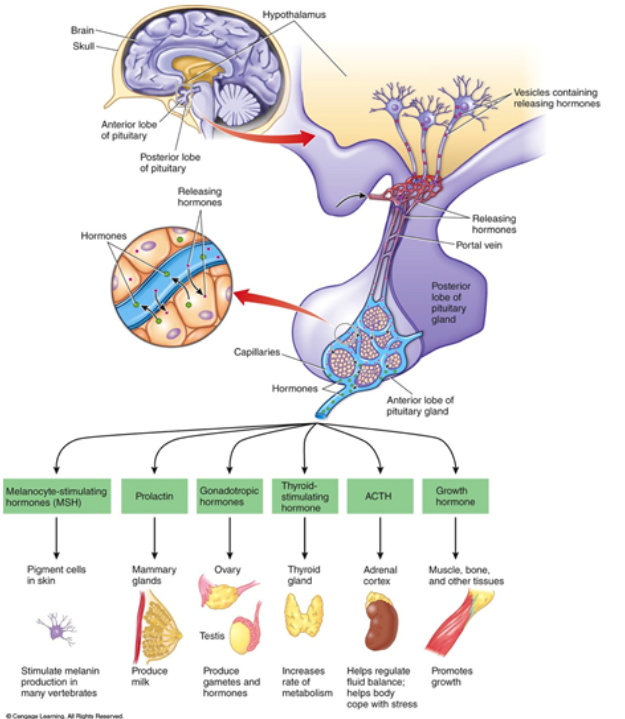
Hormone: Prolactin
Anterior Pituitary
-produce milk in mammary glands
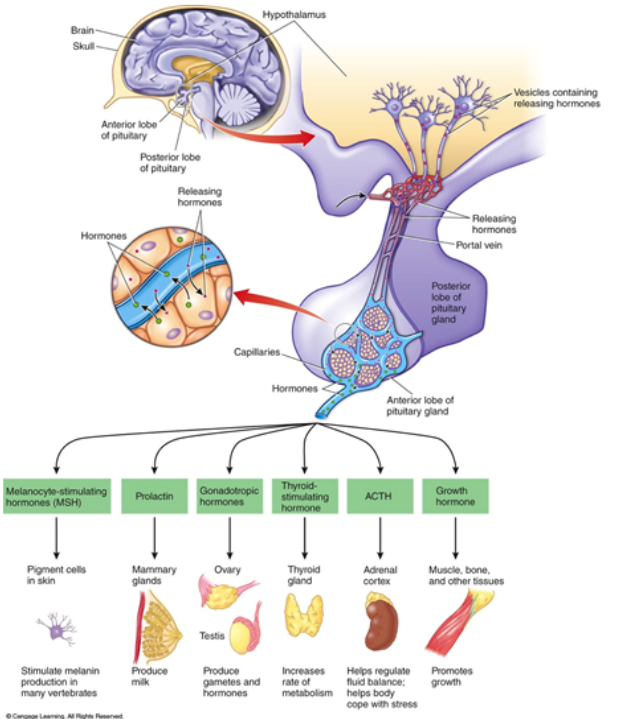
Hormone: Gonadotropic hormones
Anterior Pituitary
-ovaries and testies: produce gametes and hormones
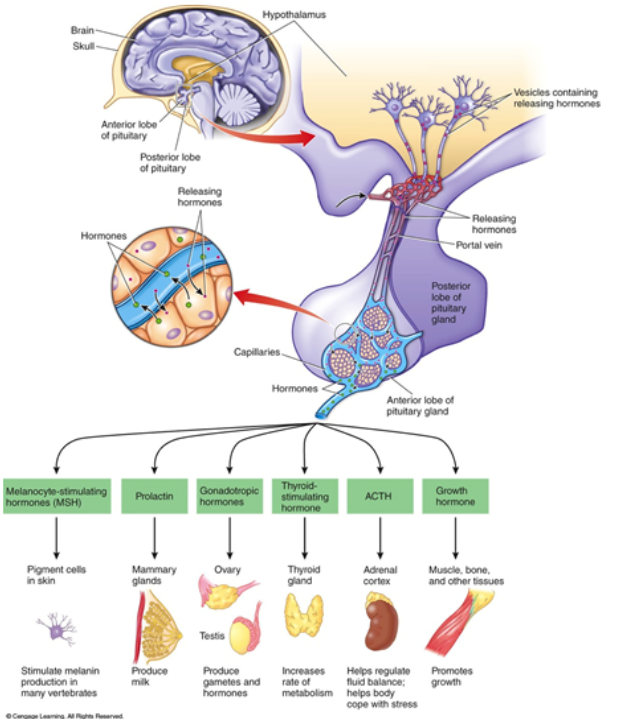
Hormone: TSH
Thyroid-stimulating hormones: anterior Pituitary
-thyroid gland: increases rate or metabolism
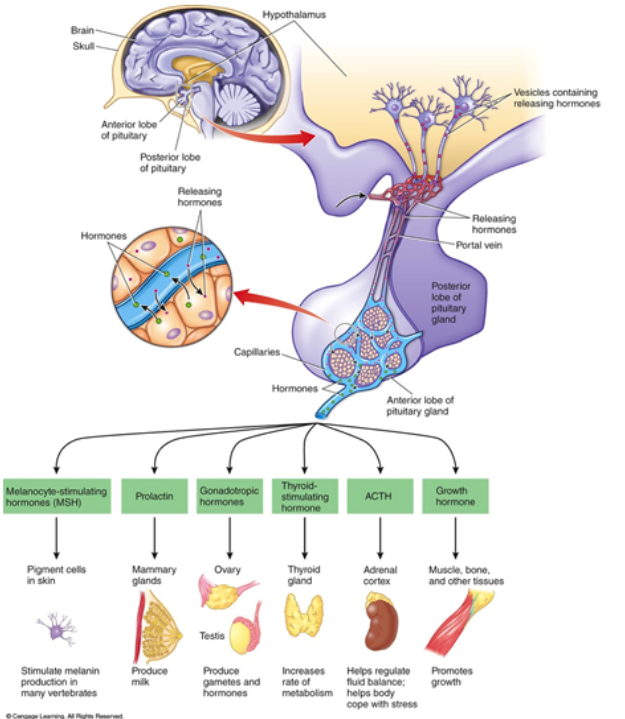
Hormone: ACTH
Anterior Pituitary
-Adrenal Cortex: helps regulate fluid balance: helps body cope with stress
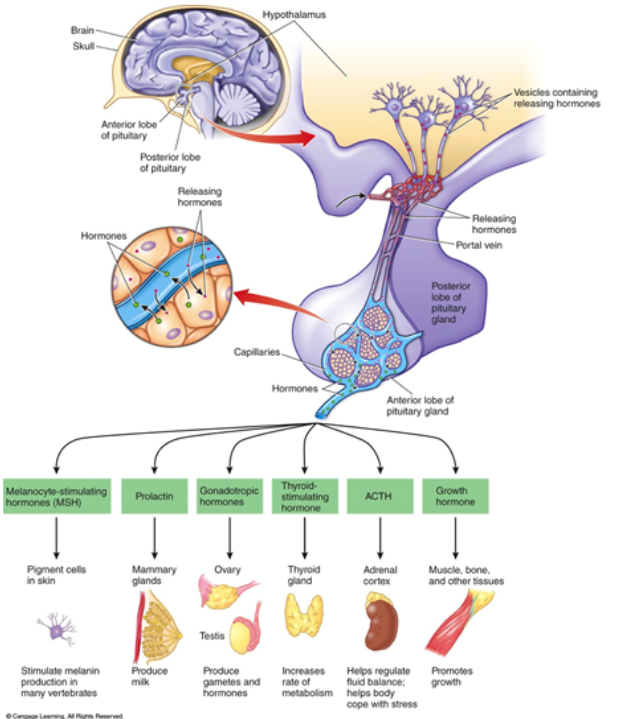
Hormone: GH
Growth Hormone: Anterior Pituitary
-Muscle, bone, and other tissues: promotes growth
Abnormal secretion of growth hormone (GH) (3)
Pituitary Dwarfism, Gigantism, Acromegaly
extreme GH deficiency during childhood
Pituitary Dwarfism
excessive GH amounts during childhood
Gigantism
hypersecretion GH during adulthood
Acromegaly: connective tissue thickens and bones may increase in diameter (hands, feet, and face)
Thyroid gland: Location
front of trachea, below larynx
Thyroid gland: hormones
T3 and T4 synthesized from tyrosine and iodine
Thyroid gland: Function
-metabolic rate, regulate proteins for cell differentiation, Ca2+ metabolism (later)
Thyroid gland: heat
Heat production (cold snap example)
-Cold temperature
-Hypothalamus increases secretion of TSH-releasing hormone which increases heat production
Thyroid disorders:
-Hypothyroidism (cretinism and myxedema)
-Hyperthyroidism (graves’ disease and goiter)
Infancy and childhood: Low metabolic rate, may occur (retarded mental and physical development)
Cretinism
In adulthood characterized by slowing down of physical and mental activity
Myxedema
an autoimmune disease causing high metabolism, weight loss, and irritability
Graves’ disease
Enlarged thyroid: result is either hyposecretion or hypersecretion of hormones
Goiter
Parathyroid Glands: Location
surround thyroid gland
Parathyroid Glands: Secretion
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
PTH function
works antagonistically to calcitonin (thyroid hormone) in regulating Ca2+ level
Regulation of calcium homeostasis:
-Parathyroid hormone: stimulate the removal of calcium from bone/urine and uptake of calcium in digestive tract
-Calcitonin (thyroid): take excess and but back in bone and no longer uptake
-Calcitonin and PTH regulate Ca2+ level
-Negative feedback cycle
Pancreas: Function (mixed)
Endocrine (insulin and glucagon) (alpha-a-glucAgon) (beta-insulin)
Exocrine (digestive enzymes)
Endocrine function of Islets of Langerhans in pancreas
Alpha cells - glucagon
Beta cells - insulin
Insulin stimulates…
-Glucose uptake from blood
-Inhibits glucose release from liver
-Result: Free glucose level reduced
Glucagon stimulates…
-Glycogenolysis: Liver converts glycogen to glucose
-Gluconeogenesis: Production of glucose from non-carbohydrates
Result: Glucose level rise
group of related disorders characterized by high blood glucose level. Most common endocrine disorder (may lead to blindness and possibly death)
Diabetes mellitus
Decline in number of beta cells, injections of insulin, Autoimmune disorder
Type 1 [Insulin dependent]
Lack functional receptors on target cells, Regulation by exercise and diet
Type II [insulin independent]
Metabolic disturbances in diabetes mellitus (50
- Decreased use of glucose: cells have difficulty taking up glucose (glucose in urine)
-Dehydration: water follows glucose osmotically into urine
-Increased fat mobilization: energy source needed (ketone bodies may accumulate)
-Electrolyte imbalance: ketones take Na, K, and other cation with them not urine
-Increased protein use: another energy source and often = thin, emaciated
Low blood glucose concentration
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia Develpoment
Delayed response to carbohydrate (glucose) intake followed by overreaction of islets
- Insulin hypersecretion: Glucose levels fall, and individual becomes drowsy, uncoordinated or unconscious
Can develop is diabetic receives too much insulin
Serious Hypoglycemia (insulin shock)
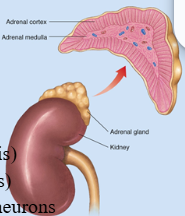
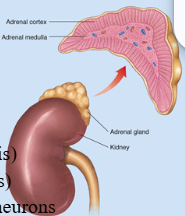
Location of adrenal glands:
above kidneys
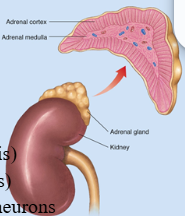
Structure of adrenal glands
Adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
Adrenal cortex Location and hormones
outer tissue region
-Androgens: precursors to sex hormone testosterone and estradiol
-Aldosterone: acts on kidneys to regulate Na+ and K+ to maintain blood volume and pressure
-Cortisol: stimulates glucose production by liver cells during stress
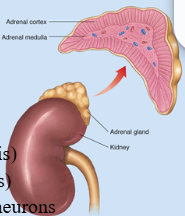
Adrenal medulla Location and hormones
inner tissue region
- epinephrine and norepinephrine
Adrenal medulla hormones increase….
Metabolic rate, Circulation of brain, muscles, and heart, Conversion of glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis)
Hormones of medulla Controlled by s
sympathetic nervous system (hypothalamus)
-During stress, hypothalamus signals sympathetic neurons triggers hormone release