Oxidative Stress
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
Is normally produced by ________ (s) ■ important & widespread signaling molecule ■ vasodilator, neurotransmitter, role in inflammation, etc.
Nitric Oxide Synthase
2
New cards
________ may increase 8- OH- G levels by 30- 50 %.
Cigarette smoking
3
New cards
○ Has a major role in many (almost all) pathologies ROS: Generation ● ________ has two unpaired electrons ● When O2 picks up another electron → superoxide radical (O2)- ○ Some oxidant activity with limited membrane permeability ● Superoxide production by ETC of Mitochondria ○ Mitochondria (MTC)- Major Source of Intracellular ROS ○ Electron transport chain (ETC)- responsible for 4 e- reduction of O2 to H2O ○ A small quantity of is generated as e- escapes ■- 1- 3 % of e- going through the ETC leak and generate ROS ■ Mainly from Complex I and Complex III of ETC ● Generation of the Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydroxyl Radical ○ O2-
Molecular oxygen
4
New cards
Is converted to the more stable H2O2 via the action of superoxide dismutase (SOD) ○ H2O2 is somewhat lipid soluble and diffuses across cell membranes ○ H2O2 is not a radical but is considered a(n) ________ as it easily generates the hydroxyl radical via two mechanisms ■ Fenton reaction.
ROS
5
New cards
________ may reverse oxidation of methionine ■ Degradation of Modified Proteins by the PROTEASOME ● Oxidation of proteins may expose hydrophobic patches of the protein that target it for destruction ○ Many proteins must be degraded by the cell ■ This degradation might be a part of "normal "protein turnover to regulate amount of protein; OR ■ A defense mechanism to destroy "bad "proteins (e.g.
Enzymatic system
6
New cards
increase in cell size; response to increased demand
hypertrophy
7
New cards
● Free radicals such as ROS are metabolized via antioxidant enzymes and non-enzymatic processes; i.e
UV exposure) ● Your cells know that you produce free radicals and are prepared
8
New cards
cell has mechanisms that attempt repair of free radical-induced damage ● Cell-to-cell variation in how well-equipped they are to handle free radical production ● Free radicals are detrimental when balance is lost and repair mechanisms are not working or overwhelmed → oxidative stress
defense mechanisms ○ If this fails
9
New cards
use oxygen to generate free radicals to kill organism in conjunction with phagocytosis ○ Xanthine Oxidase ■ necessary for final steps of purine catabolism to uric acid ■ In process, molecular oxygen is reduced to O2 free radical ○ Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) ■ Metabolism of catecholamines in nerve terminals and other cells ■ Generates H2O2 ● Environmental Factors that may Increase ROS ○ Ionizing radiation (ultraviolet, X-rays) ■ Pollutants ■ Cig smoke ■ Environmental/Workplace chemicals ■ Drugs Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS) ● Nitric Oxide (NO
neutrophils, macrophages) ■ Activated as response to invading pathogens ■ "The respiratory/oxidative burst"
10
New cards
a free radical that possesses a single electron ○ NO
)
11
New cards
combines with O2 or to form ○ Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS) or if also containing an oxygen (RNOS) ■ NO
is usually at low concentrations that do not cause damage ○ High concentrations
12
New cards
Regeneration of active form of Vitamin E ■ May interact with free radicals directly (donates electrons)
■ ○ Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) ■ Principal role
13
New cards
● Inhibit free radical producing enzymes (e.g
■ ○ Flavonoids ■ Multiple compounds with a flavone backbone ■ May have multiple mechanisms
14
New cards
● DNA ○ -10,000 DNA assaults/cell/day ○ Usually mediated by OH
xanthine oxidase) ● May chelate Fe2+ and therefore inhibit Fenton rxn ● May act as free radical scavengers ○ Lycopenes ■ Linear unsaturated hydrocarbon ● Red pigment of plants ■ Antioxidant Effects ● Quench free radicals ● Increase expression of antioxidant enzymes Free Radical-Induced Damage ● Free radicals set off chain reactions in which e-are extracted from other molecules
15
New cards
■ Mispairing ■ Strand breaks ■ Excision of bases ■ Cross-linking ○ Certain anti-cancer drugs depend on these mechanisms to produce their tumor cell killing ○ Mitochondrial DNA may be very sensitive to oxidative stress
○ Many regions of DNA molecule are susceptible (bases, deoxyribose backbone) ○ For DNA bases -existing DNA double helix as well as nucleotide pool may be modified ○ Mechanisms of damage include
16
New cards
e.g
○ Defenses ■ Depending on protein or amino acid structure and type of modification there may be a few specific defenses
17
New cards
increase in cell number; response to increased demand
hyperplasia
18
New cards
change in cell type
metaplasia
19
New cards
decrease in cell size; response to decreased nutrients or decreased demand
atrophy
20
New cards
cell injury is __________ especially if the stressor is removed
reversible
21
New cards
when cell death is irreversible, it frequently results in ___________
cell death
22
New cards
molecule with a single unpaired electron
radical
23
New cards
radical atom or molecule capable of independent existence
free radical
24
New cards
oxygen-containing radical species
reactive oxygen species
25
New cards
cellular repair mechanisms are not working/overwhelmed; free radicals are detrimental
oxidative stress
26
New cards
major source of intracellular ROS
mitochondria
27
New cards
O2. is converted to the more stable H2O2 via the action of what enzyme?
superoxide dismutase
28
New cards
conversion of O2.- to H2O2 using iron or copper as an electron donor
fenton reaction
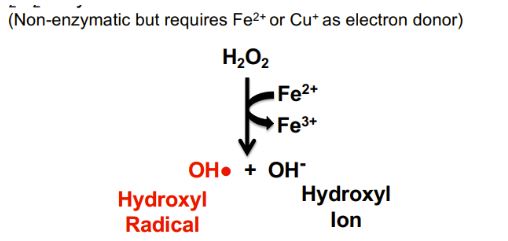
29
New cards
conversion of O2.- to H2O2 using hydroxyl as an electron donor
haber-weiss reaction
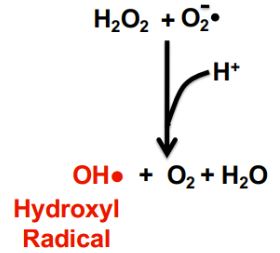
30
New cards
enzyme predominant in liver; uses electrons to activate oxygen for reactions & increases ROS
cytochrome p450 enzymes
31
New cards
enzyme that increases ROS in response to invading pathogens
NADPH Oxidase
32
New cards
enzyme that increases ROS that is necessary for the final steps of purine catabolism to uric acid; molecular oxygen is reduced to O2 free radical
xanthine oxidase
33
New cards
enzyme that increases ROS through metabolism of catecholamines in nerve terminals
monoamine oxidase
34
New cards
free radical that is important in vasodilation, neurotransmission, inflammation; also called RNS
nitric oxide free radical
35
New cards
primary defense against oxidative stress
antioxidant dismutase (SOD)
36
New cards
ion expressed in the mitochondria that works with SOD to protect from ROS
Mn 2+
37
New cards
ions expressed in the cytosol that work with SOD to protect from ROS
Cu +, Zn 2+
38
New cards
tripeptide of glutamate-cysteine-glycine
glutathione
39
New cards
enzyme that handles H2O2 outside the peroxisome; contains selenium
glutathione peroxidase
40
New cards
enzyme necessary to cycle GSSG back to reduced form
glutathione reductase
41
New cards
enzyme found in most plant and animal cells that functions as an oxidative catalyst; highest levels in liver and kidney
catalase
42
New cards
transcription factor that regulates the work of antioxidant proteins that can help protect against oxidative damage
NRF2
43
New cards
nonenzymatic antioxidant that breaks chains of lipid peroxidation; obtained via diet
vitamin e
44
New cards
nonenzymatic antioxidant that regenerates the active form of vitamin e; may interact with free radicals directly
vitamin c; ascorbic acid
45
New cards
nonenzymatic antioxidant that inhibits free radical-producing enzymes, inhibit the fenton rxn, and/or act as free radical scavengers
flavonoids
46
New cards
nonenzymatic antioxidant that gives plants red pigment; quenches free radicals, increases expression of antioxidant enzymes
lycopenes
47
New cards
mechanisms of free-radical damage of dna
mispairing, strand breaks, excision of bases, cross linking
48
New cards
certain anti-__________ drugs depend on dna damaging mechanisms to produce their tumor cell killing
cancer
49
New cards
free radical attack of __________ includes attack at the membranes in a chain reaction known as ___________ peroxidation
lipids
50
New cards
free radical attack of __________ causes modifications in fully synthesized _________, peptides, or individual amino acids
protein
51
New cards
loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra - functions with other basal ganglia units as it acts as an integration area
parkinson's disease
52
New cards
intraneuronal structures that lack membranes found in substantia nigra of parkinson's patients
lewy bodies