Lecture 4- peptide and steroid hormones synthesis and
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
hormone
substance released from endocrine gland into circulation and transported to distant organ where it exerts specific action
molecular varieties of hormone
GPCR ligands e.g. vasopressin, growth hormone, parathyroid hormone
receptor tyrosine kinase ligands e.g. insulin
steroids e.g. cortisol, aldosterone, sex hormones
GPCR ligands
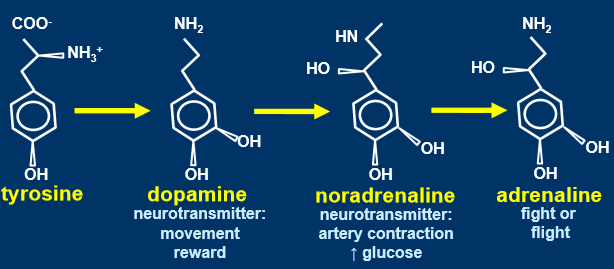
respond to polypeptide or modified amino acids
change structural amino acid into signal through slight change
tyrosine is amino acid, othrs are modified amino acids
amino acid multitasking
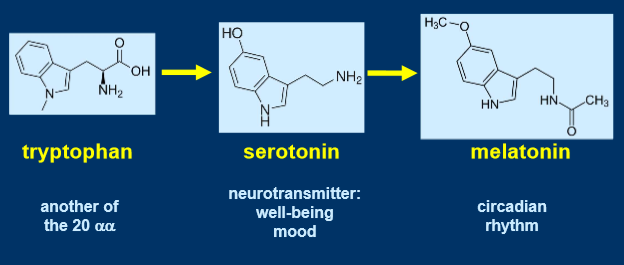
tryptophan is an essential amino acid
tryptophan can’t be made by itself
when some amino acids are modified, they can produce 2 hormones
efficiency
cost to getting tryptophan into the body, need to eat, digest and absorb into the body
need a few enzymes to turn amino acid into hormones
use chemicals already there instead of having completely new ones
being less efficient makes it more adaptable
adaptability in stressful environment important to adapt and evolve
peptide hormone formation and secretion - peptide hormone synthesis
synthesised on ribosomes as prehormone or preprohormone, initial signal sequence 15-25 amino acids
signal sequence binds to signal recognition particle
complex binds to receptor to rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane
signal sequence cleaved off, inactive storage form, further processing
leader sequence directs the protein, allows protein to form correctly, gets cut off before secreting as mature protein
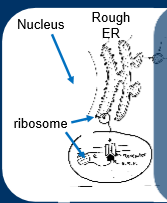
peptide hormone formation and secretion- formation of transport vesicles to transfer peptide to Golgi
post-translational modification
sorting and packaging of proteins to different places, use chaperones
filter incorrectly synthesised proteins
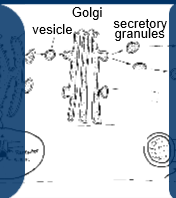
peptide hormone formation and secretion - secretion(exocytosis)
secretory granules translocate to plasma membrane, involves cytoskeleton(microfilaments and microtubules)
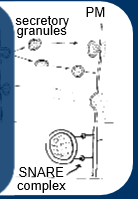
docking and fusion of secretory granules with plasma membrane, involves docking and fusion proteins (SNAPS,SNARES,VAMPS)
secretion is regulated
rate of hormone secretion> > rate of synthesis
vesicles dock at cell membrane, wait for signal to dock and fuse with membrane, signal usually intracellular calcium
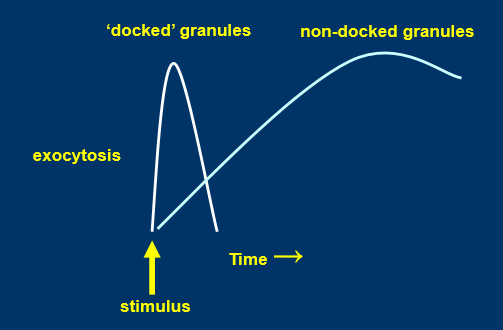
biphasic secretion of peptide hormones
2nd wave of secretion due to non docked granules
adrenaline creates a short spike
more extended period of secretion keeps vesicles docked longer
peptide hormone action
transported via circulation
bind with high affinity and specificity to cell surface receptors on target cell
hormone binding, conformational change in receptor, relayed to effector, generation of intracellular signals, cellular response
sequence can dissolve, aqueous can dissolve in blood
some cells have extracellular space feeding into blood
receptor
plasma membrane protein with 3 functional domains- extracellular(hormone binding), 1-7 membrane spanning domains(hydrophobic amino acids), intracellular(effector function)
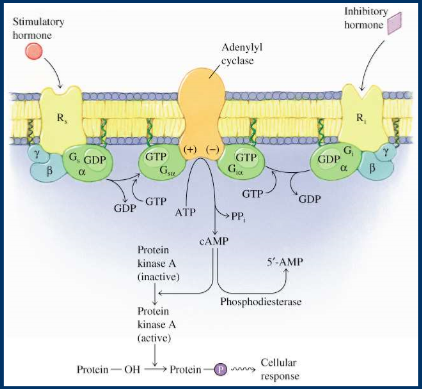
adenylate cyclase, cyclic AMP
adenylyl cyclase converts ATP into cAMP
GPCR has 3 different proteins, alpha, beta, gamma
alpha binds to GDP when turned off, binds to GTP when on
Gi inhibitory hormone, inhibits AC, lower cAMP
need mechanisms that can modulate each other
cAMP activates protein kinase A
tyrosine, serine, threonine can be phosphorylated
GPCR pathways involve serine and threonine more
proteins phosphorylated on serin, threonine and tyrosine
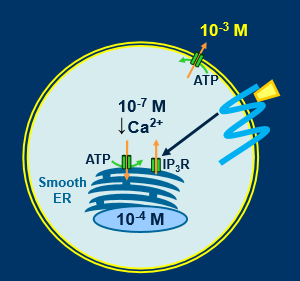
calcium mobilising receptors
cytosolic calcium maintained at low levels(10-7M)
can pump big fluxes of Ca very quickly
calcium floods in, contracts cell, pumps out, relaxes cell
IP3 receptors on calcium store
cells can be activated by rise in cytosolic calcium
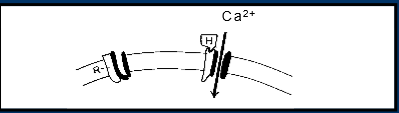
Ca entry from extracellular fluid
via membrane Ca channels
receptor operated Ca channels e.g. H1 histamine receptor
voltage sensitive Ca channels
histamine directly couples to channel, opens pore, Ca can enter
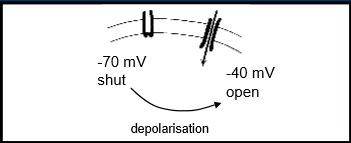
Ca channel kept shut at -70mV
Ca mobilisation from smooth endoplasmic reticulum
phosphatidylinositol cleaved into inositol 1,4,5 triphosphate
rise in cytosolic Ca detected by calcium binding protein
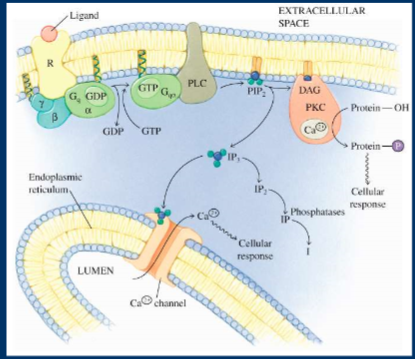
tyrosine kinase coupled receptor
hormone binding, activation of tyrosine kinase, phosphorylation of target proteins on tyrosine residues, cascade of protein phosphorylation, cellular response
span membrane once
work as homodimers
stimulate receptor, auto-phosphorylate each other
small signal gets amplified, small amount of hormone to spark signal that turns into large response
small amount of insulin affects the whole body
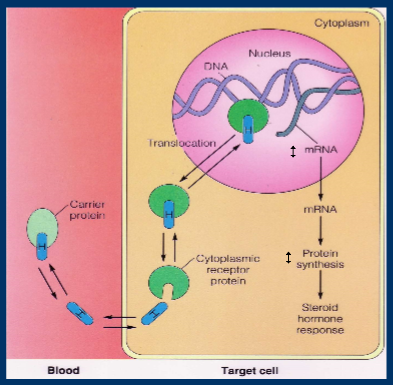
steroid hormones
made from cholesterol
cholesterol stabilises cell membrane
insoluble in blood, need carrier proteins to transport them around the blood
binding proteins specific to each steroid hormone
enters the cell and has intracellular effects
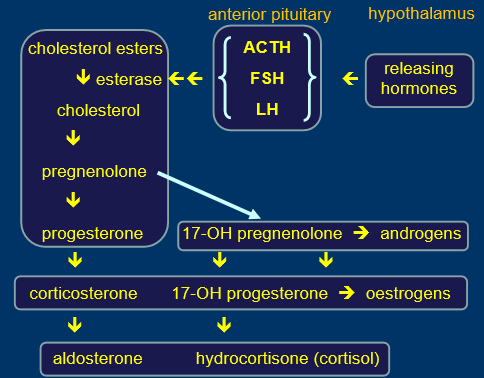
steroid hormone synthesis
made in adrenals
hypothalamus secretes releasing hormone, signal for cholesterol esters
all steroid hormones are very similar, can make one from another
closely related and interchangeable
don’t need vesicular fusion
steroids not stored
rate of synthesis=rate of release
transported in protein bound form
mechanism of steroid hormone action
expression of specific genes altered, increase or decrease specific cellular proteins, cellular response
cellular response is slow and prolonged
big burst of cortisol drives gene expression of a lot of cells
adrenaline very rapid burst, no long term consequence