Cell biology (P1)
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What do both plant and animal cells have? (3)
cell membrane
cytoplasm
genetic material enclosed in a nucleus
what are eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and which is smaller?
Eukaryotic = plant + animal cells
Prokaryotic = bacteria
Prokaryotic are the smallest.
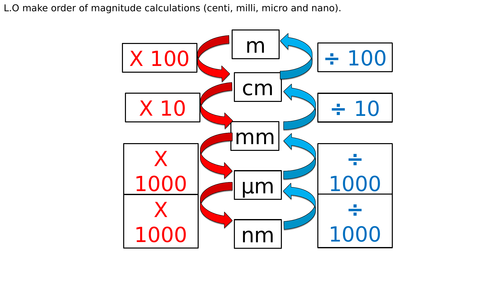
how do you convert? (Order of magnitude)
Name the parts of animal cells. (5)
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Cell membrane
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
What is the function of the nucleus?
Contains genetic material, including DNA, which controls the cell’s activities.
What is the function of cytoplasm?
A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. It is where many of the chemical reactions happen.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its structure is permeable to some substances but not to others. It therefore controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration.
What is the function of ribosomes?
Tiny structures where protein synthesis occurs.
In addition to the parts found in animal cells, what parts do plant cells have? (3)
Chloroplasts
A permanent vacuole filled with cell sap
Cell wall
What is a cell wall made of?
Cellulose
Why are sperm cells specialised?
Sperm cells are specialised for reproduction. They have a streamlined shape for efficient swimming, a flagellum for motility, and contain enzymes in the acrosome to penetrate the egg.
Why are nerve cells (neurones) specialised?
Nerve cells are specialized for transmitting signals. They have long axons for distance communication, dendrites to receive signals, and myelin sheaths for faster signal conduction.
Why are muscle cells specialised
Muscle cells are specialized for contraction and movement. They contain numerous mitochondria for energy, and their elongated structure allows for coordinated contractions and force generation.
Why are root hair cells specialised?
Root hair cells are specialized for water and nutrient absorption. They have a large surface area and thin walls to facilitate efficient uptake from the soil.
Why are xylem cells specialised?
Xylem cells are specialized for water transport. They have thick, lignified walls for structural support and are hollow to allow for the efficient flow of water and minerals from roots to leaves.
Why are phloem cells specialised?
Phloem cells are specialized for transporting sugars and nutrients. They have sieve plates for efficient flow and companion cells that support metabolic functions and help manage the transport process.
Why is cell differentiation important?
Cell differentiation is crucial because it allows organisms to develop specialized cells that perform specific functions, contributing to the overall complexity and functionality of the organism.
When do most types of animal cells differentiate?
Most types of animal cells differentiate at an early stage of development, leading to the formation of various specialized cell types.
How does cell differentiation differ in plants?
Many types of plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughout their life, allowing for continuous growth and adaptation.
What is the role of cell division in mature animals?
In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacement of cells rather than growth.
What happens as a cell differentiates?
As a cell differentiates, it acquires different sub-cellular structures that enable it to carry out specific functions, resulting in the formation of specialized cells.
What should students understand about microscopy techniques?
Students should understand how microscopy techniques have developed over time.
How has electron microscopy increased our understanding of sub-cellular structures?
Electron microscopy has much higher magnification and resolving power than light microscopy, allowing for the study of cells in finer detail.
What is a key difference between electron microscopes and light microscopes?
An electron microscope has much higher magnification and resolving power than a light microscope, enabling the observation of more sub-cellular structures.
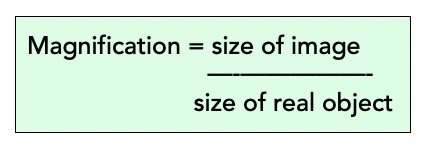
What is the formula for magnification?
How do bacteria multiply?
Bacteria multiply by simple cell division (binary fission) as often as once every 20 minutes if they have enough nutrients and a suitable temperature.
How can bacteria be grown?
Bacteria can be grown in a nutrient broth solution or as colonies on an agar gel plate.
Why are uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms required?
Uncontaminated cultures are required for investigating the action of disinfectants and antibiotics.
What should students describe regarding preparing uncontaminated cultures?
Students should be able to describe how to prepare an uncontaminated culture using aseptic technique.
Why must Petri dishes and culture media be sterilized before use?
Petri dishes and culture media must be sterilized to prevent contamination.
Why must inoculating loops be sterilized by passing through a flame?
Inoculating loops must be sterilized to eliminate any existing microorganisms that could contaminate the culture.
What conditions are important for incubating bacterial cultures?
Incubation conditions include maintaining the right temperature, humidity, and oxygen levels to promote bacterial growth.
What characteristics can be observed in bacterial colonies?
Characteristics include shape, size, color, texture, and elevation, which help in identifying different bacterial species.

JAKE BREAK 💝
JAKE BREAK 💝

What does the nucleus of a cell contain?
Chromosomes made of DNA molecules
What is the process in which cells divide called?
The cell cycle
What happens to genetic material during the cell cycle?
It is doubled and then divided into two identical cells
What must a cell do before it can divide?
Grow and increase the number of sub-cellular structures (e.g., ribosomes and mitochondria).
Why does DNA replicate before cell division?
To form two copies of each chromosome.
What happens during mitosis?
One set of chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell, and the nucleus divides.
What happens after mitosis to complete cell division?
The cytoplasm and cell membrane divide, forming two identical cells.
Why is mitosis important for multicellular organisms?
It is essential for growth and development.
Do students need to know the different phases of mitosis?
No, they only need to understand the three overall stages of the cell cycle.
What should students be able to recognize regarding mitosis
Situations in given contexts where mitosis is occurring.
What is a stem cell?
A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell capable of producing many more cells of the same type and differentiating into other specialized cells.
What is the function of stem cells in embryos?
They can differentiate into most different types of human cells.
What is the function of stem cells in adult animals?
They can form many types of cells, such as blood cells from bone marrow stem cells.
What is the function of stem cells in plant meristems?
Meristem tissue can differentiate into any type of plant cell throughout the plant’s life.
What is a key ability of stem cells from human embryos?
They can be cloned and made to differentiate into most types of human cells.
What type of cells can stem cells from adult bone marrow form?
They can form many types of cells, including blood cells
How long can meristem tissue in plants differentiate into new cells?
Throughout the entire life of the plant.
How might stem cell treatment help certain medical conditions?
It may help treat conditions such as diabetes and paralysis
What is therapeutic cloning?
In therapeutic cloning, an embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient. Stem cells from the embryo are not rejected by the patient’s body and may be used for medical treatment.
What are potential risks of using stem cells?
Stem cell use carries risks such as the transfer of viral infection. Additionally, some people have ethical or religious objections.
How can stem cells from meristems in plants be used?
Stem cells from meristems can be used to produce clones of plants quickly and economically
How can cloning help protect rare species?
Rare species can be cloned to help protect them from extinction.
How can cloning benefit agriculture?
Crop plants with special features, such as disease resistance, can be cloned to produce large numbers of identical plants for farmers.

JAKE BREAK 💝
JAKE BREAK 💝

What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the spreading out of the particles of any substance in solution or particles of a gas, resulting in a net movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
How do substances move into and out of cells?
Substances move into and out of cells across the cell membrane via diffusion.
What substances are transported by diffusion in cells?
Oxygen and carbon dioxide in gas exchange, and the waste product urea from cells into the blood plasma for excretion in the kidney.
What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
1. The difference in concentrations (concentration gradient)
2. The temperature
3. The surface area of the membrane
Why can a single-celled organism transport molecules efficiently?
A single-celled organism has a relatively large surface area to volume ratio, allowing sufficient transport of molecules into and out of the cell to meet its needs.
How do you calculate and compare surface area to volume ratios?
Surface area to volume ratios are calculated by dividing the total surface area of an object by its volume. A higher ratio means more efficient exchange of materials.
Why do multicellular organisms need exchangesurfaces and a transport system?
Multicellular organisms have a smaller surface area to volume ratio, so they require specialised exchange surfaces and transport systems to move sufficient molecules into and out of cells.
How are the small intestine, lungs, gills, roots, and leaves adapted for exchanging materials?
These structures have adaptations such as a large surface area, thin membranes for a short diffusion path, and (in animals) efficient blood supply and ventilation for gaseous exchange.
Why are surfaces and organ systems specialised for exchanging materials in multicellular organisms?
Specialised surfaces allow sufficient molecules to be transported into and out of cells to meet the organism’s needs.
What increases the effectiveness of an exchange surface?
1. A large surface area
2. A thin membrane for a short diffusion path
3. An efficient blood supply (in animals)
4. Ventilation for gaseous exchange (in animals)
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane.
What is active transport?
Active transport moves substances from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution (against a concentration gradient). This process requires energy from respiration.
How do plants use active transport?
Plants absorb mineral ions into root hairs from very dilute soil solutions using active transport. These ions are essential for healthy growth.
How is active transport used in the human body?
In the gut, active transport absorbs sugar molecules from lower concentrations into the blood, which has a higher concentration. These sugars are used for cell respiration.
What are the three ways substances move into and out of cells?
1. Diffusion – movement from high to low concentration, no energy needed.
2. Osmosis – diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane from high to low water concentration.
3. Active transport – movement from low to high concentration (against the gradient), requiring energy.
What is the key difference between diffusion, osmosis, and active transport?
• Diffusion & osmosis do not require energy, while active transport does.
• Diffusion & active transport move solutes, while osmosis moves water.
• Diffusion & osmosis move substances from high to low concentration, while active transport moves substances from low to high concentration.

JAKE BREAK 💝
JAKE BREAK 💝
