module 1 studyguide atoms, ions and chemical bonds
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Atom
Smallest particle still characterizing a chemical element
Cannot be cut into smaller particles, the atoms of modern parlance are composed of subatomic particles: electrons, neutrons, and protons
Electron
Have a negative charge, a size which is so small as to be currently unmeasureable
Proton
Positive charge, and are about 1836 times more massive than electrons
Neutron
No charge, and are the same size as protons.
Both this and protons make up the nucleon (nucleus). Electrons make up the electron cloud surrounding it.
Atomic mass
The sum of the proton and neutrons in an atom is equal to the atomic mass of the atom
Atomic number
The number of protons in an atom is given as its atomic number
ex: carbon has six protons → atomic number is 6
Isotopes
Of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons.
Covalent bond
bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms
Ionic bond
bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom, resulting in positive and negative ions which attract each other
Hydrogen bond
H, N, O, F
stronger IMF than covalent bond, making it more polar
Acids
Are ionic compounds (a compound with a positive/negative charge) that break apart in water to form a hydrogen ion (H+)
Characteristics:
Taste sour
React strongly with metals
Are dangerous and can burn your skin
ex: vinegar, stomach acid (HCl), citrus fruits
Bases
Are ionic compounds that break apart to form a negatively charged hydroxide ion (OH-) in water.
OH-
Characterisitics:
Taste bitter
Feel slippery
Are very dangerous and can burn your skin
ex: sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and ammonia
Neutralization reaction
When acids and bases are added to each other they react to neutralize each other if an equal number of hydrogen and hydroxide ions are present.
When this occurs, salt and water are formed.
pH
The strength of an acid or base in a solution is measured on a scale.
>7 is base
<7 is acid
7 is neutral
0-14
Galactosemia
An inherited autosomal recessive trait that affects the way the sugar galactose is broken down, due to the lack of the enzyme galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase.
In this, galactose builds up and becomes toxic from the body using glucose for energy. In reaction to this build up of galactose, the body makes some abnormal chemicals.
Treatment for galactosemia
restrict galactose and lactose from the diet for life
Signs and symptoms from galactose build up
swollen and inflamed liver
kidney failure
ovarian failure in girls
mental growth
cataracts in the eyes
Functions of proteins
Binding, transport and storage - small molecules are often carried by proteins in the physiological setting (for example, the protein hemoglobin is responsible for the transport of oxygen to tissues). Many drug molecules are partially bound to serum albumins in the plasma
Molecular switching - conformational changes in response to pH or ligand binding can be used to control cellular processes .
Coordinated motion - muscle is mostly protein, and muscle contraction is mediated by the sliding motion of two protein filaments, actin and myosin
Structural support - skin and bone are strengthened by the protein collagen
Immune protection - antibodies are protein structures that are responsible for reacting with specific foreign substances in the body
Generation and transmission of nerve impulses - some amino acids act as neurotransmitters, which transmit electrical signals from one nerve cell to another. In addition, receptors for neurotransmitters, drugs, etc. are protein in nature. An example of this is the acetylcholine receptor, which is a protein structure that is embedded in postsynaptic neurons.
Control of growth and differentiation - proteins can be critical to the control of growth, cell differentiation and expression of DNA. For example, many hormones and growth factors that regulate cell function, such as insulin or thyroid stimulating hormone are proteins
If protein and caloric intake are both inadequate, a condition called marasmus occurs.
Marasmus
Form of severe protein-energy malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency. Cachexia.
Presents stoppage of growth, extreme muscle loss, and weakness.
Signs:
dry skin, loose skin folds hanging over the gluti, axillae, etc.
drastic loss of adipose tissue from normal areas of fat deposits like buttocks and thighs
are fretful, irritable, and voraciously hungry
alternate bands of pigmented and depigmented hair or flaky paint appearance of skin due to peeling
Atherosclerosis
A condition in which fatty material collects along the walls of arteries. This fatty material thickens, hardens, and may eventually block the arteries.
Ketone bodies
are three water soluble compounds that are produced as by-products when fatty acids are broken down for energy
they are used as a source of energy in the heart and brain
in the brain, vital source in fasting
name
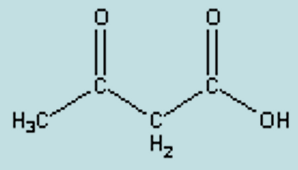
acetoacetate
name
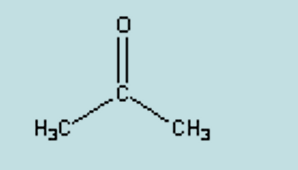
acetone
name
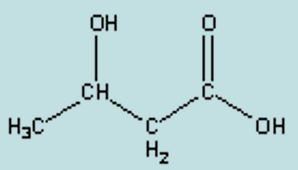
B-hydroxybutyrate
Ketoacidosis
Too many ketone bodies in the blood
In some people with diabetes mellitus, the pancreas releases insufficient amounts of insulin or no insulin at all. Consequently, glucose goes largely undelivered.
In a desperate attempt to provide fuel, the body begins feeding on itself -- that is, it breaks down muscle and fat to burn as fuel. Ketone bodies are a byproduct of this process.
Ketone bodies consist chemically of three substances (beta-hydroxybutyric acid, acetoacetic acid, and acetone).
When ketone bodies are released, they enter the bloodstream, acidify the blood, and are eventually excreted mostly in urine. (One type of ketone body exits via the lungs.) Without treatment, glucose and ketone bodies may build to dangerous levels in the blood. Stress and illness can increase the risk of glucose and ketone buildup.
Symptoms:
thirst, frequent urination
dehydration
nausea, vomiting
heavy breathing
dilation of the pupils and confusion resulting from the toxic effects of ketone bodies and acid accumulation on the brain
a breath odor resembling the smell of fruit
Treatment: with insulin and intravenous fluids, can restore normal levels of blood sugar and end ketoacidosis and ketonuria
Steroids
In term of structure, steroids differ considerably from triglycerides or phospholipids, cholesterol is an important molecule in the body because it serves as the precursor for the steroid hormones produced by gonads and adrenal cortex.
Is from cholesterol.
Prostaglandins
Is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Are found in virtually all tissues and organs.
Role:
cause constriction or dilatation in vascular smooth muscle cells
sensitize spinal neurons to pain
constrict smooth muscle
regulate inflammatory mediation
regulate calcium movement
regulate hormone regulation
control cell growth