Innovation and patents
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is an invention
Creating a new idea and overcoming practical difficulties
What is innovation?
The commercialisation of an invention
What is diffusion
Increasing the use of innovation
What types of innovation are there
Product → making products
Process → reduction in COP
Schumpeter
Monopoly associated with most innovation
have profits to invest
Willing to take risk of investment
Arrow
Compared monopoly and perfectly competitive firm for process innovation
Arrow case 1
Dramatic reduction in costs
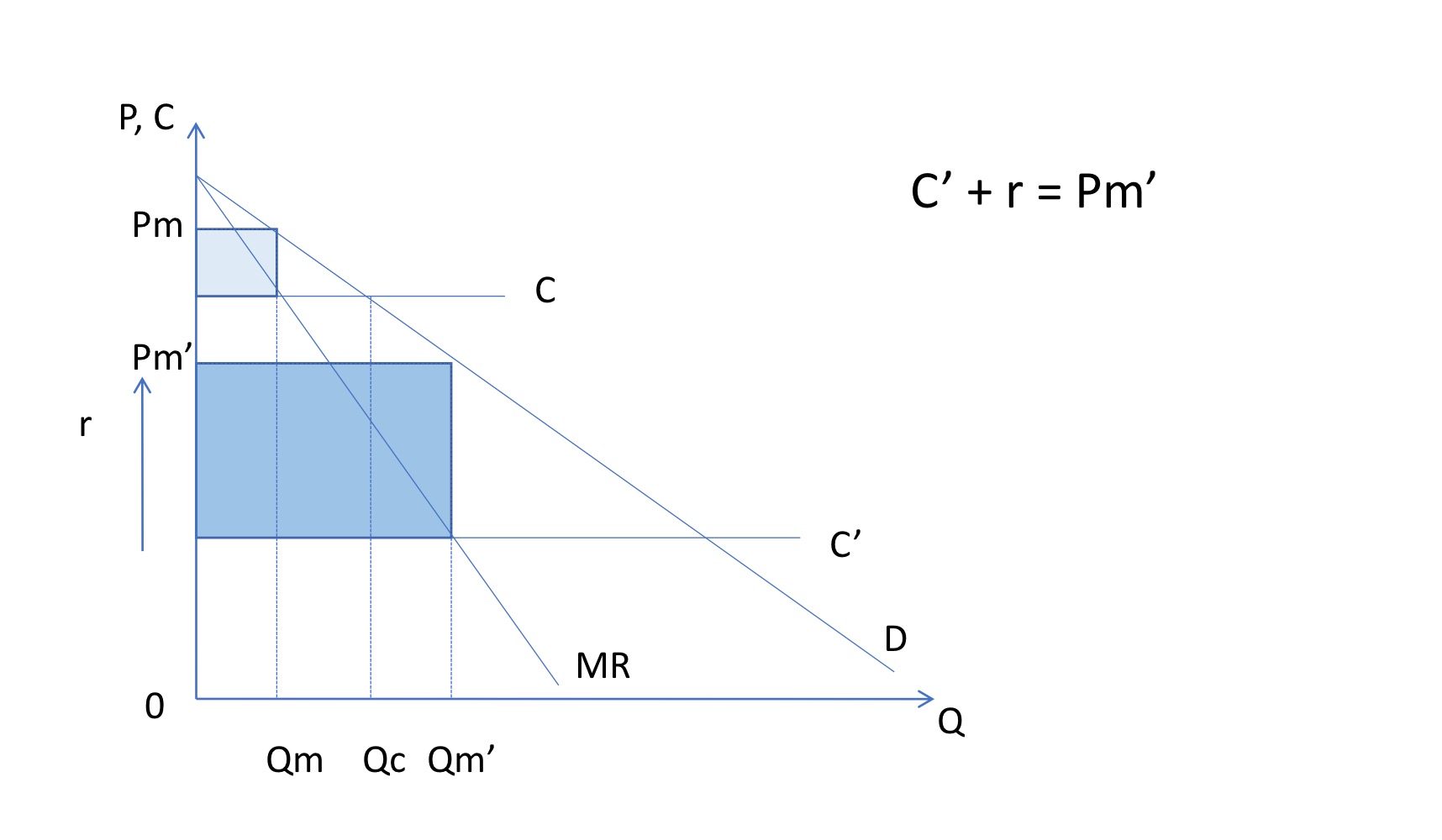
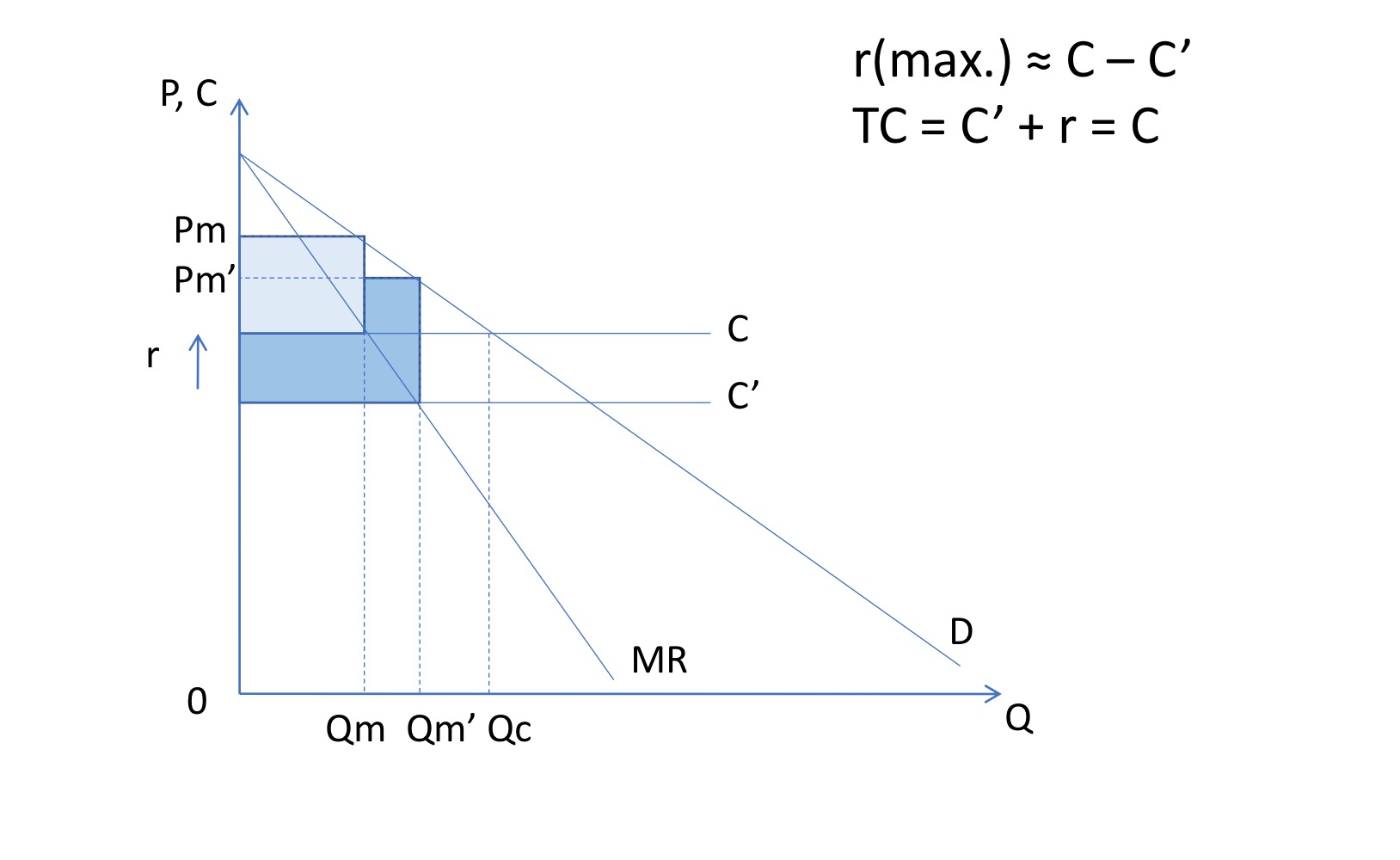
Arrow case 2
Reduction in costs isnt that big
Maximum extent of r is approximately equal to the difference between c and c’
Just tends to be slightly below c, so they have incentive to invest in innovation, because by not investing in it, they would have lower costs
Perfectly competitive firm has more incentive to innovate
What does empirical evidence say about innovation investment?
Oligopoly has most innovation spending
Results of oligopoly
New firms enter until excess profits fall to zero
As they enter, industry output increases, but firm output fall and spending on R&D falls
What is r&d to sales ratio in the short run?
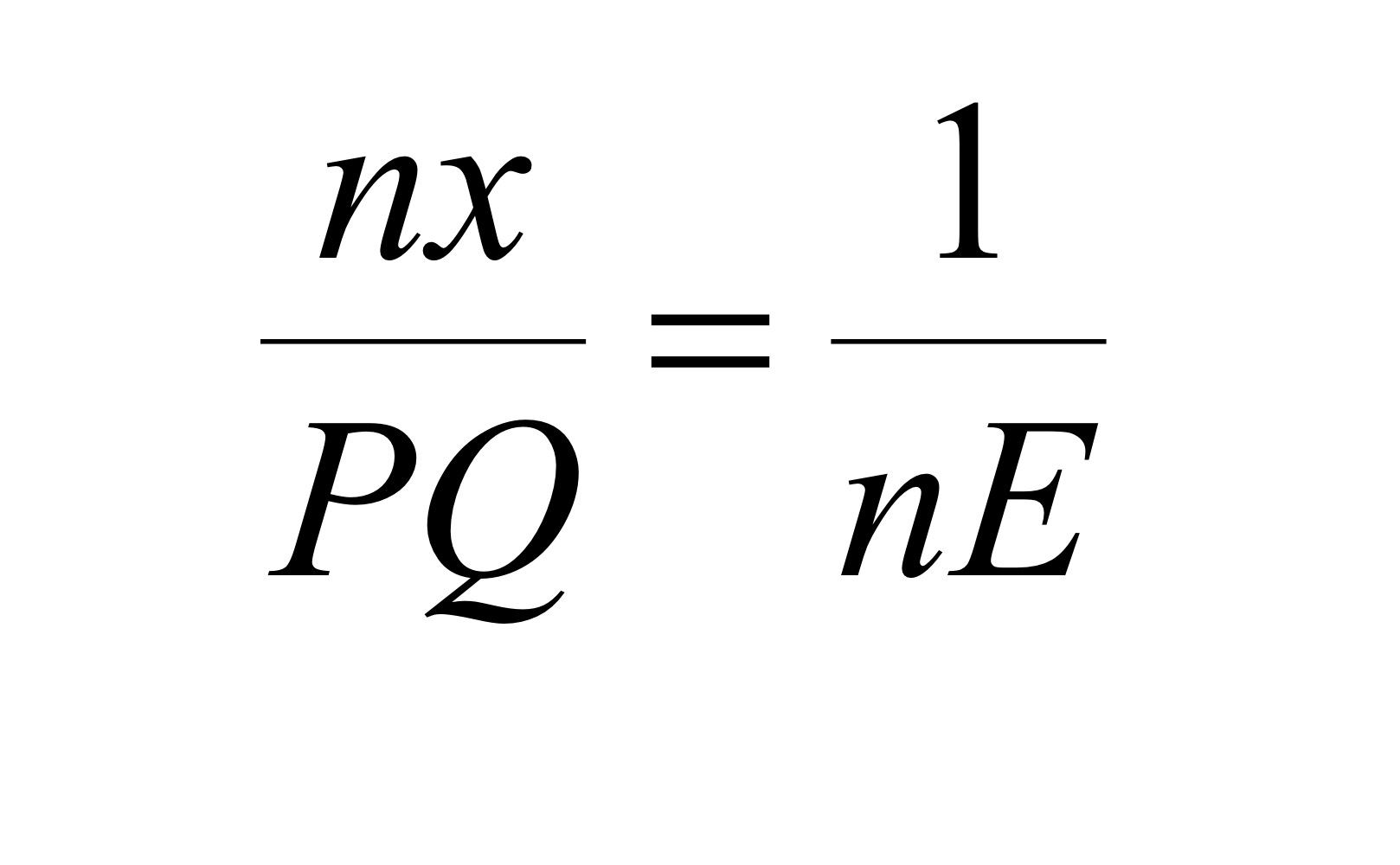
In the long run, what is the sales ratio?
Higher ita is associate with higher R&D expenditure and less firms
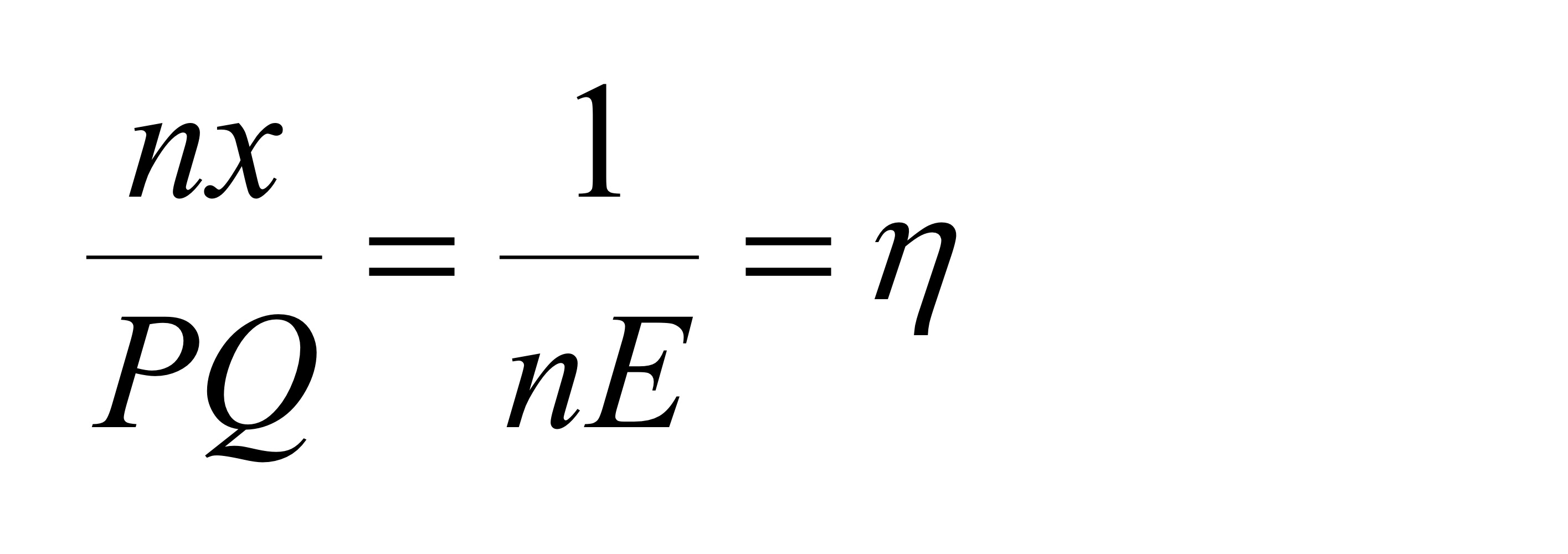
Diffusion curve?
Sigmoid
S shape
X axis, time
Y axis, prop. Adopters
Factors affecting rate of diffusion
Communication
Management inertia
Protection of market position
Worker resistance
Risk and liquidity
Regulation
Patents
Patents design
Has Qc’ and second period post innovation
Includes cost of investing → X
Case 1:
X < (r*Qm’)
Cost of innovation is les than the one period return
Meaning in period 2, worthwhile to invest
Case 2
With no patent, innovation isnt worthwhile because X is more expensive than return
There is allocative efficiency, but not at the lowest possible cost
Second best solution, but consumer and producer surplus is higher in period 2 if there is a patent