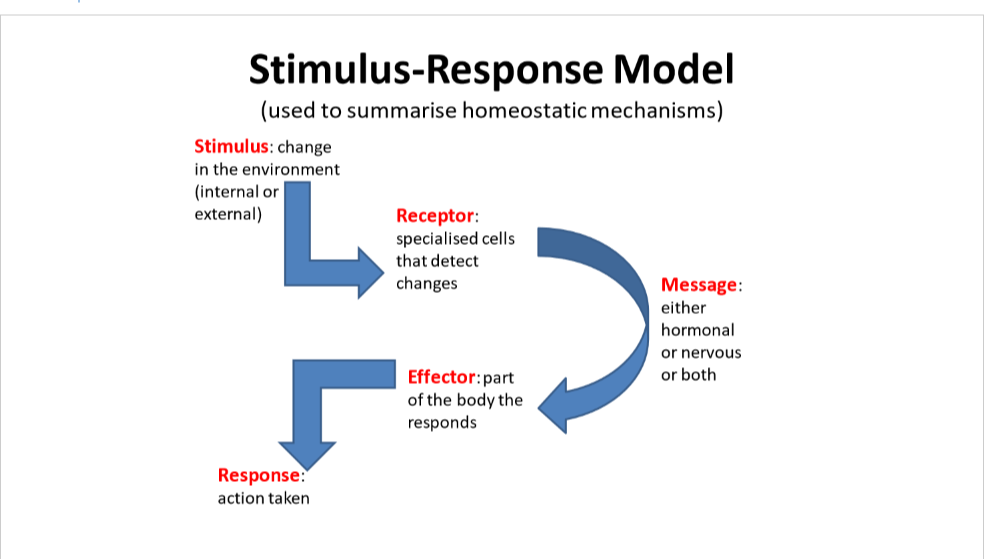
stimulus response models
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
homeostatic mechanism
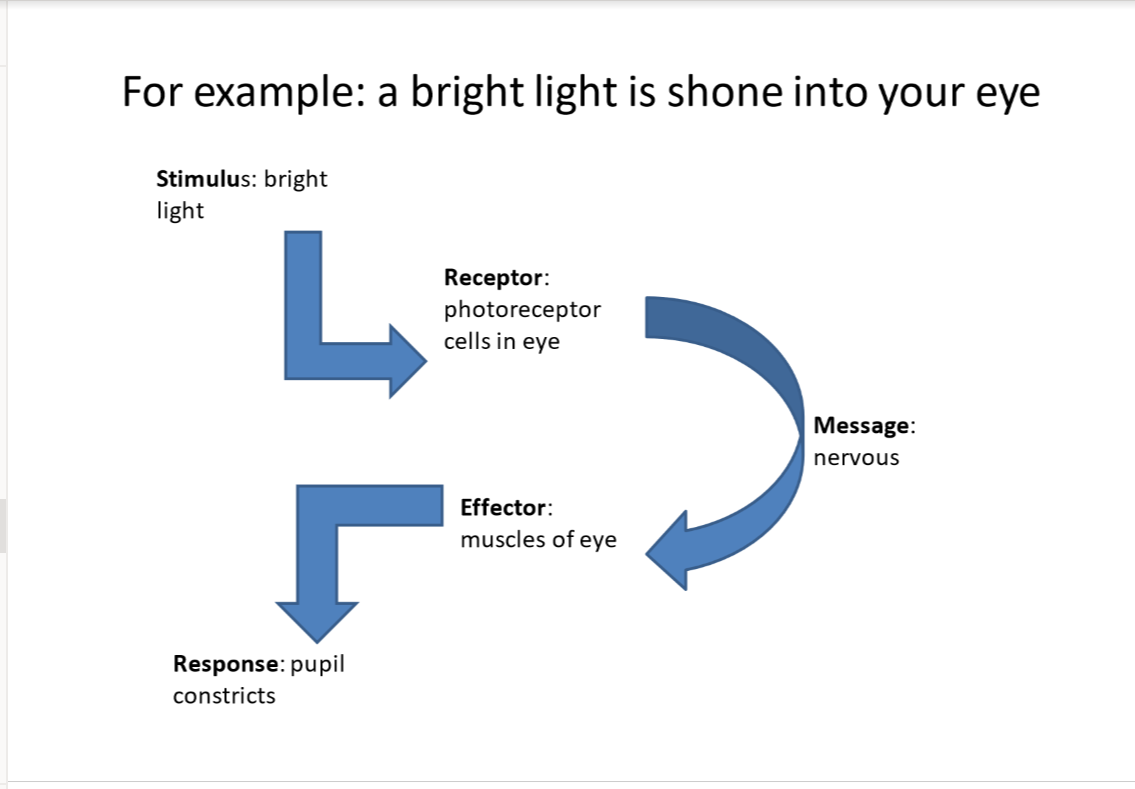
scenario: bright light being shone in your eyes
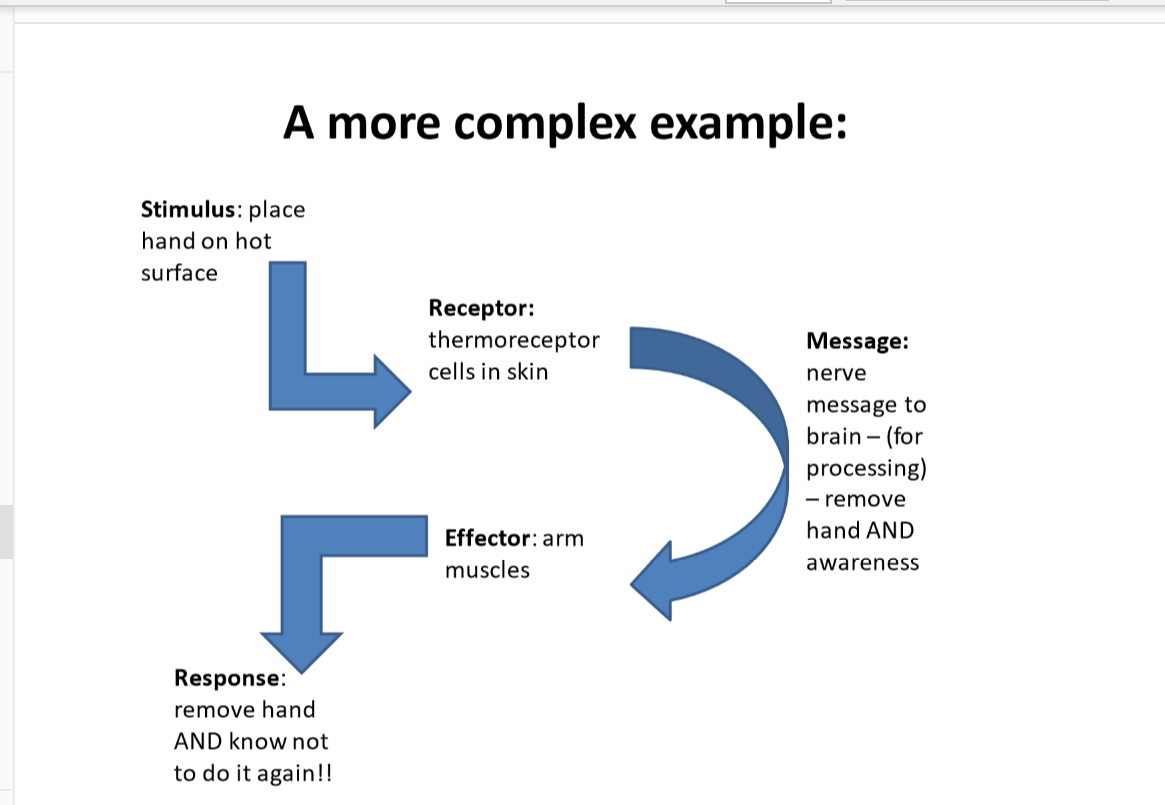
placing hand on hot stimulus
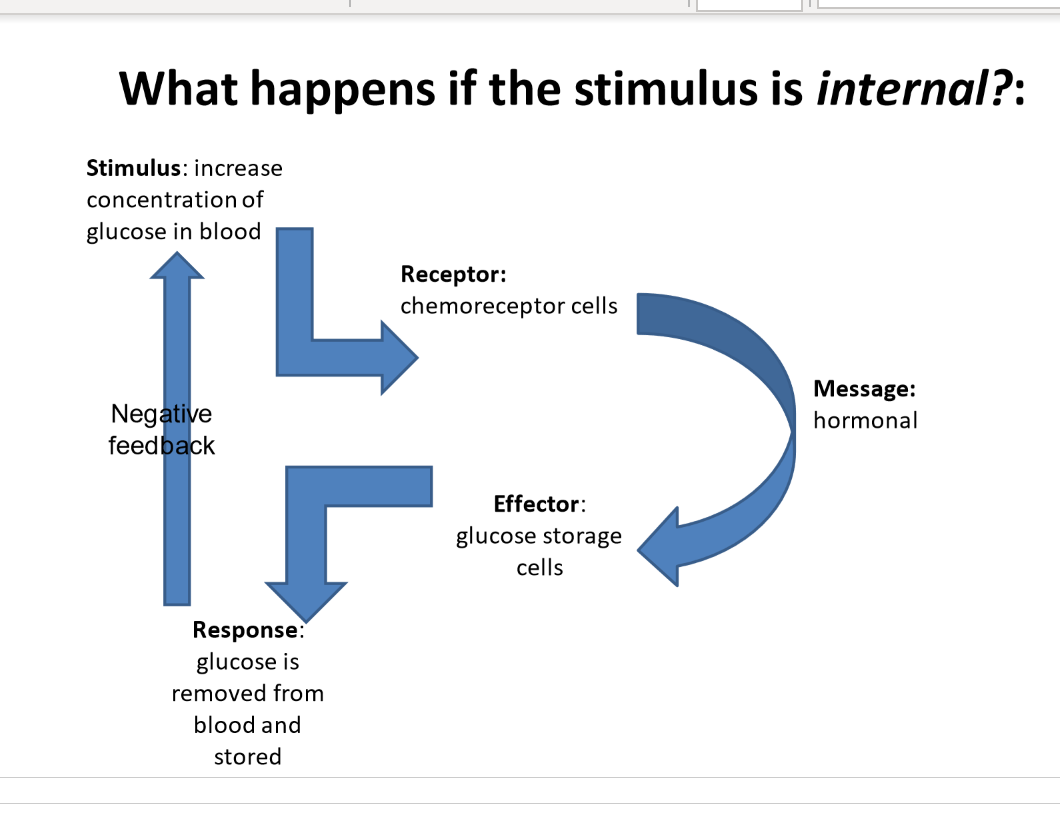
what happens if the stimulus is internal
feedback
said to occur when the response alters the original stimulus
if the feedback opposes the intensity of the original stimulus, the feedback is said to be negative
if the feedback promotes the intensity of the original stimulus, the feedback is said to be positive
control of blood glucose
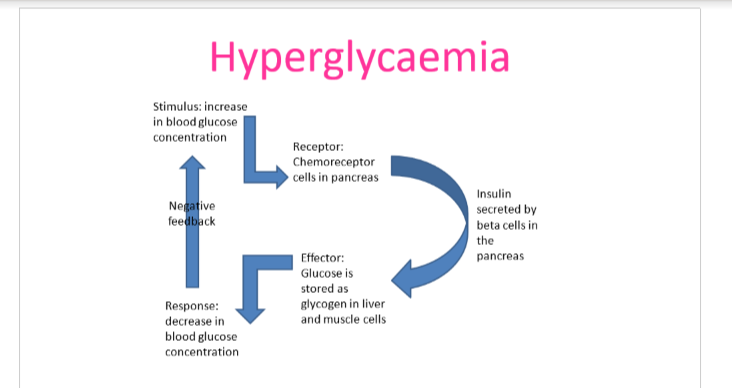
insulin produced by beta cells in the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas—receptor molecules for insulin are located on liver and skeletal muscle cells
effect: uptake of glucose from blood and storage as glycogen
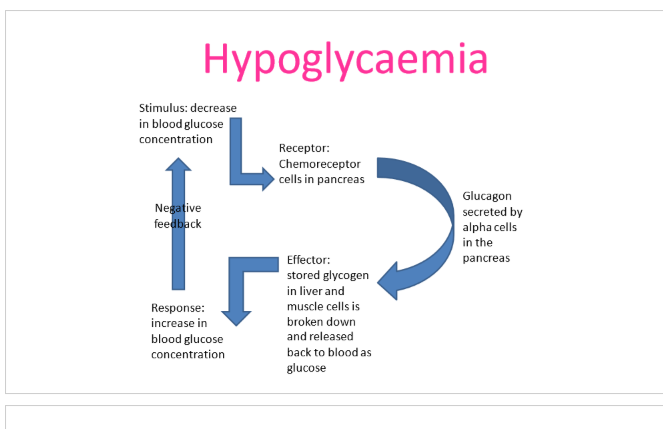
glucagon produced by alpha cells in the islets of Langerhans—receptor molecules on liver and skeletal muscle cells
effect: breakdown of stored glycogen into glucose and release of glycogen into blood
insulin and glucagon are both protein hormones
hyperglycaemia
hypoglaecemia
the relationship between insulin and glucagon
this is because insulin and glucagon are antagonistic hormones, they oppose each other’s actions

diabetes mellitus
caused by a lack of ability to produce insulin
symptoms include glucose in urine (non diabetics do not have glucose n their urine)
types of diabetes
type 1 diabetes: juvenile diabetes- detected early in life. Patients needs injections of insulin as insufficient insulin is produced.
type 2 diabetes- adult onset diabetes- gradual lack of ability to produce and metabolise insulin. may require modified diet, oral medication and/or insulin injection
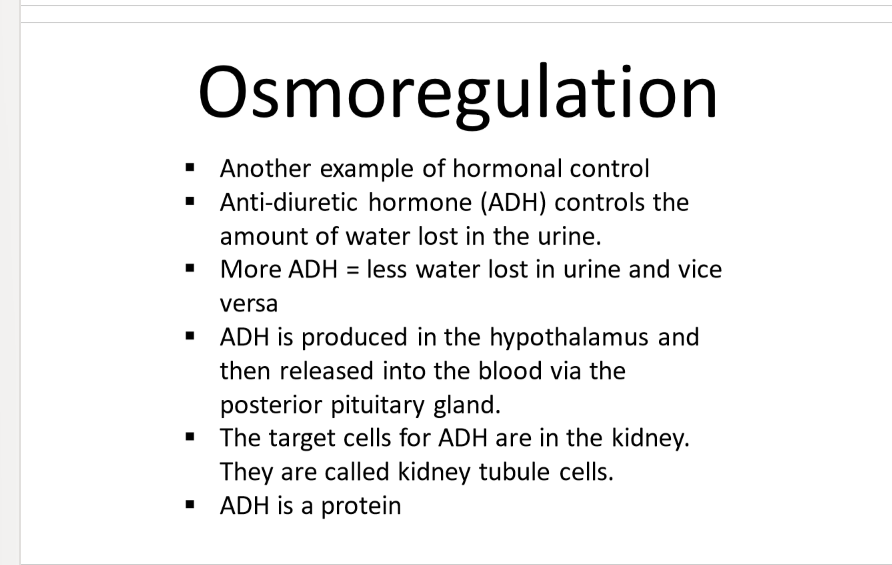
osmoregulation
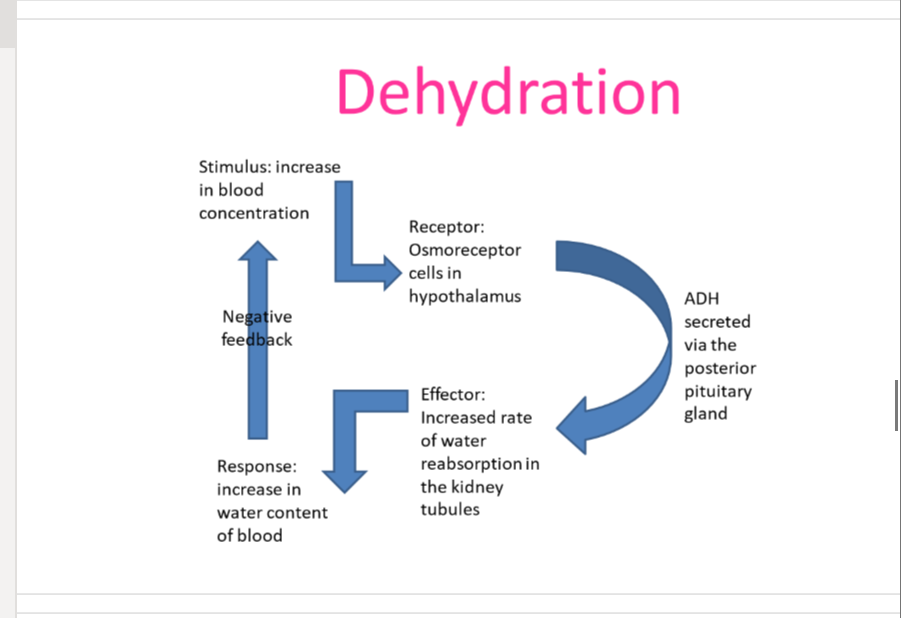
dehydration
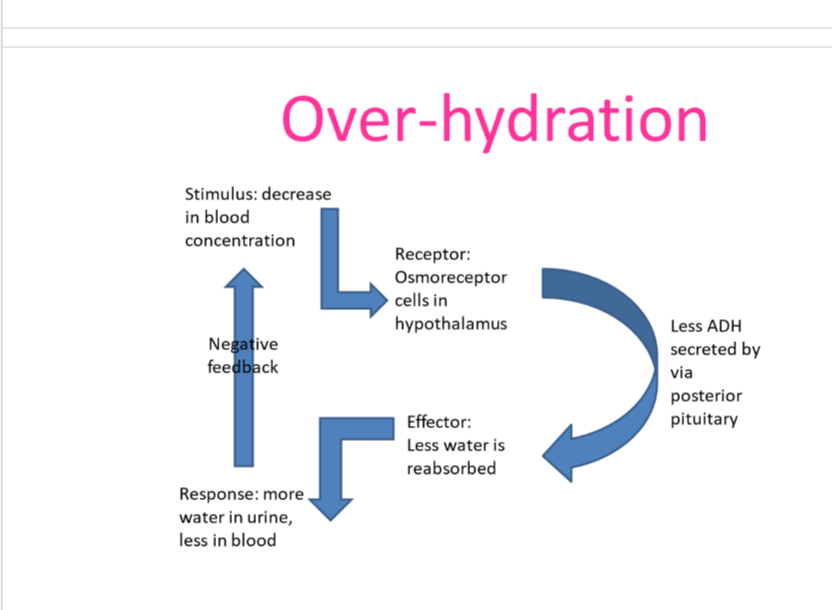
over hydration
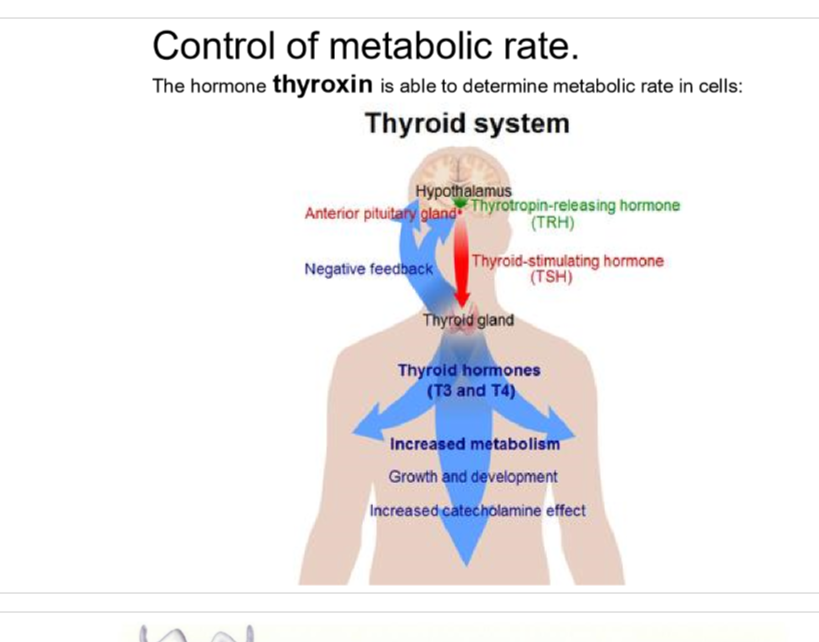
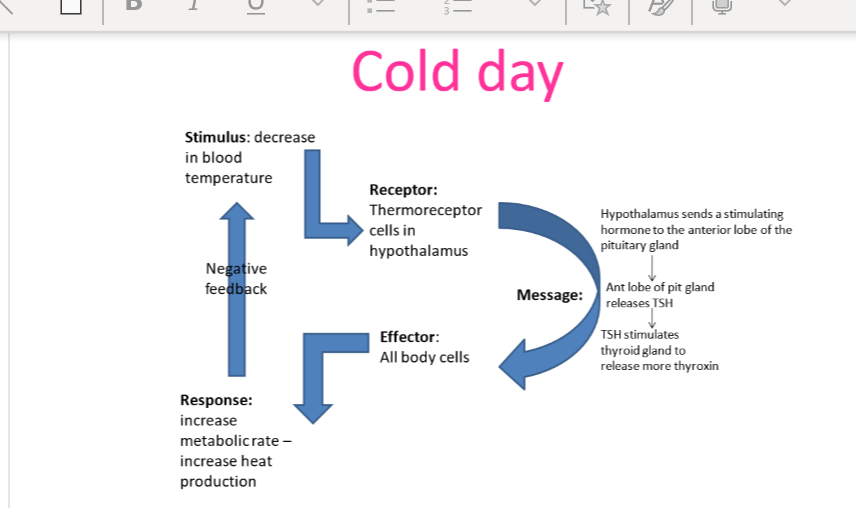
control of metabolic rate
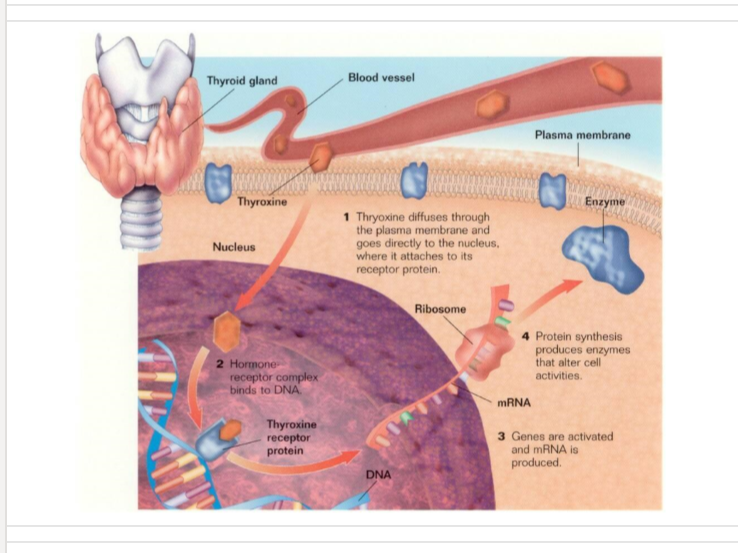
glands +
cold day
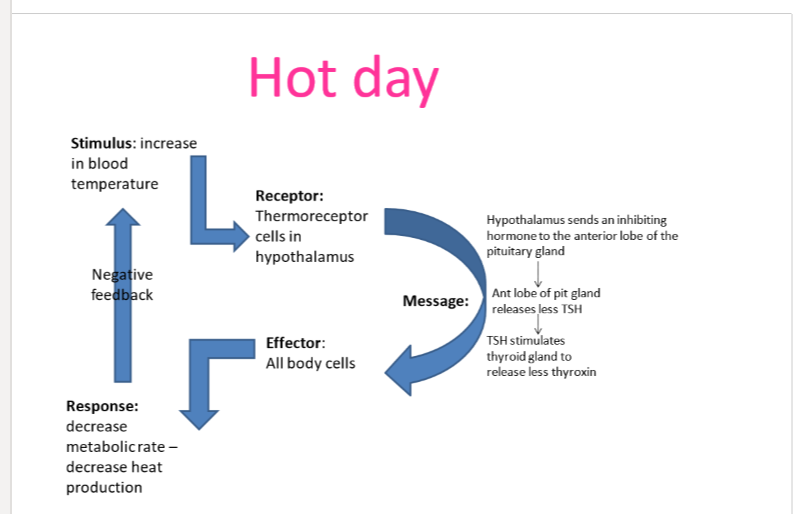
hot day