Functional Neuroanatomy
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
1
New cards
Fill in the blanks
2
New cards
Frontal Lobe function
Sense of self, associated with reasoning and higher cognition
3
New cards
Temporal Lobe Function
auditory system and limbic system
4
New cards
Parietal lobe function
processing of sensory information and spatial navigation, language processing
5
New cards
occipital lobe
interpreting visual stimuli (primary visual cortex)
6
New cards
efferent sensory axons
from brain to body
7
New cards
afferent motor axons
neurons from body to brain
8
New cards
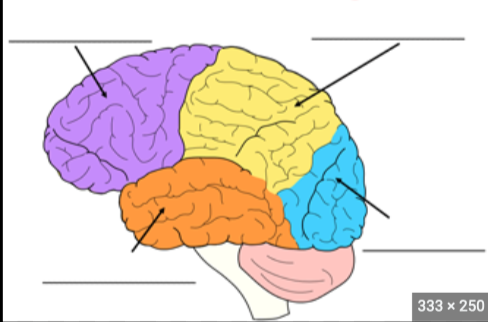
Fill in blanks + fissures/sulcus
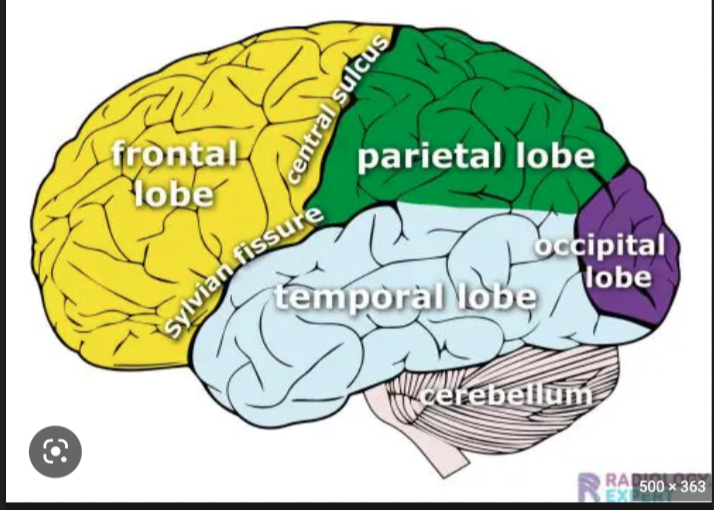
9
New cards
Forebrain parts
telencephalon + diencephalon
10
New cards
Midbrain parts
mesencephalon
11
New cards
Hindbrain parts
metencephalon + myelencephalon
12
New cards
telencephalon parts
cerebral cortex, olfactory system, lateral ventricle
13
New cards
diencephalon parts
hypothalamus, thalamus, third ventricle
14
New cards
mesencephalon parts
tectum, tegmentum, cerebral aquiduct
15
New cards
metencephalon parts
cerebellum and pons
16
New cards
myelencephalon
medulla oblongata
17
New cards
embryo development of brain
Steps of development of nervous system 1 formation of the neural groove (dent in the system)
2 walls of the groove (neural folds) come together and fuse -> neural tube formed [ENTIRE CNS DEVELOPS FROM THE NEURAL TUBE]
3 bits of neural ectoderm that are pinched off – neural crest [FROM WHICH PNS WILL DEVELOP]
2 walls of the groove (neural folds) come together and fuse -> neural tube formed [ENTIRE CNS DEVELOPS FROM THE NEURAL TUBE]
3 bits of neural ectoderm that are pinched off – neural crest [FROM WHICH PNS WILL DEVELOP]
18
New cards
Anterior/rostral
Toward the nose
19
New cards
Posterior
Toward the tail
20
New cards
Dorsal
upper surface area
21
New cards
Ventral
Lower surface area
22
New cards
Medial
Toward the midline
23
New cards
Lateral
Away from the midline
24
New cards
Ipsilateral
2 structures on the same side of the body
25
New cards
Contralateral
2 structures on opposite side of the body
26
New cards
saggital plane
midline of the braind
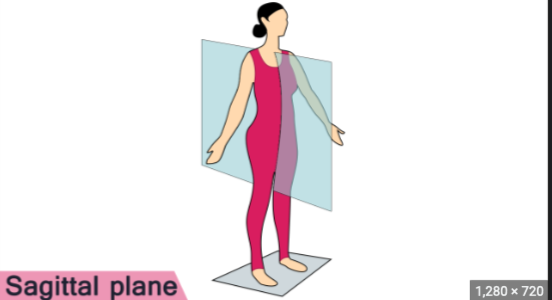
27
New cards
Coronal plane
Plan that runs ear to ear
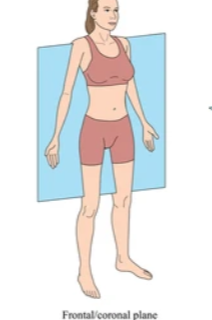
28
New cards
Ventricular system function and anatomy
Creates CSF
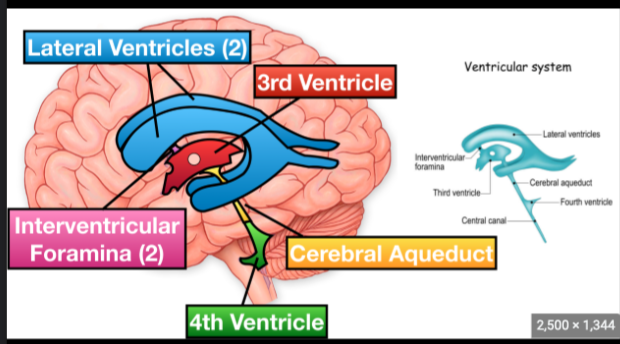
29
New cards
Meninges Anatomy
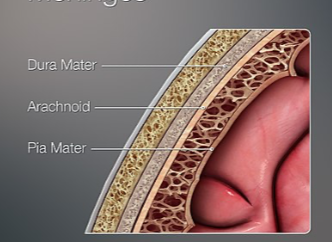
30
New cards
Ventral Ramus
Nerves of spinal cord, collects information for the brain
31
New cards
Dorsal Ramus
Nerves of spinal cord, commands muscle
32
New cards
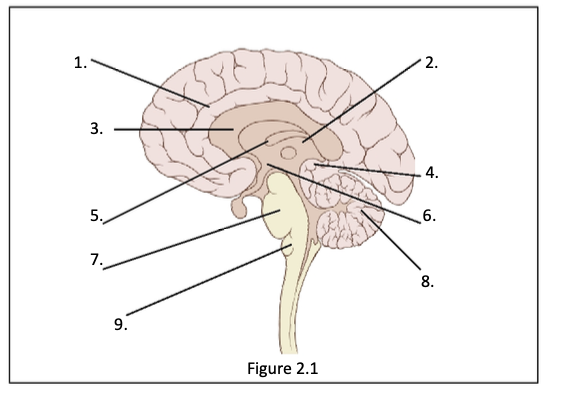
1. Cingulate Gyrus 2. thalamus 3. corpus callosum 4. pineal body 5. fornix 6. hypothalamus 7. pons 8. cerebellum 9. medulla
33
New cards
Corpus Callosum function
Connects communication between the two hemispheres
34
New cards
Pineal Body Function
Neuroendocrine organ responsible for secreting melatonin
35
New cards
Fornix
Part of limbic system, connects the hippocampus and hypothalamus
36
New cards
Hypothalamus Function
Controls homeostasis
37
New cards
Pons Function
Connects the cerebellum and cerebral cortex
38
New cards
Cerebellum Function
Important movement control center, receives input from spinal cord and pons
39
New cards
Medulla Function
Contains sensory and motor neurons that control respiration, cardiac function, vasodilation and several reflexes (vital function control)
40
New cards
What is the resting potential?
The electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane when the neuron is not in a excited stage (-65mV)
41
New cards
Ionic concentration (high/low) inside and outside the cell during resting potential
Inside: High potassium (K+), low sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-), Outside: high sodium, high chloride, low potassium
42
New cards
Sodium-Potassium pump
Pump involved to maintain the resting potential, lets 2 K+ in, while 3 Na+ are pumped out. Uses ATP
43
New cards
Ion Channels vs Ion Pumps
Ion channels facilitate ion diffusion, similar to opening a gate (no energy), whereas ion pumps actively pump out/in ions (energy)
44
New cards
Membrane Anatomy
Phospholipid bilayer, hydrophilic heads, hydrophobic tails + channels + pumps
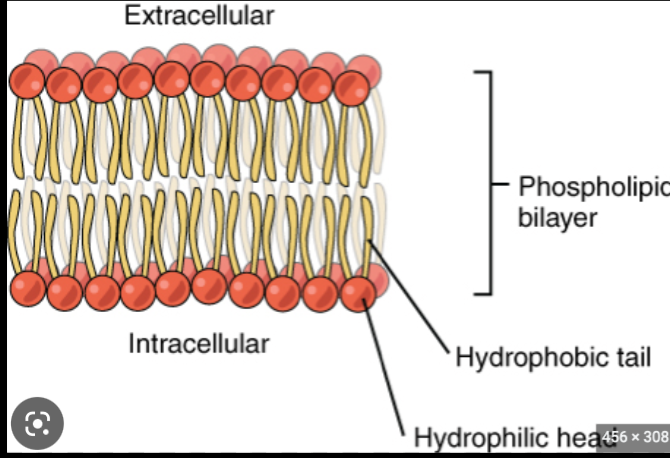
45
New cards
Action Potential Definition
An action potential is a signal that conveys informations over distance in the nervous system
46
New cards
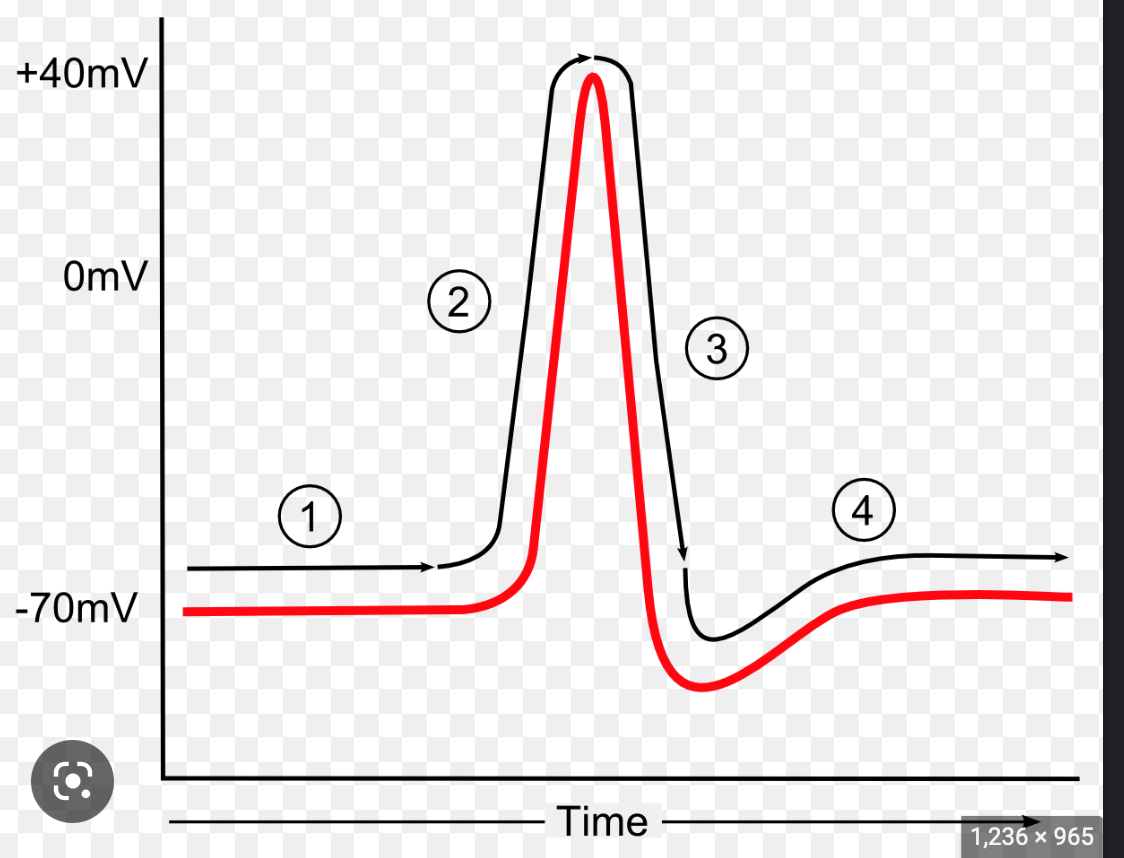
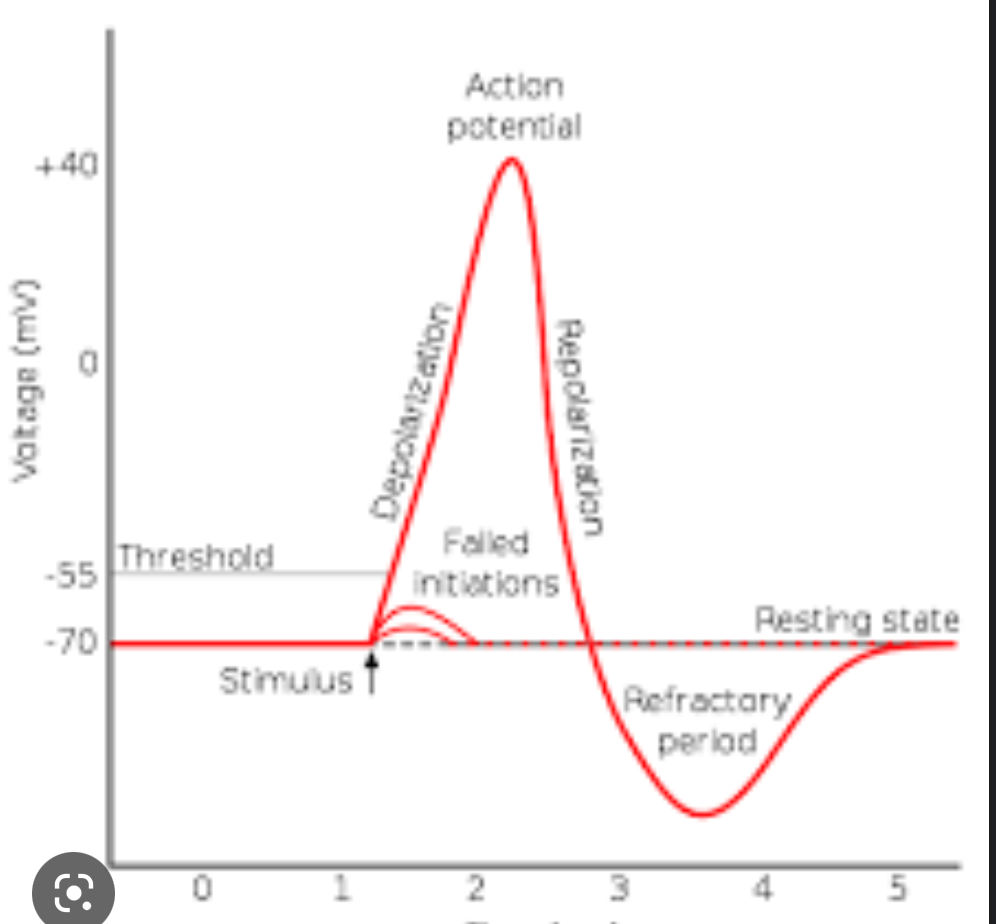
Stages of Action Potential
1. Threshold reaching, 2. Rising Phase 3. Overshoot (+40mV), 4. Falling phase 5. Undershoot 6. refractory period
47
New cards
Threshold action potential meaning
The threshold is the membrane potential at which enough voltage-gated sodium channels open so the relative ionic permeability of the membrane favors sodium over potassium (initiation of the action potential)
48
New cards
Rising Phase action potential meaning
When the outside of the membrane has a negative electrical potentail, there is a large driving force on Na to enter the cell. Therefore, through rapid Na movement into the cell, the membrane depolarizes
49
New cards
Overshoot action potentail meaning
The relative permeability of the membrane greatly favors sodium, therefore sodium enters the cell where there is already a lot of K+ making it temporarily positive (40mv)
50
New cards
Falling phase action potential meaning
1. voltage gated sodium channels are inactivated 2. voltage gated potassium channels open --> potassium leaves cell, --> depolarization of cell --> negative membrane potential
51
New cards
Undershoot action potential meaning
The open voltage gated potassium channels stay open a little longer than needed, creating an undershoot
52
New cards
Absolute refractory period
Sodium channels are still inactivated from falling phase, therefore a new action potential is impossible
53
New cards
Relative refractory period meaning
Part where the cell is hyperpolarizing to resting potential, action potentials are possible but the threshold is higher
54
New cards
55
New cards
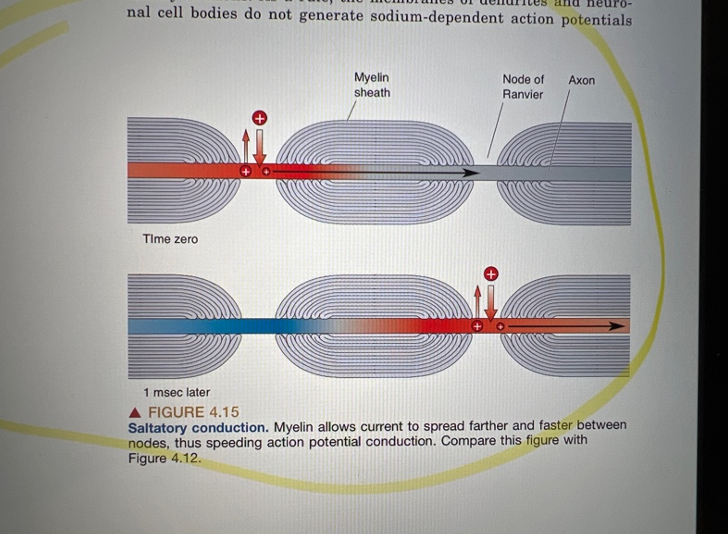
Action potential transfer through myelin/schwann
Myelin sheets insulate to facilitate fast transfer, action potential occurs in nodes of ranvier between myelin sheets.
56
New cards
Steps of chemical neurotransmission
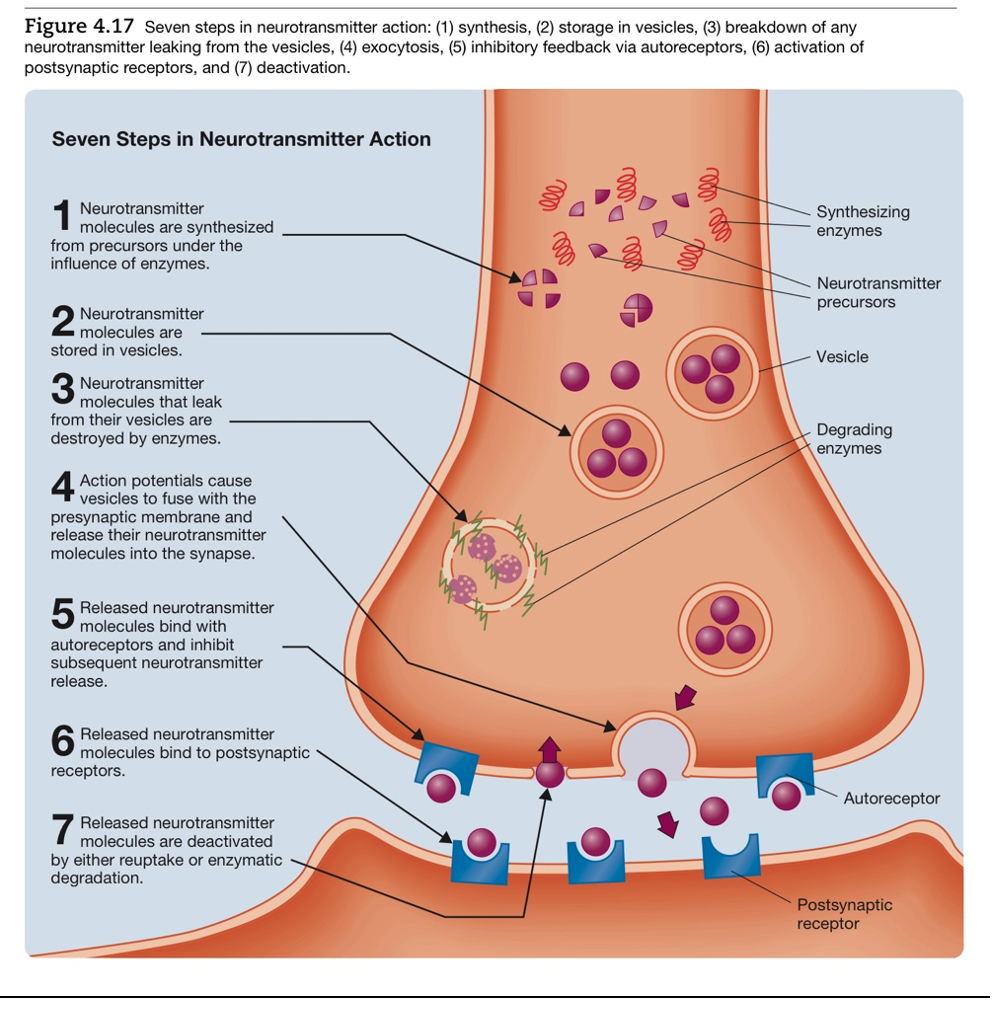
57
New cards
Small neurotransmitters
Single amino acid neurotransmitters that are able to bind to ionotropic receptors to illicit APs (e.g. glutamate)
58
New cards
Large neurotransmitters
Neuropeptides that bind to G-coupled receptors and manipulate a cell through second messenger systems (e.g. epinephrine)
59
New cards
Gap junction and
Channels between adjacent cells that mediate the transfer of small neurotransmitters and electrical transmission
60
New cards
Hypothalamus endocrine function
Send and regulate the pituitary gland hormone release through releasing factors
61
New cards
How is the anterior pituitary activated by the hypothalamus?
Hypothalamic releasing factors travel to the anterior pituitary gland through a capillary system.
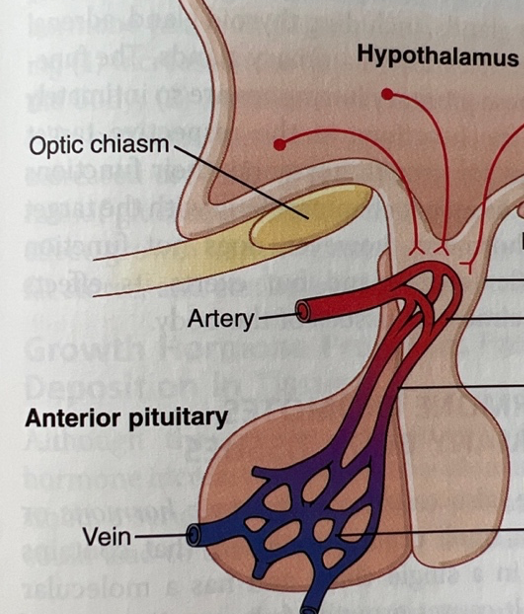
62
New cards
Hormones released by the anterior pituitary gland
thyrotropin, growth hormone, corticotropin, FSH, LH, prolactin
63
New cards
How is the posterior pituitary activated by the hypothalamus
Long axises from the hypothalamus extend into the posterior pituitary which activate the gland
64
New cards
Hormones released by the posterior pituitary gland
ADH, oxytocin
65
New cards
How are sex hormones regulated?
Hypothalamus --> anterior pituitary gland --> fsh+lh --> gonads --> estradiol/ testosterone --> negative feedback to hypothalamus and pituitary
66
New cards
How does the SRY gene affect development?
The SRY gene stimulates testes development through stimulating wolfian ducts to develop and mullarian ducts to degrade. Absence of SRY does the opposite. In reality, more genes are involved
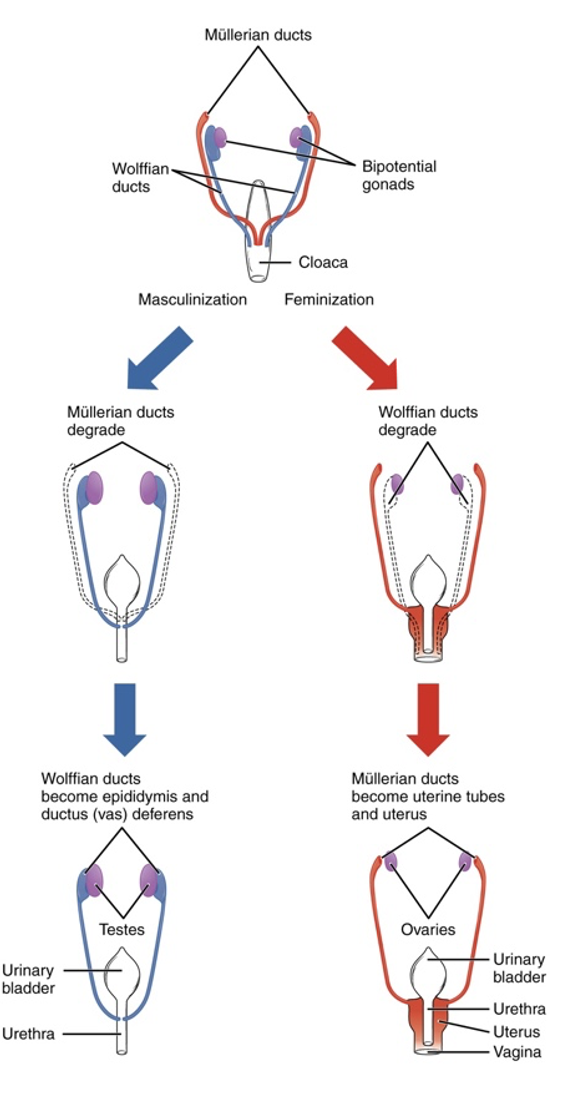
67
New cards
What is a steroid hormone
Steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol and can therefore travel through the membrane. Within the cell, they bind to nuclear receptor. Together with the nuclear receptor, they bind directly to DNA to alter expression. The steroid hormone does not use second messengers as opposed to other hormones
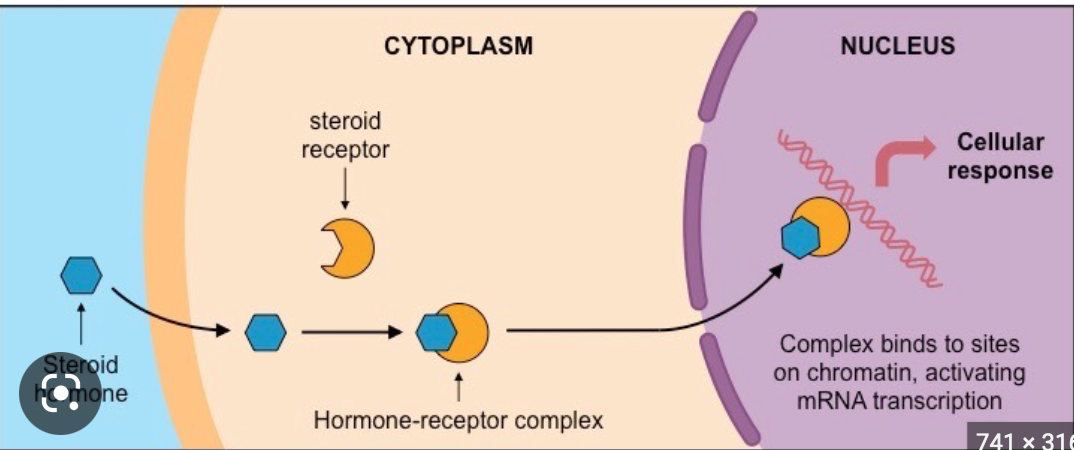
68
New cards
Organisational vs activational effects of hormones
Organisational hormones organise tissue in an irreversible way (testosterone, estradiol), activational hormones activate usually temporary processes like hunger
69
New cards
What happens when Leptin levels rise?
A rise in leptin levels stimulates the release of MSH and CART from arcuate nucleus neurons. These peptides act on the brain, in part by activating the MC4 receptor, to inhibit feeding behavior and increase metabolism.
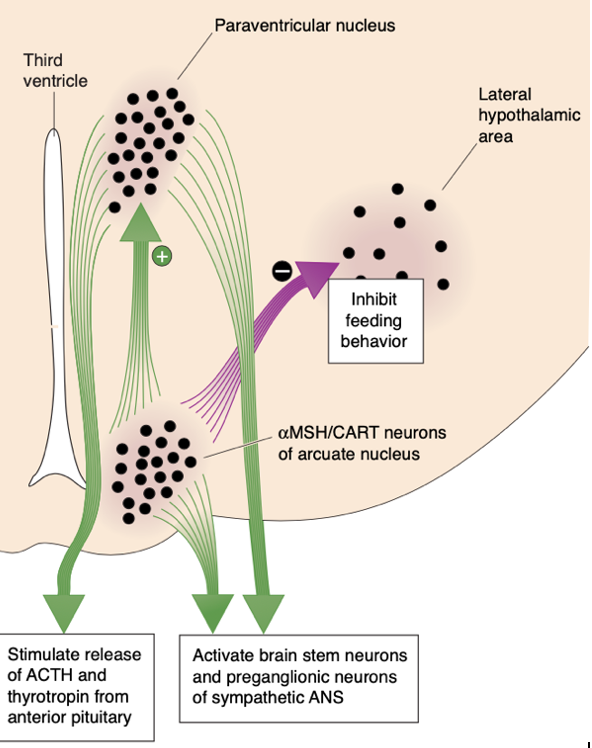
70
New cards
What happens when Leptin levels fall?
A fall in leptin levels stimulates the release of NPY and AgRP from arcuate nucleus neurons (situated in the hypothalamus), and the release of MCH and orexin from neurons in the lateral hypothalamic area. These orexigenic peptides act on the brain to stimulate feeding behavior and decrease metabolism.
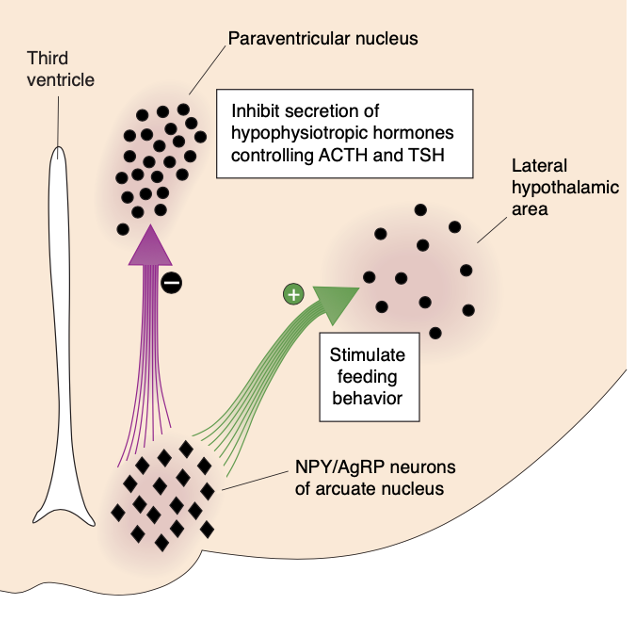
71
New cards
Insulin
Is released into the bloodstream by the β cells of the pancreas Glucose needs insulin to be transported in the other cells of the body
Important during anabolism AND catabolism
When the levels of glucose are high in the blood: levels of insulin decrease
When levels of glucose are low in the blood: levels of insulin increase
insulin acts directly on the hypothalamus
Important during anabolism AND catabolism
When the levels of glucose are high in the blood: levels of insulin decrease
When levels of glucose are low in the blood: levels of insulin increase
insulin acts directly on the hypothalamus
72
New cards
Ghrelin
Released in the stomach and small intestines
Stimulates hunger through NPY neurons in the hypothalamus
Stimulates hunger through NPY neurons in the hypothalamus
73
New cards
MCH and food
Leptin sensitive cells in the arcuate nucleus release MCH when leptin levels drop
MCH system informs the cortex of leptin levels
MCH induces feeding behaviour
MCH system informs the cortex of leptin levels
MCH induces feeding behaviour
74
New cards
Orexin and food
Receive input from arcuate nucleus
Stimulates feeding behavior
Levels rise when leptin levels decline
Orexin promotes meal initiation, MCH prolongs consumption
Also a role in wakefulness
Stimulates feeding behavior
Levels rise when leptin levels decline
Orexin promotes meal initiation, MCH prolongs consumption
Also a role in wakefulness
75
New cards
CCK and food
released with gastric distension --> satiety
76
New cards
Dopamine and feeding
Dopamine induces food seeking behavior, however, does not play a big role in enjoyment of food
77
New cards
Serotonin and feeding
Serotonin is low in postabsorptive period, rise in anticipation of food and spike during a meal especially to carbohydrates
78
New cards
High level motor control
Associated with strategy, involves the basal ganglia and neocortex
79
New cards
Mid level motor control
represented by the motor cortex and cerebellum, is concerned with tactics: the sequences of muscle contractions, arranged in space and time, required to smoothly and accurately achieve the strategic goal.
80
New cards
Low level motor control
The lowest level, represented by the brainstem and spinal cord, is concerned with execution: activation of the motor neuron and interneuron pools that generate the goal-directed movement and make any necessary adjustments of posture.
81
New cards
Lateral corticospinal tract
Distal muscle control
Cortex (area 4/6) --> internal capsule between telencephalon and thalamus --> cerebral peduncle --> pons --> medulla (medullary pyramid) --> runs down the ventral surface of the medulla (pyramidal tract) --> spinal cord
Cortex (area 4/6) --> internal capsule between telencephalon and thalamus --> cerebral peduncle --> pons --> medulla (medullary pyramid) --> runs down the ventral surface of the medulla (pyramidal tract) --> spinal cord
82
New cards
Ventromedial pathways (function)
voluntary movement of proximal muscles through multiple pathways, all originate in the brain stem
83
New cards
vastibulospinal tract (ventromedial)
originates in vastibular nuclei of the medulla and balances the body
84
New cards
tectospinal tract (ventromedial)
originates in the superior colliculus and receives input from auditory and visual stimuli. Helps orient head and eyes
85
New cards
Pontine reticulospinal tract (ventromedial)
originate from the reticular formation of the brain stem. Enhances antigravity reflexes of the spinal cord in the lower limbs
86
New cards
Medullary reticulospinal tract
Liberates the antigravity muscles from reflex control
Counteracts pontine tract to keep balance
Counteracts pontine tract to keep balance
87
New cards
Basal ganglia and movement
The basal ganglia may facilitate movement by focusing activity from widespread regions of cortex onto the SMA. Importantly, however, they also serve as a filter that keeps inappropriate movements from being expressed.
88
New cards
Area 4 of the cortex
Primary motor cortex (M1)
89
New cards
Area 6 of cortex
Higher motor control
Lateral area --> premotor area (PMA)
Medial region --> supplementary motor area (SMA)
Lateral area --> premotor area (PMA)
Medial region --> supplementary motor area (SMA)
90
New cards
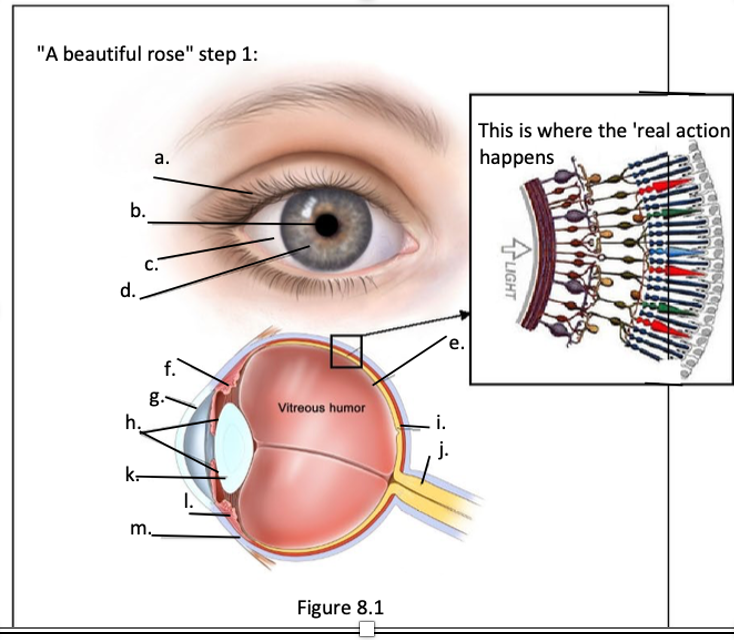
a. eye lids
b. pupil
c. sclera
d. iris
e. retina
f. ciliary muscle
g. cornea
h. iris
i. fovea
j. optic nerve
k. lens
l. conjuctiva
m. sclera
b. pupil
c. sclera
d. iris
e. retina
f. ciliary muscle
g. cornea
h. iris
i. fovea
j. optic nerve
k. lens
l. conjuctiva
m. sclera
91
New cards
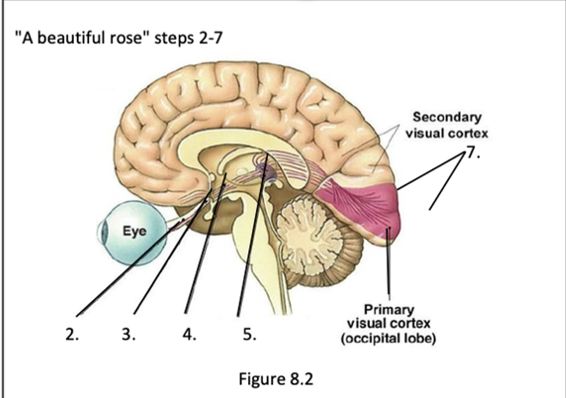
1. optic nerve
2. optic chiasm
3. lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
4. optic tract
5. visual cortex
2. optic chiasm
3. lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
4. optic tract
5. visual cortex
92
New cards
Laminar organisation of the retina
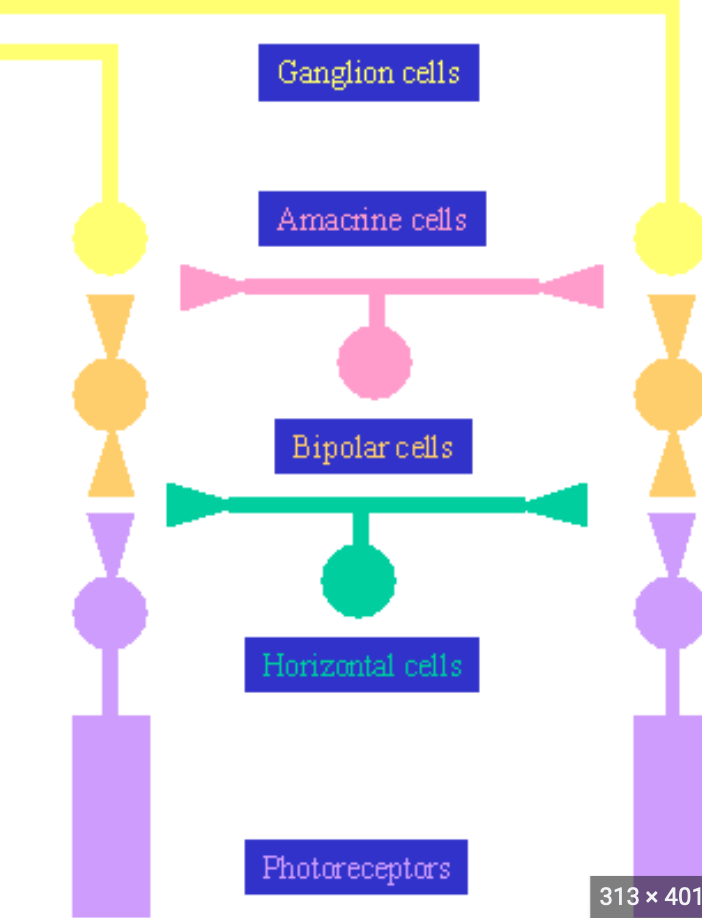
93
New cards
How does light get transformed into neural activity
Light enters eye --> refraction into the fovea --> passes through ganglion and horizontel cells --> hits the photoreceptors --> transformed into neural activity --> horizontal cells --> ganglion cells --> action potential
94
New cards
Cones
Photoreceptors responsible for more detail and help with spatial sensitivity; have different types of photo pigments that are sensitive to different wavelengths of light
95
New cards
Rods
contain more membranous disks; help with night vision because they are more sensitive to light; responsible for seeing contrast
96
New cards
LGN
Situated in the dorsal thalamus, consists of 6 layers to filter and relay visual information
97
New cards
non-thalamic visual targets
pineal body --> melatonin / circadian rhtyhms
superior colliculus --> eye and head movement
superior colliculus --> eye and head movement
98
New cards
Light, visual hemifields and optic chiasm
Light form the right hemifields, hits the left part of the eye, light from the left hits the right part of the eye. In the optic chiasm, input from the right hemifields goes to the left brain, and input from left hemifield goes to the right brain
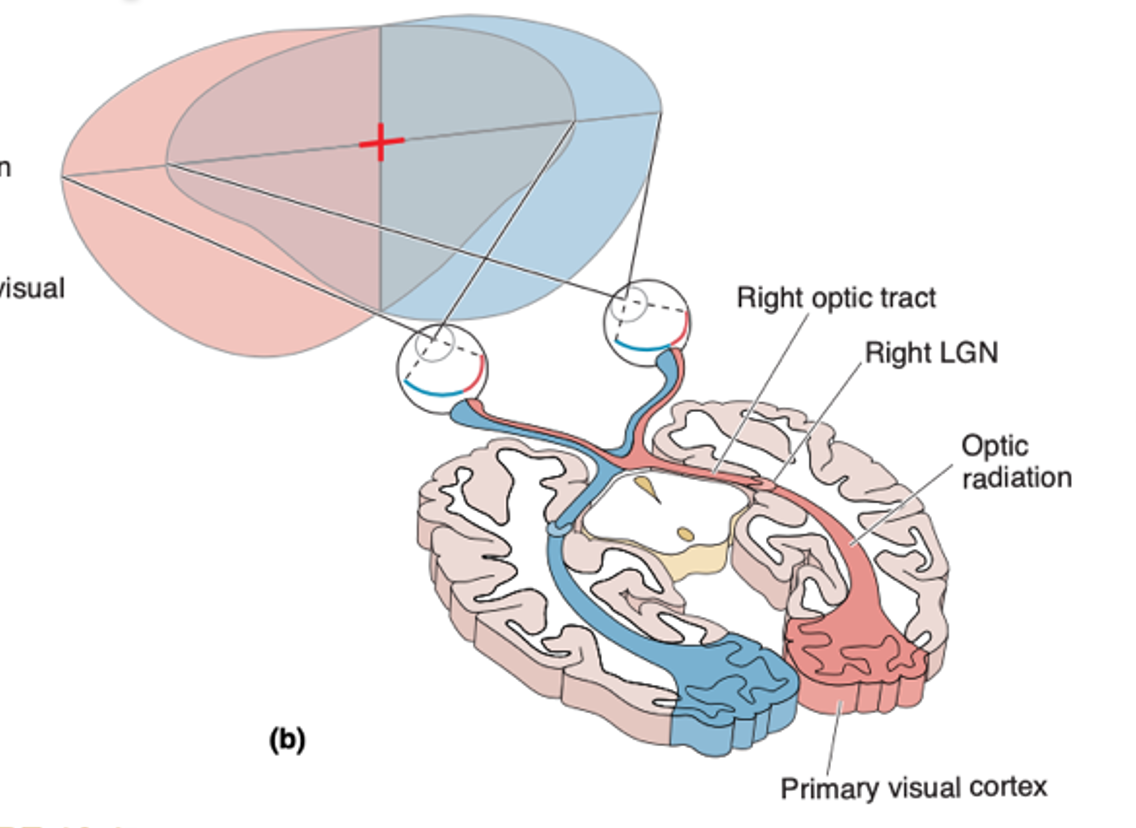
99
New cards
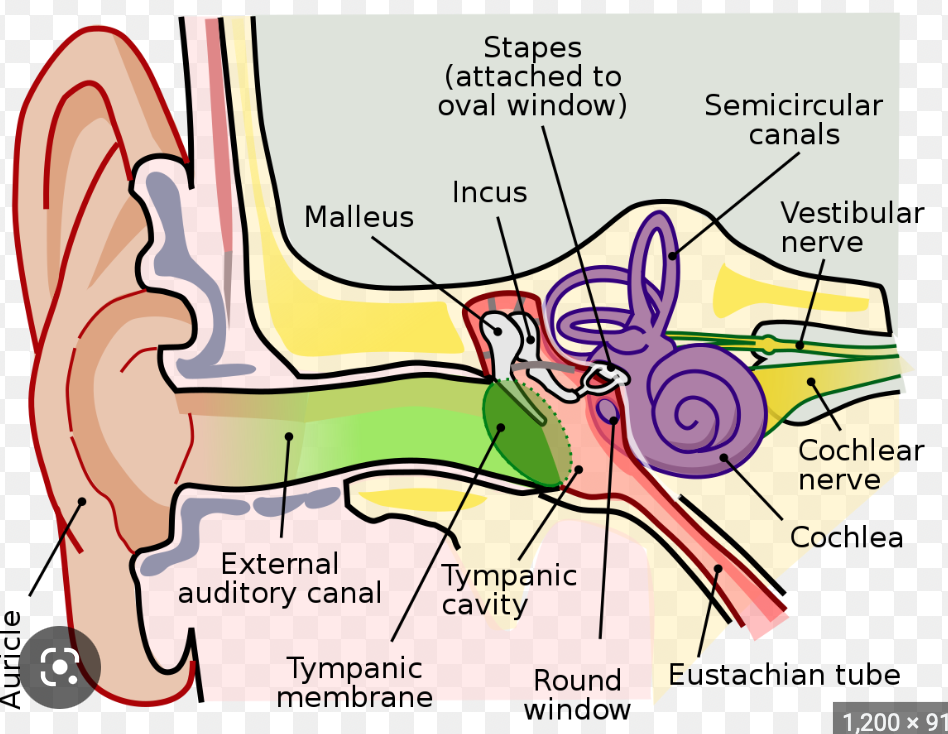
100
New cards