Chapter 6--Consumer Behavior
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
The consumer decision process
The steps consumers go through before, during, and after making purchases.
-B2C
-need recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, purchase and consumption, post-purchase
need recognition
The beginning of the consumer decision process; occurs when consumers recognize they have an unsatisfied need and want to go from their actual, needy state to a different, desired state.
-the greater discrepancy between these two states, the greater the need recognition will be
-goods or services seek to satisfy functional as well as psychological needs (need the right balance)
wants
goods or services that are not necessary but that we desire or wish for (like the color of a car)
functional needs
pertain to the performance of a product or service (like the need or a car to transport you)
Psycological Needs
pertain to the personal gratification consumers associate with a product or service
(wanting a jaguar because its a beautiful car)
search for information
search for info abt the various options that exist to satisfy that need
-want to rely on what we know first
-the length and intensity of the search are based on the degree of perceived risk associated with purchasing the product or service
-internal and external search for information
internal search for information
the buyer examines their own memory and knowledge about the product or service gathered through past experience
external search for information
buyer seeks information outside of their personal knowledge base to help make a buying decision
-might fill personal knowledge gaps by talking with family, friends, or sales person or look online
factors affecting consumer's search process
-The Perceived Benefits vs. Perceived Costs of Search
-The Locus of control
-actual or perceived risk
The perceived benefits vs perceived costs of search
-people can get stuck on this step by keep researching and not buying anything
-is it worth the time and effort to search for information about a product or service?
-weight cost and benefit
internal locus of control
believe they have some control over the outcomes of their actions, in which case they generally engage in more search activities
external locus of control
consumers believe that fate or other external factors control all outcomes
-it does not matter how much information they gather if they make a good decision it wasnt to their credit and it isnt their fault if they make a wring one
-do not really need to search if someone chooses for you
5 types of risks
performance, financial, social, physiological/safety, psychological
Performance risk
the perceived danger inherit in a poorly performing product or service
Financial Risk
risk associated with a monetary outlay; includes the initial cost of the purchase, as well as the costs of using the item or service
social risk
the fears that consumers suffer when they worry others might not regard their purchases positively
Physiological risk
AKA Safety Risk. The fear of an actual harm should a product not perform properly (like a car)
psychological risks
those risks associated with the way people will feel if the product or service does not convey the right image
Evaluation of alternatives
sift through the choices available and evaluate the alternatives
-happens when you are engaged in information search
-this step does not happen when you are buying habitual (convince) product (like buying coke vs pepsi)
Attribute sets
consumer's mind organizes and categorizes alternatives to aid his or her decision process
-universal sets, retrieval sets, evoked sets
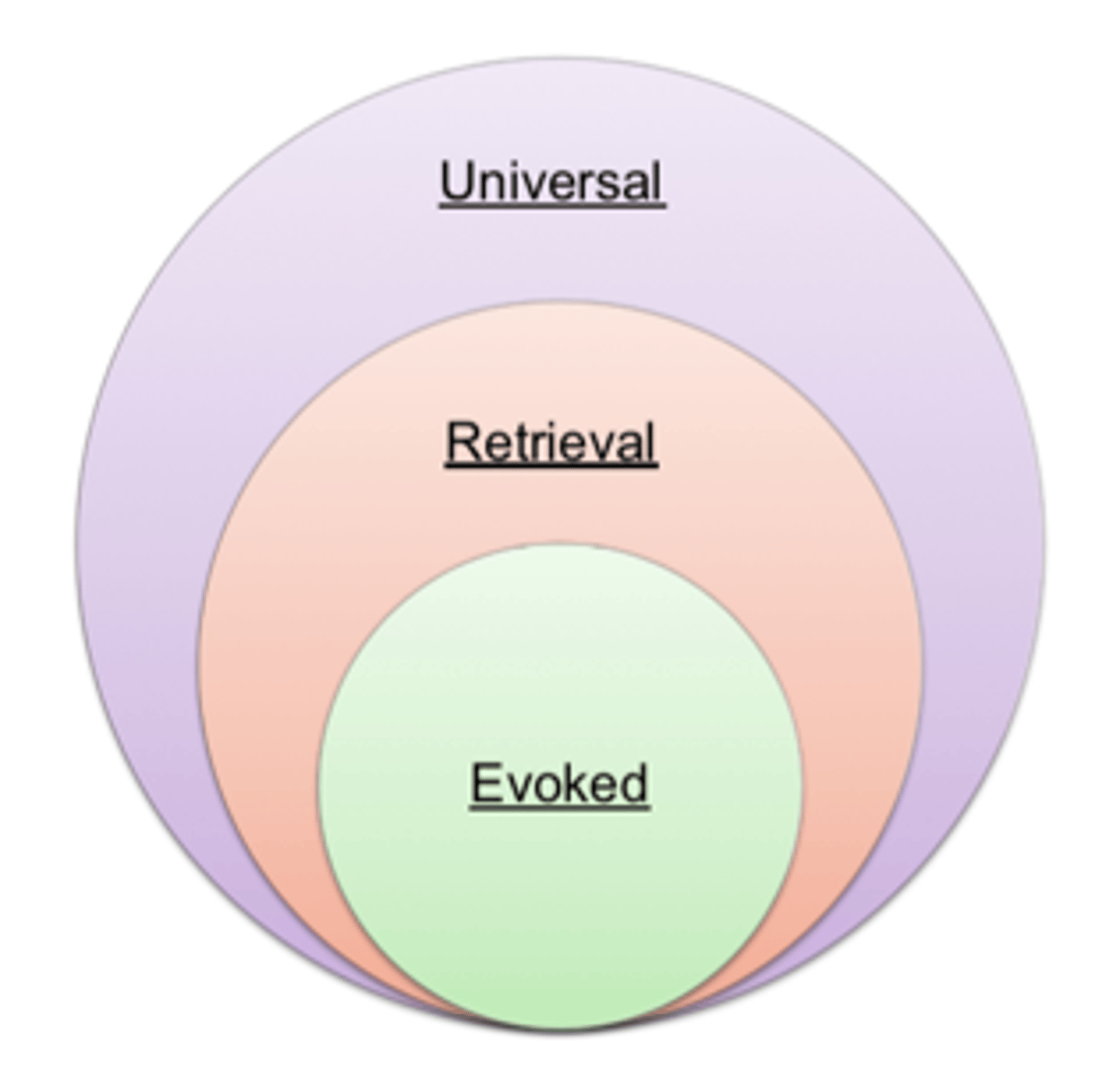
Universal sets
all possible choices for a product category, but because it would be unwieldy for a person to recall all possible alternatives for every purchase decision, marketers tend to focus on only a subset of choices
retrieval sets
brands and stores that can be readily brought forth from memory
evoked set
comprises the alternative brands or stores that the consumer states he or she would consider when making a purchase decision
-brands want to be here
evaluative criteria
consist of salient, or important, attributes about a particular product
determinant attributes
product or service features that are important to the buyer and on which competing brands or stores are perceived to differ
-something it absolutely must have
Consumer decision rules
the set of criteria that consumers use consciously or subconsciously to quickly and efficiently select from among several alternatives
-can be compensatory or noncompensatory
compensatory decision rule
assumes that the consumer, when evaluating alternatives, trades off one characteristic against another, such that good characteristics compensate for bad characteristics
multi-attribute model
A compensatory model of customer decision making based on the notion that customers see a product as a collection of attributes or characteristics. The model uses a weighted average score based on the importance of various attributes and performance on those issues.
noncompensatory decision rule
choose a product or service on the basis of one characteristic or one subset of a characteristic, regardless of the values of its other attributes
choice architecture
Various methods that marketers use to present different choices to consumers, which have a pertinent effect on their decision making.
impulse products
A buying decision made by customers on the spot when they see the merchandise
nudge
one element of the choice architecture (environment) that alters behavior in a predictable way, without forbidding other options or significantly changing any economic incentives
default
An element of choice architecture (the environment) that deals with a "no-action" condition by imposing a choice on a person who fails to make a decision or does not actively opt for a different alternative.
opt-out
consumers engage in a dedicated effort not to share personal data each time they visit a website
opt-in
agreement to share information to marketer
-GDRP requires a choice option
Conversion rate
measures how well they have converted purchase intentions into purchases
abandoned real or virtual cart
have people actually purchased what they put in their cart
post purchase
three outcomes; customer satisfaction, post purchase cognitive dissonance, and customer loyalty
Customer satisfaction
need realistic expectations, demonstrate correct product use, money back guaranteed or warranties, encourage customer feedback, thank customers and contact them
post purchase cognitive dissonance
internal conflict that arises from an inconsistency between two beliefs or between beliefs and behavior
-question how appropriate your purchase was after you buy it
=happens the most to infrequent, expensive, and risky purchase
customer loyalty
loyal customers are valuable
undesirable customer behavior
Negative word of mouth occurs when customers spread negative information about a product/service/store to others
-you dont usually say anything when your needs are met
factors influencing consumer decision process
1. Marketing Mix
2. Psychological Factors
3. Social Factors
4. Situational Factors
Marketing mix
Product, Price, Place, Promotion
psychological factors
motives, attitudes, perceptions, learning and memory, lifestyle
social factors
family, reference groups, culture
situational factors
purchase situation, sensory situation, temporal state
Motive
a need or want that is strong enough to cause the person to seek satisfaction
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
(level 1) Physiological Needs, basic biological necessities of life like food, drink, rest, and shelter
(level 2) Safety needs, protection and physical well-being
(level 3) Love needs, interactions with others like haircut and makeup
(level 4), Esteem needs, allows people to satisfy their inner decisions like yoga, meditation and self-help books
(level 5) Self Actualization feels completely satisfied with your life and how you live
attitude
A person's enduring evaluation of his or her feelings about and behavioral tendencies toward an object or idea; consists of three components that influence our decisions and actions: cognitive, affective, and behavioral.
-we dont like dissonance, so we avoid it by convincing ourselves that the decision was good in some way
-marketers can influence us and change the way we think and feel about something
cognitive component
what we believe to be true
affective component
what we feel about the issue at hand
behavioral component
actions we undertake based on what we know and feel
perceptions
the process by which people select, organize, and interpret information to form a meaningful picture of the world
-we tend to assign meaning to something based on color and packages, and how we were brought up and our culture
learning
a change in a person's thought processes caused by prior experience and takes place through the consumer decision process
memories
information that has been acquired and stored in the brain, to be available and utilized when needed
three stages of memory that influence decision making
1. informative encoding stage: consumers transform informative that they receive about products and services into storable information
2. information storage stage: that knowledge gets integrated and stored with what consumers already know and remember
3. Retrieval stage: consumers access desired information
-learning and memory affects attitudes and perceptions
lifestyle
the way consumers spend their time and money to live
-does it fit your actual lifestyle or your perceived lifestyle
family
usually purchase something entire family will use
-want to influence the group with the spending power
reference groups
one or more persons whom an individual uses as a basis for comparison regarding beliefs, feelings, and behaviors
-friends family, coworkers, celebrities, influencers
-these reference groups affect buying decisions by offering information and enhancing a consumers self-interest
-can be in person or virtual
culture
shared set of beliefs, values, knowledge, and patterns of behavior common to a group of people
-ex: your culture at school
situational factors definition
factors specific to the situation override or at least influence psychological and social interests
purchase situation
Customers may be predisposed to purchase certain products or services because of some underlying psychological trait or social factor, but these factors may change in certain purchase situations
-usually thrifting but splurging on a friends birthday
visual sense
colors, lighting, brightness, size, shape, and setup of a retail space and the products within it
auditory senses
A sensory stimulation that involves hearing and influences the shopping experience, e.g., music.
olfactory sense
involves smell and influences shopping experience like cinnamon roll sent
tactile
relating to the sense of touch
-first sense humans developed. interactive with merchandise
taste
important to restaurants and food and bev retailers
temporal state
our state of mind at any particular time can alter our preconceived notions of what we are going to purchase
-mood swings, being a morning or night person
involment
the relative importance of perceived consequences of the purchase to a consumer
-two people make based on level of involvement elaborate likelihood model
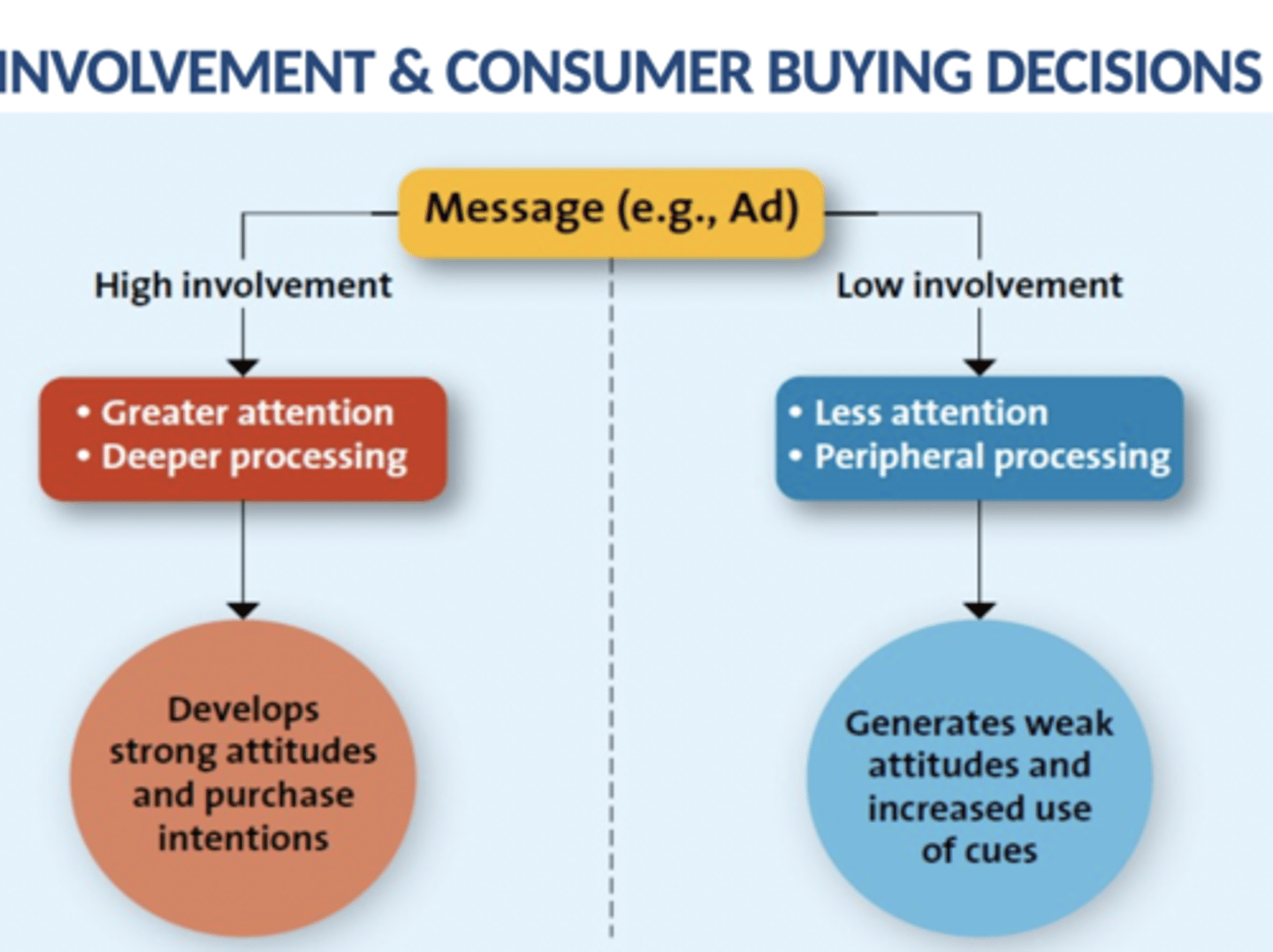
extended problem solving
customer devotes considerable time and effort to analyze alternatives done for high risk decisions
-buying process begins when customers realize they have an unsatisfied need
limited problem solving
happens during a purchase decision that calls for, at most, a moderate amount of time and effect
-had prior expense and risk is moderate
habitual decision making
requires little conscious effort, routine