7 Aberrations & Lens Design
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
T or F: a theoretically perfect optical surface would still have aberrations
T
Aberrations are caused by
the way light is refracted by a surface
index of medium
location of object point
Chromatic aberrations are dependent on
lens material
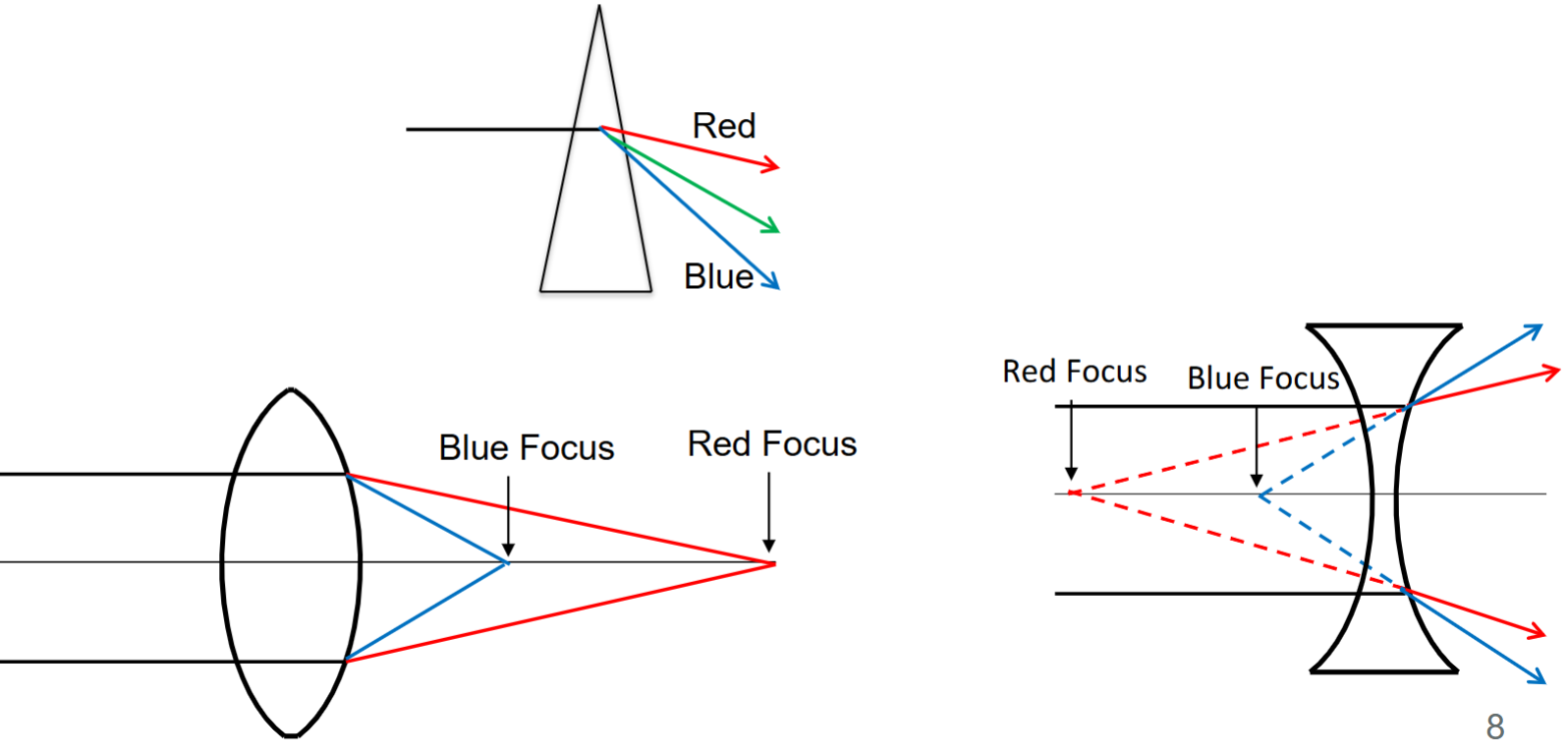
monochromatic aberrations are dependent on
lens design (form)
For most materials, the refractive index is higher for (short or long) wavelengths
short (blue)
Abbe value equation with blue and red
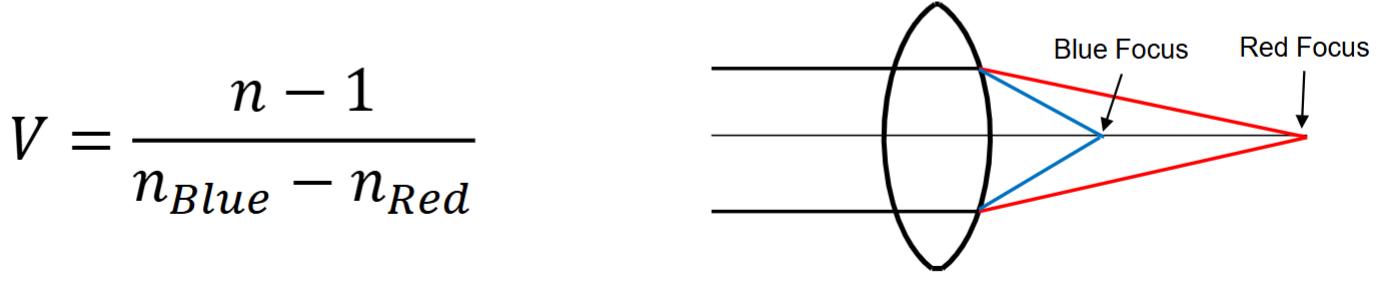
Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration (LCA)
dioptric distance between red and blue focus = P/V
aka axial CA
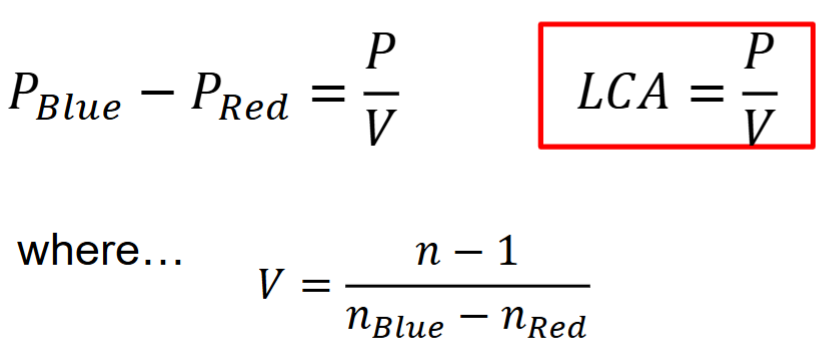
What clinical test makes use of eye’s longitudinal chromatic aberration?
Duochrome (red/green) test
Transverse Chromatic Aberration (TCA)
aka lateral chromatic aberration
differences in prismatic effects (angular dispersion) of lens for various wavelengths
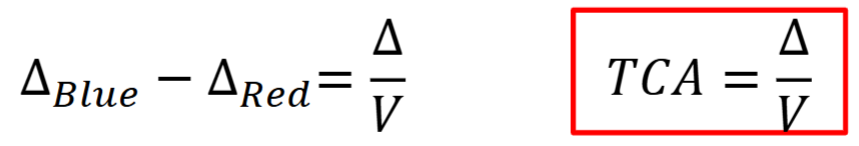
What would be the TCA at the optical center?
0
What aberration causes colored fringes around borders and blurs image?
TCA
How can we control chromatic aberration?
achromatic doubleta
Achromatic doublet
controls chromatic aberration by having a plus and minus lens together (lenses of different Abbe Values)
not a practical design for spectacle lenses
How much of an issue are chromatic aberrations with spectacle lenses?
not significant, there are ways to control
Ways to control chromatic aberration
use material with higher Abbe Value (trivex > polycarb)
center pupil in frame (Frame PD = Patient PD, and centered vertically) → no decentration decreases lens thickness and chance of induced prism → less TCA
use shorter VD
If we could limit light passing through the lens to one wavelength (monochromatic light), what aberration would be eliminated?
chromatic aberrations
Monochromatic aberrations: The Seidel Aberrations
S1 Spherical aberration
S2 Coma
S3 Oblique Astigmatism
S4 Curvature of Field
S5 Distortion
Which Seidel Aberrations cause the most problems with spectacle lenses?
Oblique Astigmatism and Curvature of Field
Spherical aberration
blur when a pencil of light [parallel to optic axis] is refracted by a large-aperture optical system
occurs because different zones of the aperture have different focal lengths
![<ul><li><p>blur when a pencil of light [<u>parallel </u>to optic axis] is refracted by a large-aperture optical system</p></li><li><p>occurs because different zones of the aperture have different focal lengths</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/321625c4-89d0-4d19-8713-3ea84bd322ca.png)
Positive spherical aberration is when peripheral lens zones have (shorter or longer?) focal lengths than paraxial zones
shorter (=periphery more powerful)
Which is more common, positive or negative spherical aberration?
positive
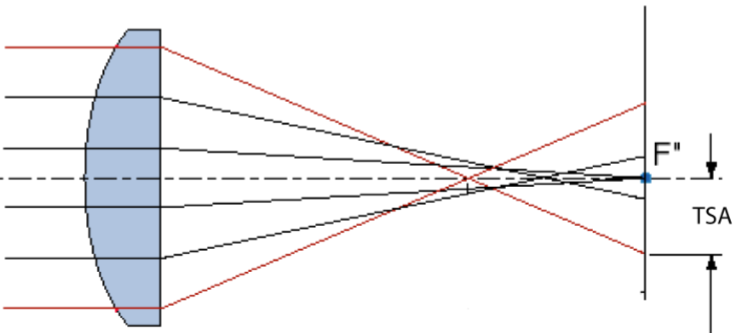
Longitudinal (axials) spherical aberration is
the dioptric separation of foci of paraxial and peripheral zones
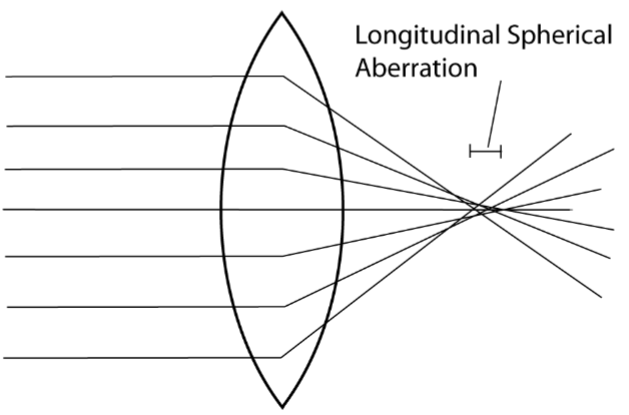
Lateral (transverse) SA is
linear diameter of image formed (called confusion disc) on a screen at any point between paraxial and peripheral foci
Making the entrance pupil (smaller/larger) would help reduce spherical aberration
smaller
Bottom line: spherical aberration is of minor significance with moderate lens power, and is only considered for high powered (concave/convex?) lenses
convex, for which plastic aspheric lenses are routinely used
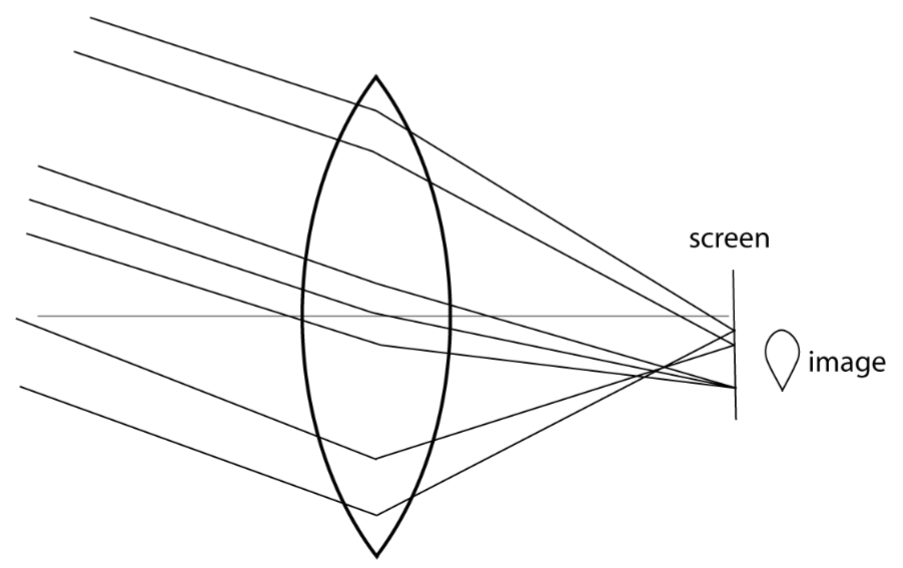
Coma occurs when
oblique rays are refracted by a large aperture optical system
affects sharpness of image points
Resulting image of coma is __-shaped
teardrop or comet
Which is the least important monochromatic aberration in spectacle design?
coma
Oblique astigmatism aka
radial
marginal
off-axis
peripheral
oblique astigmatism (the aberration) occurs when
narrow pencil of light from an object passes obliquely through a spherical surface
rays of light form interval of Sturm
Interval of Sturm
occurs with oblique astigmatism, made of 2 line foci and a COLC
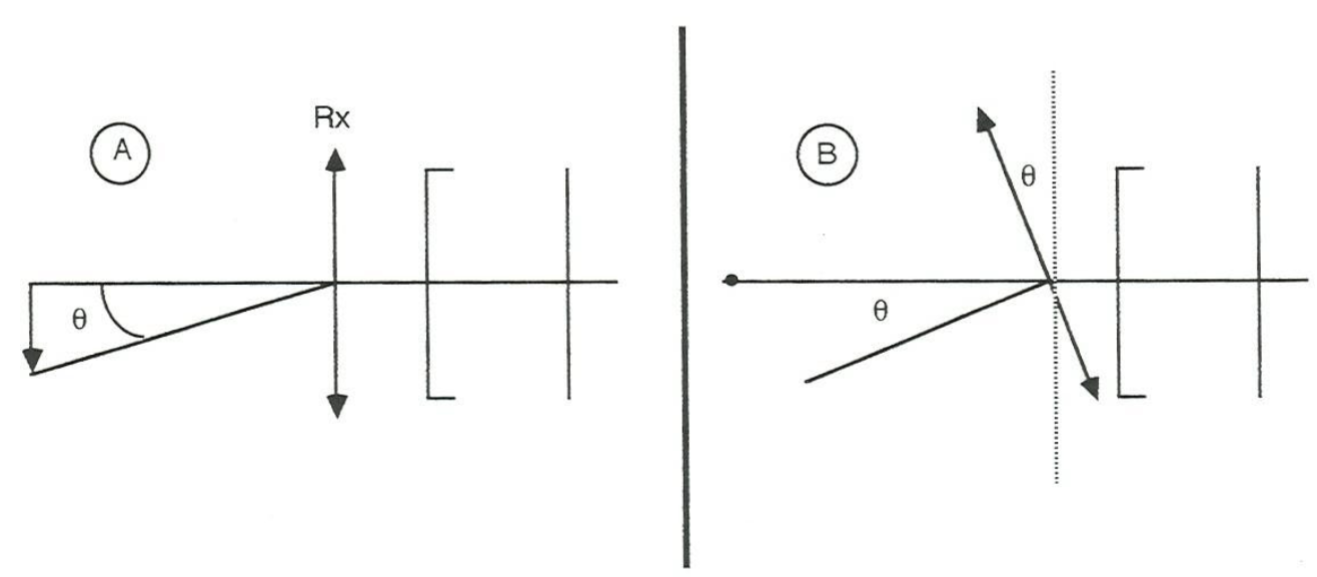
The two line images formed with oblique astigmatism are called
Tangential and Sagittal Focus/Image
Tangential Plane contains the chief way from the object point and optic axis
the object point and optic axis
Sagittal plane contains chief ray from
the object point, and is perpendicular to tangential plane
The dioptric separation of the T and S images is the amount of
oblique astigmatism
The goal of spec lens design is to bring the tangential and sagittal planes
as close together as possible
Petzval surface
spherical image surface that touches the two focal surfaces at their common axial point - Google
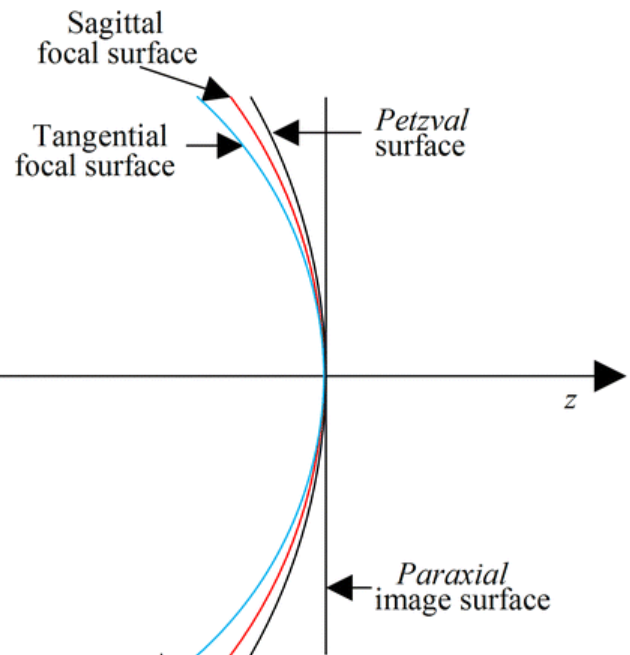
When oblique astigmatism is present, a true _ surface does not exist, and the T and S foci fall on the same side of that surface
Petzval
The curvature of the tangential surface is always (flatter/steeper) than the sagittal
steeper
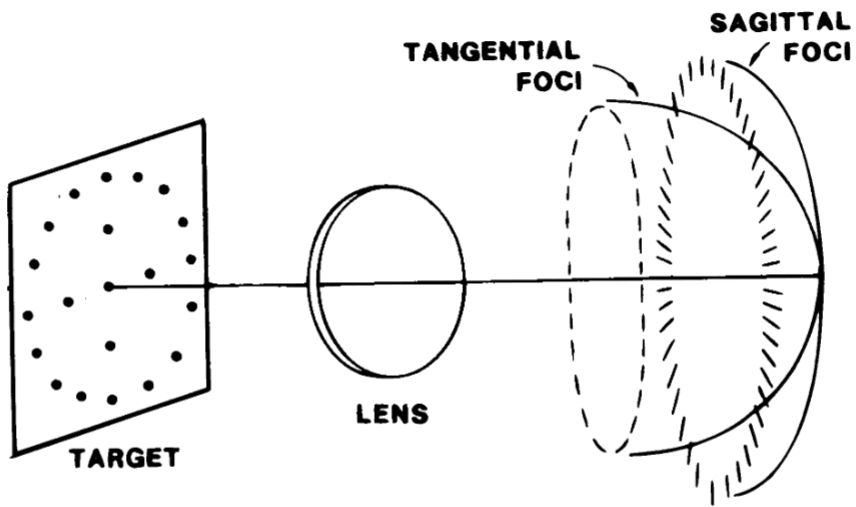
A Point Focal lens
spherical lens with no oblique astiematism
Features of a Point Focal lens
CoR is 27 mm behind lens
n = 1.523
power is between -23D and +7.25D
How many solutions are there for each lens power in Jalie’s equation?
2 (front curves for each power that give no oblique astigmatism)
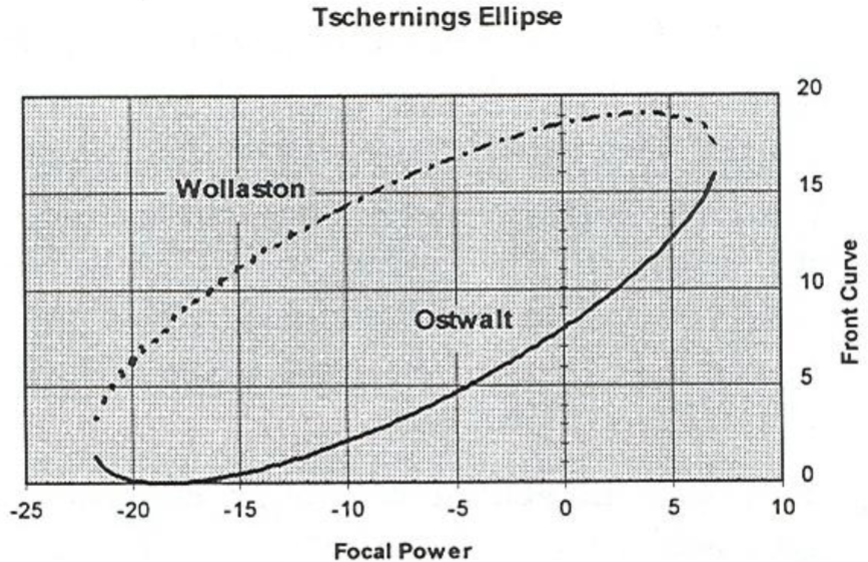
Wollaston and Ostwalt
branches of Tscherning Ellipse, each are one solution of front curve needed to eliminate oblique astig in a given lens power
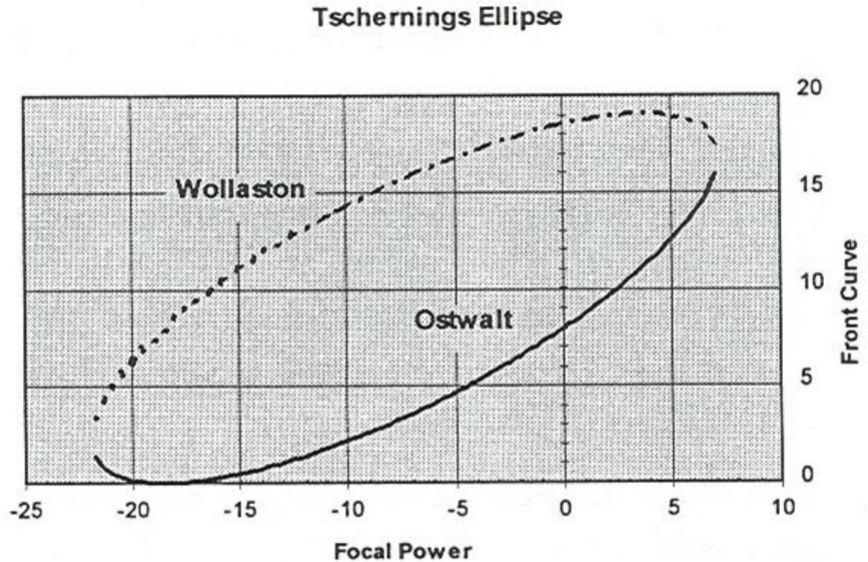
Which branch of Tschernings Ellipse is flatter and more cosmetically appealing?
Ostwalt
Which branch of Tschernings Ellipse minimizes distrotion?
Wollaston
When is there no curvature of image?
If the far point sphere coincides with the Petzval surface
How can we control curvature of image?
adjust base curve
What aberration must exist if curvature of image is corrected for?
oblique astigmatism
T of F: Distortion causes blur
F, just makes the image different from the shape of the original object
What is it called when the ratio of image size to object size has a constant value
orthoscopy (no distortion)
distortion is present when ratio of
image size to object size varies for diff obj sizes
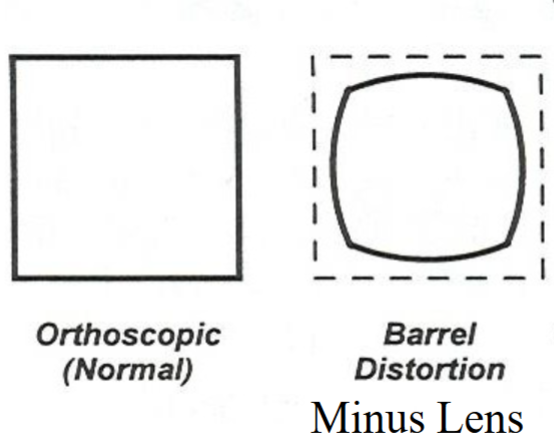
Barrel Distortion
image size : obj size ratio decreases with increase in obj size
(with a minus lens, periphery has more minification than center)
Pincushion distortion
image size : object size ratio increases with increase in obj size
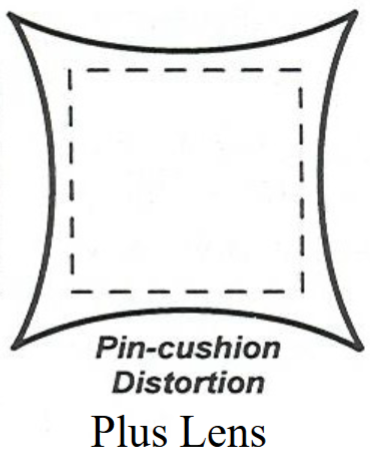
Plus lenses give what kind of distortion?
pincushion
minus lenses give what kind of distortion?
barrel
Distortion is mainly a problem for (low/high) powered lenses
high
Distortion can be minimized using
steep back surfaces
Potential Lens Design Variables
Number of lenses
n
Lens thickness
VD
Lens form
What lens design variable is usually used to minimize aberrations?
Lens Form
Chart to summarize how we control aberrations
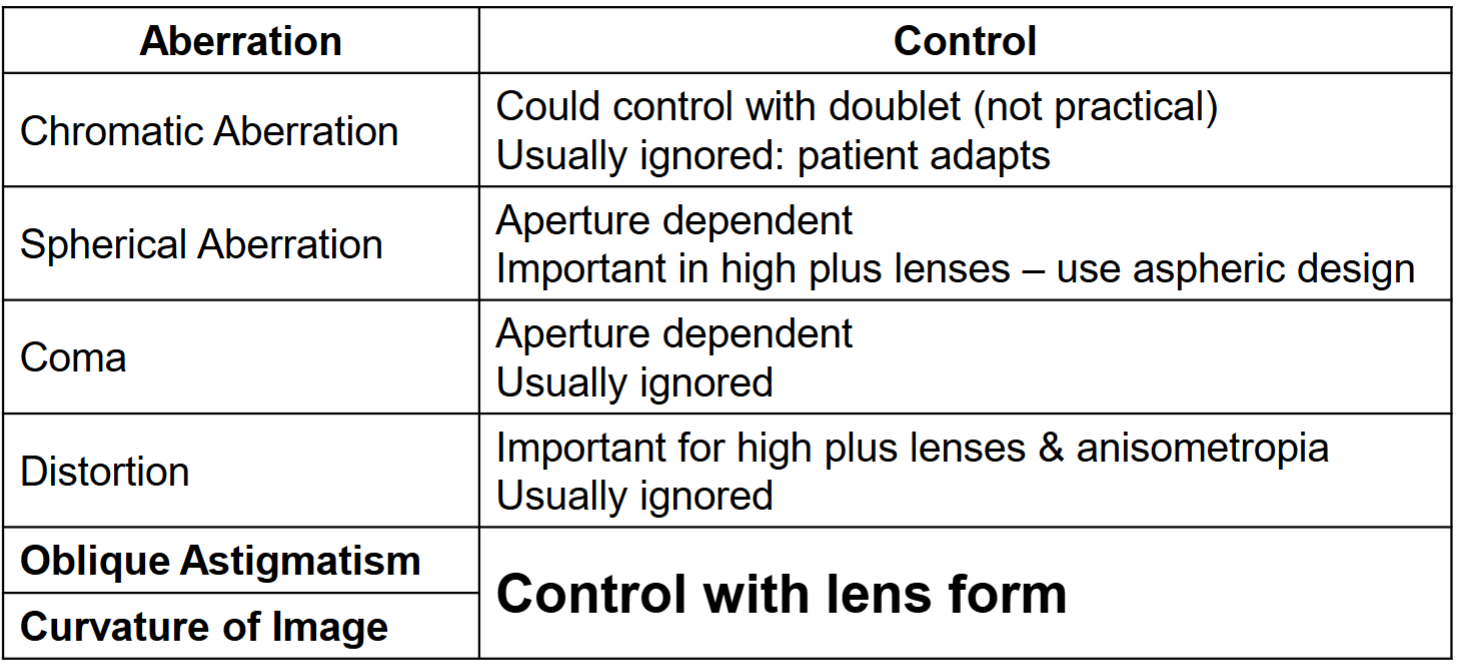
What are the generic terms for lenses that correct for oblique astig and curvature of image?
Corrected Curve and Best Form
Point-focal lenses
Lens design that concentrates on oblique astig and ignores curvature of image
Oblique astigmatism is an __ error
astigmatic
Curvature of image is a __ error
spherical
Lens Design Assumptions
The center of rotation of the eye is a fixed point with respect to the cornea (not true, there’s a cloud of locations=body centrode)
The optic axis of the correcting lens passes through the center of rotation of the eye (relatively true, with minimal tilt)
The foveal chief ray passes through the center of rotation of the eye (almost, the fovea is slightly temporal)
Minus cyl design advantages
less meridional mag
better cosmetic appearance
How is base curve chosen?
Table (now computer programs) of sphere and cyl powers → base curve: Compromise between using single base curve for all lenses (and grinding the needed power on back surface) and using different base curve for each lens power (using Tscherning Ellipse)
High plus lenses would theoretically have very (flat/steep) base curves, causing several problems…so we use aspheric lens designs
steep
Functional and cosmetic problems of steep base curve for high plus lenses
Thicker/heavier lens
More magnification (from thickness and increased VD)
Cosmetically not pleasing
Why are aspheric lens designs used?
To control oblique astig in lenses +7.50 (see problems with steep base curves with high plus lenses)
Advantages of aspheric design
Correct off axis astig
Thinner → better cosmetic appearance
reduced mag
Disadvantages of aspheric design
Off axis power errors from improper fitting are greater than for spherical lenses (blur from not looking through correct power)
Cannot use prism by decentration (they would be looking through the wrong power)
More expensive than spherical lenses
For what powers should aspheric lenses be considered?
> +- 4.00