Scapula & Clavicle
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the shoulder girdle made up of?
clavicle and scapula
What is the function of the shoulder girdle?
attach the upper extremity to the axial skeleton
What kind of bone is the scapula classified as?
flat bone
Explain the location of the scapula
lies in the superior, posterior aspect of the thorax
goes from the 2nd to the 7th rib
sits at a 30-45o angle
What is the anterior surface of the scapula called?
costal surface (comes in contact with the ribs)
What is the posterior surface of the scapula called?
dorsal surface
The scapular spine/crest divides the dorsal surface of the scapula into what 2 portions?
infraspinous/infraspinatus fossa
supraspinous/supraspinatus fossa
What is another term for the medial border of the scapula?
vertebral border
What is another term for the lateral border of the scapula?
axillary border
Which border of the scapula is thicker, medial or lateral?
lateral
What makes up the superior angle of the scapula?
junction of superior and medial borders
What makes up the inferior angle of the scapula?
junction of medial and lateral borders
What vertebrae does the inferior angle of the scapula correspond with?
T7
What is located at the lateral angle of the scapula?
head (glenoid) and neck of scapula
What is the coracoid process of the scapula?
fingerlike process extending anteriorly from the scapular notch
What is the acromion process of the scapula?
posterior flattened oval process at the lateral end of the scapular spine
What is the scapular notch?
prominent indentation along the superior border of the scapula
What is the glenoid fossa?
the head/neck of the scapula (point where humeral head articulates with scapula to form the scapulohumeral/glenohumeral joint)
What is the name of the fibrocartilage rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity of the scapula?
glenoid labrum
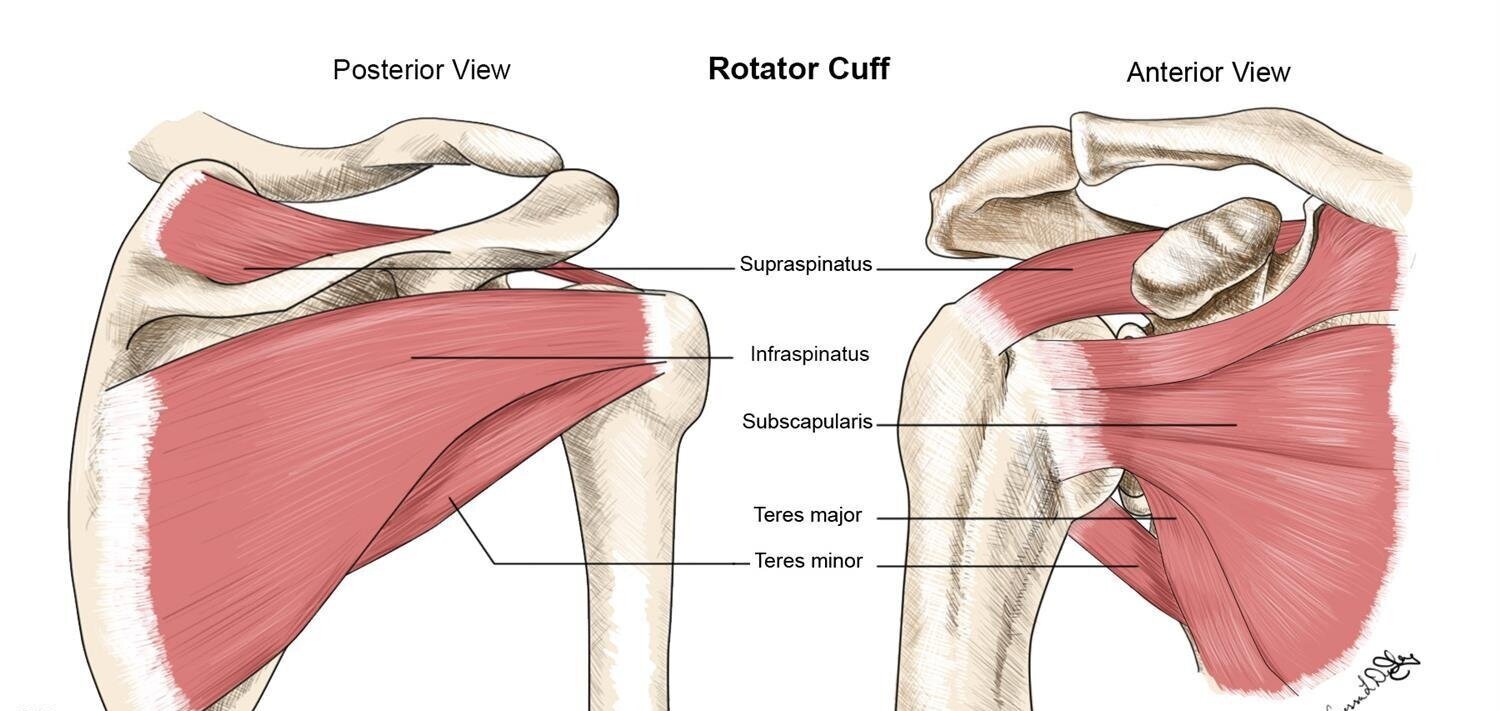
What is the rotator cuff?
group of muscles that stabilize the shoulder joint by pulling the humeral head into the glenoid fossa
What 4 muscles make up the rotator cuff?
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor
Explain the location and function of the supraspinatus muscle
originates on the upper border of the posterior scapula
allows for abduction
Explain the location and function of the subscapularis muscle
originates on the anterior surface of the scapula
allows for internal rotation
Explain the location and function of the infraspinatus muscle
originates on the posterior inferior aspect of the scapula
allows for external rotation
Explain the location and function of the teres minor muscle
originates on the posterior lateral scapular border
allows for external rotation
Label the muscles of the rotator cuff
What are the routine views of the scapula?
AP and lateral (Y-view)
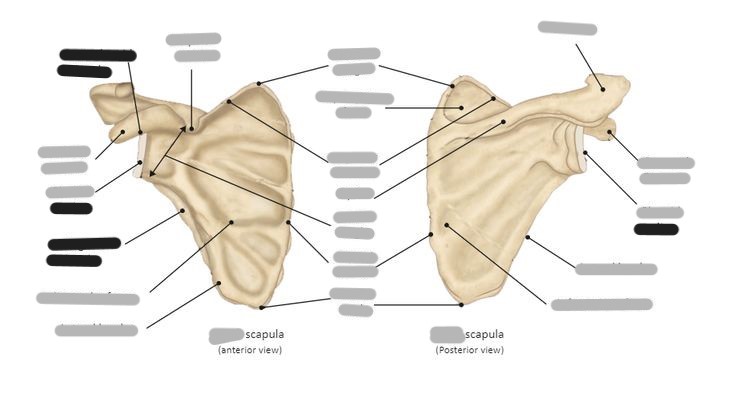
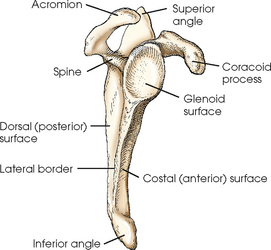
Label the scapula (and determine whether it is a right or left)
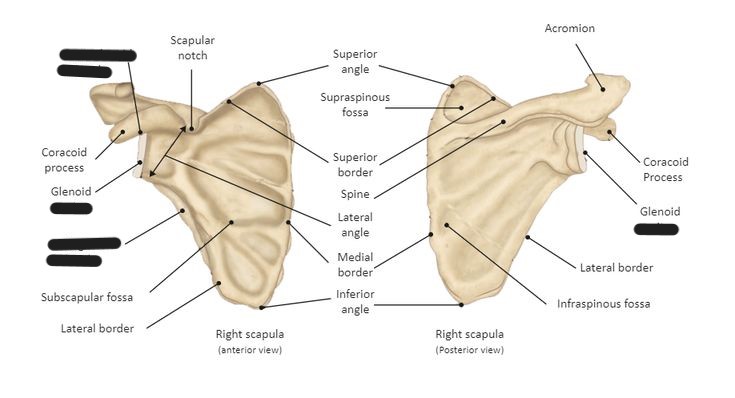
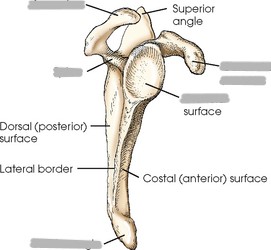
Label the scapula
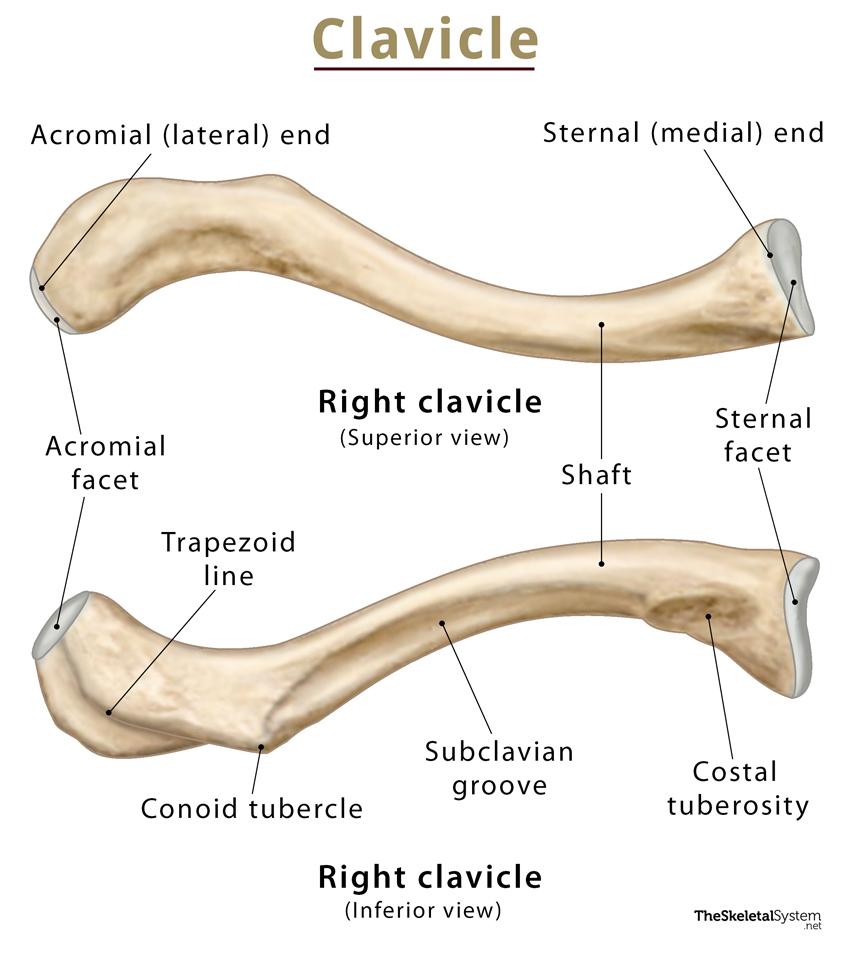
What kind of bone are the clavicles classified as?
long bones
Where are the clavicles located?
they lie horizontal in the superior and anterior part of the thorax
What is the sternal extremity of the clavicle?
the medial 1/3, convex, expanded end
What is the acromial extremity of the clavicle?
the lateral 1/3, concave, flatted end
What is the body of the clavicle?
the junction of the two curves (the weakest point of the clavicle and the site of 80% of clavicle fractures)
How do male and female clavicles differ?
male clavicle are thicker, longer, and more curved
What is the articular end of the sternal extremity of the clavicle called?
sternal facet (makes up the SC joint)
What is the costal tuberosity?
the broad, roughened surface on the inferior aspect of the medial end of the clavicle (serves as a point of attachment for the ligaments)
What is the sternoclavicular (SC) joint? What are the classifications?
joint between the clavicle and sternum
diarthrodial, gliding/plane joint
What is the articular end of the acromial extremity of the clavicle called?
acromial facet (makes up the AC joint)
What is the conoid tubercle?
inferior lateral aspect of the clavicle (serves as attachment point for ligaments)
What is the acromioclavicular (AC) joint? What are the classifications?
joint between the acromial extremity of the clavicle and the acromion of the scapula
diarthrodial, gliding/plane joint
How can clavicles differ between different body habituses?
asthenic will be more vertical
hypersthenic will be more horizontal
What are the routine clavicle images?
AP and AP axial
Explain the AP axial view of the clavicle
uses a 15-30o cephalic angle (like lordotic)
*make sure to annotate what angle you used*
How can body habitus affect how angled an AP axial view is?
asthenic will be closer to a 30o angle
hypersthenic will be closer to a 15o angle
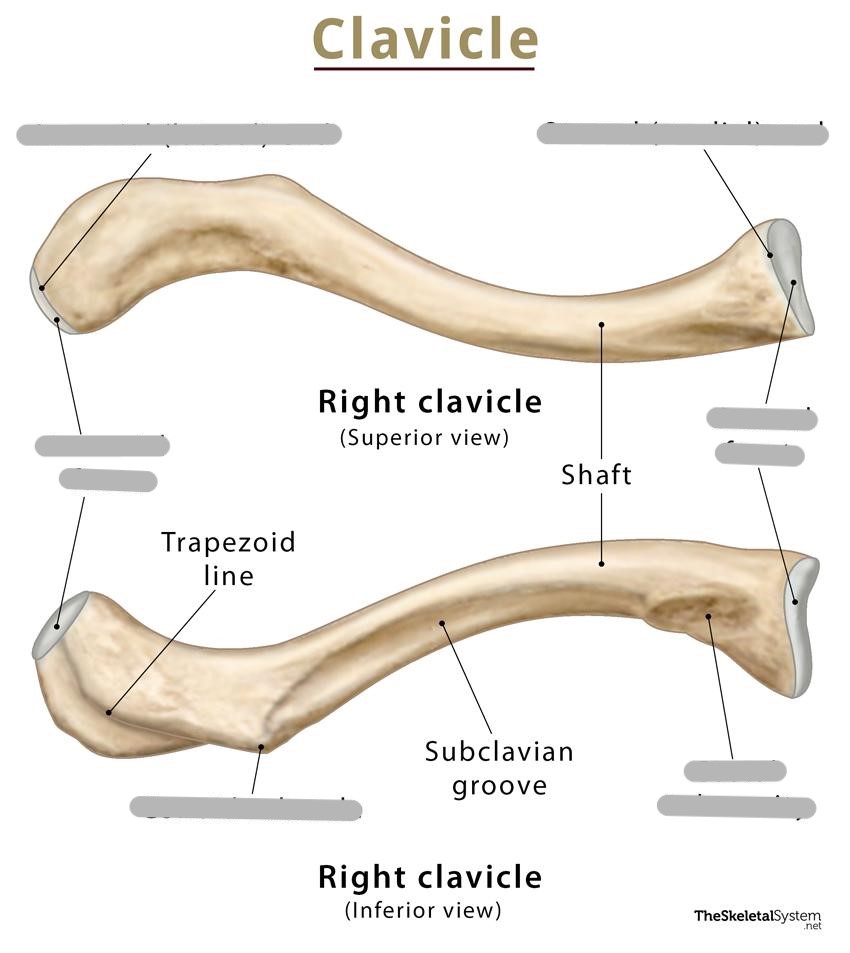
Label the clavicle