MKTG4506 Segmentation Study Guide
1/37
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is segmentation?
dividing market into meaningful smaller markets (submarkets) based on common characteristics
What are six characteristics that a good segment should have?
(ISADA)
identifiable
sustainable
accessible
stable
differentiable
actionable
What are 3 main types of group needs? List examples with each one.
singular (every person has a unique need): customizable shoes, segmented (groups that want and need the same thing): gluten free people who want good tasting gluten free pita, undifferentiated (everyone needs and wants the same thing): toothpaste
What is target marketing?
identifying how to prioritize market, then directing marketing efforts into specific segments (target markets)
What are four different strategies for targeting consumers, in order of most specific to most general?
customized target marketing (unique product is created for unique need, individual based)
concentrated target marketing (product serves large portion of small market)
Differentiated Target Marketing (develops different value offerings to target different targets segments, serves small portions of large market)
undifferentiated target marketing (ie: mass marketing, differentiate on price)
What is positioning?
communicating value to target market by connecting consumer needs and wants to what your company has to offer (what consumers want + what your brand does best = winning zone of positioning)
What are four different positioning strategies? Provide an example of each:
price: “always low prices”- Walmart
core-benefit: “your safety remains our main priority”- Volvo
Usage Situation: “Have a break, have a KitKat”- KitKat (usage = use food to relieve yourself)
Product User: “real women. real beauty.”- dove (relating with customers to promote sense of authenticity and connection)
What are the potential benefits of segmentation?
enables us to respond to our consumers’ unique wants and needs, escapes majority fallacy (instead of pursuing the largest segment, we pursue the segment that fits our offerings best)
What are the potential drawbacks of segmentation?
sales-cost tradeoff (although sales may increase with specialized products tailored to customers’ unique needs → so do costs), new products may cannibalize sales of old products
Explain the pathway for segmentation → positioning.
(STP) market segmentation (identifying and dividing a market into meaningful smaller markets based on common needs), target marketing (evaluating the market segments → prioritizing investment for development), and positioning (connect product offering with consumer needs through communication)
What is demographic segmentation? Why is it important? Provide some examples:
segmenting based on demographic characteristics of a population, important because our buying habits and behaviors are heavily influenced by our demographic characteristics
examples: age, gender, income, education, occupation, social class, marital status, culture, ethnicity
What demographic characteristics define a person’s “social class”?
occupation, income, wealth, education
What differentiates Gen Z, Millennial, Gen X, and Senior consumers?
Gen Z: most racially and ethnically diverse cohort, on track to be the most educated generation, digital natives, value personalization and ability to express identity
Millennials: largest cohort, segment filled with debt, similar to gen Z (high technical knowledge), value convenience, access (vs ownership), cost, and experience
Gen x: small cohort, savvy yet skeptical, entrepreneurial and adaptive, values authenticity, independence, stability
Seniors: controls >50% discretionary income (high spending ability), most loyal age group, often neglected by markets, value benefits (VS aesthetics), ownership (vs assess)
Why might marketers target different age cohorts?
values and needs differ across age, generations have unique shared language and experiences (nostalgia is a powerful tool!)
What are the advantages and limitations of demographic segmentation?
advantages: easy to apply and use (gov statistical data is readily available in most countries), data can be obtained quickly and cheaply, easy for management to understand
limitations: assumes all consumers who have similar demographic traits share same needs → shallow and often stereotypic
What are four different methods of geographic segmentation? Provide an example of each method:
climate: temperate, hot, rainy, dry
population density: urban, suburb, exurb, rural
region: landscape of environment (neighborhood, town, city, state, country), geographic orientation (Northeast, midwest, south, west), topography (mountains, plains, deserts, ocean, jungle)
geodemography: rating index by PRIZM
List an example of geographic segmentation by country
McDonalds creating new menus for different locations of chains to cater towards cuisine of location/country (ie: gluten free bread in Switzerland, Iberia Ham sandwhich in Spain, macaroon in France)
What are the advantages and limitations: of geographic segmentation?
advantages: easy to apply and use, works well in areas where there are significant differences across regions (ie: west coast VS east coast)
limitations: generalizes needs (assumes all consumers in geographic cluster have same needs), often needs to be used in conjunction with another type of segmentation
What is geographic segmentation?
segmenting based on regions/locations of customers
What is geodemographic segmentation? Provide an example.
segmenting base on a combination of geographic and demographic needs (most ideal method of segmentation)
example: targeting “Connected Bohemians”- midscale social-status, younger mostly, without kids who live in urban areas
What is the PRIZM system of segmentation?
provides information about segments’ demographic, lifestyle, and media traits (ie: urbanization, socioeconomic ark, age, presence of children at home, family life, mature years, younger years)
How are consumers grouped into social and lifestyle groups in the PRIZM system?
social groups: based on urbanization and socio-economic status (on an urbanization scale from urban → suburban → second city → town & rural)
lifestage groups: based on age and presence of children at home and socioeconomic rank (Lifestage scale: younger years → mature years)
[examples: movers and shakers- upwardly mobile executives who are highly educated and wealthy, young digerati- affluent, well-educated, ethnically diverse, technology-proficient, upward bound- “soccer moms and dad” who are child-centered, made of upper-class families]
What sort of information does the PRIZM system provide to marketers?
66 distinct segment of customers combined into 14 broad social groups made of a combination of geographic data (from where a person lives and their household level) demographic data, and consumption and media usage data
What are the three main types of psychographic segmentation?
personality (ie: the big 5), values, lifestyles
What is psychographic segmentation
the measurement of lifestyle: combined with measures of attitudes, beliefs, and personalities, measures how we live and provides insights to a persons’ activities (where they spend their time and money)
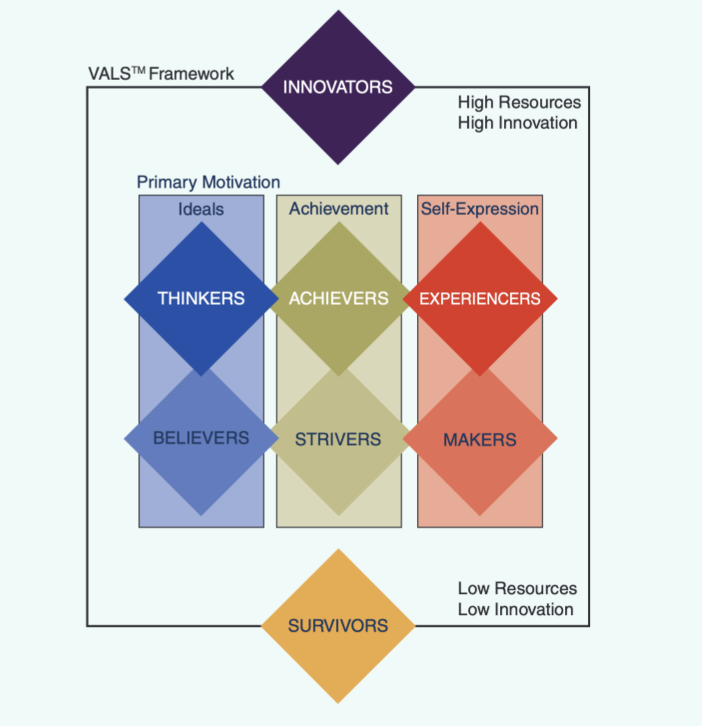
Explain a widely used market segmentation tool that employs psychographics in the US.
VALS System: segments individuals into 8 distinct consumer segments along 2 dimensions based on their social values and lifestyle variables.
dimensions: primary motivation (made of ideals, achievement, and self-expression) and resources
types of innovators (individuals with high levels of primary motivation (across ideals, achievement and self -expression) and resources)
ideals = thinkers
achievements = achievers
self-expression = experiencers
types of survivors (has levels of primary motivation, but lacks resources)
ideals = believers
achievement = strivers
self-expression makers
What is the Big Five system of personality segmentation? Define each of the Big Five personality traits:
(OCEAN):
Openness: appreciation for new experiences, imaginative, curious (ie: art, emotion, adventure, unusual ideas)
Conscientiousness: tendency to show self-discipline, act dutifully, aims for achievement
Extraversion: tendency to seek stimulation and company of others
Agreeableness: tendency to be compassionate and cooperative with others, rather than suspicious and antagonistic
Neuroticism: tendency be emotionally unstable (experience radical emotions like anxiety, anger, or depression)
What are the characteristics of the Big Five (e.g., stability, heritability, etc)?
stable (traits stay relatively the same over lifespan)
heritable (up to 50% per dimension)
cross-cultural
predictive of interpersonal relationships/compatibility (ie: martial satisfaction and dating apps)
found in both self and peer reports
What are the advantages and disadvantages of psychographic segmentation?
advantages: more comprehensive (than other types of data), gives better insight into underlying motives and values of consumer as a person, enables more targeted messaging
disadvantages: detailed data and research needed on consumers may be beyond capabilities of small firms (too costly or intensive), can be better at predicting messaging rather than resonating with behavior, context-specific (situation specific/culture specific)
What are four methods of behavioral segmentation? Provide an example of each:
product benefits: price, convenience, ease of use, status
ie: toothpaste = purchase the cheapest option
usage occasions: morning, evening, leisure, work, rush, holiday, special day
ie: sleep gummies for the evening, wedding services
usage frequency: current user, potential user, lapsed user, are they light, medium, or heavy consumers of product
ie: someone who goes to life alive a lot
purchase history: past purchases, search history
ie: purchase history of company
What is behavioral segmentation?
segmenting market based on behavior of customers (what is their perceived pain and perceived value of a product and how can the company cater to this)
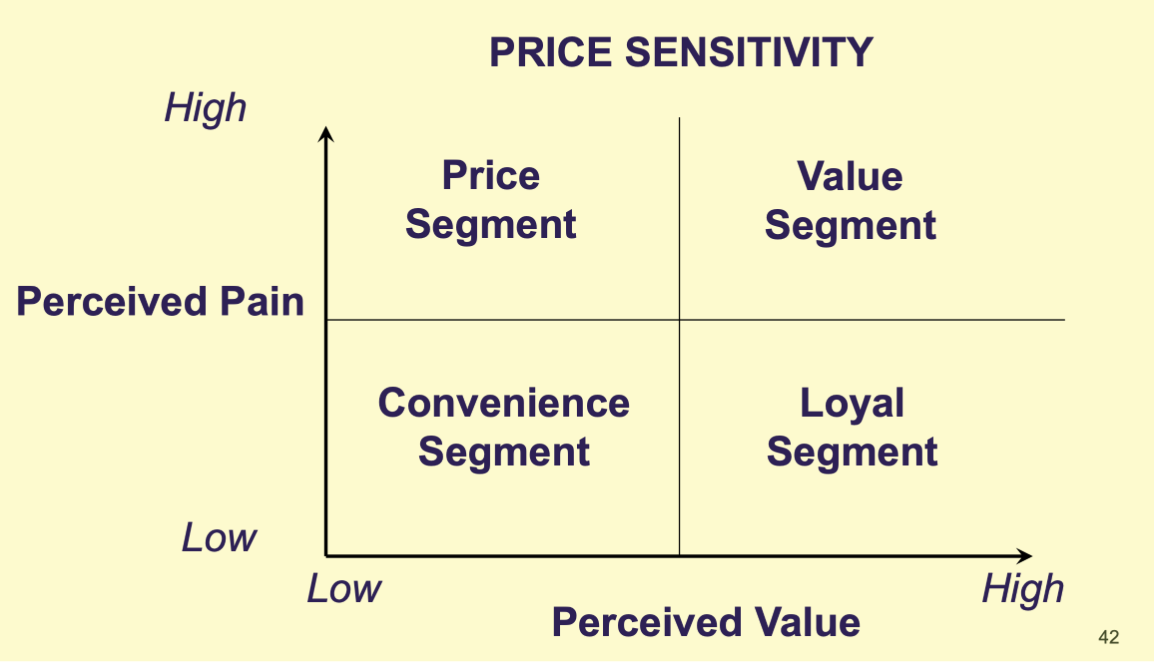
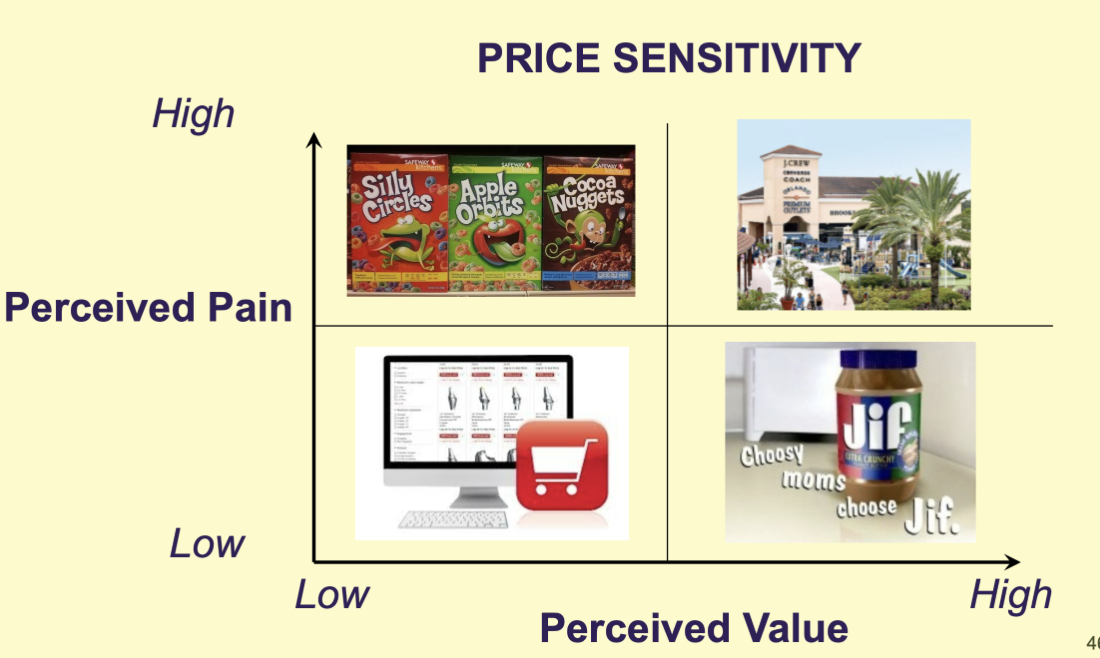
Price sensitivity is a behavioral segmentation method based on perceived pain, the amount of anxiety and negative feelings consumers experience when paying what they believe to be a high price for a product, and perceived value, the amount of product differentiation a consumer perceives among products. What are the four customer segments that result from this model?
Price Segment: high price sensitivity, high perceived pain, low perceived value
Convenience Segment: (low all around) low perceived value, low perceived pain, low price sensitivity
Loyal Segment: high perceived value, low price sensitivity, low perceived pain
Value Segment: (high all around) high perceived value, high perceived pain high price sensitivity
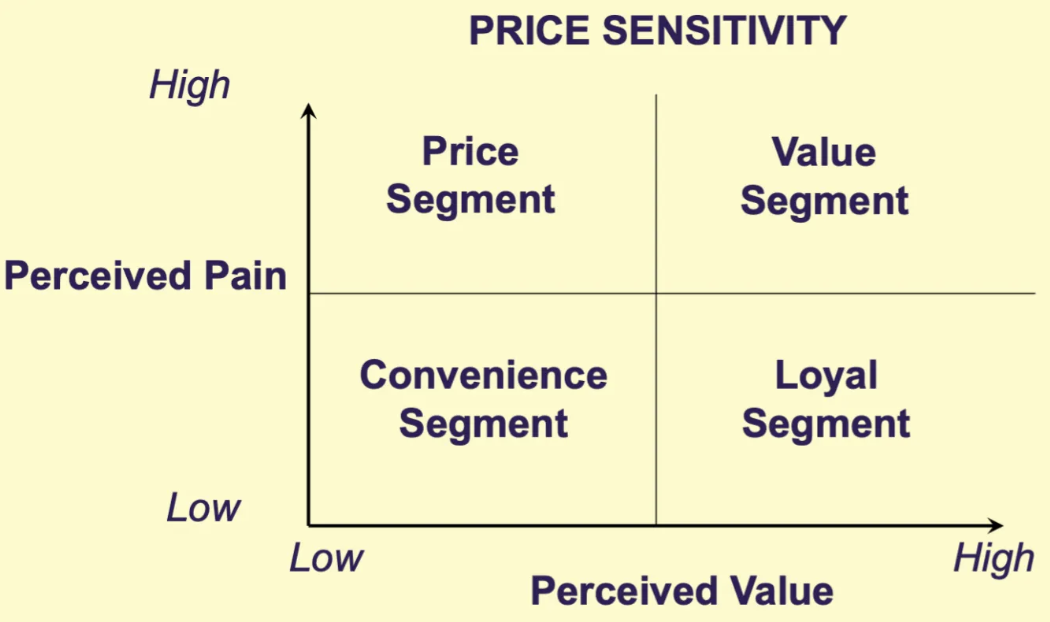
Describe the price segment from the behavior segmentation model. List examples
people who are sensitive on price > brand, will choose the “off brand” product over the name because it is cheaper
example: purchasing CVS band-aids, over name brand band-aids because they are cheaper
Describe the value segment from the behavior segmentation model. List examples
will go out of their way (save up or travel) just to purchase their desired product
example: outlet malls
Describe the convenience segment from the behavior segmentation model. List examples
least intuitive customer, doesn’t mind spending a lot of money to have something nice and/or convenient
example: food delivery service (uber eats/doordash)
Describe the loyal segment from the behavior segmentation model. List examples
will purchase their desired product no matter what
ie: “choosy moms chose Jiffy”, designer brands
What are the advantages and disadvantages of behavioral segmentation?
Advantages:
TONS of available data
allows for personalized, highly target marketing
obvious connection to behavior
Disadvantages:
doesn't tell us “why”
raises issues of privacy