Units 1, 2, and 3 Biology Benchmark Review
1/149
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Cell Membrane
Controls what comes into and out of a cell; found in plant and animal
Cell Wall
Ridged outer layer of plant cell
Cytoplasm
Gel-like fluid where the organelles are found
Mitochondria
Produces the energy a cell needs to carry out its functions, powerhouse of cell in EUKARYOTIC cells
Lysosomes
Uses chemical to break down food and worn out cell parts, garbage collector of cell
Vacuoles
Stores food, water, wastes and other materials in plant cells
Golgi apparatus/ Golgi Body
Receives proteins & materials from the ER, packages them, & distributes them, post office of cell
Chloroplasts
Captures energy from the sunlight and uses it to produce food in plant cells
RER/ Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
"highway" that assembles and packages proteins
ribosomes can be found on the surface
Ribosomes
Assembles amino acids to create proteins
Nucleus
Contain DNA, which controls the functions of the cell and production of proteins
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Chromatin
Tiny strands inside the nucleus that contains the instructions for directing the cells functions
Cell
Basic unit of life. All cells contain a cell membrane and DNA
Eukaryote
Cells that contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Example: animal cells, plant cells, fungus
Prokaryotes
Cells that do not contain a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Simple Example: bacteria
Nuclear envelope
membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
Organelle
Specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell
Chromosomes
Contain the genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next.
Cytoskeleton
Gives eukaryotic cells there shape and involved in movement. A network of protein filaments made up of microfilaments and microtubules.
Centrioles
In animal cells located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division.
Smooth ER
Makes lipids
Chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into glucose
ALL cells have
Genetic Material
Cytoplasm
Cell Membrane
Ribosomes
Bacteria is this type of cell
Prokaryotic
A plant Cell is this type of cell
Eukaryotic
simple diffusion
Diffusion that doesn't involve a direct input of energy or assistance by carrier proteins.
Passive Transport
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane, passive transport
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels, no energy required, passive transport
Molecular pumps
When a cell uses energy to pump molecules across the membrane through a protein channel
Active Transport
Endocytosis
A process in which a cell engulfs extracellular material through an inward folding of its plasma membrane, active transport
Exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
Molecules moved by simple diffusion
oxygen and carbon dioxide ( o2, co2)
Molecules moved through osmosis
water (h2o)
Molecules who move through cell membrane via facilitated diffusion
Glucose (sugar) and Salt (C6H12O6, NaCl)
What is moved across the cell membrane via Molecular Pumps
Ions, charged particles, Na+, K+
The reason smooth ER is referred to as "smooth"
there are no ribosomes on the smooth ER
Similarity of viruses with prokaryotes and eukaryotes
contains genetic info (DNA)
requires a host to reproduce
viruses
Hypertonic Solution
Water concentration is lower, but solute concentration is higher. Water will move out of the cell into the solution, and the cell will shrivel.
Hypotonic Solution
Water concentration is higher, but solute concentration is lower. Water will move into the cell out of the solution, and the cell will swell.
Which structures distinguish plant cells?
central vacuole, chloroplasts, cell wall made of cellulose
Fungal Cells
Eukaryotic, Have a cell wall made of chitin
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes both have
ribosomes, cell membrane, genetic material, cytoplasm
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference (Low to high concentration)
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell (High to low concentration)
permeable
Able to be passed or soaked through
synthesize
to make
The name of the molecule required for active transport
ATP
Characteristics of life
Be composed of 1 or more cells
Able to reproduce
Able to grow and develop
Able to respond to stimuli
Able to adapt and evolve
Able to obtain energy from food (metabolism)
Tissue
Groups of connected cells. The cells may all be the same type or they may be of multiple types. In either case, the cells work together to carry out a specific function. (Examples: skeletal muscle tissue, contractions)
Organ
Different tissues working together to perform a function (Examples: Kidney, lungs, heart)
Organ System
Different organs working together to perform a specific function (Example: Disgestive system)
Organism
Individual member of a species or population
Population
Multiple organisms of the same species living together
Community
Multiple populations of different species living together
Ecosystem
community PLUS all of the abiotic factors in the environment
Biome
Multiple ecosystems that share characteristics but are located in different parts of the planet (Grassland, Tundra)
Carbohydrates
First thing body uses for energy
Sugars and starches
C, H, O
Monomer- Monosaccharides (single sugar molecules)
Polymer- Polusaccharides (Larger sugar molecules)
Found in CELLULOSE (Structural support in plant cell walls)
Lipids
Energy storage (Long Term)
fats, oils, and phospholipids
C, H, O
Monomer- Fatty acids
Polymer- Triglycerides (Fatty acid chains
Phospholipids make up the cell membrane
Proteins
Enzymes, bone structure, transport, antibodies, receptors, energy
Meats, nuts, and dairy
Monomer- Amino Acids
Polymer- Polypeptides (linked amino acids)
Shape determines what it does
Nucleic Acids
Stores and expresses genetic information (DNA OR RNA)
C, H, O, N, P
Monomer- Nucleotides
Polymer- Nucleic Acids
Catabolic Chemical Reaction
break down larger molecules into simpler compounds 🡪 a release in energy = exergonic
Anabolic Chemical Reaction
build larger molecules from smaller ones 🡪 requires consuming energy to do it = endergonic
Activation Energy
the amount of energy needed to make a chemical reaction start
Reactants (Substrate)
substances that are changed during a chemical reaction
Products
substances that are made by a chemical reaction
Endothermic reaction
absorbs energy (in the form of heat or light) Ex. Photosynthesis
Exothermic reaction
releases energy (in the form of heat or light) Ex. Cellular Respiration
Enzymes
mostly proteins that speed up biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy.
Because they speed up reactions, they are called catalysts = substances that speed up reactions without being permanently altered
They have an “active site” that only fits certain substrates
Can be “denatured” (deformed) by change in temperature, pH, and solubility.
Cell Theory
All living things are made of cells
Cells are the basic unit of life
All cells come from preexisting cells
solute
what gets dissolved
solvent
does the dissolving
Producers (Autotrophs)
Get energy from non-living sources, usually through photosynthesis
Consumers (Heterotrophs)
Get energy from living or once-living organisms
Trophic Levels
the levels of nourishment in a food chain
Rule of Ten
As energy flows from organism to organism, it is used for metabolism and/or converted to heat.
Because of this, the next organism on the chain only receives 10 PERCENT of the energy obtained in the previous level.
The other 90% is used or “lost” as heat
Primary Consumer
Eats producers
Secondary Consumer
Eats primary consumers
Tertiary Consumer
Eats secondary consumers
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
made his own microscope and discovered bacteria by looking at dental scrapings
Robert Hooke
Came up with the term “cell”
Matthias Schliden
Discovered plants are made of cells
Theodor Schwann
Discovered animals are made of cells
Rudolph Virchow/Robert Remak
Proved all cells come from preexisting cells
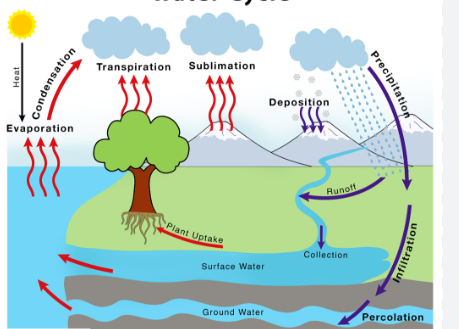
Water Cycle
Precipitation: water falls to Earth as a liquid (usually rain, sleet or snow).
The Main Stages:
Infiltration: some water seeps underground from the surface of the Earth.
Aquifer: An underground layer of permeable rock that can hold water.
Runoff: liquid water that isn’t infiltrated runs along the surface and collects in bodies of water.
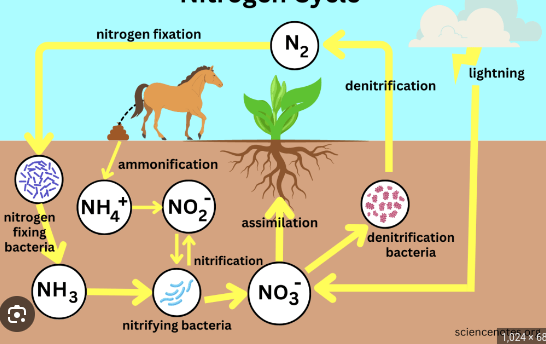
Nitrogen Cycle
a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction.
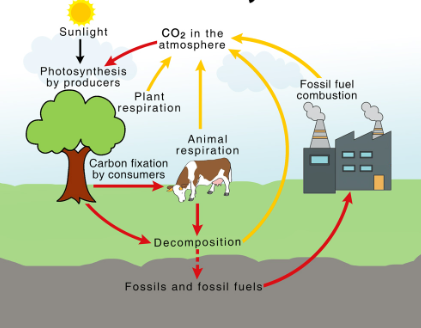
Carbon Cycle
the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere
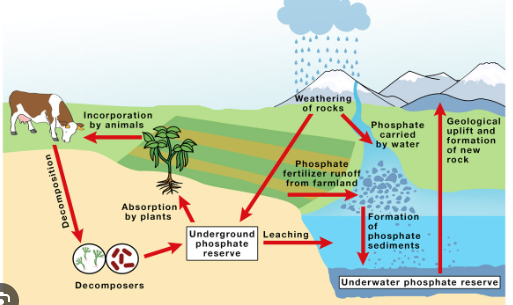
Phosphorus Cycle
the biogeochemical cycle that describes the transformation and translocation of phosphorus in soil, water, and living and dead organic material.
Doesn't involve organisms
Lightning converts nitrogen in atmosphere into a form plants can use (nitrate)
N2 gas, makes up 78% of the atmopshere
CANNOT be used by plants and animals