Human Anatomy & Physiology I: Structural Levels, Homeostasis, and Body Systems
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Anatomy
The Study of Form
Physiology
The Study of Function
Comparative Anatomy
The study of more than one species to analyze evolutionary trends.
Cadaver dissection
Cutting & separation of organs to study their relationships.
Gross anatomy
What is visible with the naked eye.
Histology
Examination of cells with a microscope.
Comparative physiology
Involves the study of different species.
Atom
Smallest unit of matter (think of periodic table).
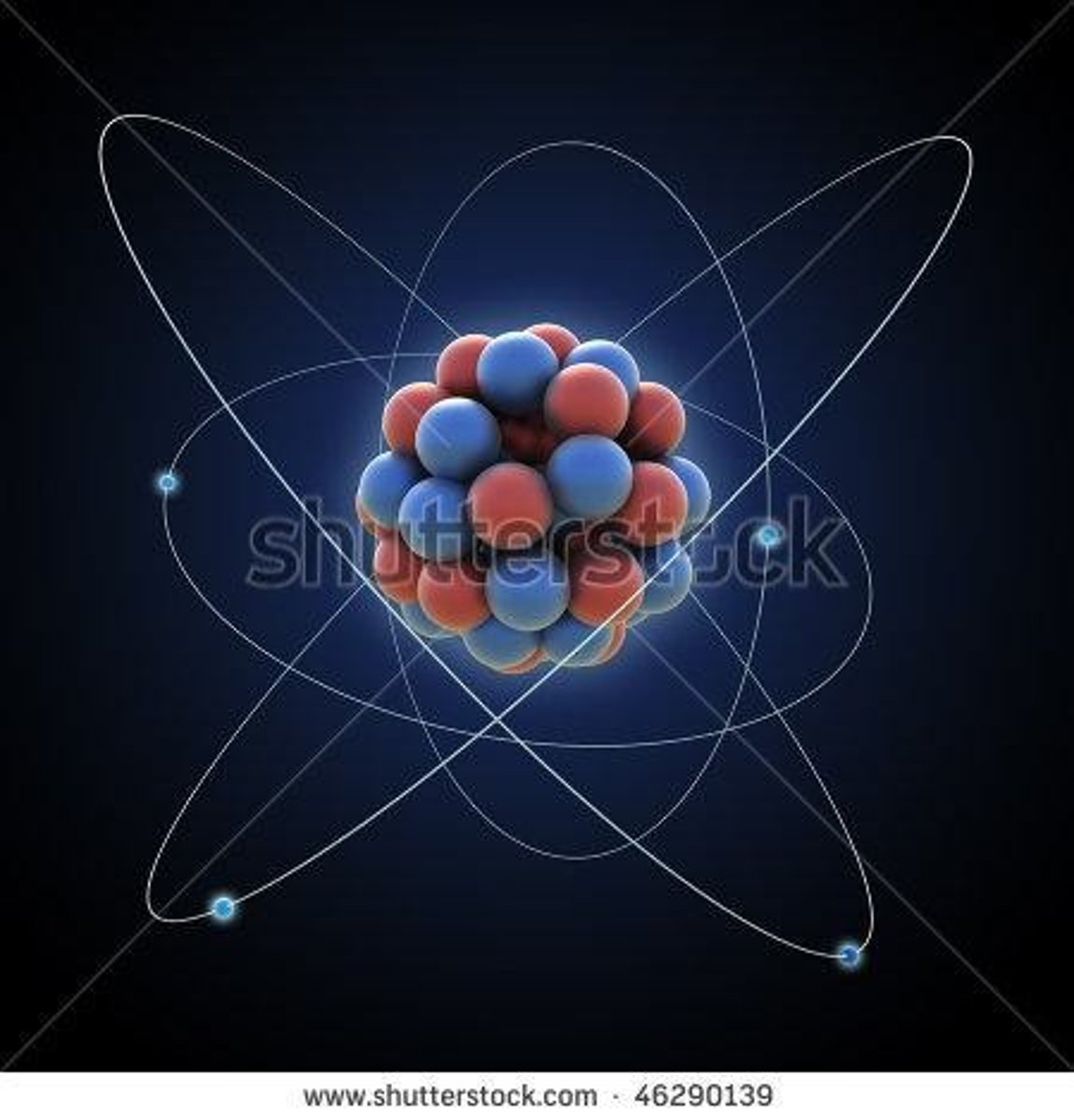
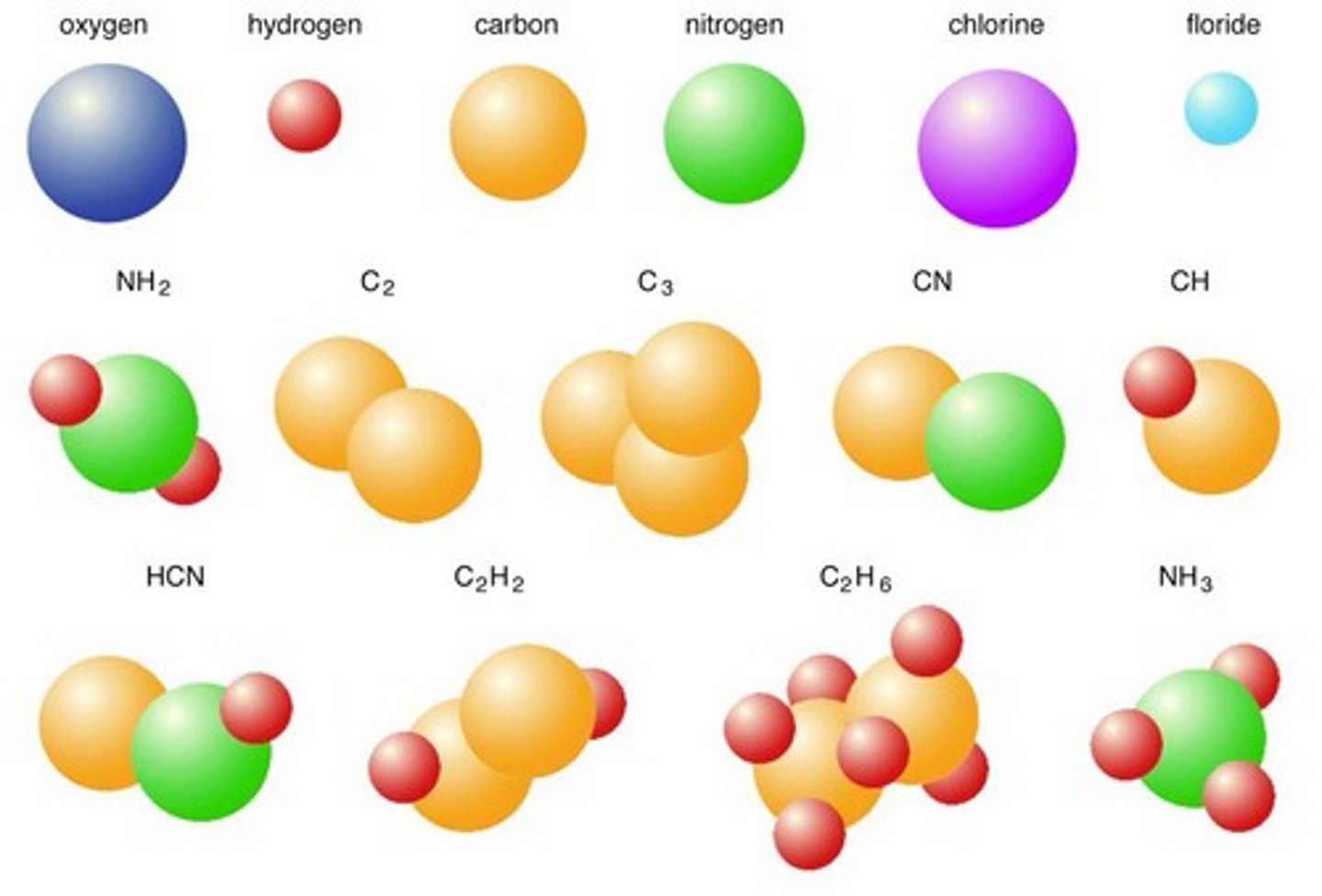
Molecules
Two or more atoms joined together chemically.
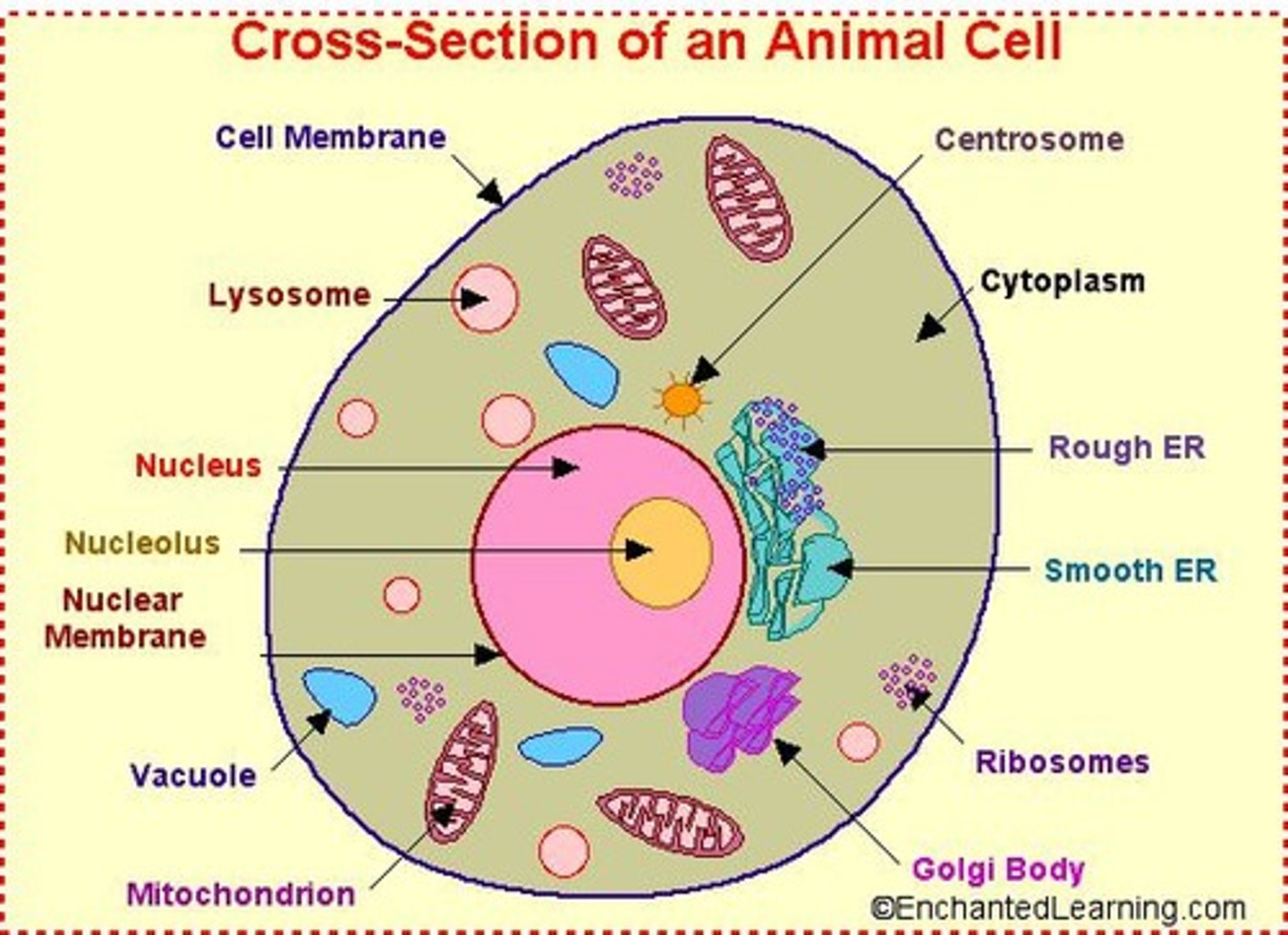
Organelles
Tiny organ-like structures inside cells.
Cell
Smallest unit of life.
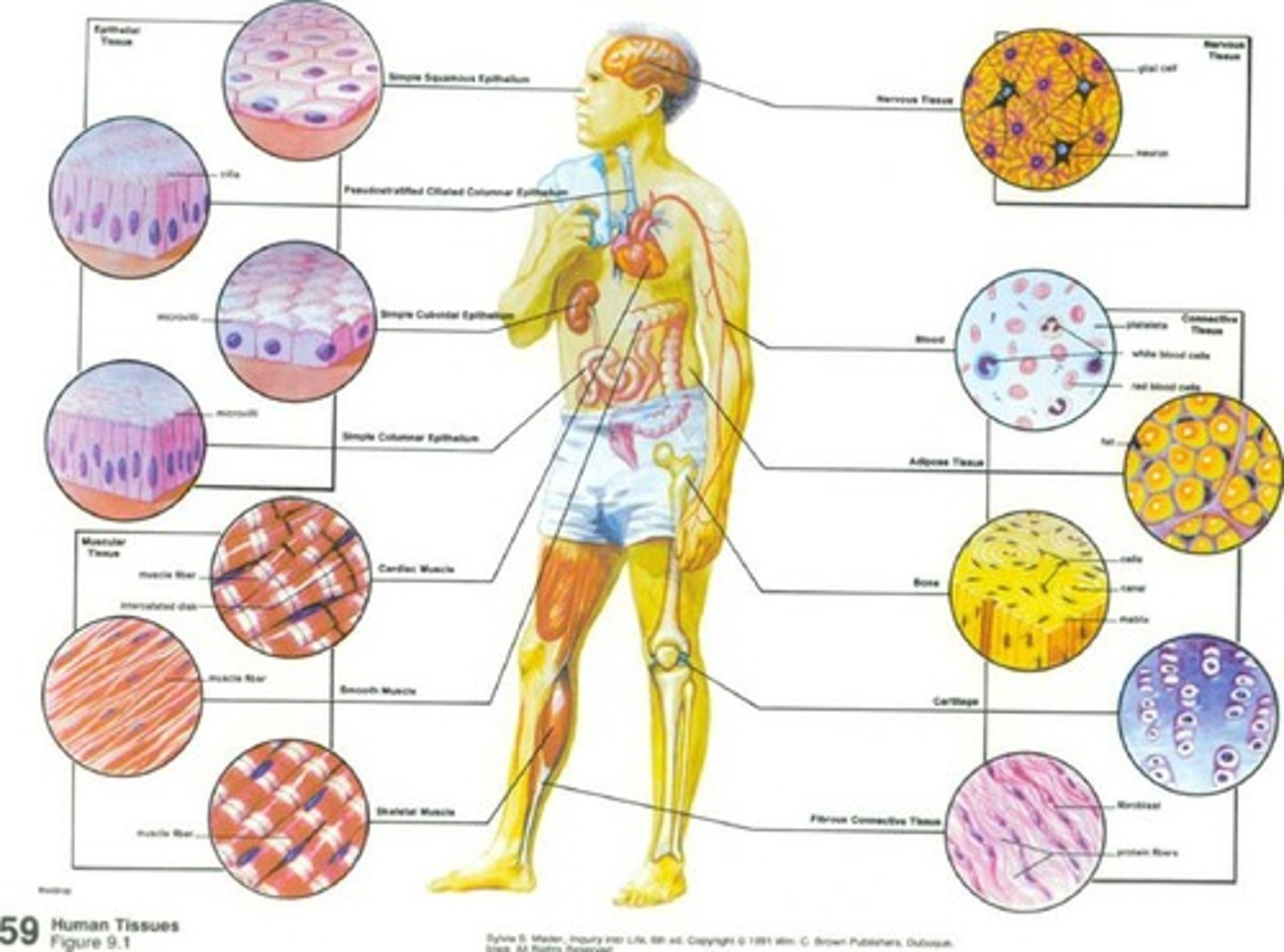
Tissue
Two or more cells of similar type working together.
Organ
Two or more tissues working together.
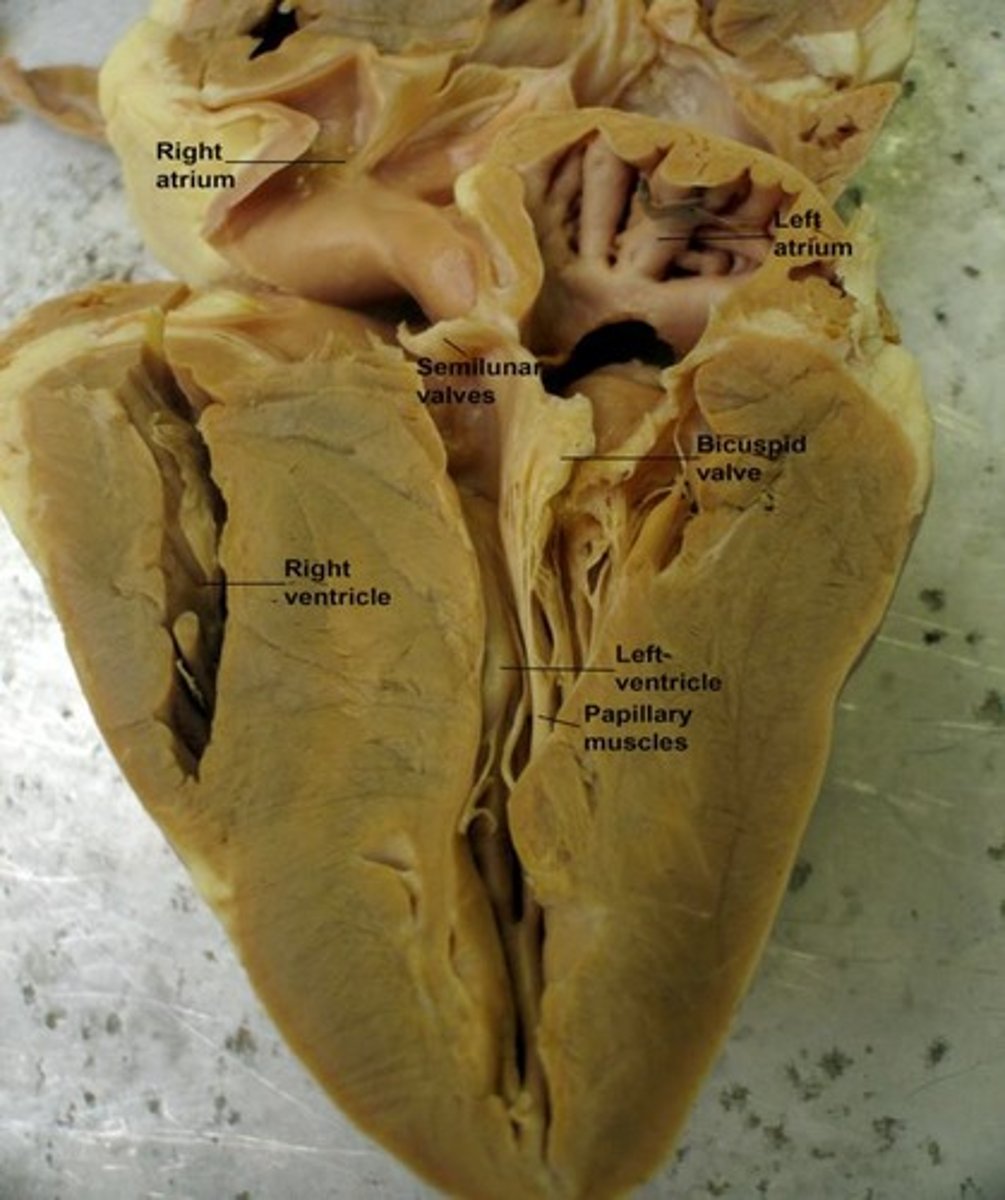
Organ System
Two or more organs working together.
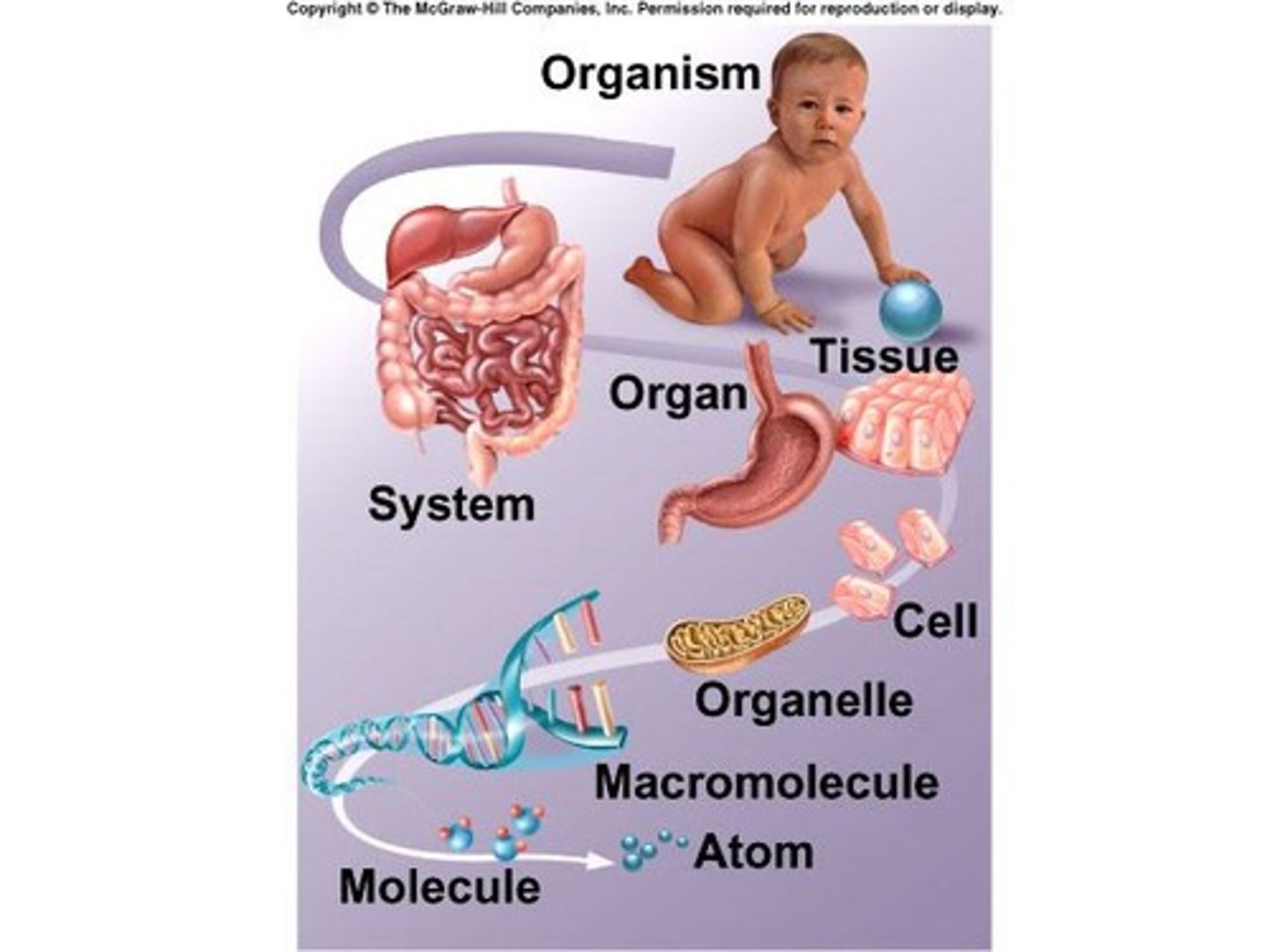
Organism
All the organs working together.
Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain balance and equilibrium within its internal environment, even when faced with external changes.
Dynamic equilibrium
Internal environment fluctuates within a range around a certain set point.
Loss of homeostatic control
Causes illness or death.
Feedback Systems
All Feedback Systems Have Three Basic Components: Receptor, Control Center, Effector.
Receptor
Detects change (stimuli).
Control Center
Receives info from the receptor, determines a set point for a normal range, analyzes the change & determines a proper response to the change.
Effector
Carries out the necessary response determined by the control center.
Acid-Base Homeostasis
Carotid & aortic bodies in the neck & heart monitor hydrogen ion concentration (pH) in the blood.
pH
If pH drops below 7.35 (acidosis), receptors send signals to the medulla oblongata of the brain.
Medulla oblongata
Acts as a control center to activate respiratory muscles.
Respiratory muscles
Act as effectors to increase breathing rate which increases pH.
Blood Glucose Homeostasis
If blood glucose exceeds 100mg/dl, the beta cells of the pancreas act as receptors & control center to evaluate the high blood glucose.
Beta (β) cells
Release insulin; the liver, muscle, and fat cells that respond to the insulin by taking up glucose from the blood are the effectors.
Hyperglycemia
High blood glucose levels that can be decreased by insulin.
Negative Feedback
A reversal process used to maintain normal ranges of activity in order to stay healthy.
Positive Feedback
The output of a system causes further increases in output, often found in processes that need to be completed rather than maintained.
Example of Positive Feedback
Uterine smooth muscle during the child-birthing process: ↑contraction → ↑↑contraction → ↑↑↑contraction.
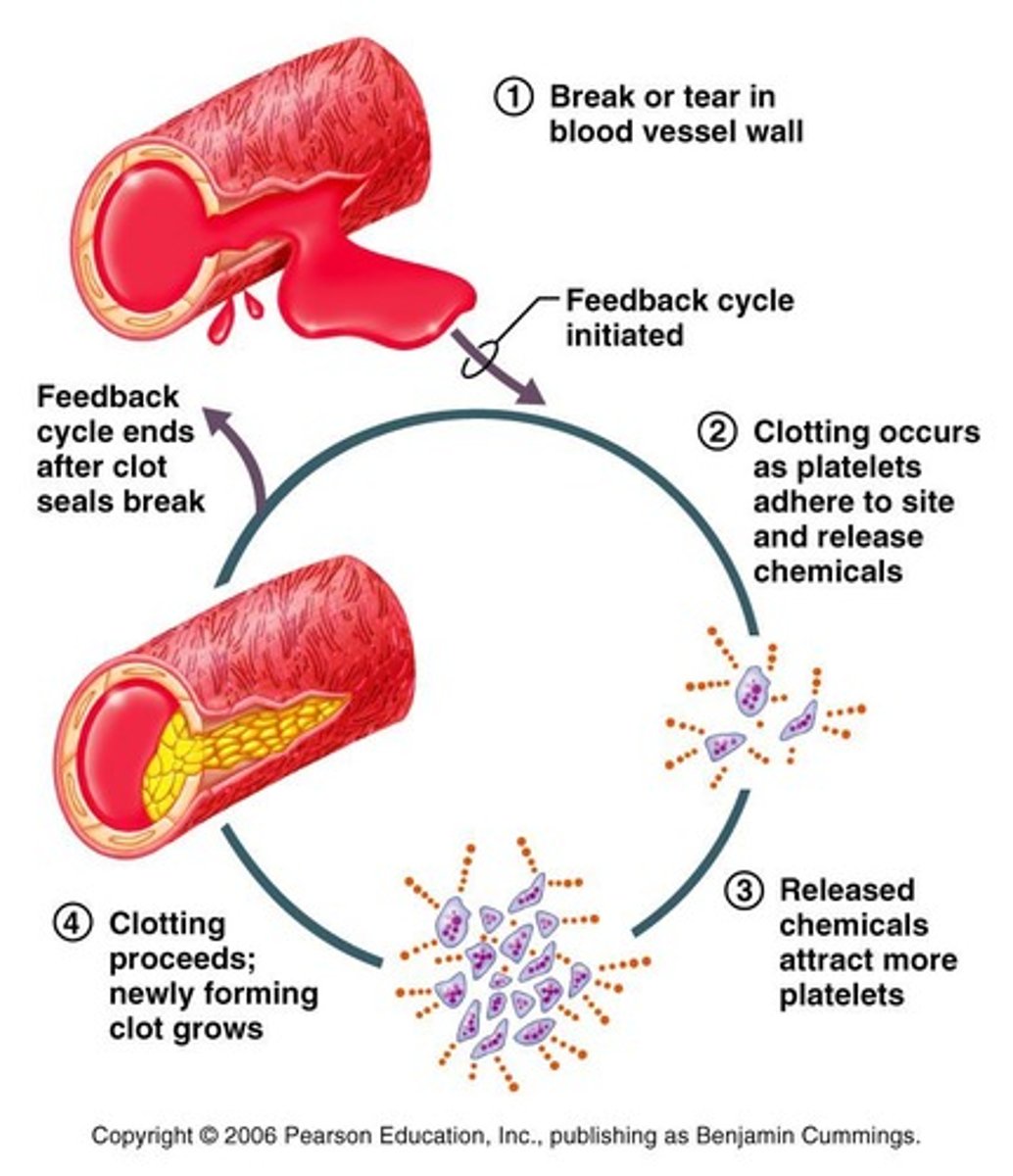
Feedback Mechanisms
Negative feedback is used to maintain a state of dynamic equilibrium (homeostasis); positive feedback amplifies changes in a feedback loop.
Integumentary System
Forms the external body covering, protects deeper tissue from injury, synthesizes vitamin D, regulates temperature.
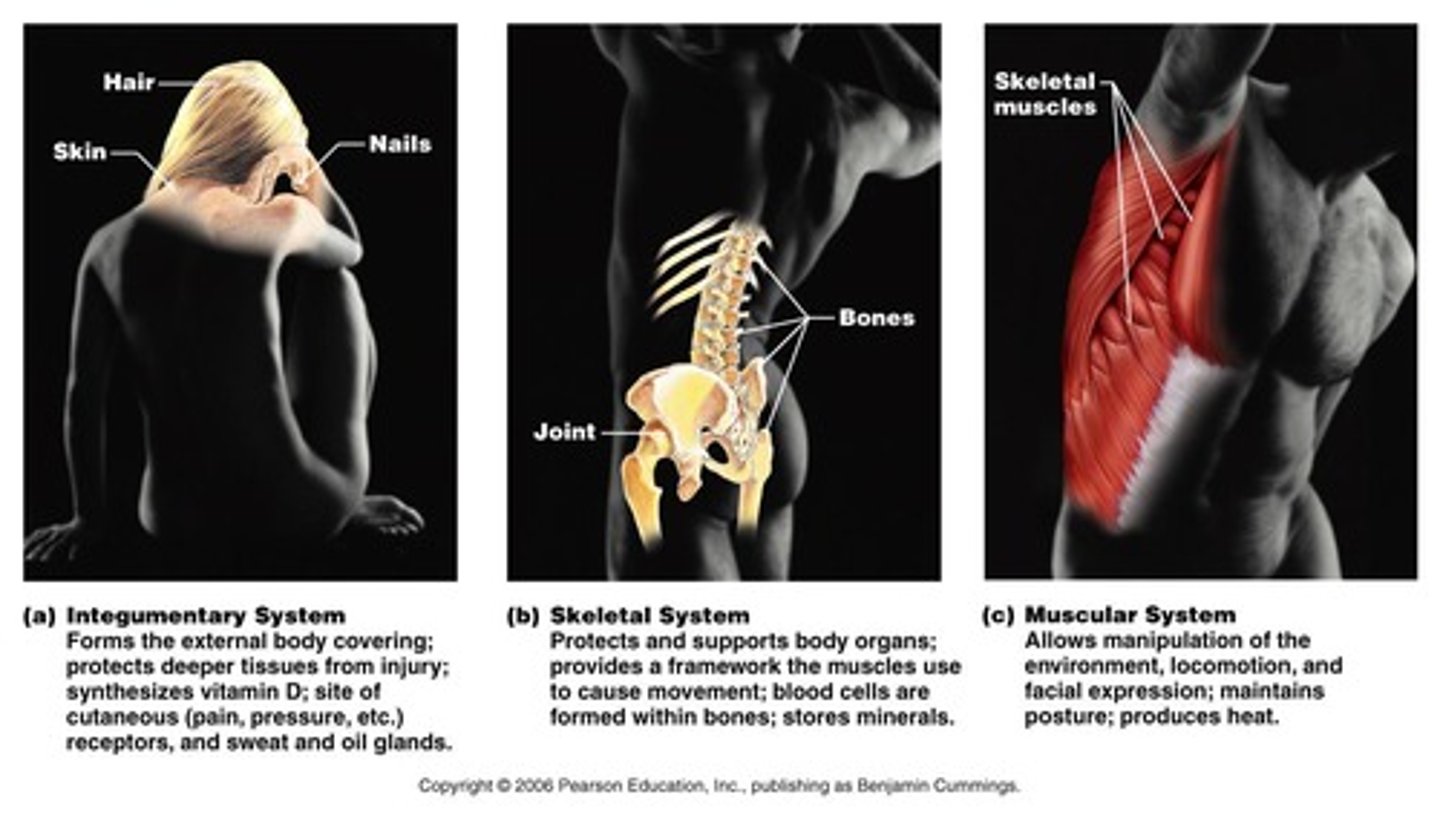
Skeletal System
Protects and supports body organs, provides muscle attachment for movement, site of blood cell formation, stores minerals.
Muscular System
Allows locomotion, maintains posture, produces heat.
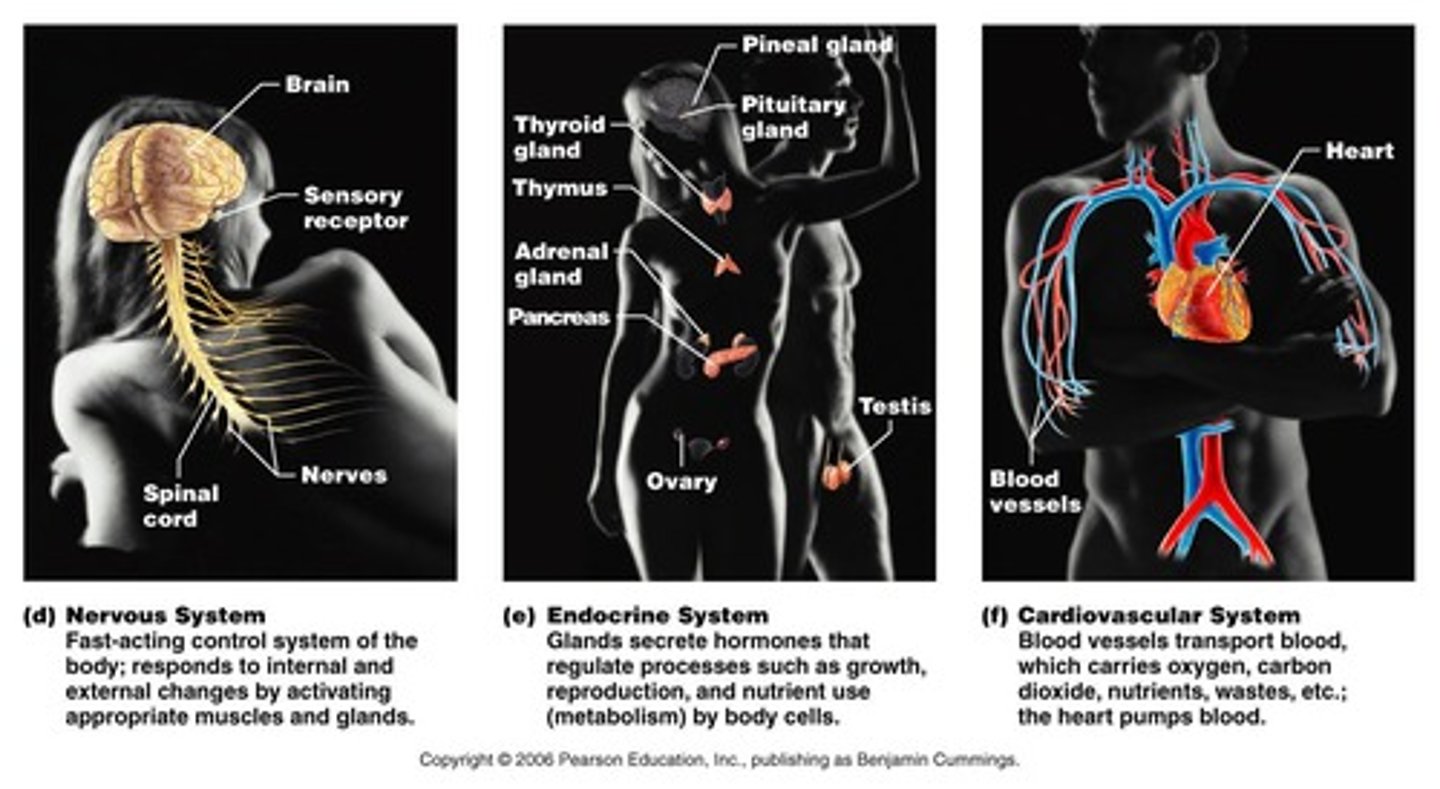
Nervous System
Fast-acting control system that responds to internal and external change and activates muscles and glands.
Endocrine System
Secretes regulatory hormones via glands including hypothalamus, pituitary, thymus, thyroid, adrenals, pancreas, and reproductive organs.
Carotid body
A structure involved in the regulation of blood pH and oxygen levels.
Aortic Bodies
Structures that help monitor blood chemistry and regulate respiratory function.
Epidermis
The outermost layer of skin.
Dermis
The layer of skin beneath the epidermis that contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
Hypodermis
The layer of tissue beneath the dermis that helps insulate the body and protects underlying muscles and organs.
Biceps brachii
A muscle located in the upper arm that flexes the elbow.
Triceps brachii
A muscle located in the upper arm that extends the elbow.
Gastrocnemius
A major muscle of the calf that is involved in walking and running.
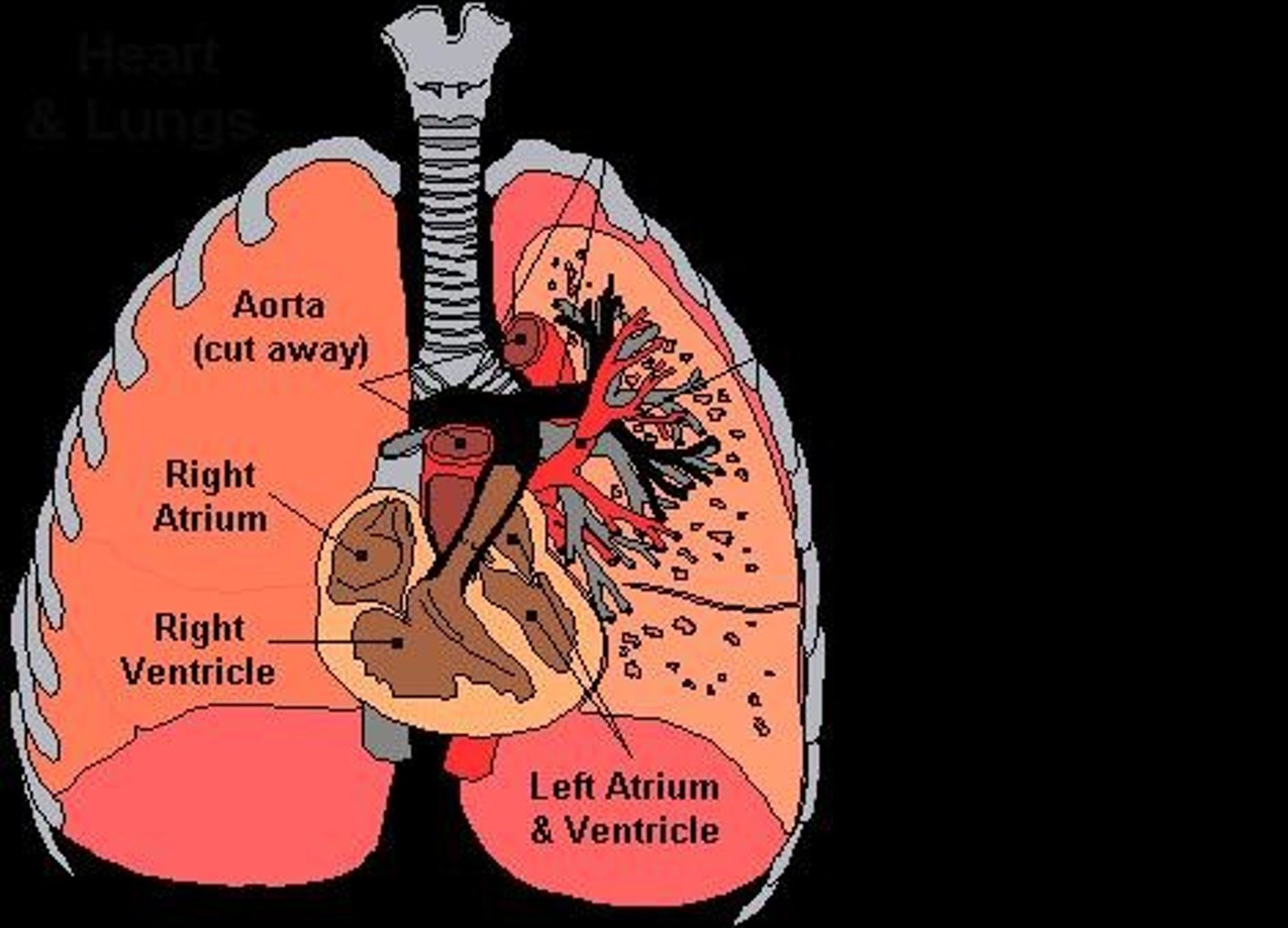
Cardiovascular System
Consists of heart, blood vessels, and blood; responsible for transportation of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, hormones, and antibodies.
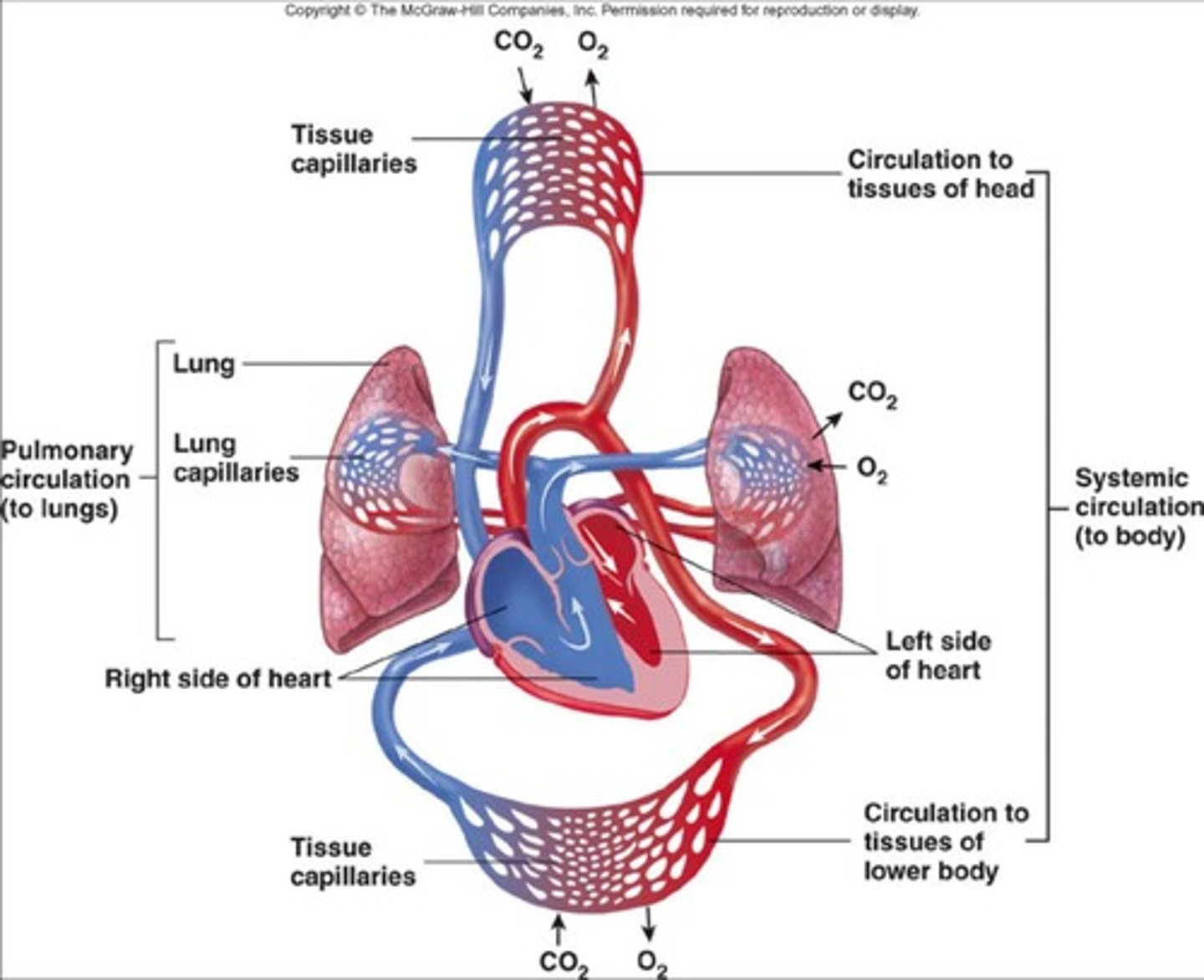
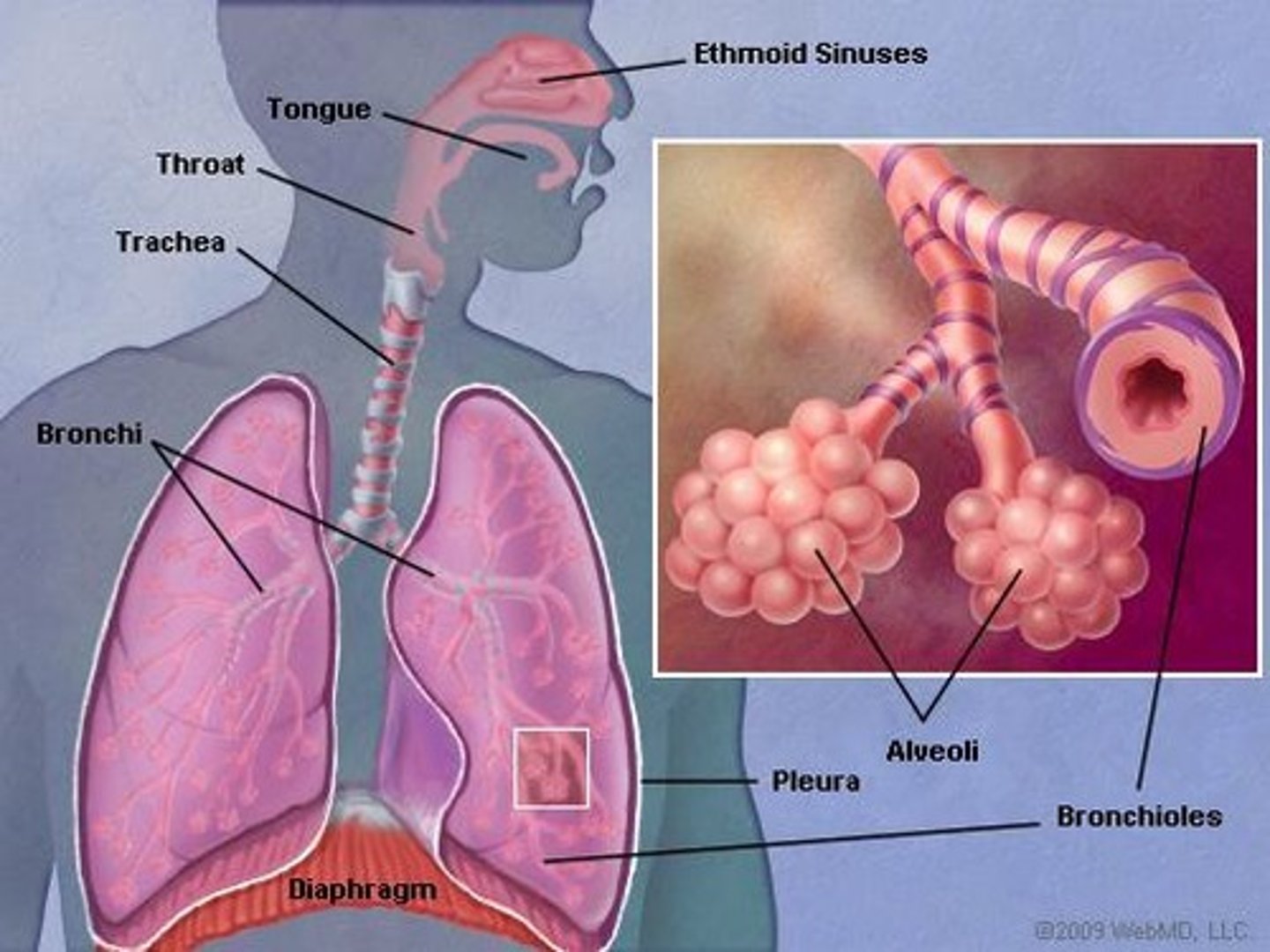
Respiratory System
Includes nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, glottis, epiglottis, bronchi, alveoli, and lungs; functions to supply oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
Lymphatic System
Responsible for transportation of fluid (lymph) from tissues back to the blood, filtering lymph and blood, and housing white blood cells for protection.
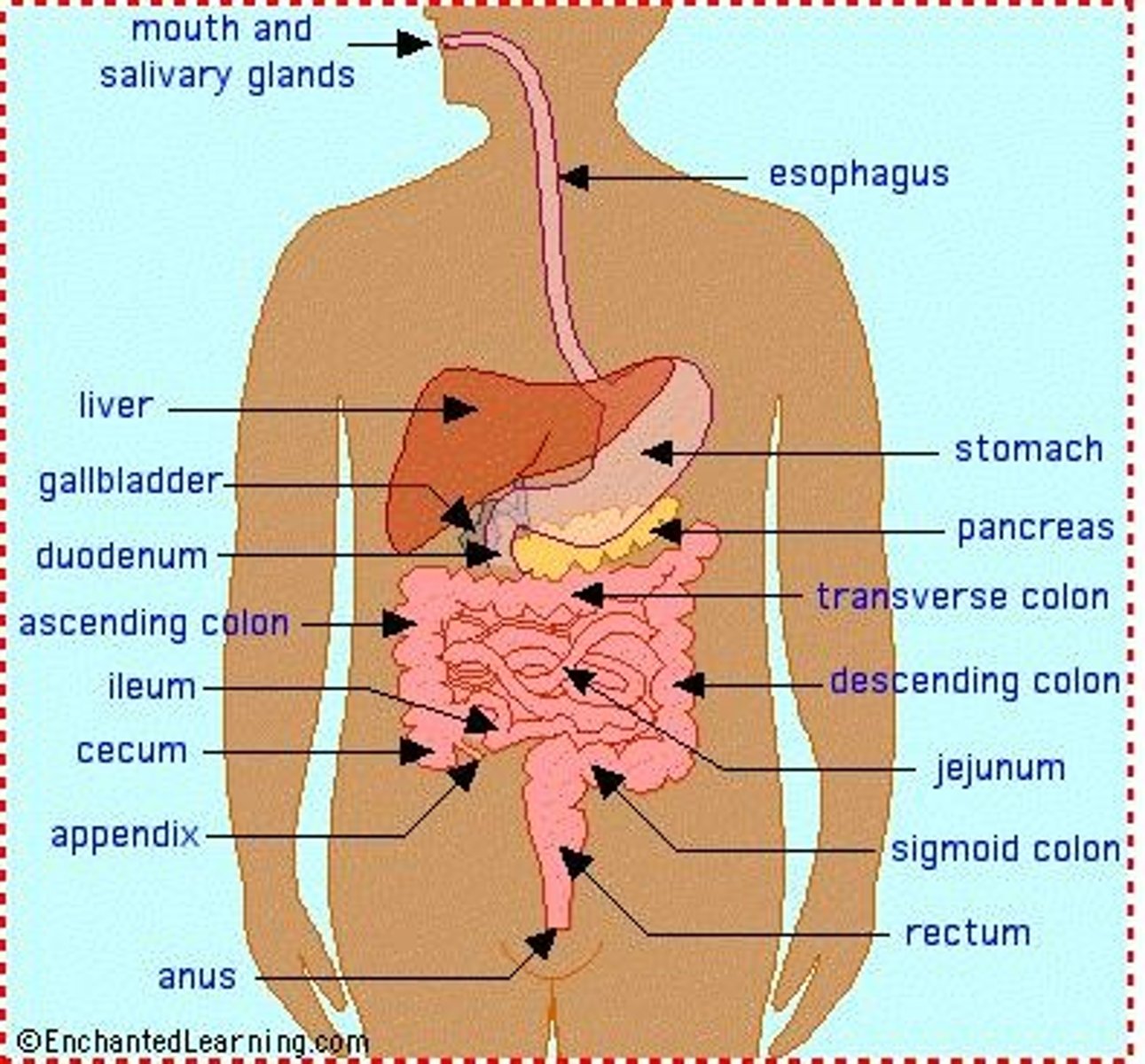
Digestive System
Comprises oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, and gall bladder; functions include food breakdown, absorption of nutrients, conversion of food waste products into fecal matter, vitamin production, and water & mineral regulation.
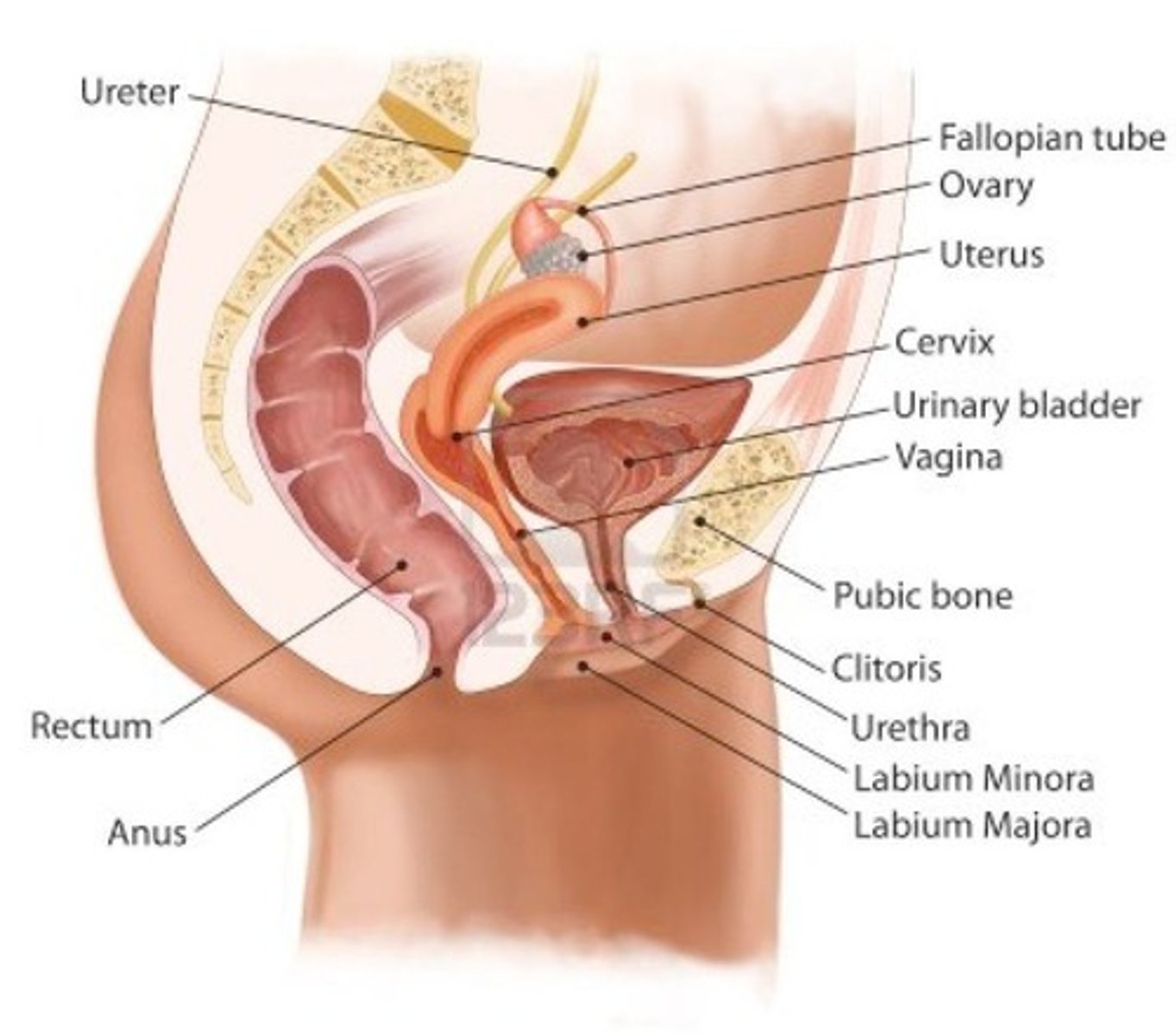
Urinary System
Includes kidney, ureter, bladder, and urethra; functions to eliminate nitrogen wastes (urea, uric acid, ammonia) and regulate electrolytes, water, and acid/base balance.
Male/Female Reproductive Systems
Includes ovaries, testes, prostate, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, and penis; functions include gamete production, producing new offspring, and hormone release to control the reproductive cycle.
Scientific Method
A systematic approach to problem-solving involving observation, hypothesis, theory, experimentation, variables, experimental group, control group, conclusions, placebo, and peer review.
Observation
The first step in the scientific method, where inductive reasoning uses observations to construct general principles.
Hypothesis
A suggested explanation that accounts for an observation; a formal testable statement.
Testable Prediction
Developed before an experiment to test the hypothesis; states expected outcomes if the hypothesis is true.
Experimentation
The process used to test whether a hypothesis is correct, where all variables but one remain constant.
Control Group
The untreated group in an experiment, used for comparison with the experimental group.
Experimental Group
The treated group in an experiment that receives the treatment being tested.
Conclusion
The result arrived at based on the outcomes of an experiment.
Peer Review
A critical evaluation by other experts in the field to ensure honesty, objectivity, and quality of research.
Scientific Theory
An explanatory statement or set of statements derived from facts, laws, and confirmed hypotheses, supported by scientific reasoning and experimental evidence.