AP Bio U3
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
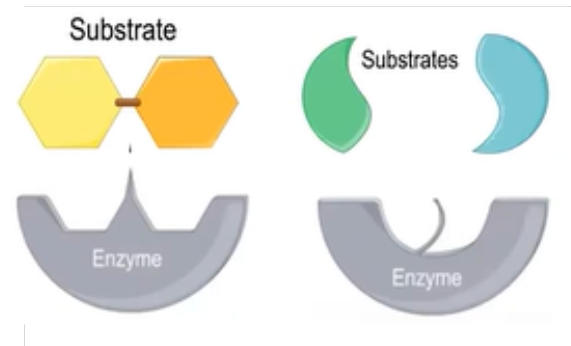
Enzymes
Biological catalysts (proteins) that speed up biochemical proteins —> lowers activation energy requirements
contain an active site to interact w substrates - must be compatible
can have chemical charge(s)
substrate
molecule that can interact w an enzyme
enzyme concentration
cells typically maintain a specific concentration
can facilitate synthesis/digestion reactions
proteins
made up of linear chains of amino acids
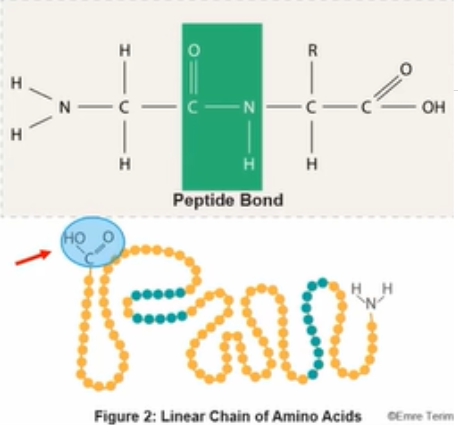
Amino acids
connected by formation of covalent bonds at carboxyl terrminus of growing peptide chain
Primary structure
determined by sequence of amino acids held together by covalent (peptide) bonds
secondary structure
arises through local folding of amino acid chain into elements
alpha helices + beta sheets
Tertiary structure
overall 3D shape of protein and often minimizes free energy; various types of bonds + interactions stabilize the protein during this structure
Quaternary structure
arises from interactions between multiple polypeptide units