Test 2 Study Arc 1013
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Dead Loads
forces from all the "immovable" elements of a building
Live Loads
forces from all the "movable" elements of a building
Compression
capacity to resist being pushed together
Tension
capacity to resit pulling appart
Post and Beam
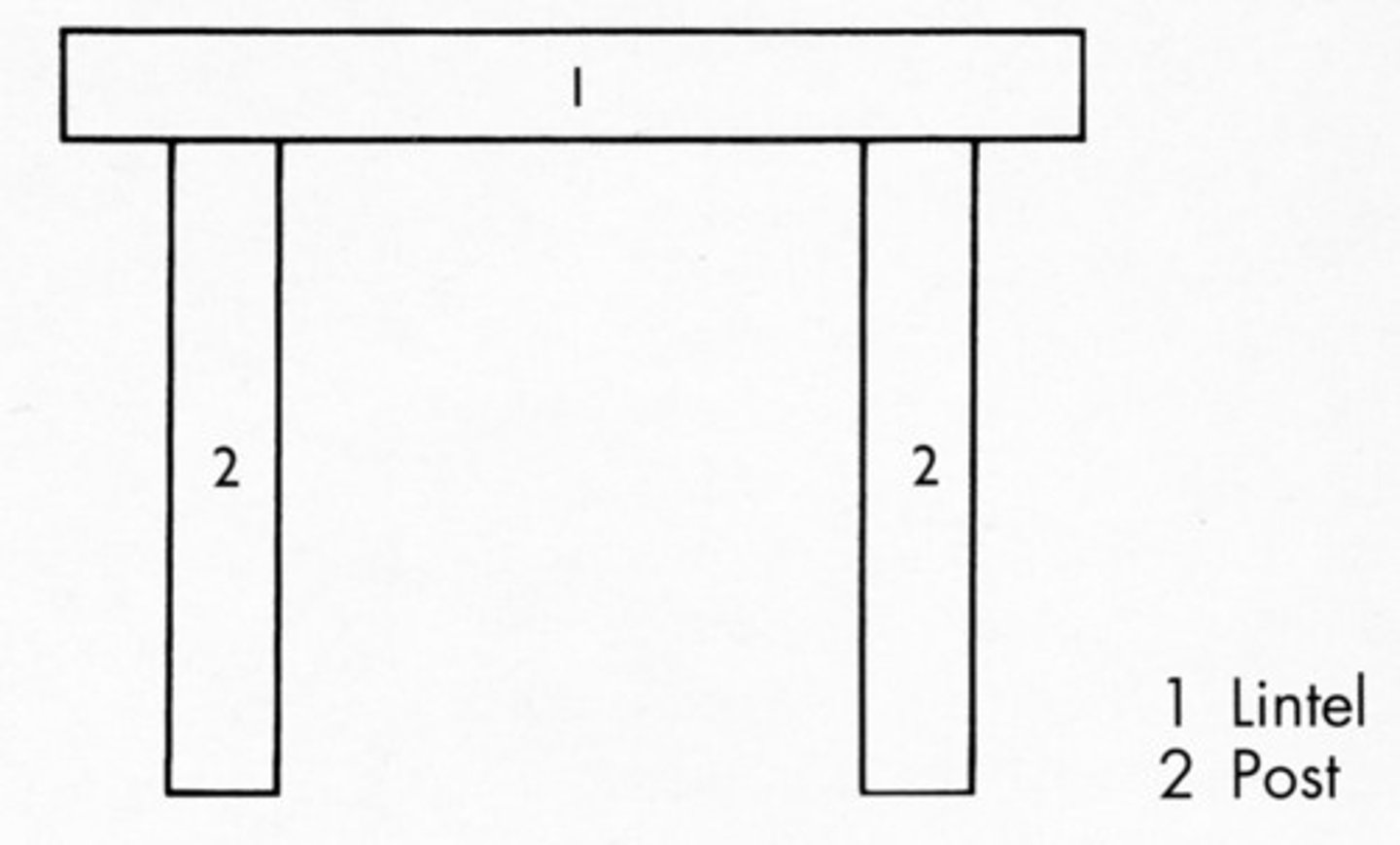
Types of construction and Structural Systems
Frame and Masonry
Freedom Tower
David Childs, FACH (SOM) and David Libeskind

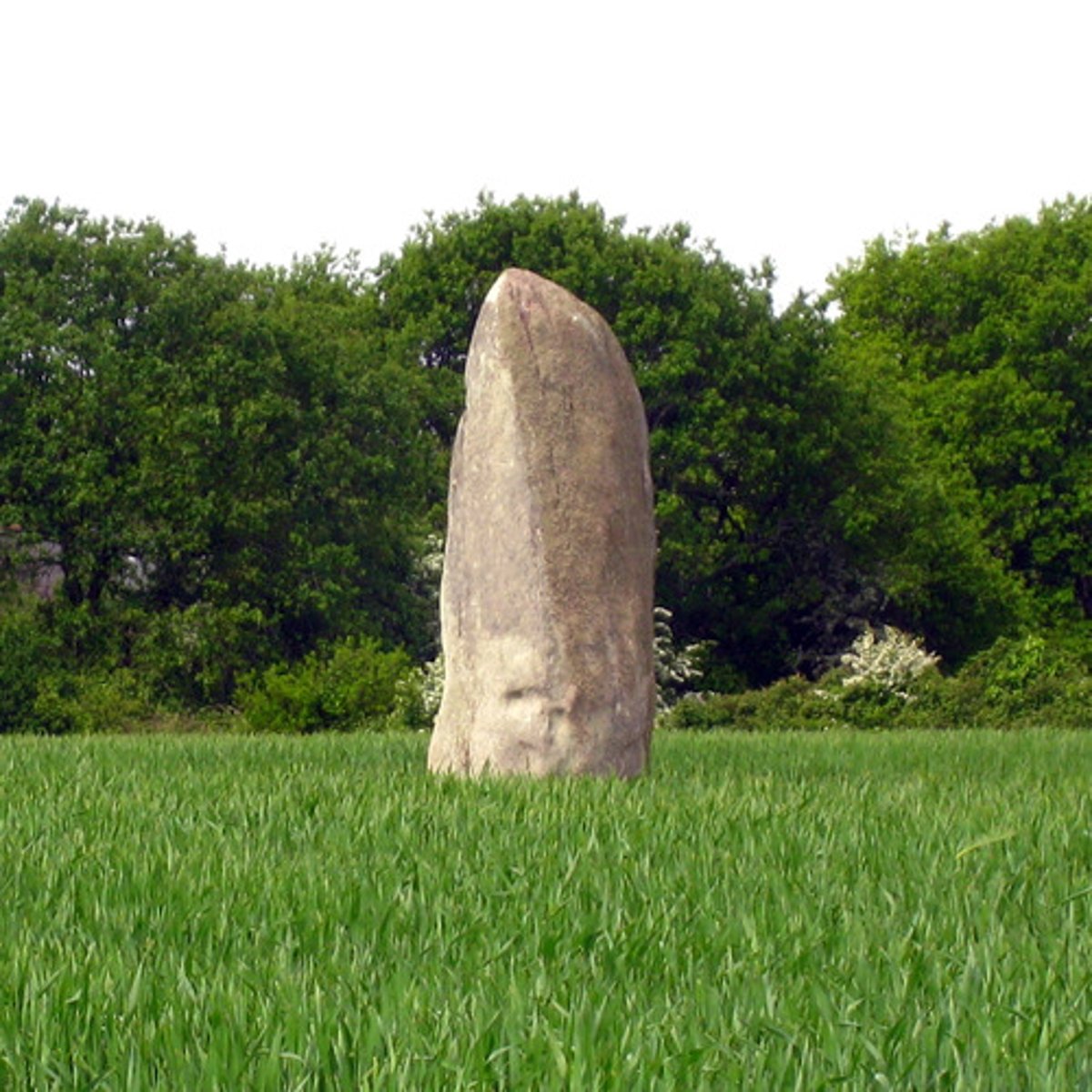
Menhirs
single stone standing upright

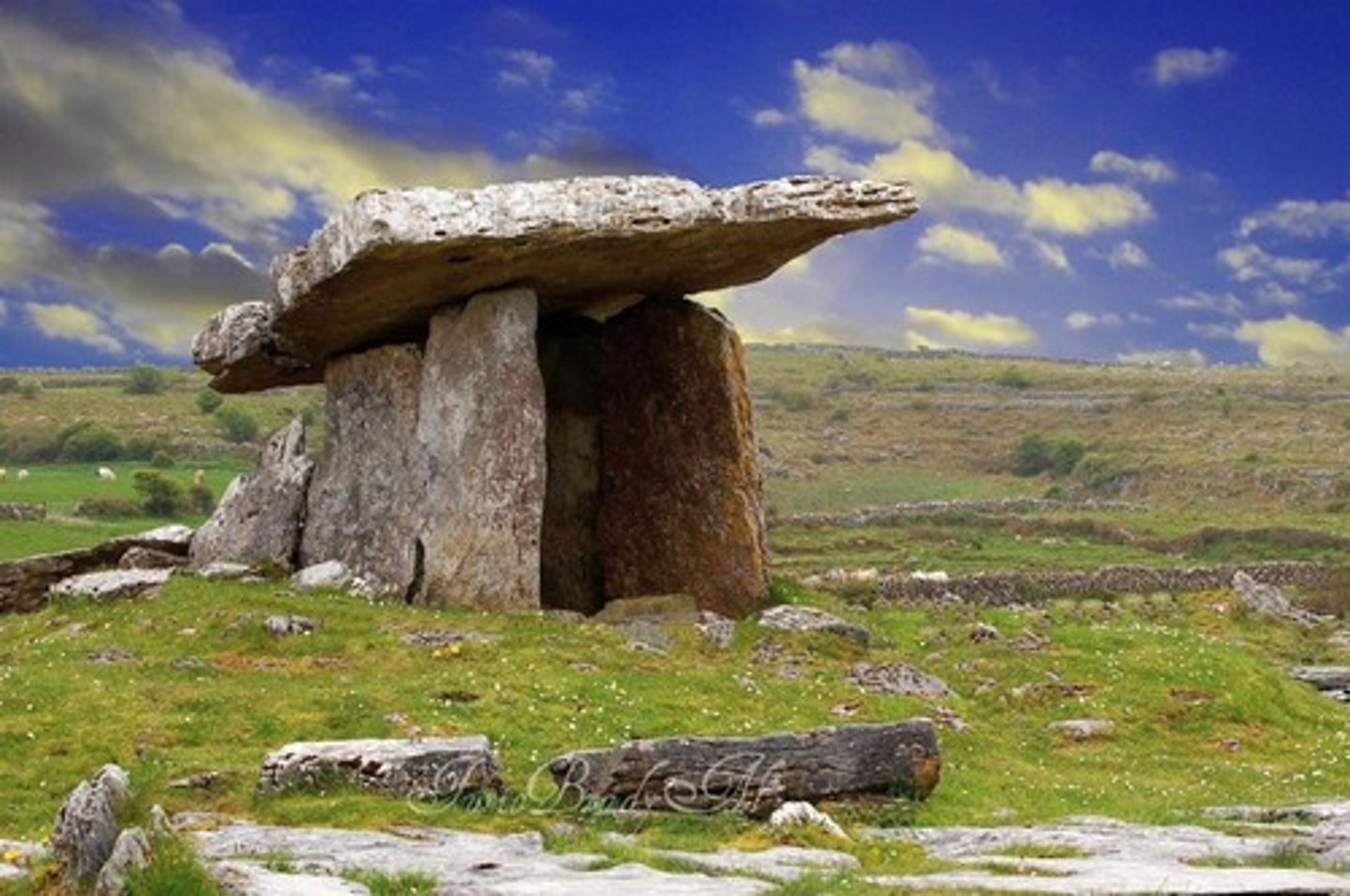
Dolmen
several stones supporting a stone slab

Henges
circular ditches around which some megalithic monuments are arranged

Cromlech
a circle of stones

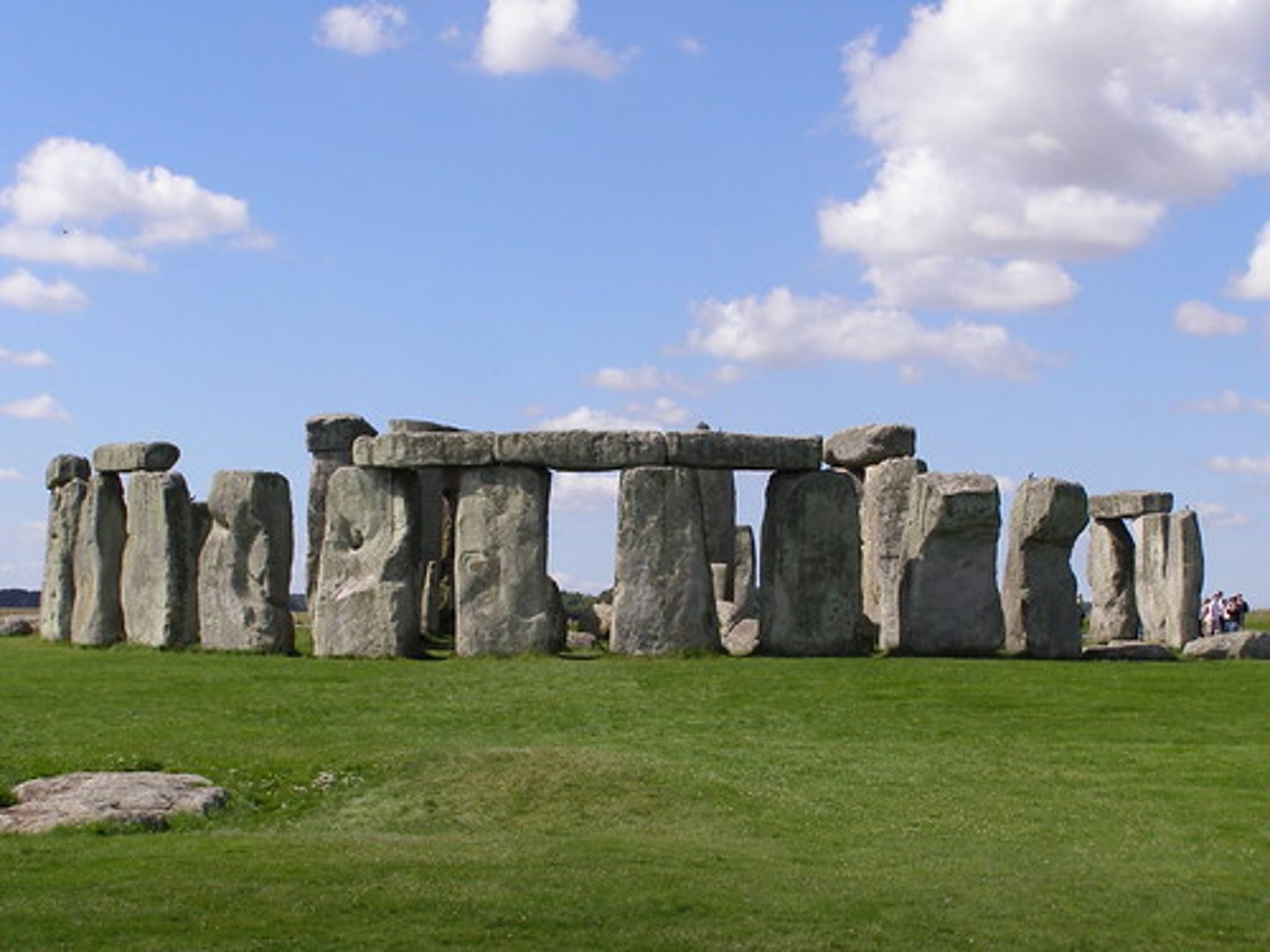
Stonehenge
-Most famous of Neolithic monuments
-Built 3000-2100 B.C.

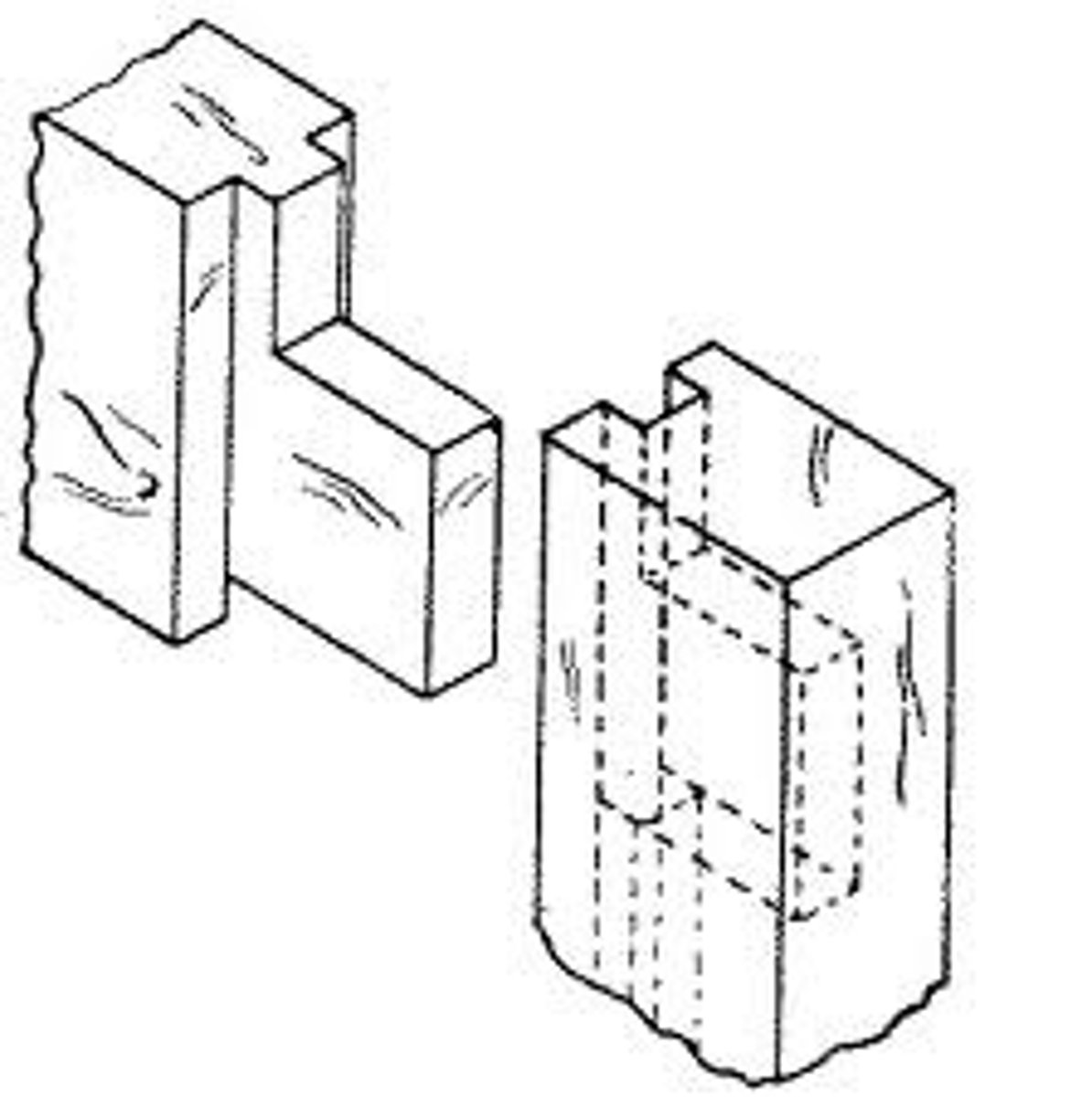
Mortise and tenon
Step Pyramid

Bent Pyramid

Straight-Sided Pyramid
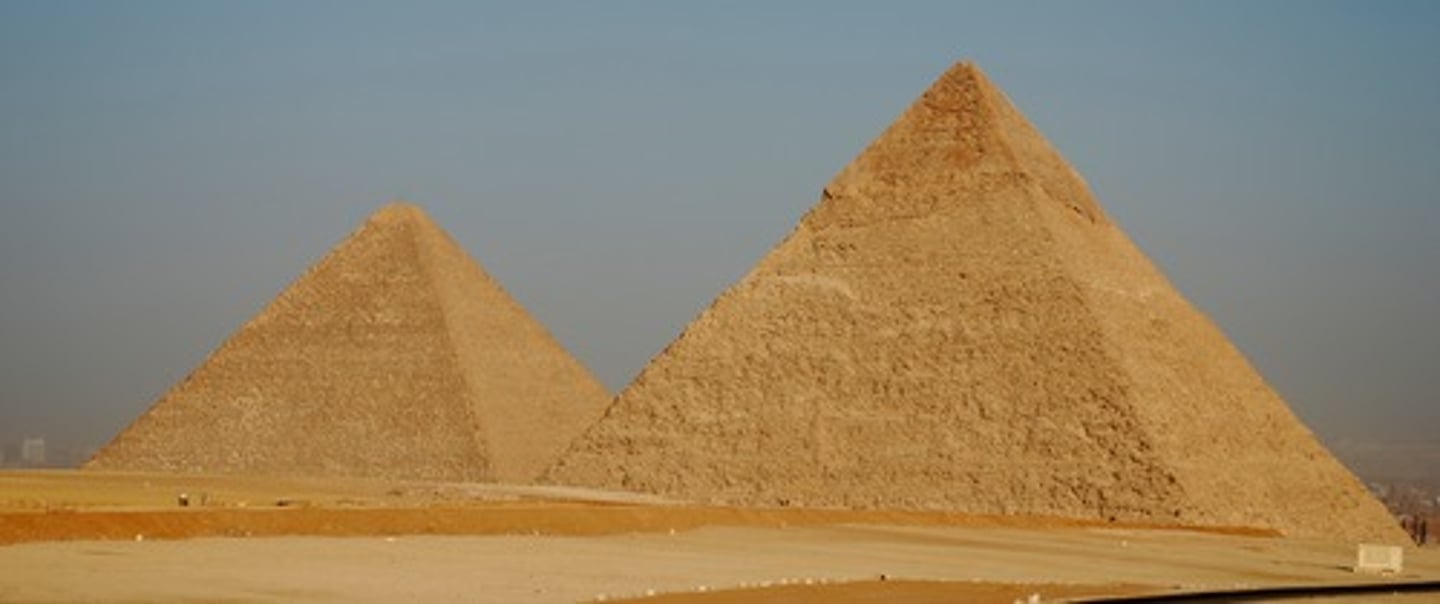

Ziggurats
stepped structures
some of the oldest pyramids
2125 B.C.
Built from mud bricks
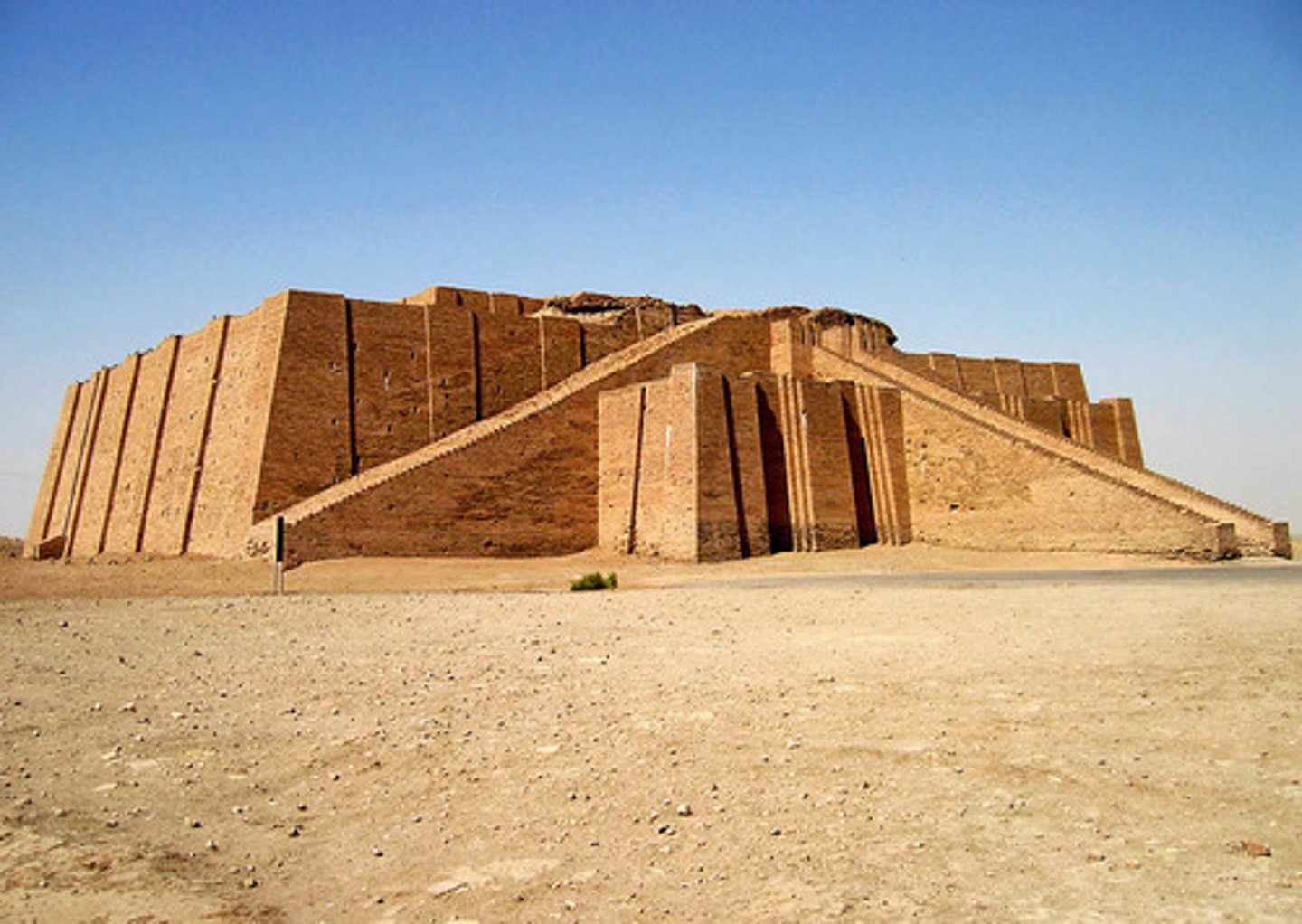

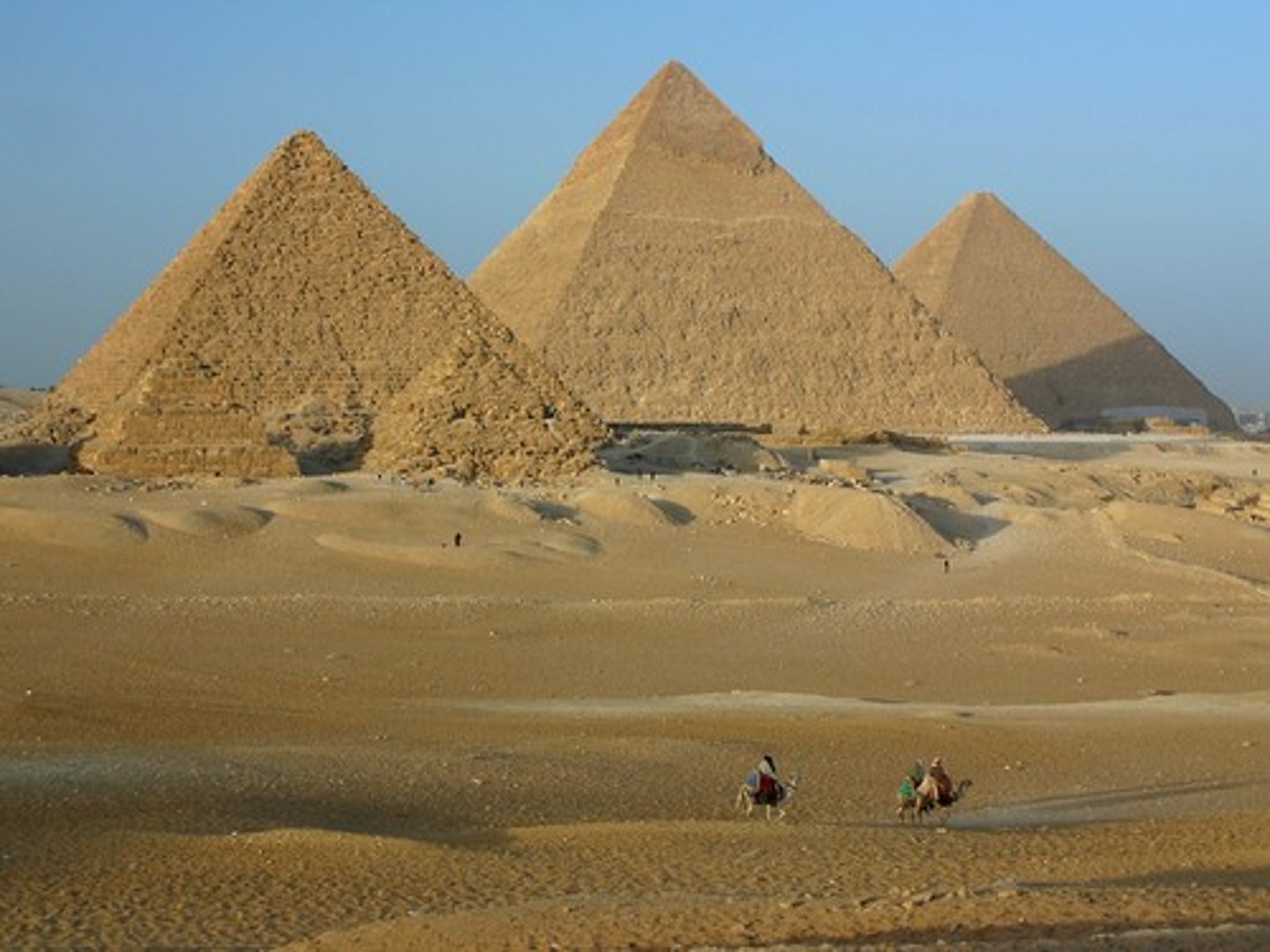
Pyramids of Giza (Great Pyramids)

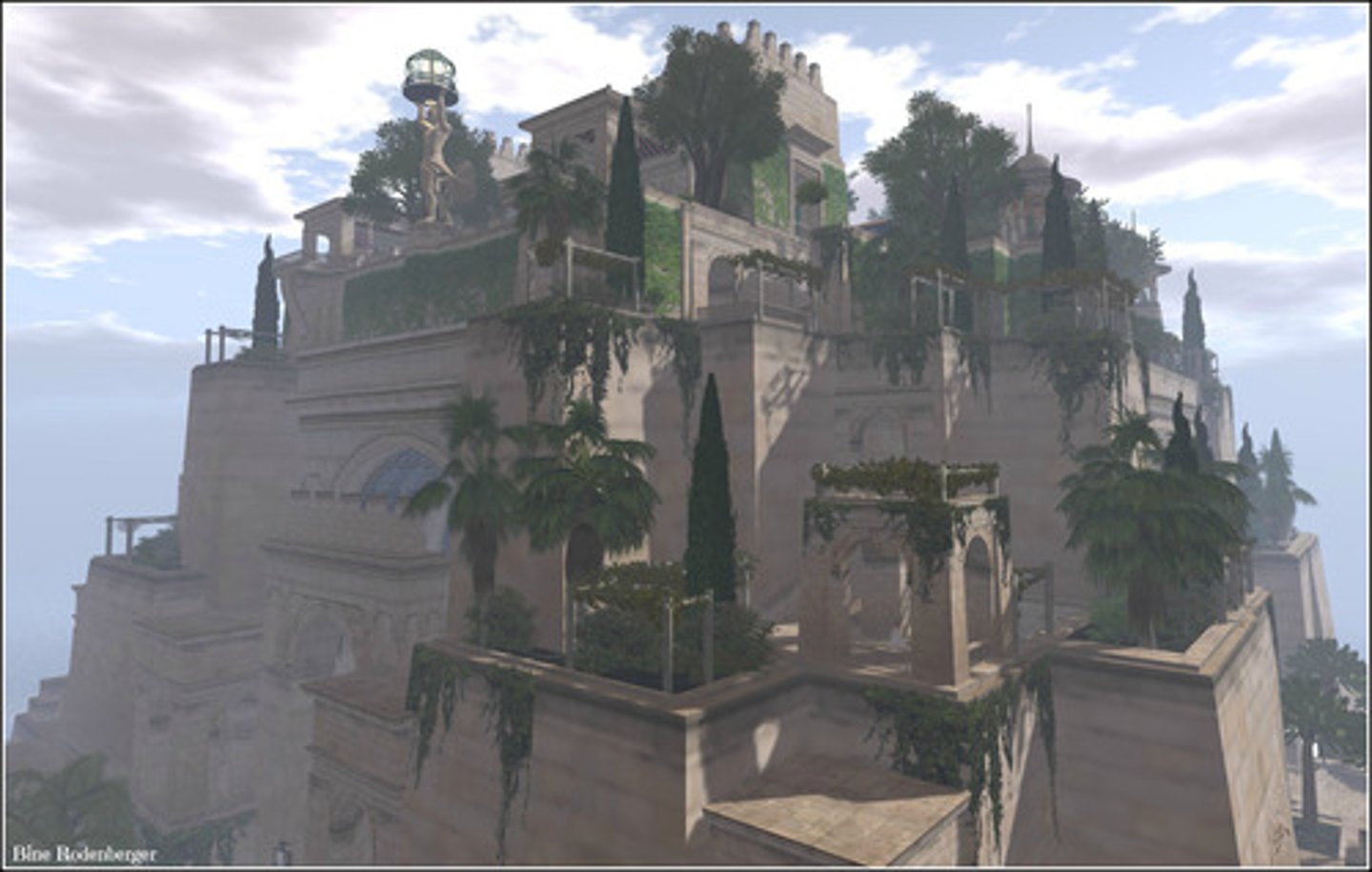
Hanging Gardens of Babylon

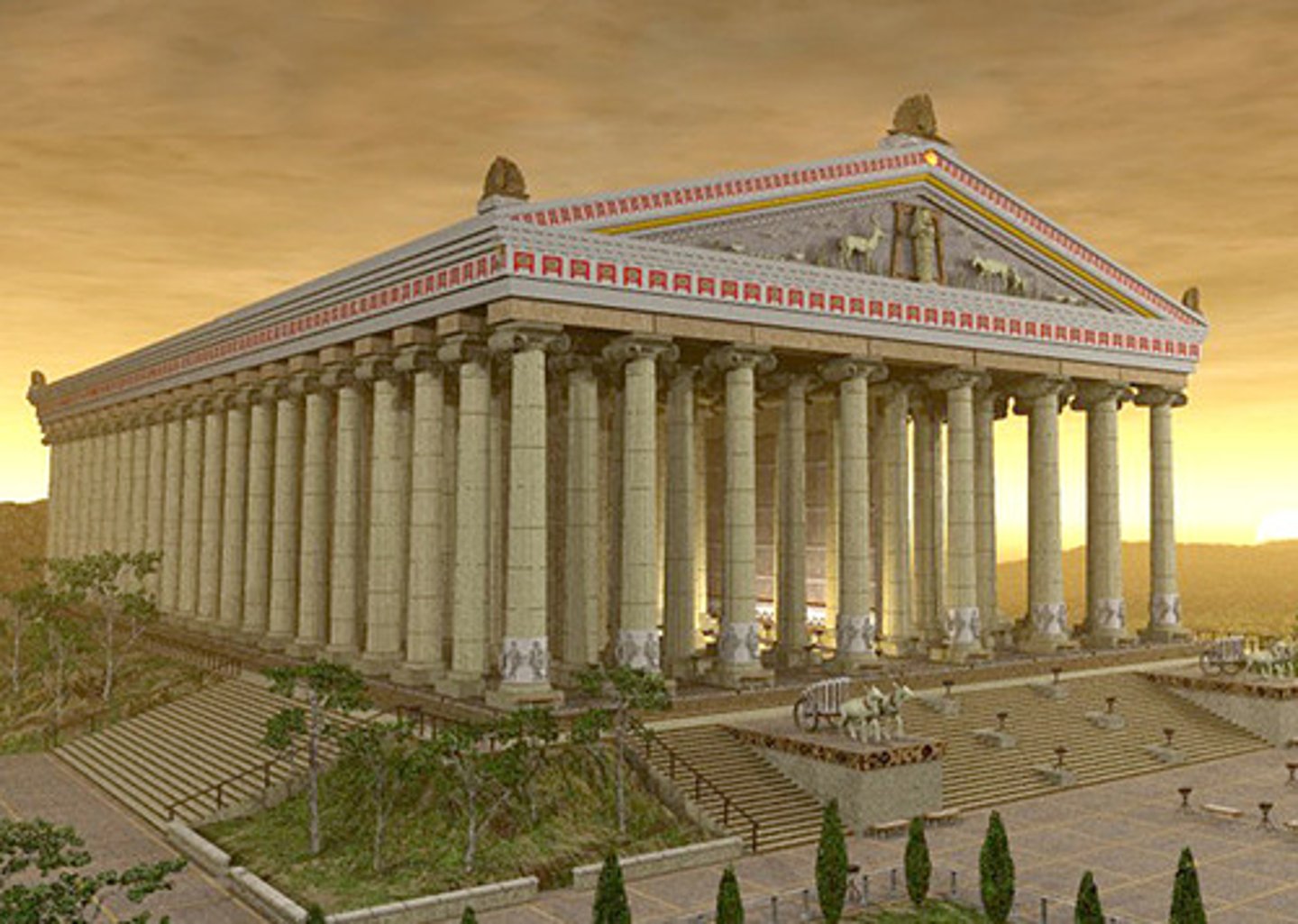
The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus

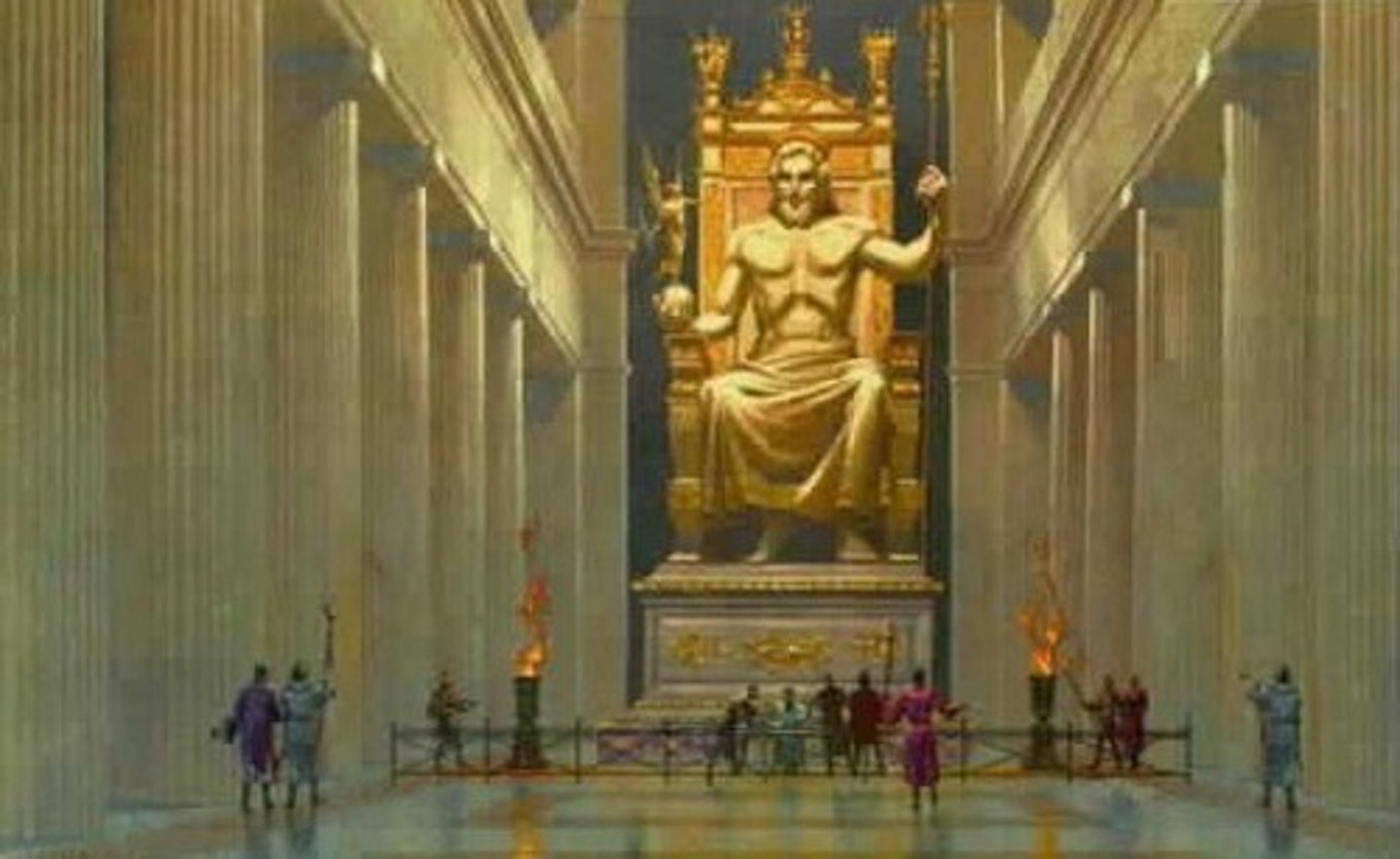
The Statue of Zeus

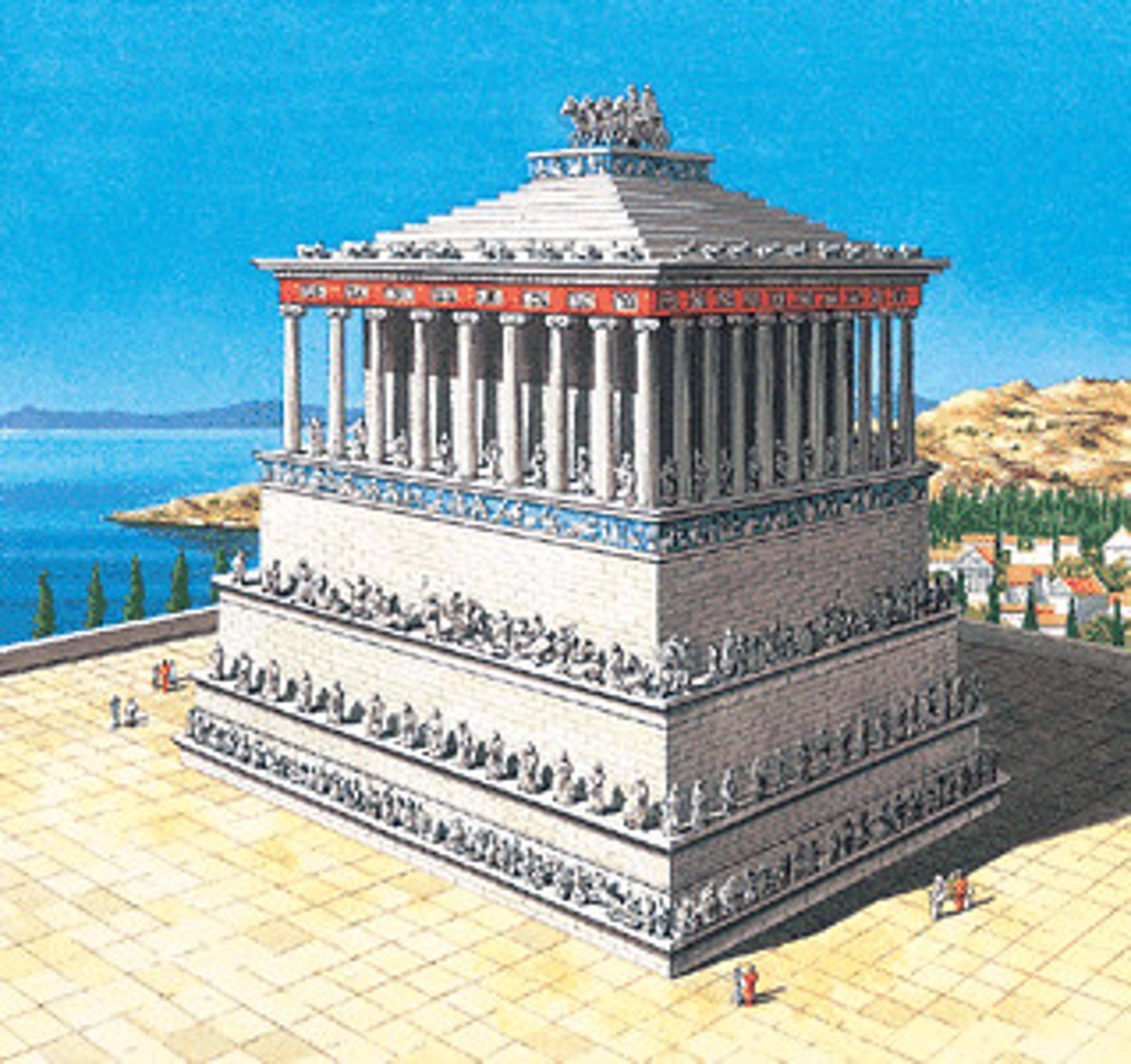
Mausoleum of Halicarnassus

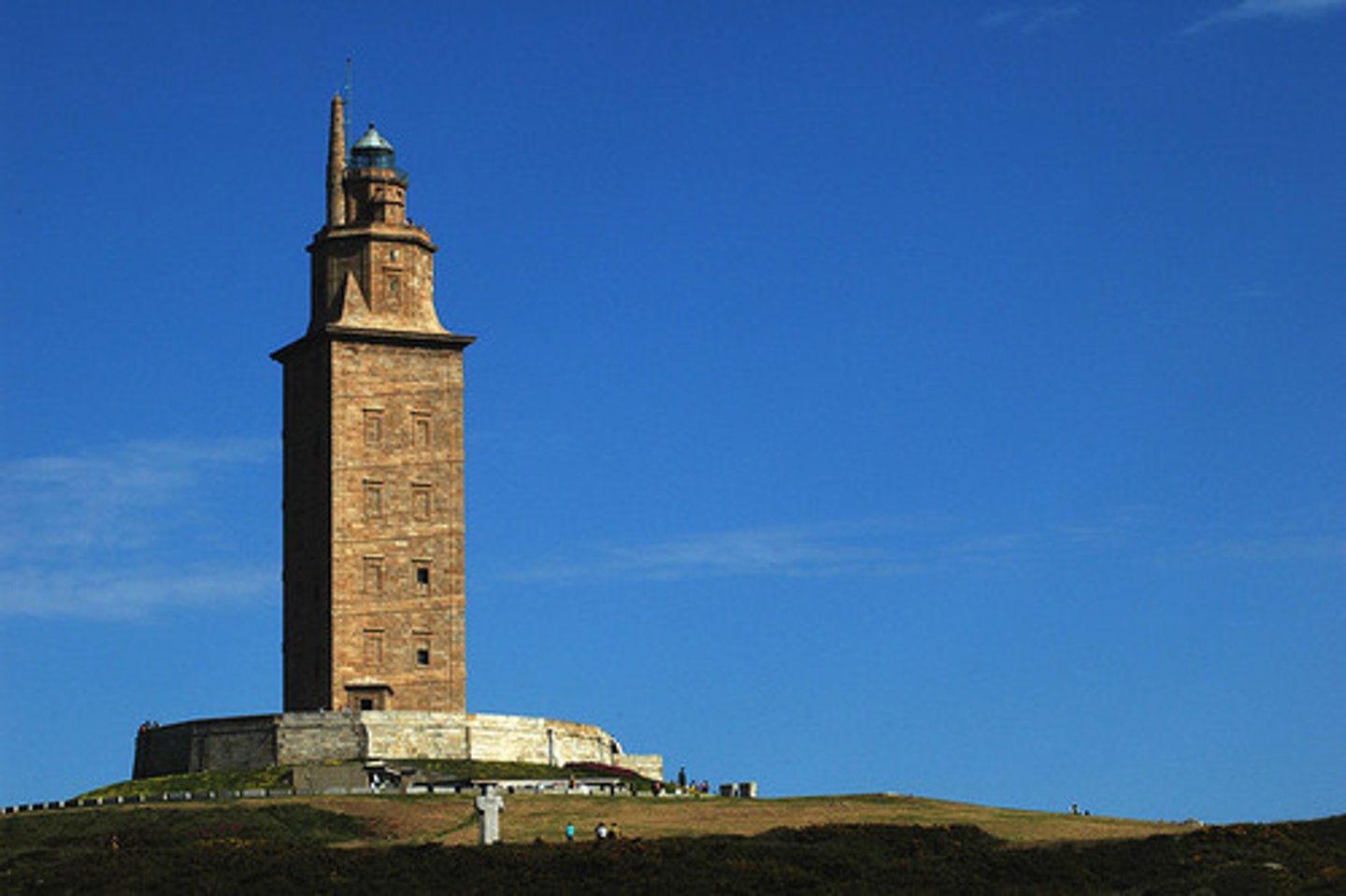
The Lighthouse of Alexandria

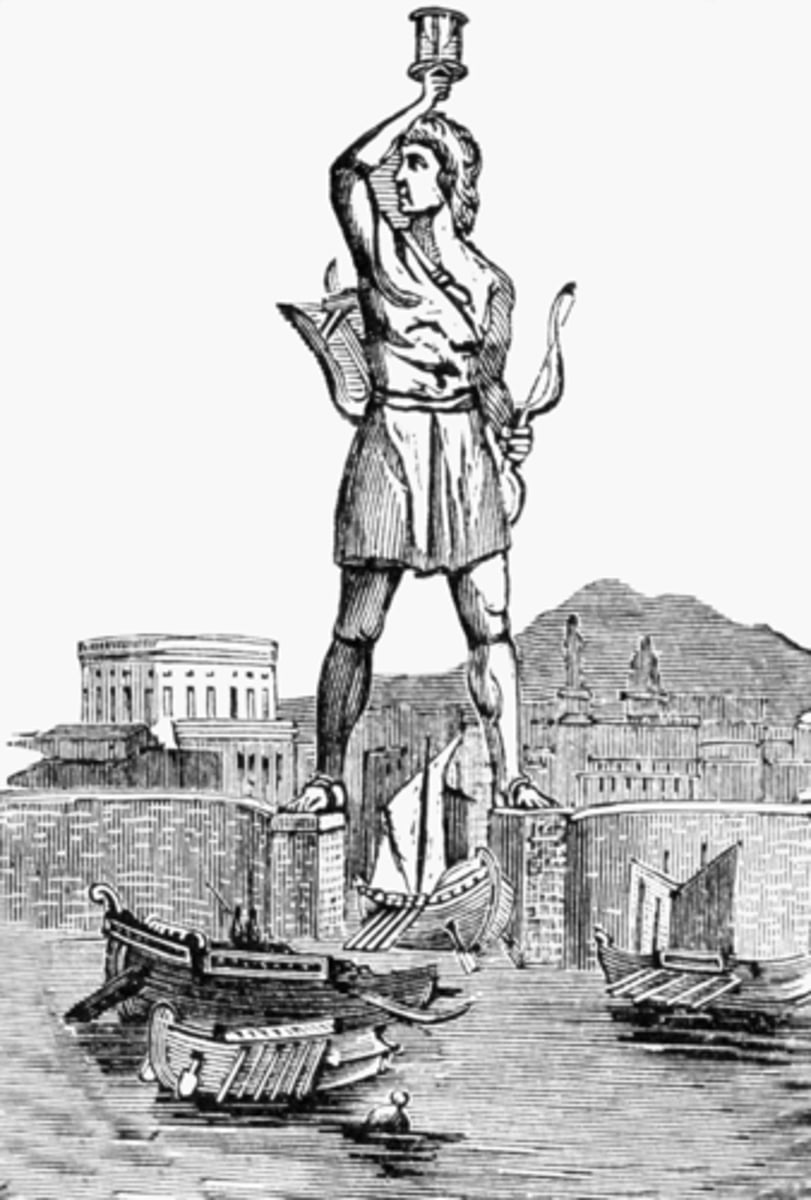
The Colossus of Rhodes

First Recorded Architect
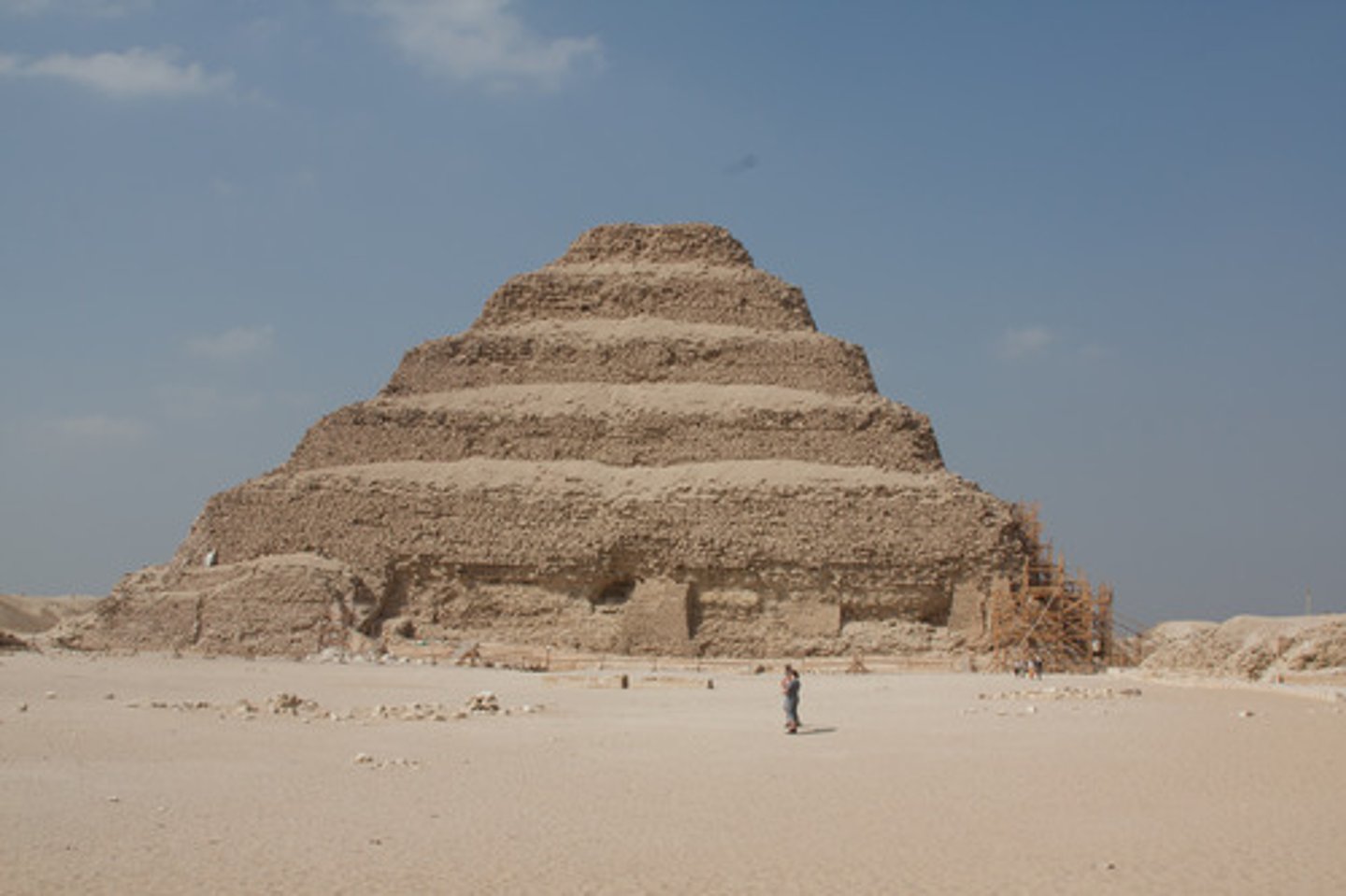
-Egyptian named Imhotep "the one who comes in peace"
- Born a commoner
-Between 2700 and 2600 Zoser hired Imhotep to design and build his tomb( Stepped Pyramid of Saqqara)
-Imhotep "translated" traditional building materials of mud, wood, and reeds into stone
-Imhotep was an architect, astronomer, magician, and a doctor
Hypostyle Hall
Large space with flat roof supported by rows of columns
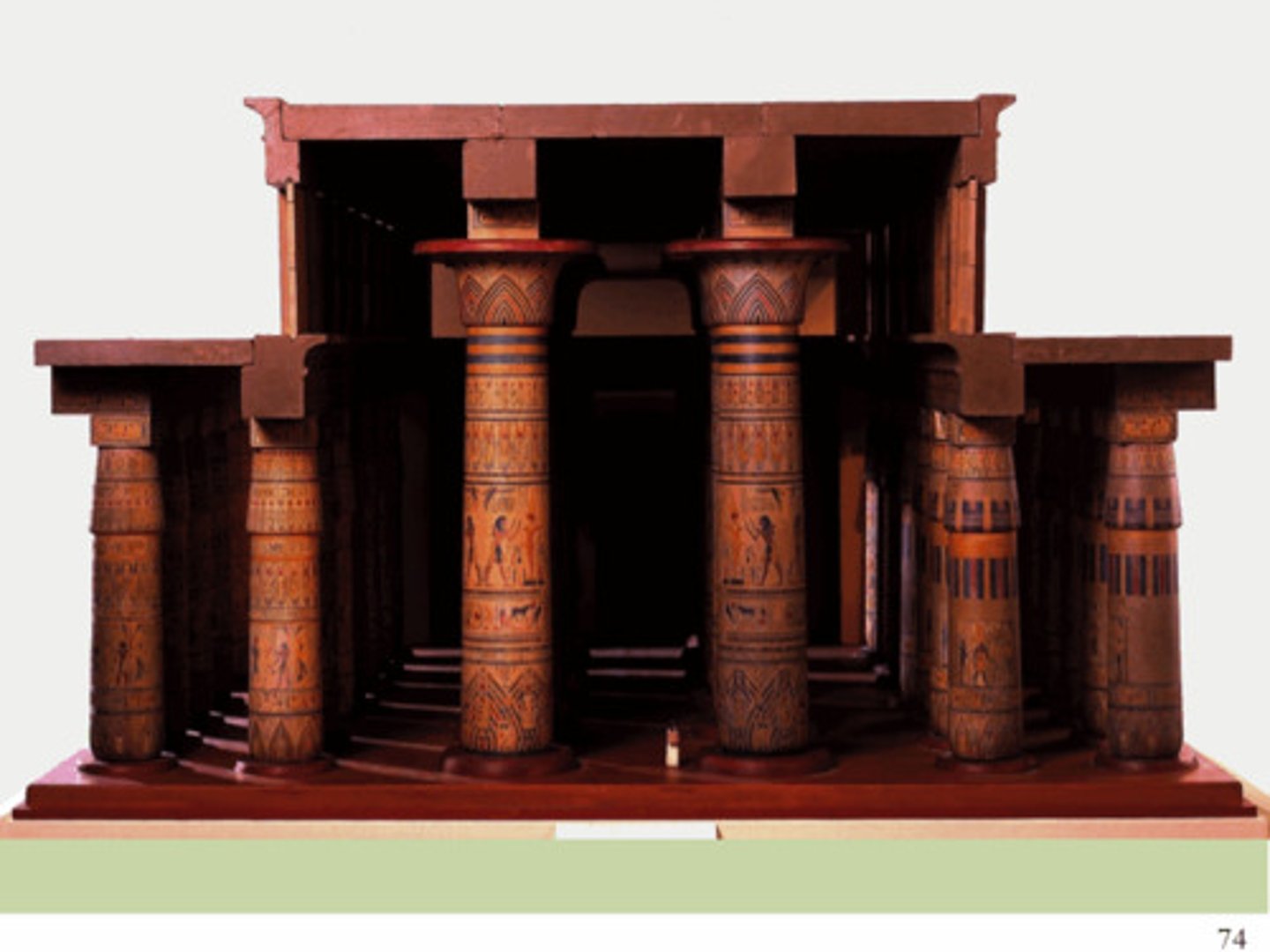

Bud Colums

Papyrus

Pyramids in Central America
-used as temples
-often built new temple over the years
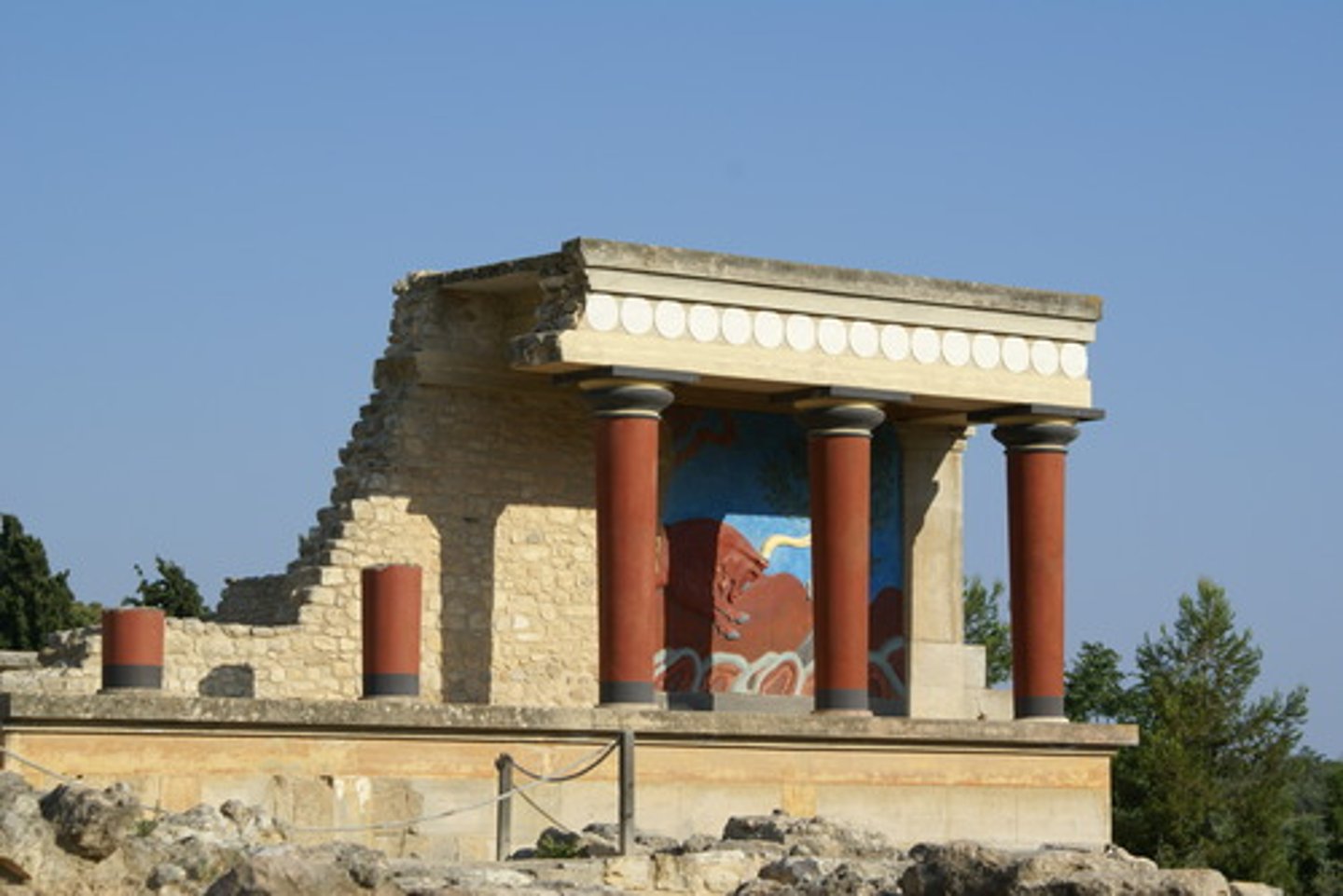
Palace at Knossos
1700-1380 BCE
Forerunner to Post and Beam (trabeated system)

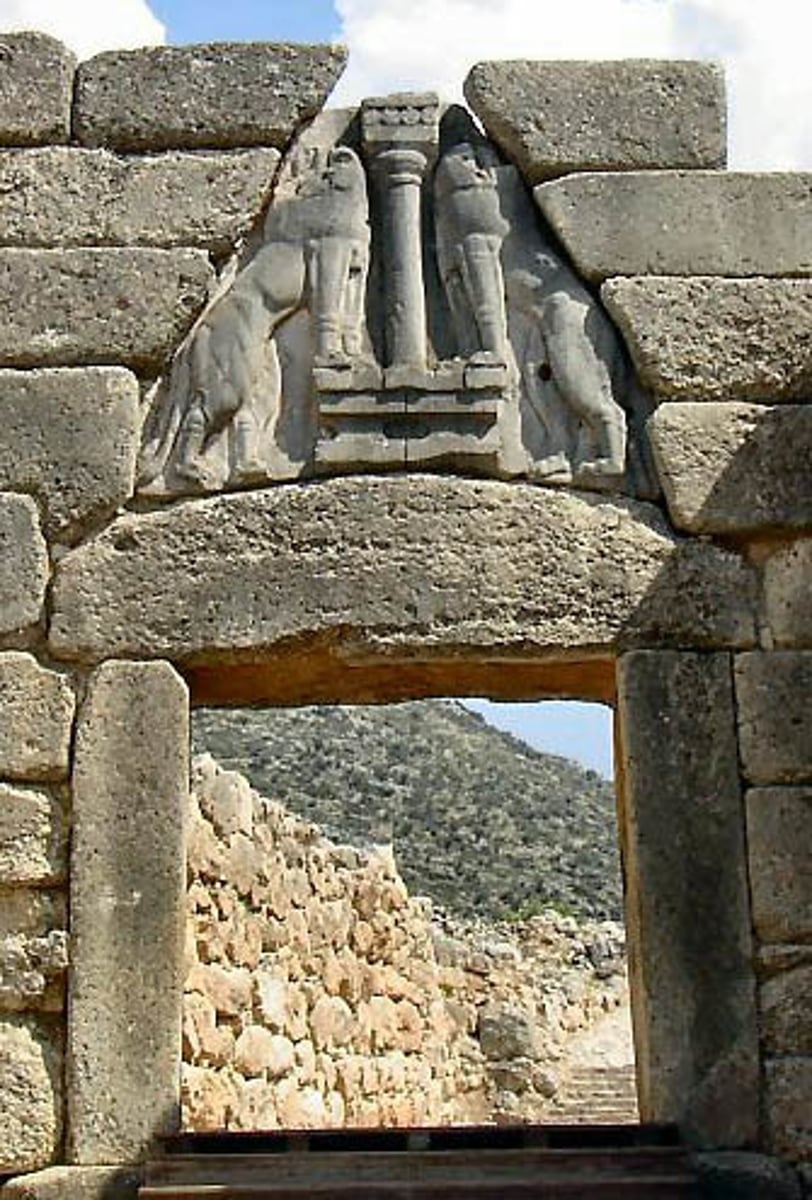
Lion's Gate

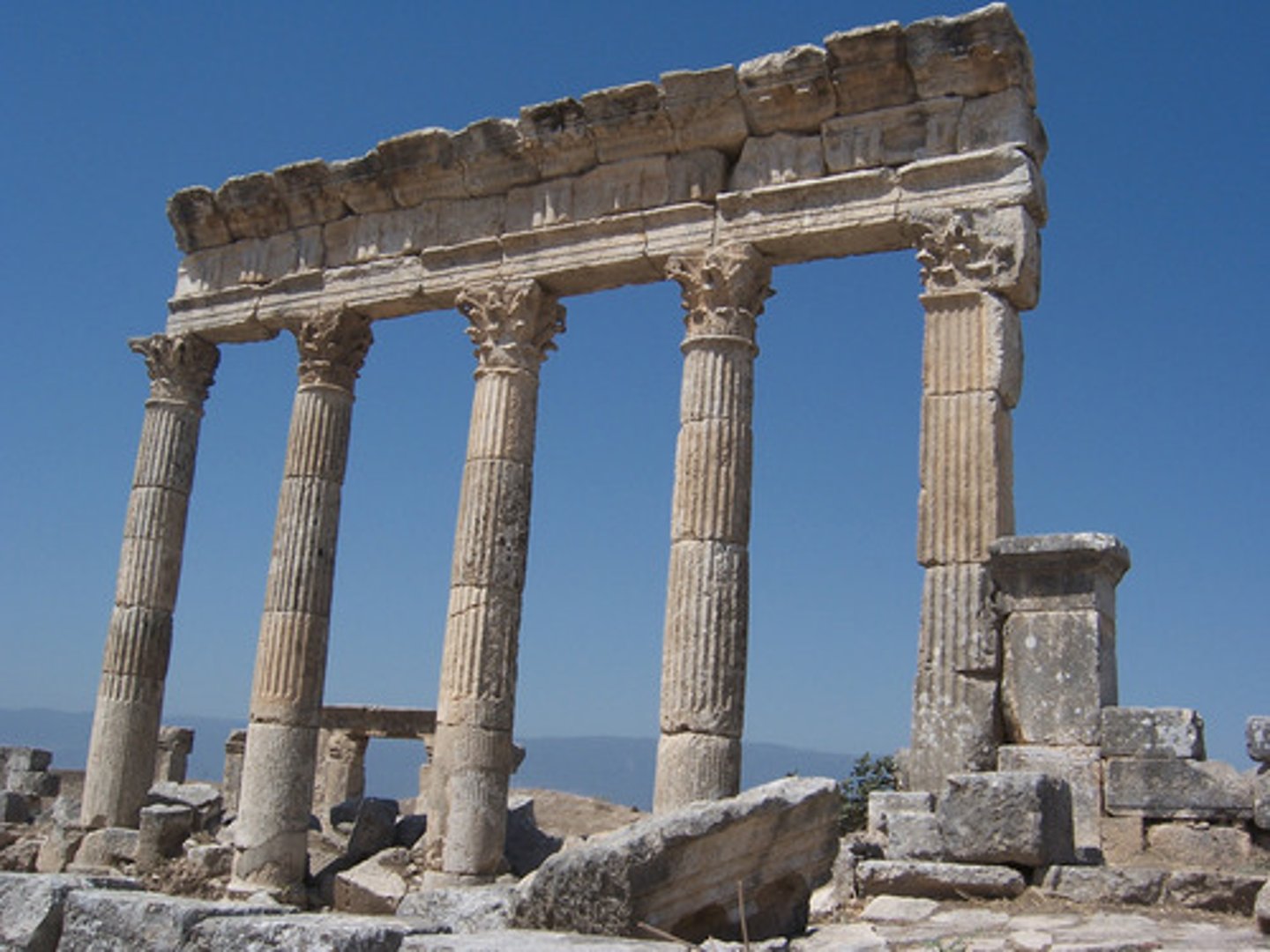
Colonnade
a series of regularly spaced columns supporting an entablature and usually one side of a roof structure

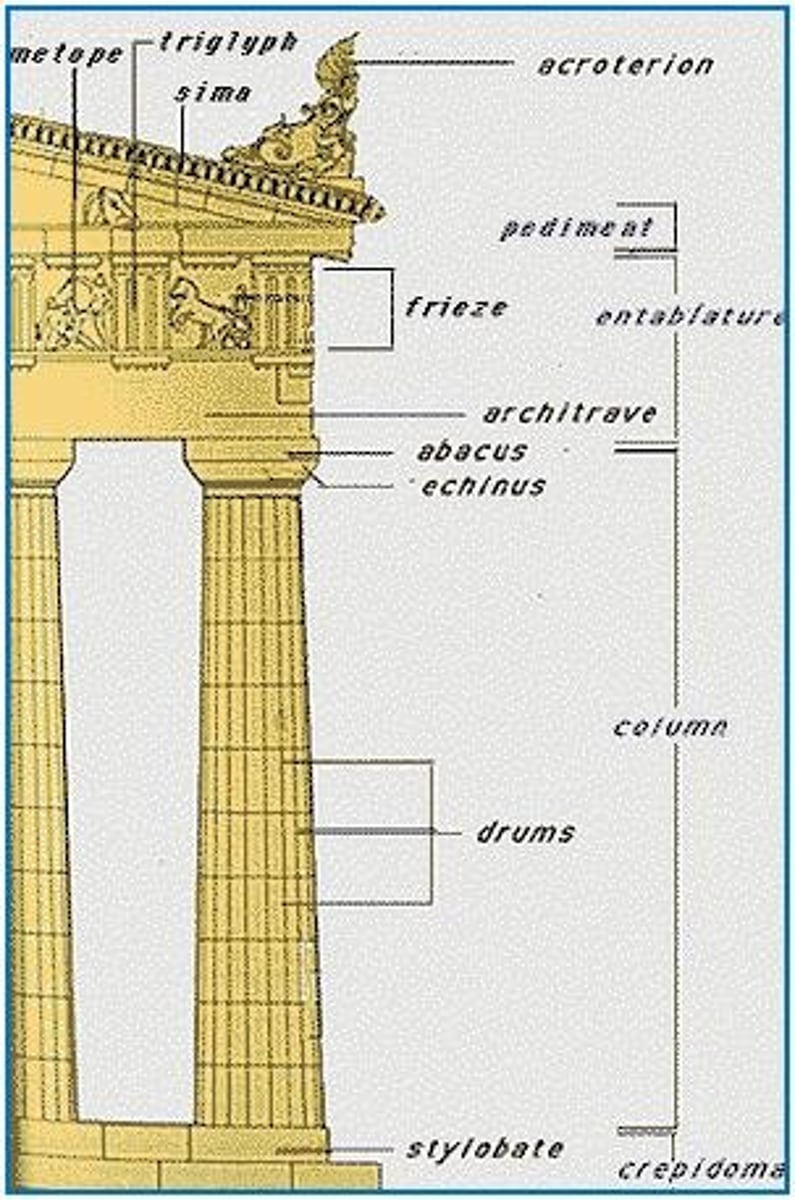
Metope
any of the panels, either decorated or plain, between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze
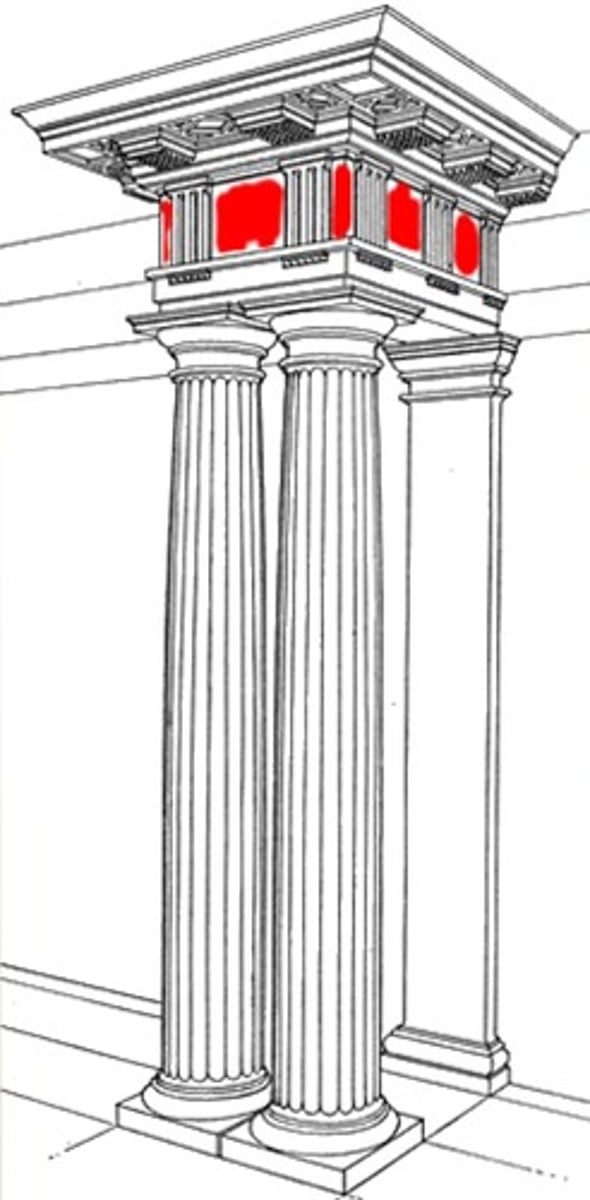
Triglyph
one of the vertical blocks separating the metopes on a Doric frieze
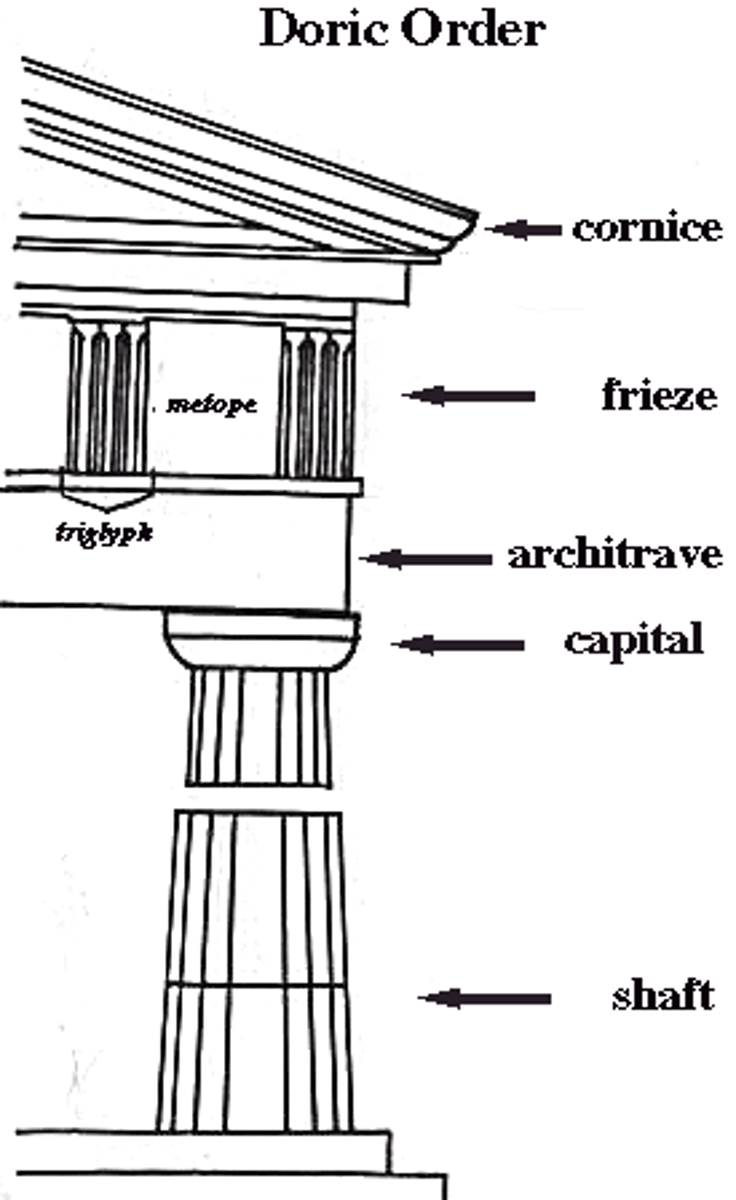
Doric Order
-oldest, simplest, most massive
-columns placed close together, often no bases
-plain capitals
-entablatures have metopes and triglyphys
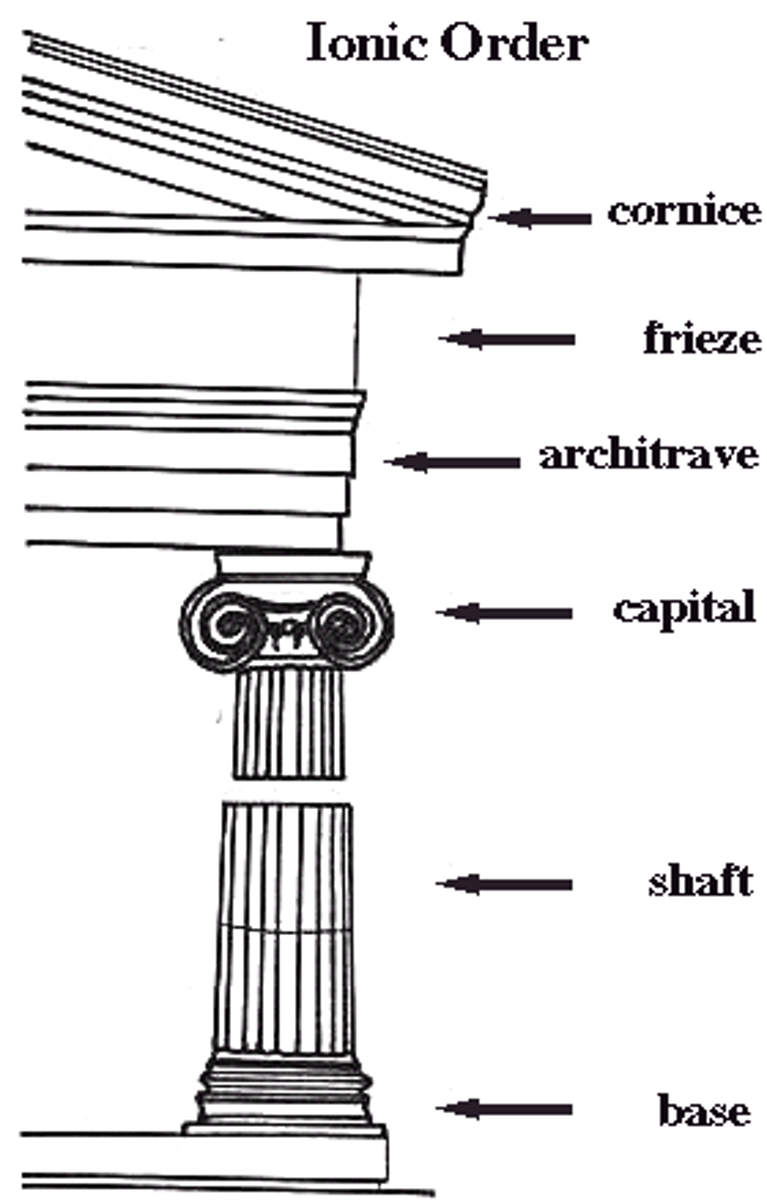
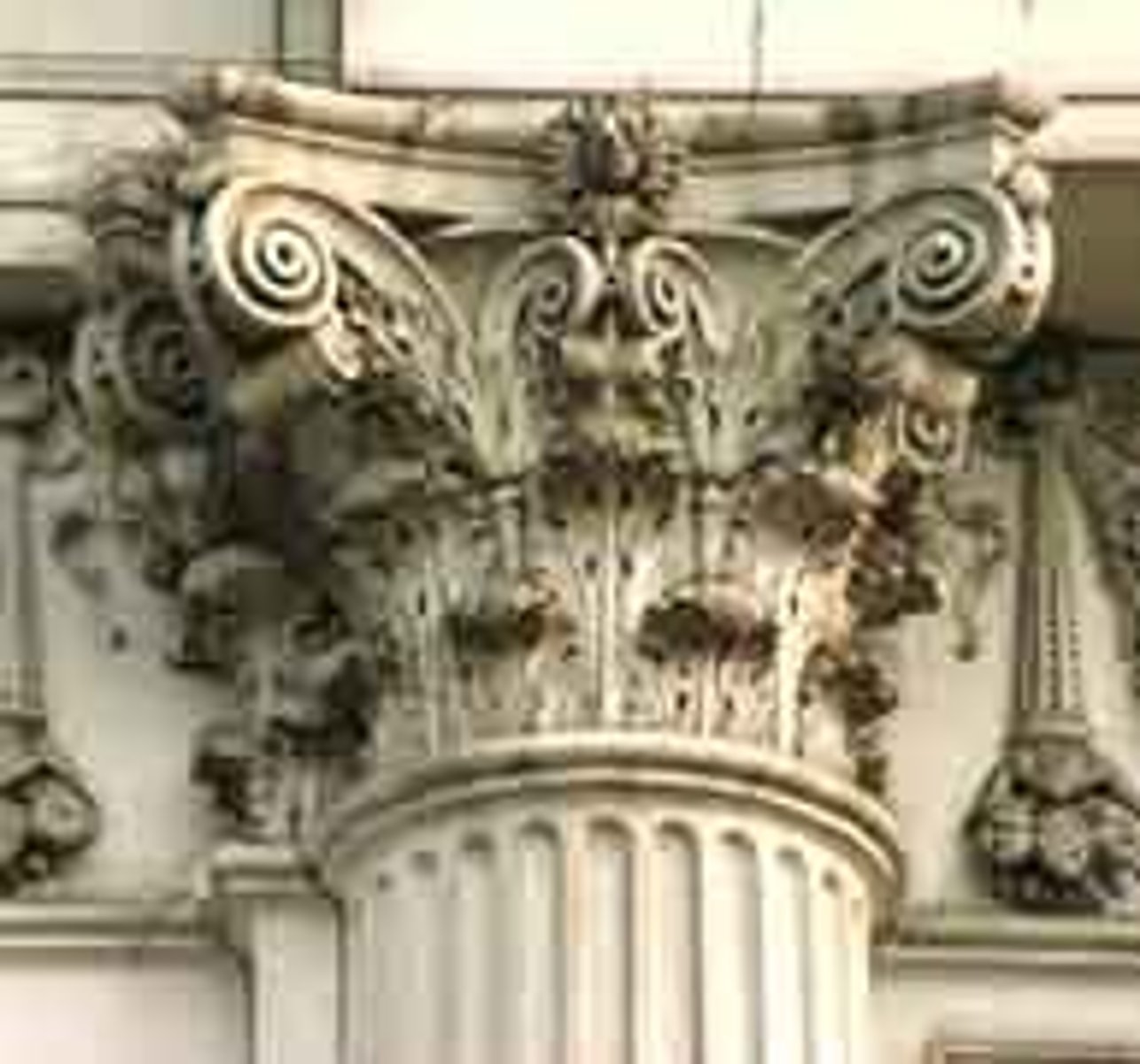
Ionic Order
-Developed in Ionian Islands
-Characterized as delicate order "female"
-contrasted with "male" doric order
-used for smaller buildings and interiors
-easily recognizable by volutes on capital(based on nautilus shells or animal horns)
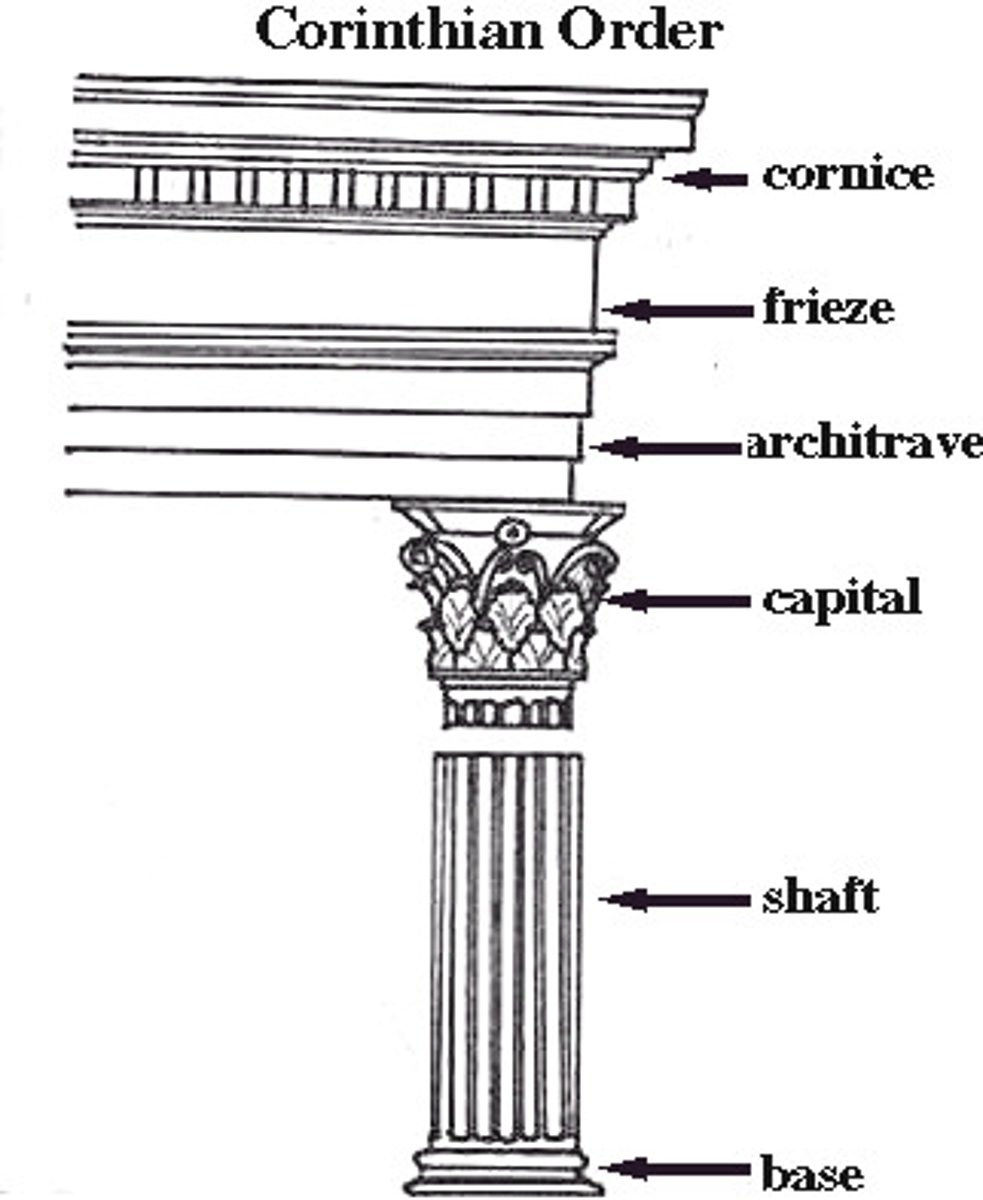
Corinthian Order
-variation of ionic order
-same as iconic except a new type of capital
-capital is more ornate-acanthus leaves
-often found on interiors
Entasis
-the slight convex bulge given to a column to offset the optical illusion that it is thinner in the middle

agora
is open meeting place or market
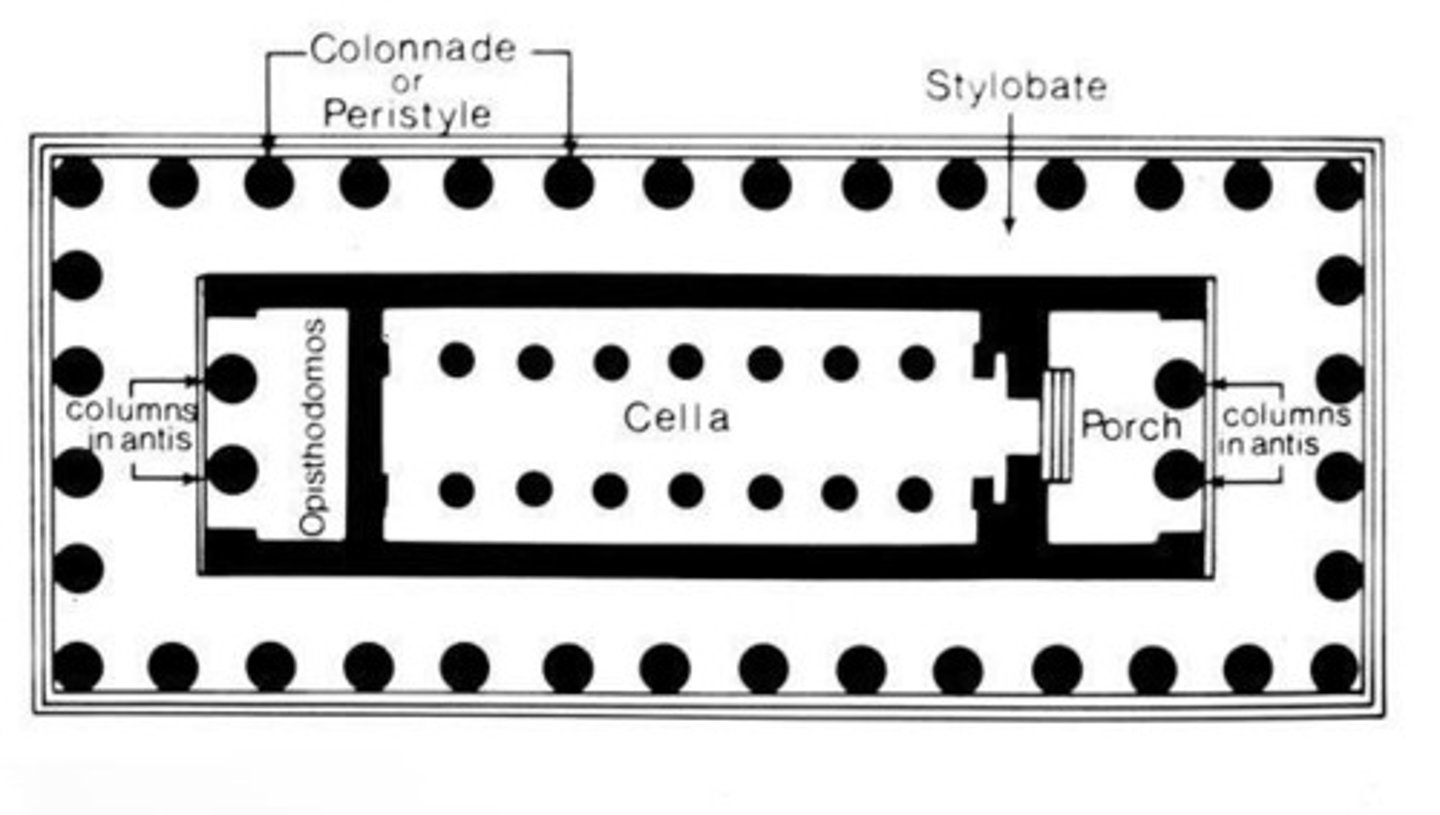
Cella
the principle chamber enclosed part of a classical temple
Elgin Marbles
Lord Elign-purchased marble from turks
British museum - Landon

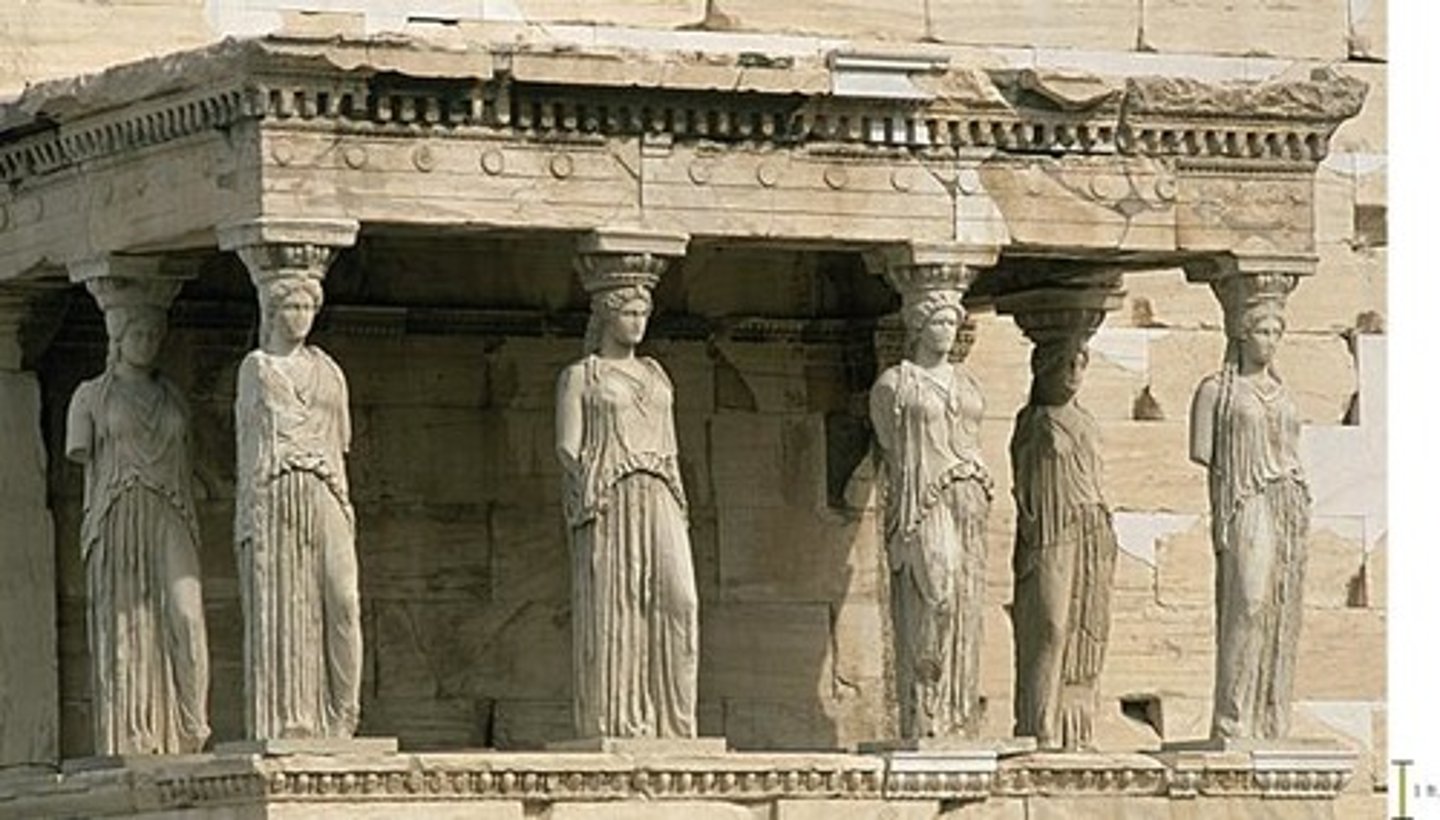
The Erechtheion Athens
on the Acropolis 421-407BC
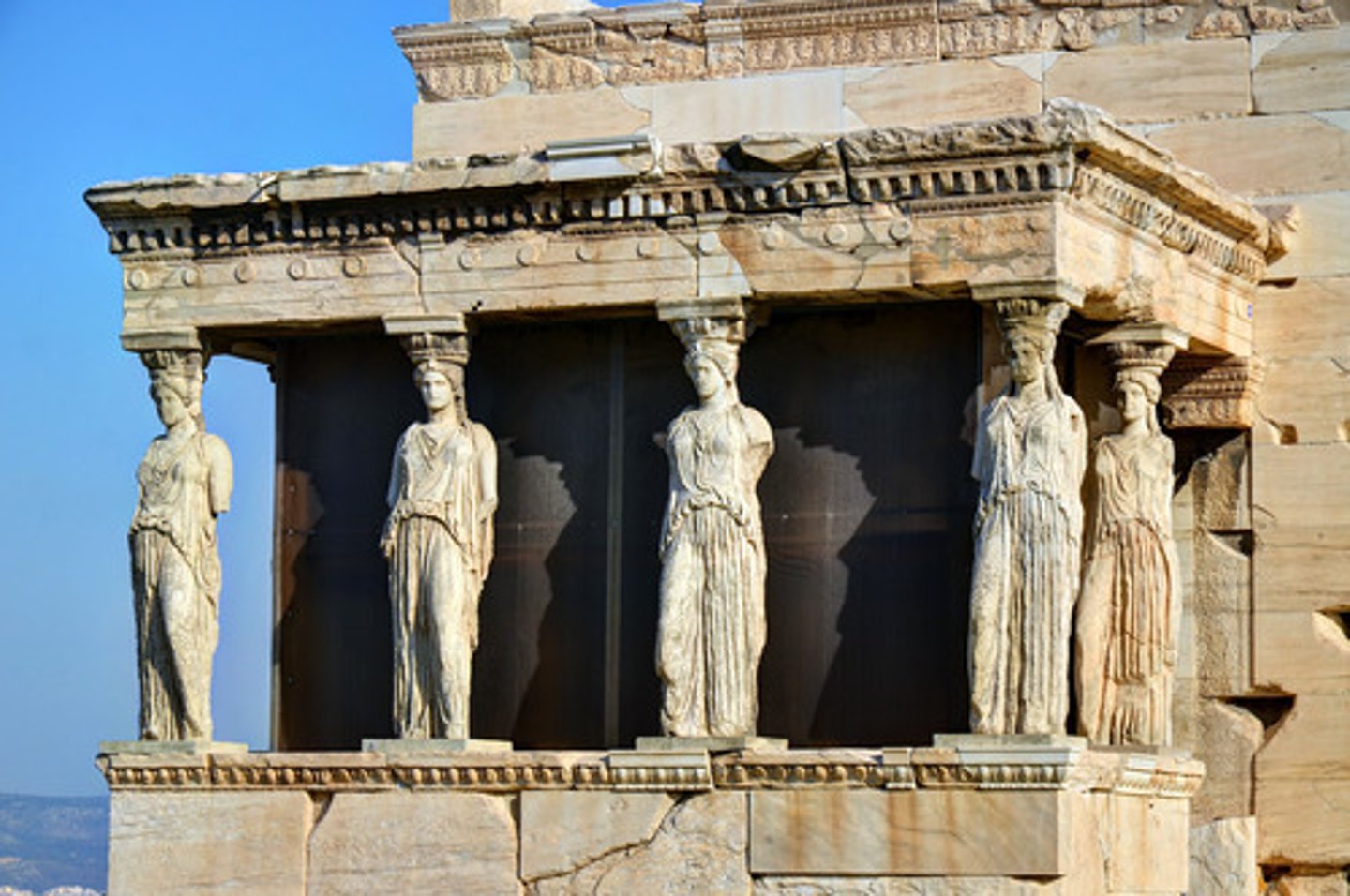

Carytids
a sculptured female used as a column

atlas
a sculptured male figured used as a column
Temple of Athena Nike
perfection of Iconic Order
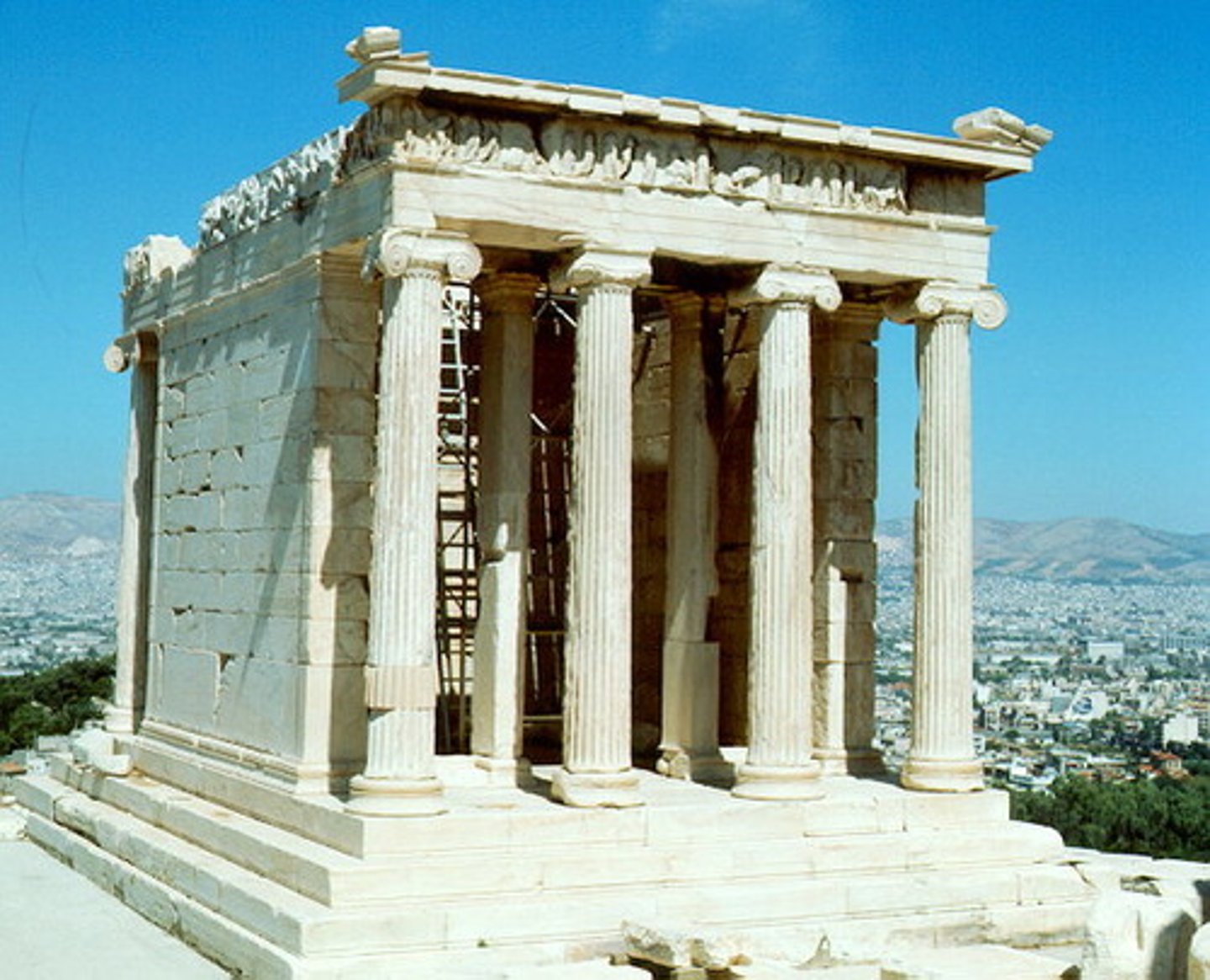

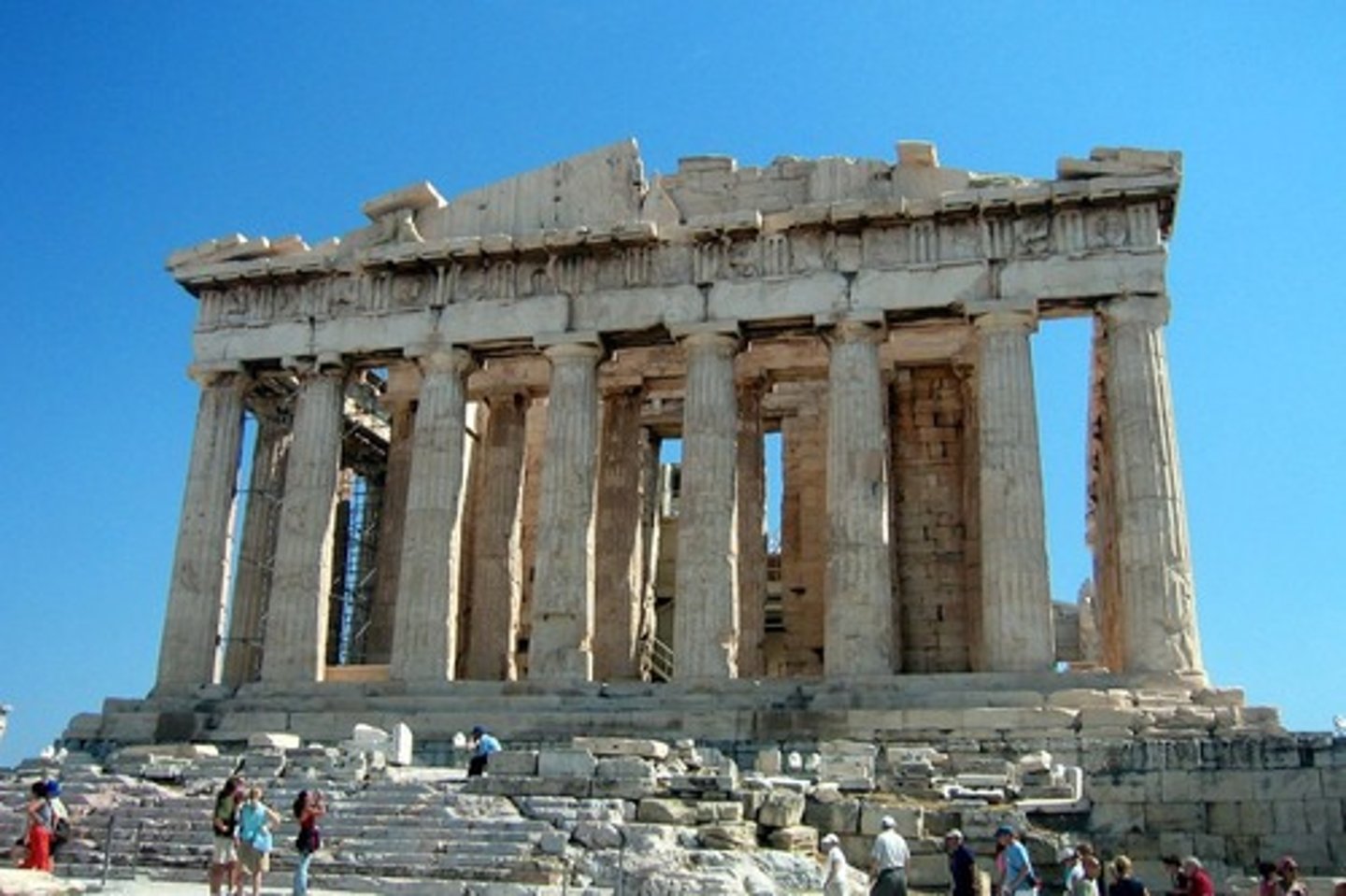
Partheon
Perfection of Doric Order
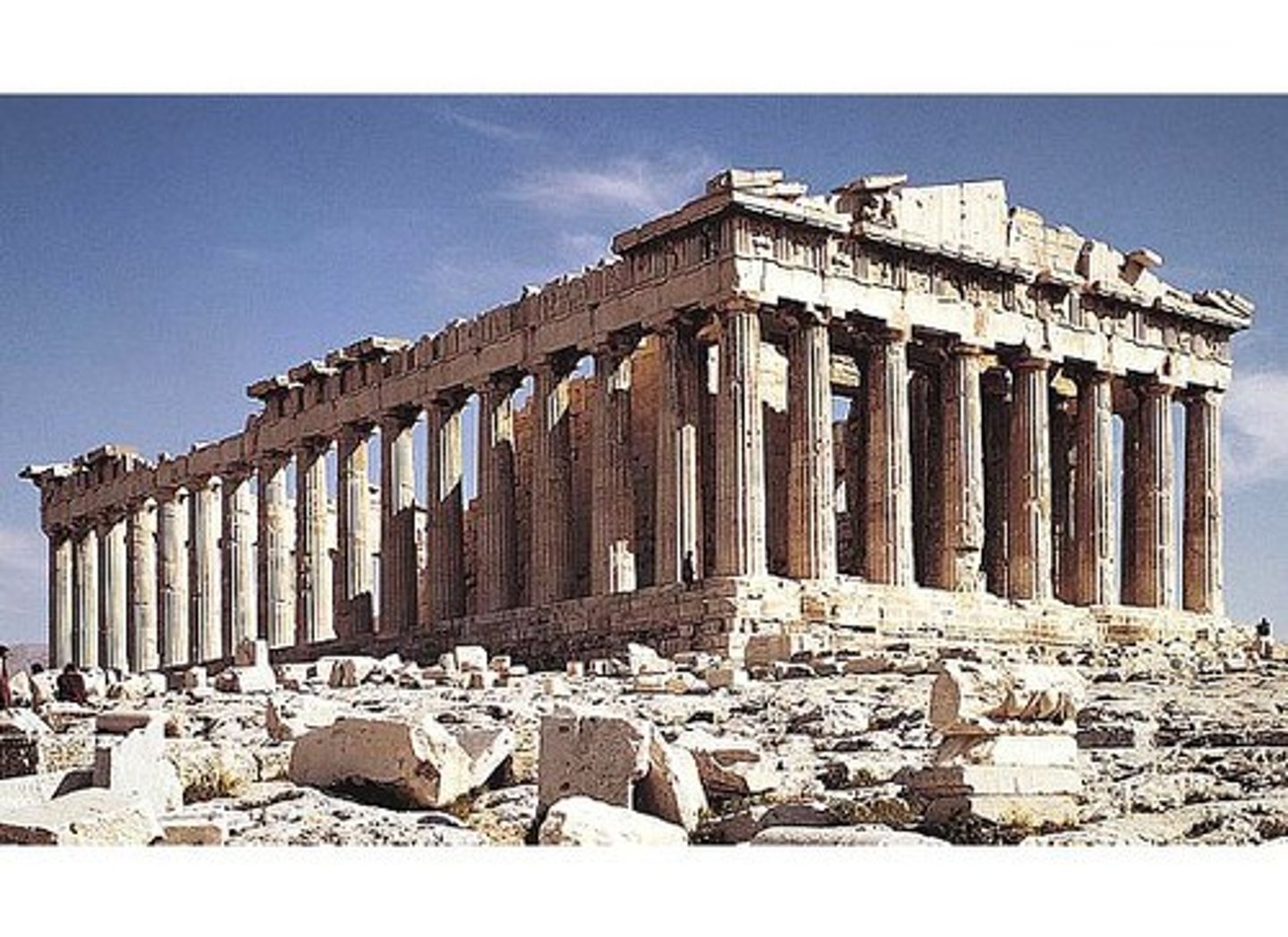

Greeks
-Made objects in the landscape
-balance
-harmony
-refinement of form not structural innovation
Post and Beam
Roman (Etruscan)
-Conquered the Greeks
-Etruscan brought Classical architecture to Roman Empire
-1/5 of the world was under Roman rule
-Made spaces
-made images in context
-made innovations in construction and technology
-THE ARCH: vault, dome, concrete
Tuscan Order
-unlike doric, supports an entableture with no decoration
-used to create wooden temple with pitches roof
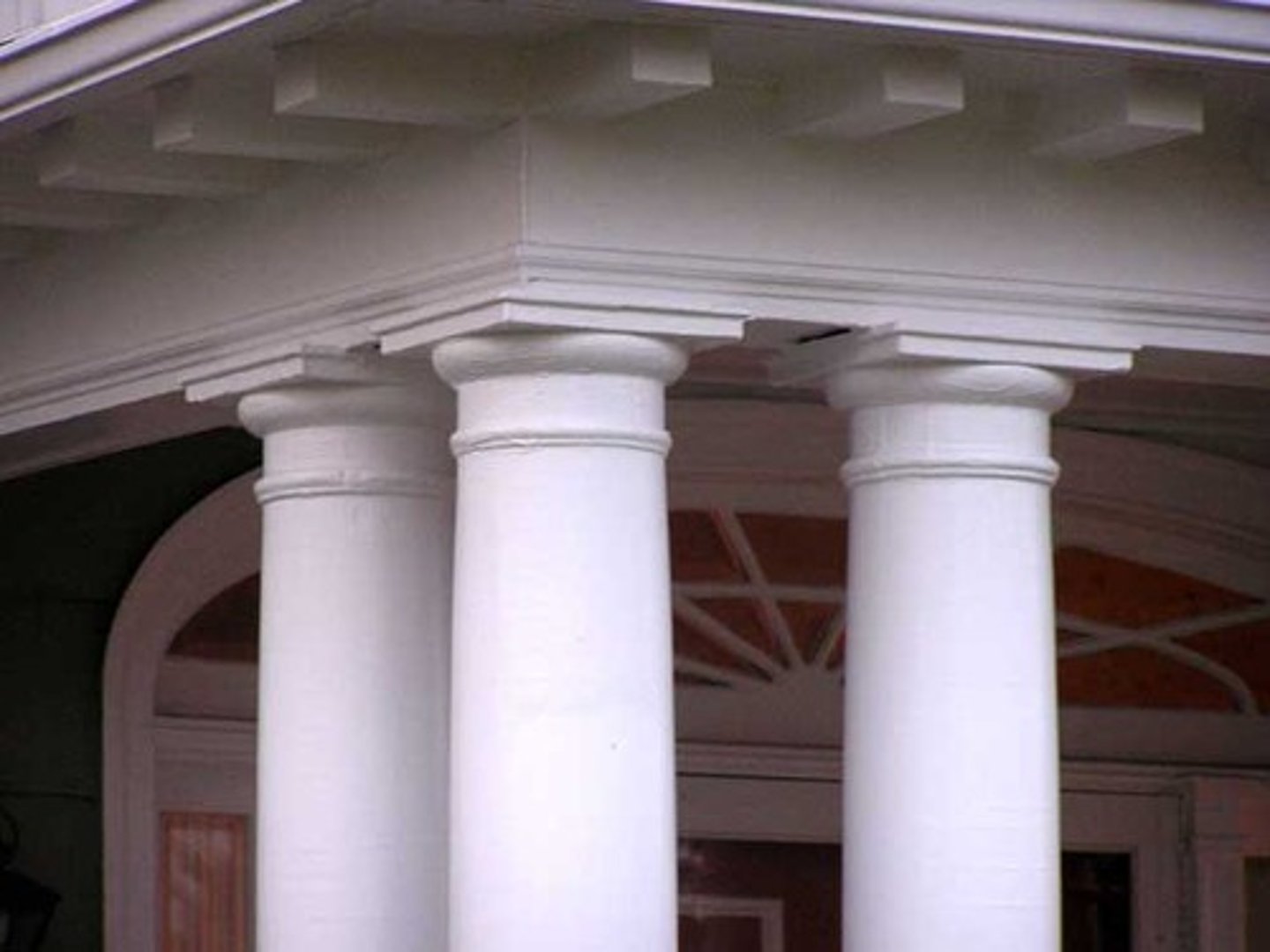

Composite order
-combines ionic volutes with Corinthian acanthus leaves
-Roman innovation

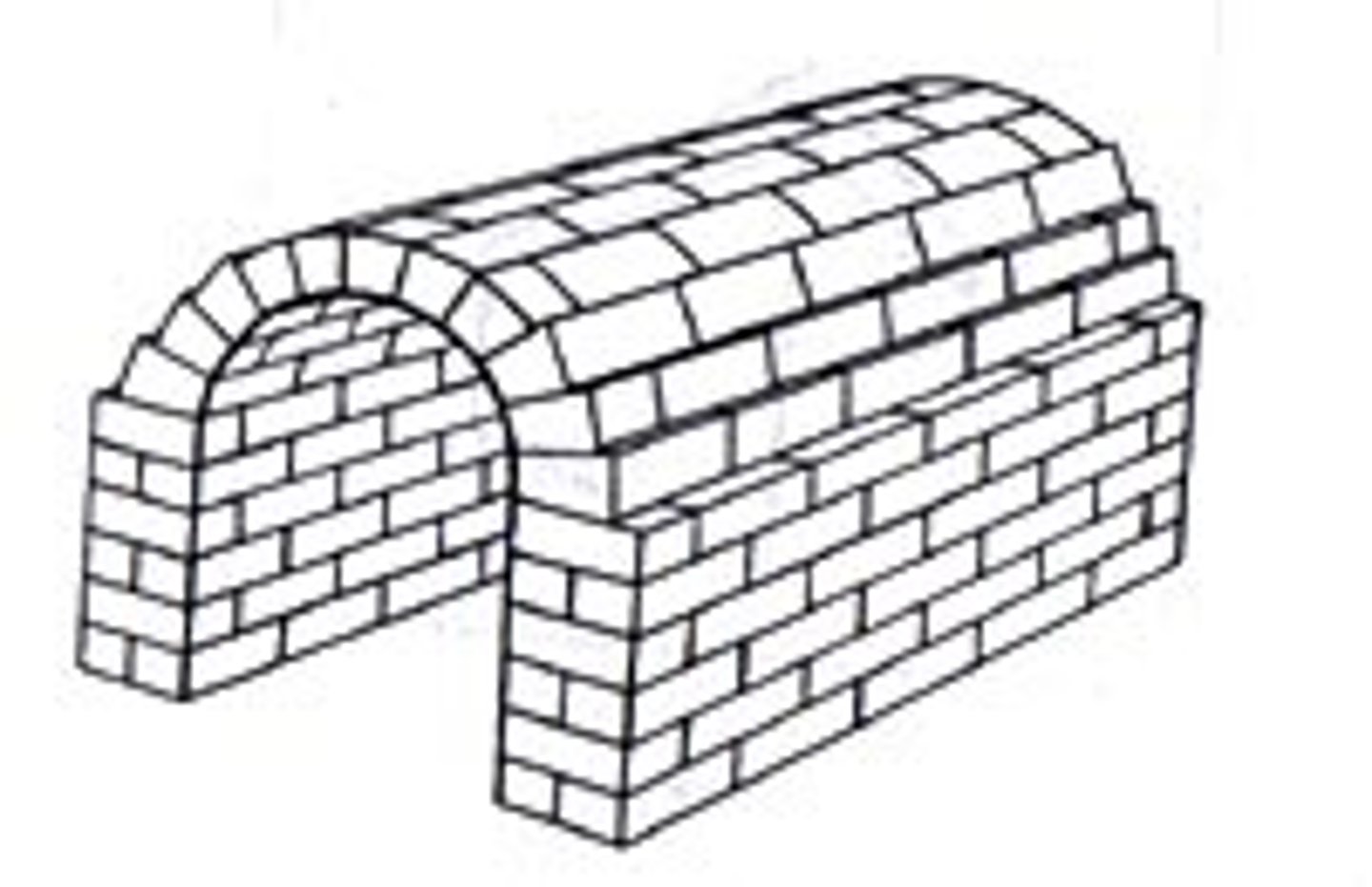
Barrel vault
extending the arch along its depth
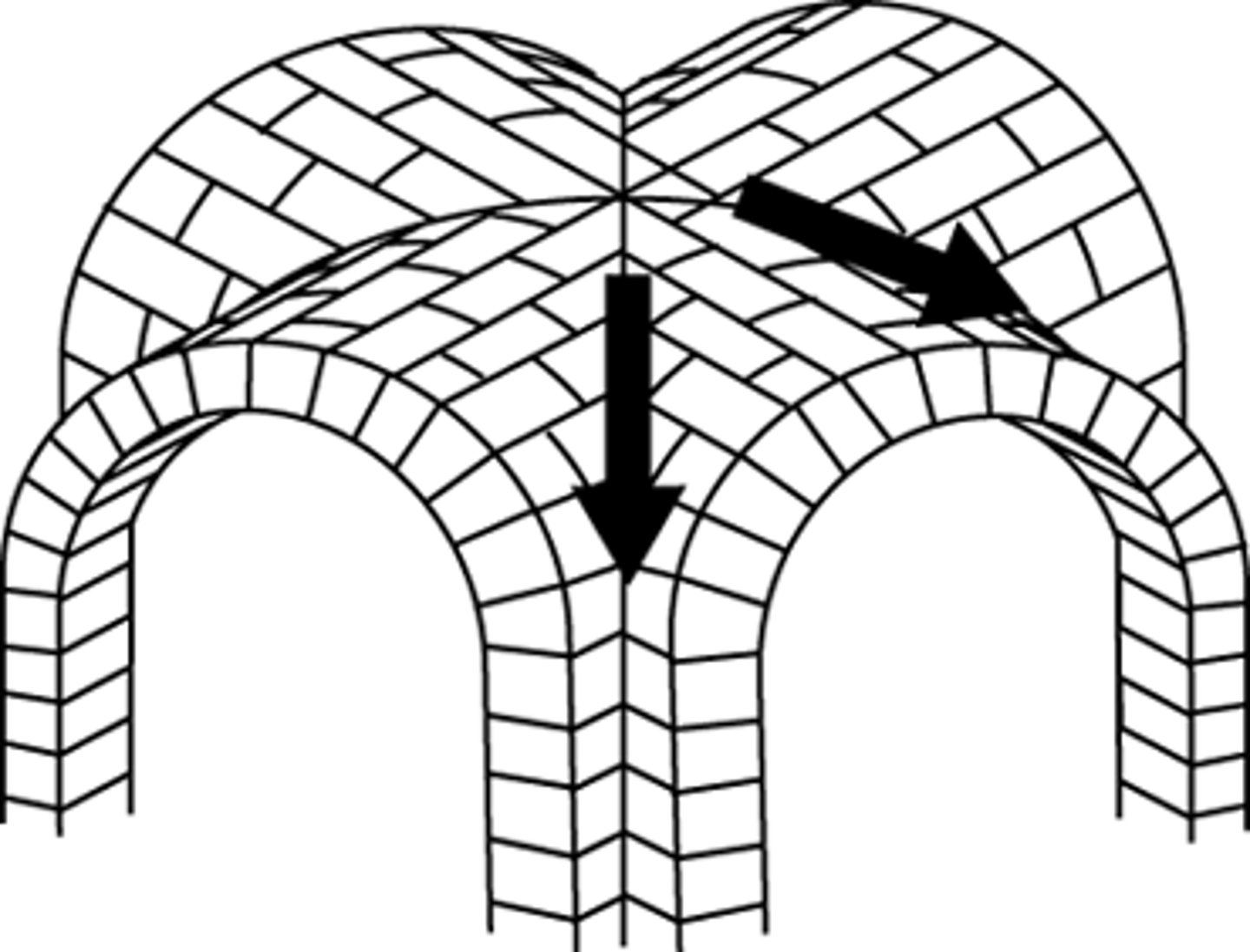
Groin Vault
-intersecting two barrel vaults
-opens space in four directions
-used to create huge interiors
-in baths
-gyms
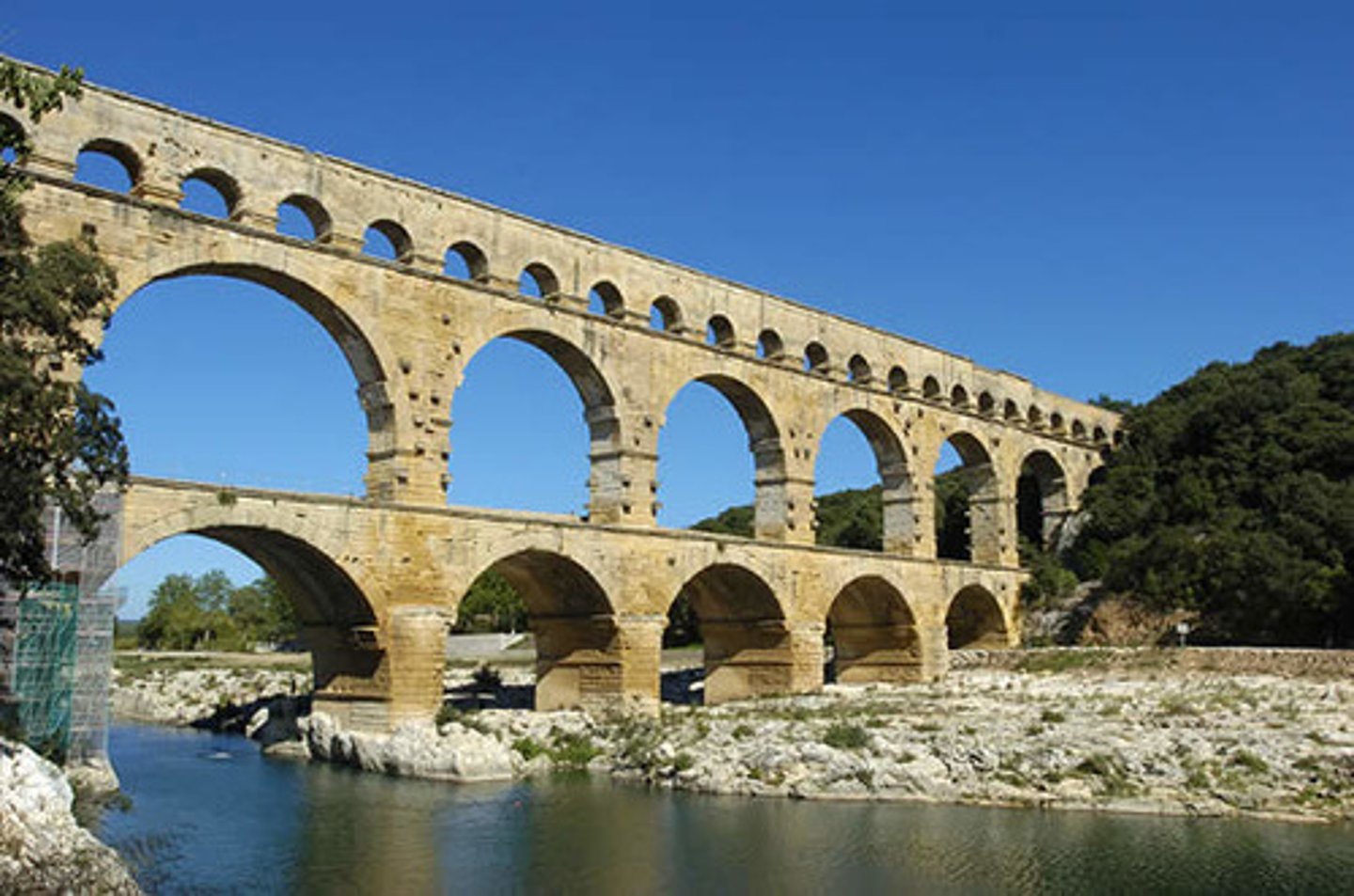
Pont Du Gard
Near Nimes France 20-16 BCE

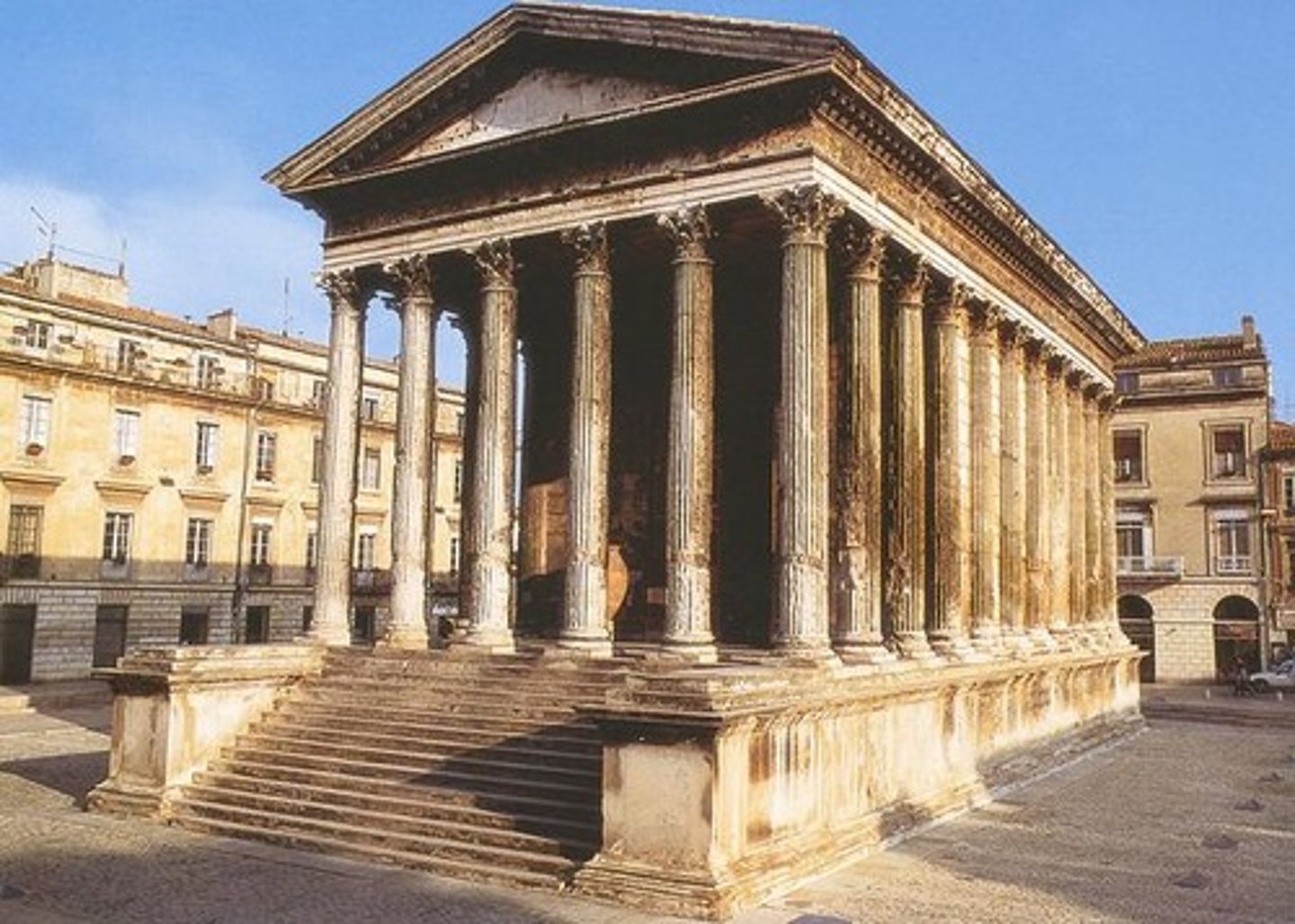
Maison Carree
Nimes France 10 BCE

Structural Innovation
Concrete
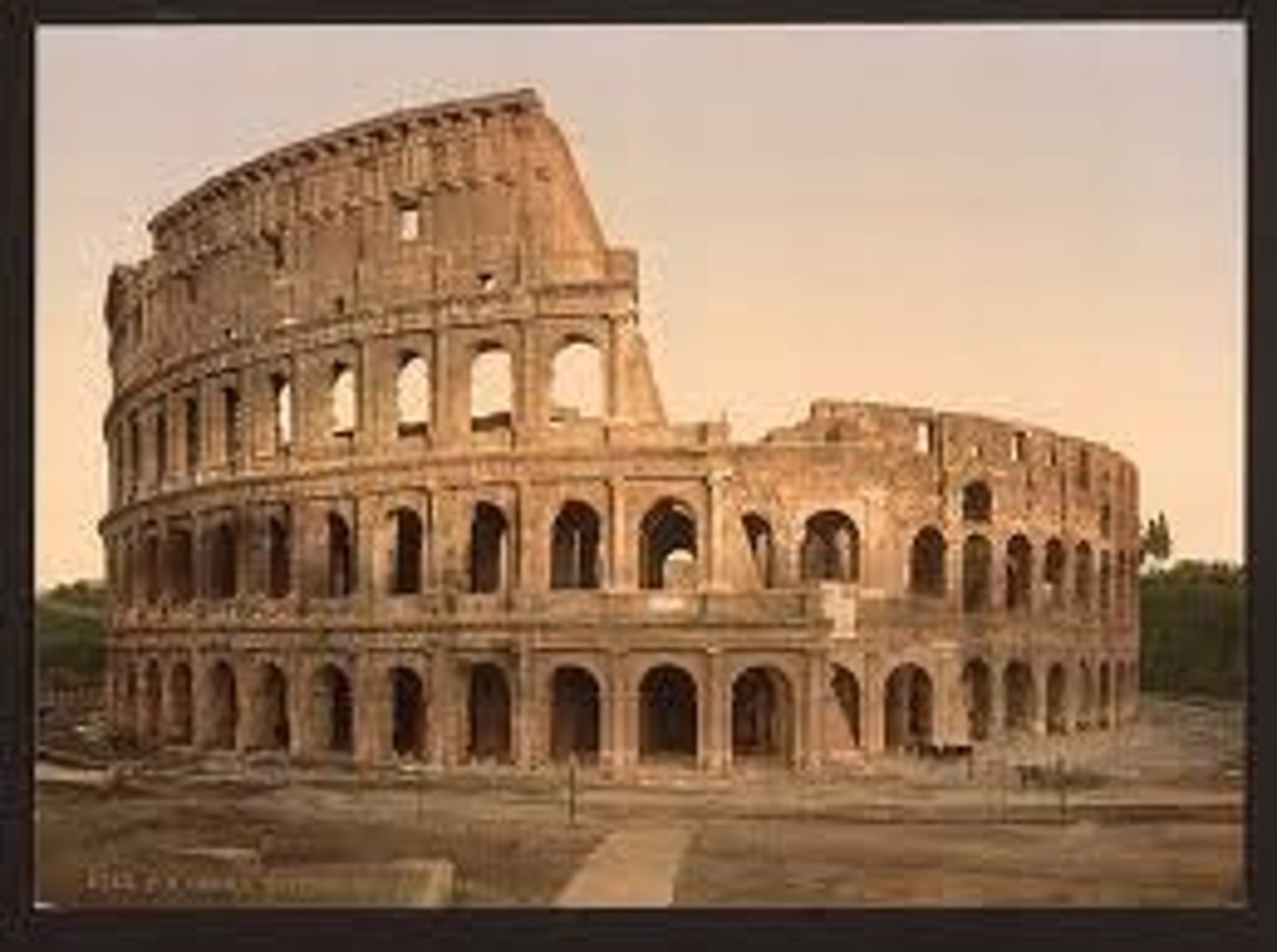
Coliseum in Rome

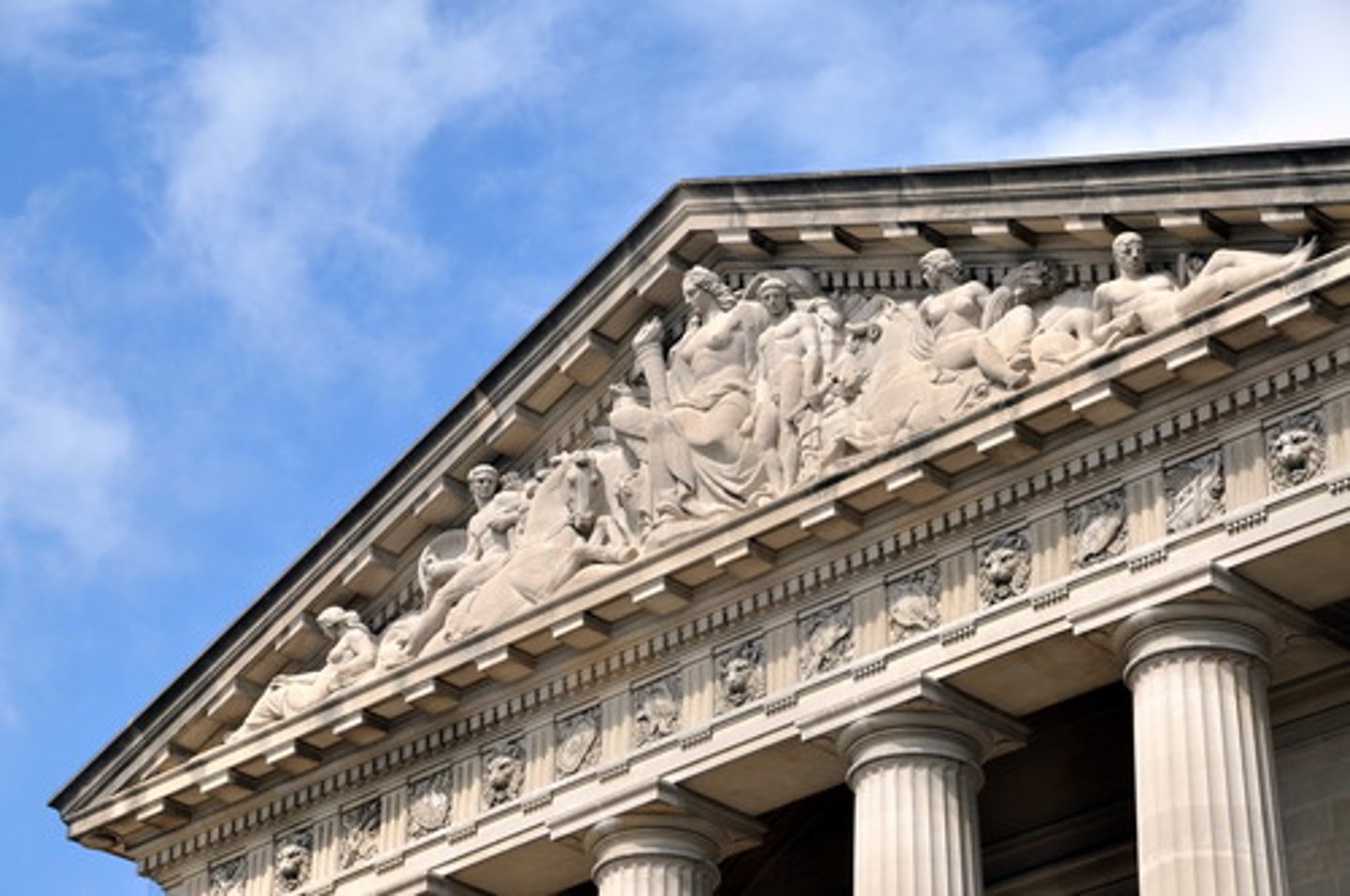
Pediment
-triangle shape over colonade

Portico
-a colonnaded space forming

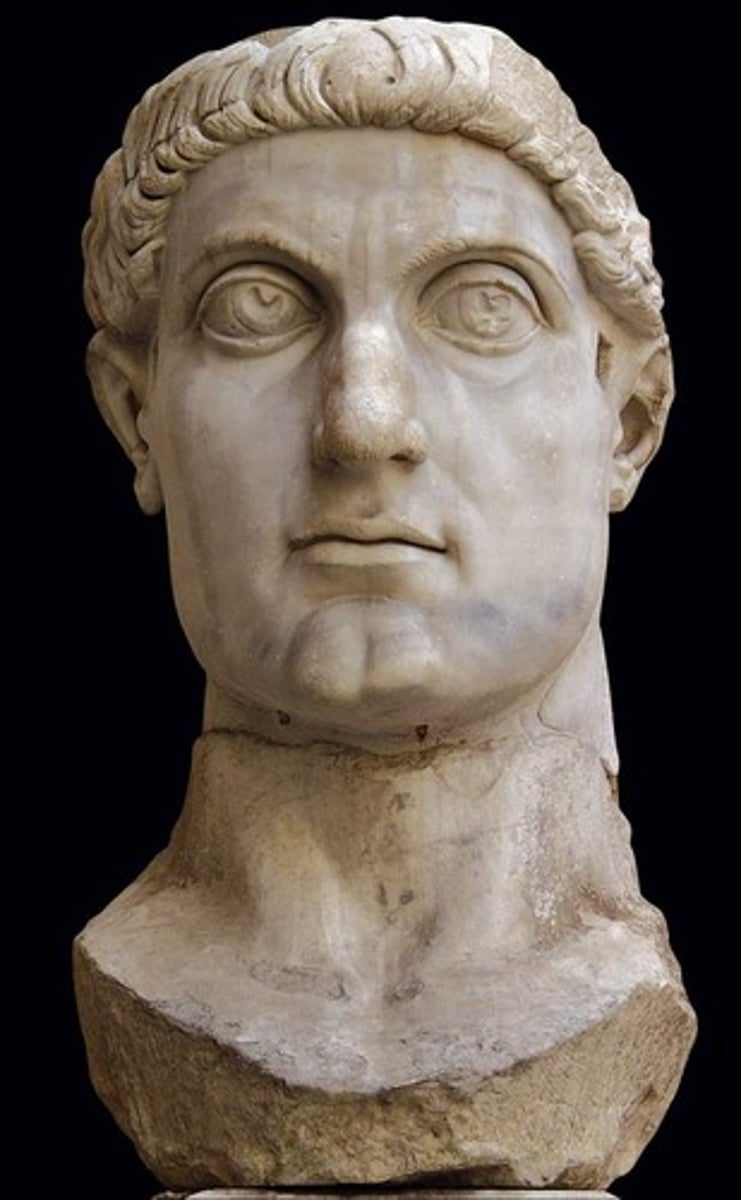
Constantine First (A.D 306-337)
-Edict of Milan 313 A.D
-Proclaimed tolerance of all religions

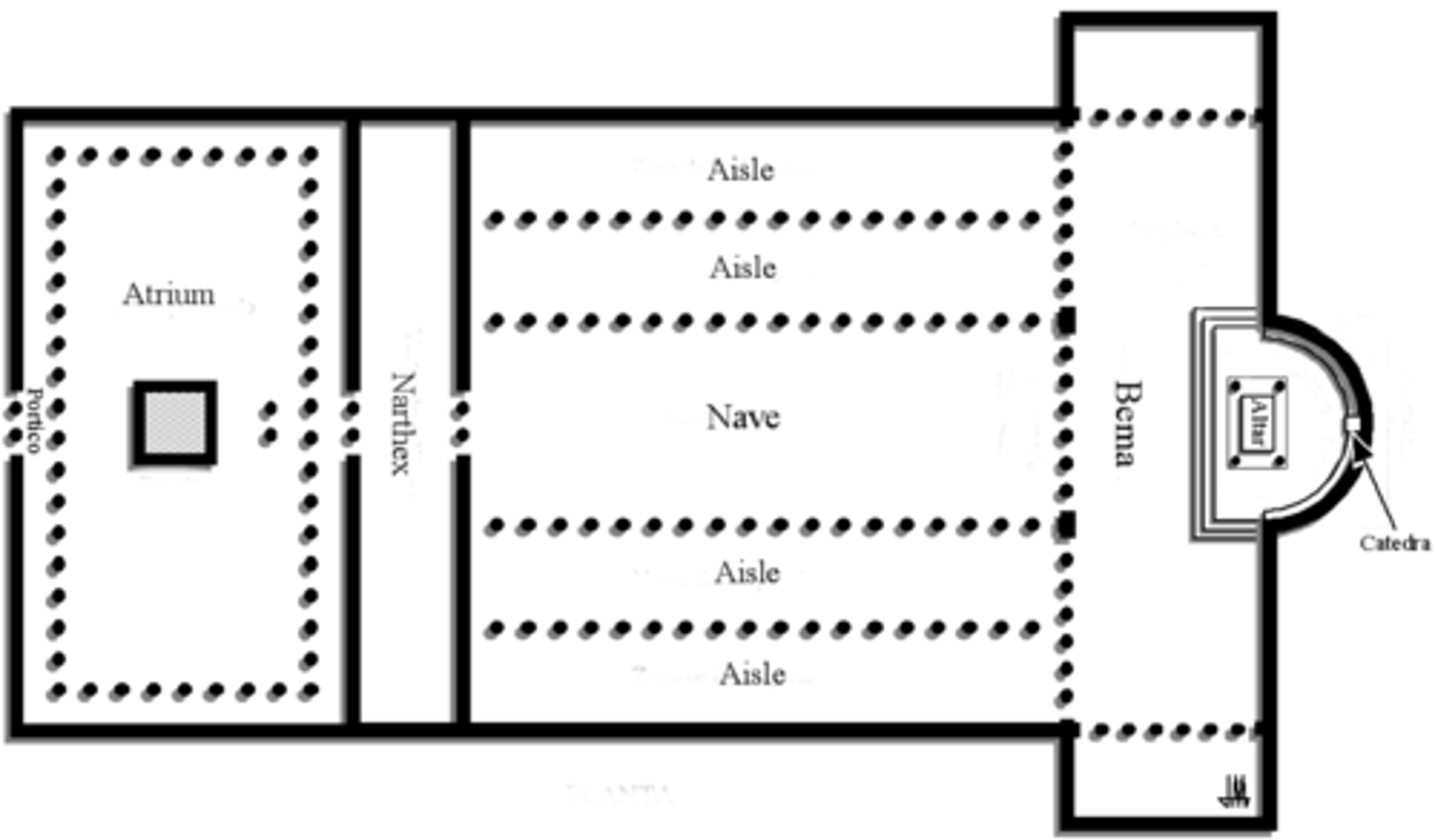
Early Christian Churches
-they were based on timber-roofed basilicas
Basilica Plan
Pendentives
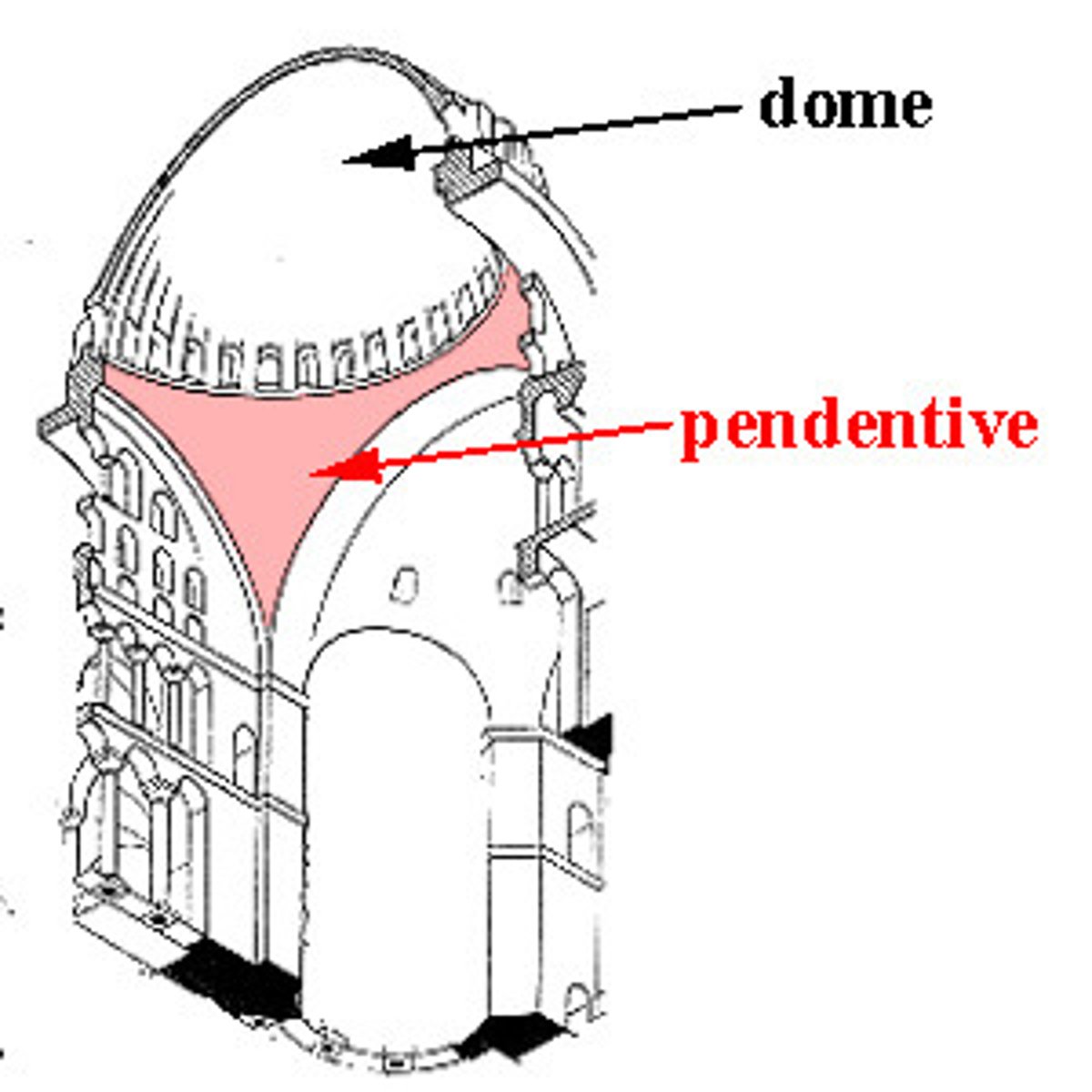
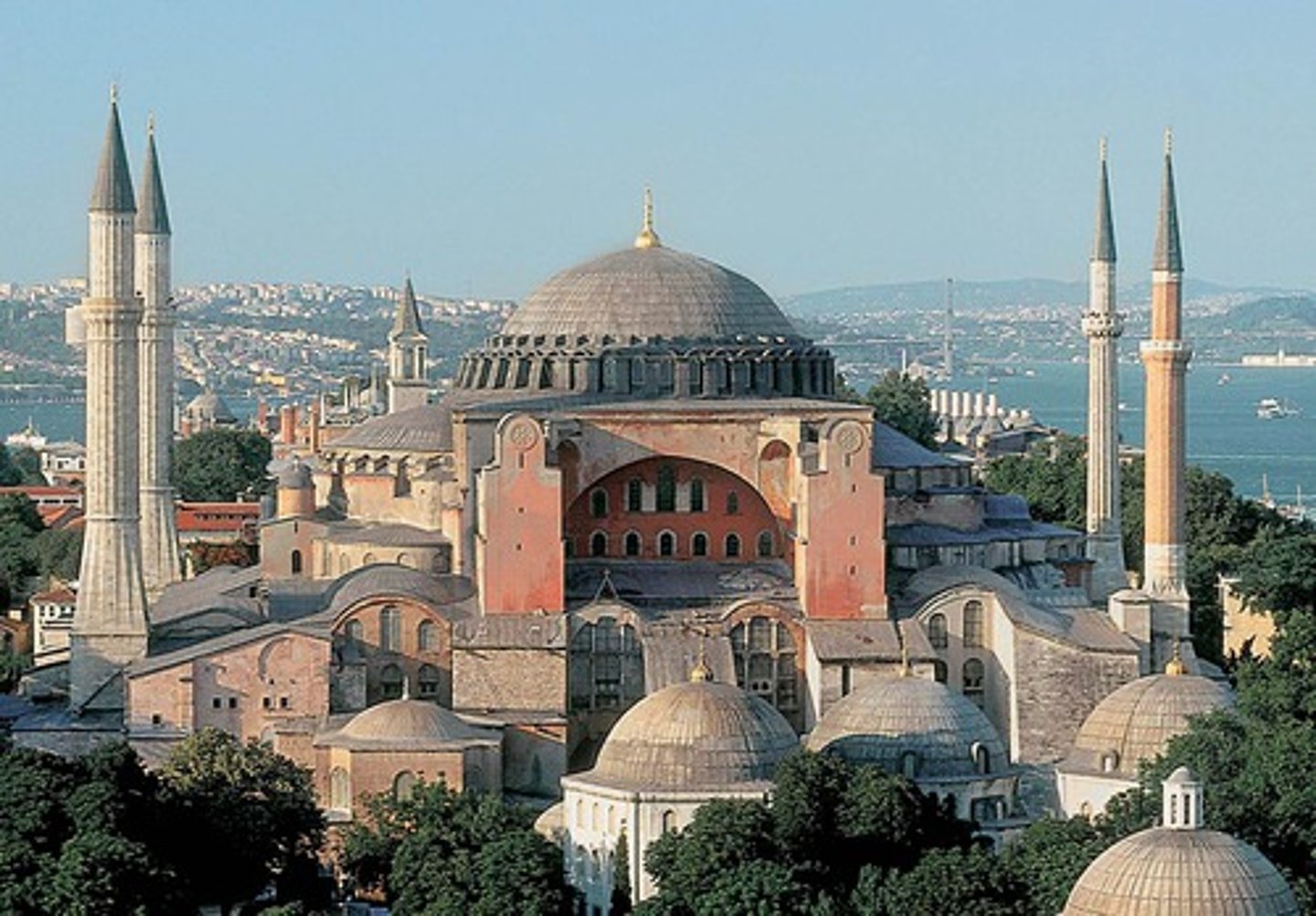
Hagia Sophia

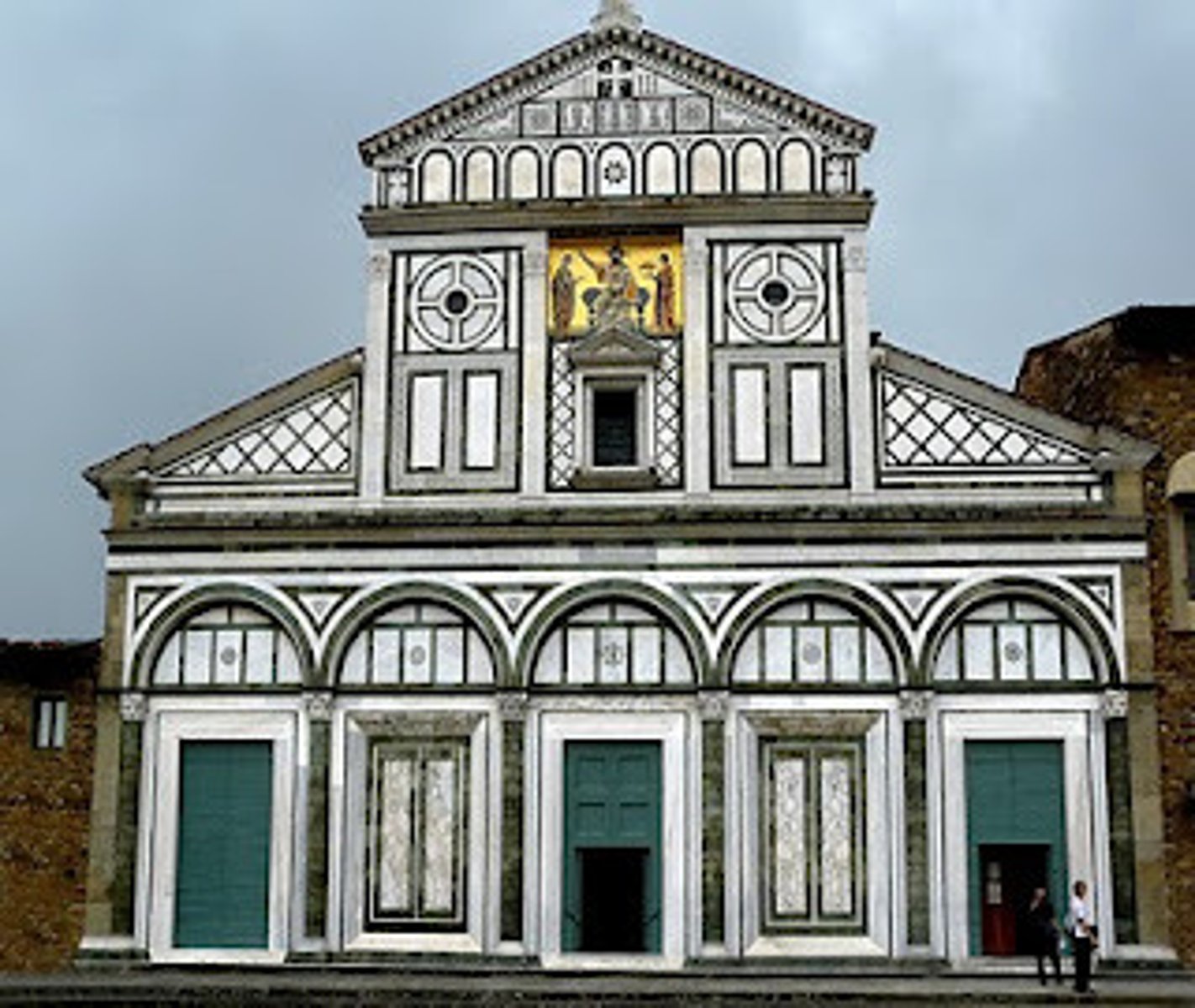
S. Minato al Monte

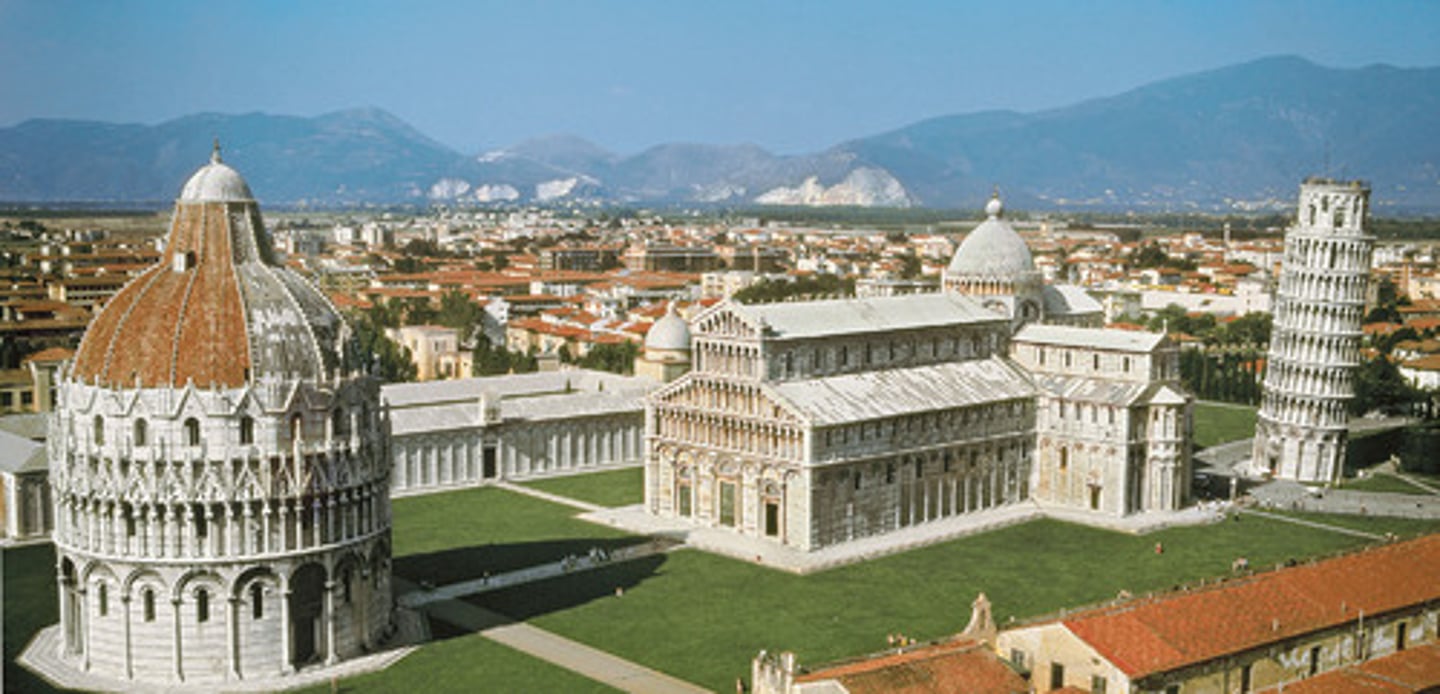
Pisa Cathedral and Campanile

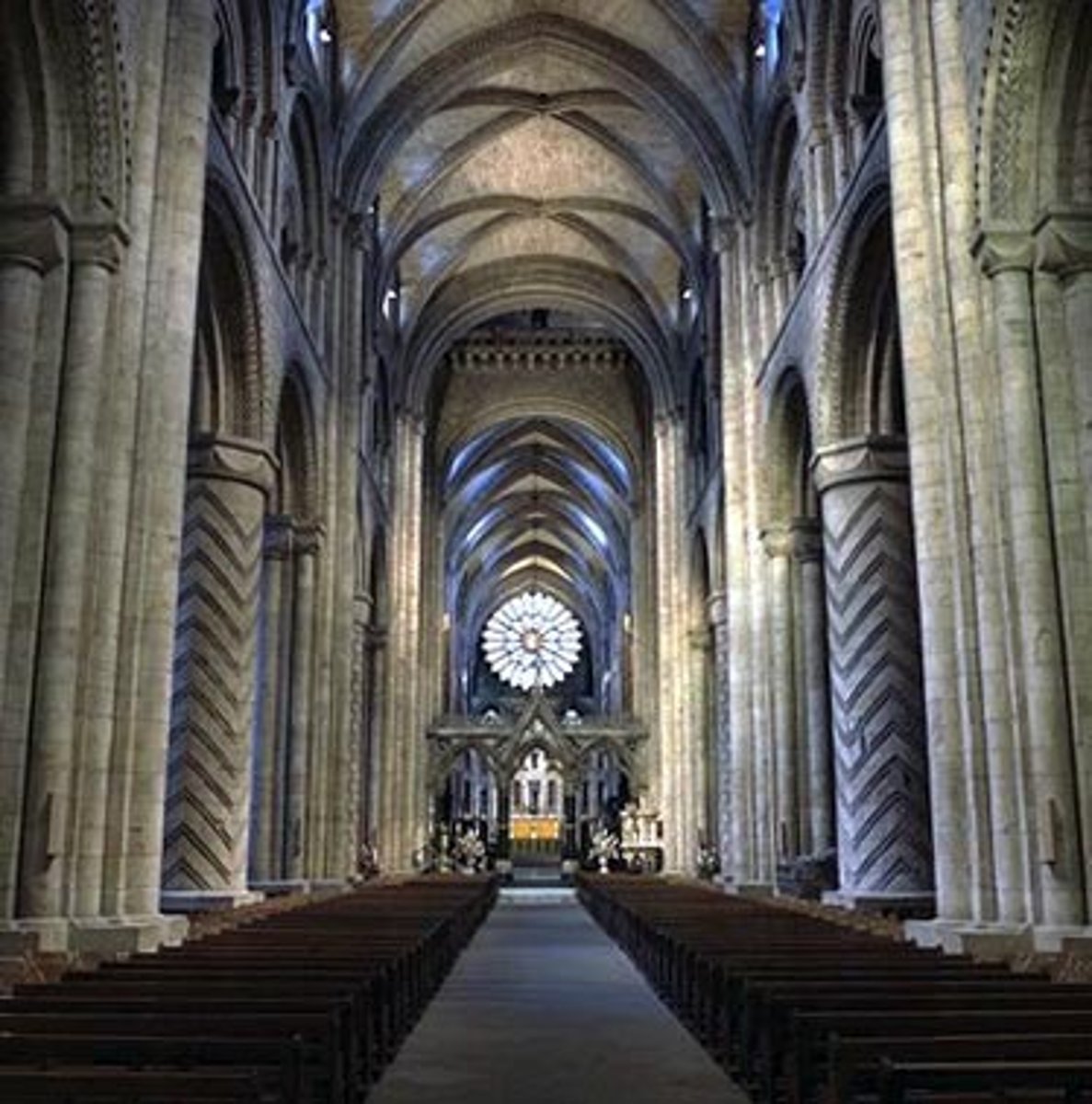
Gothic Architecture
- structure is also ornament
-pointed arch
apse
-semi-circular projection, containing an altar
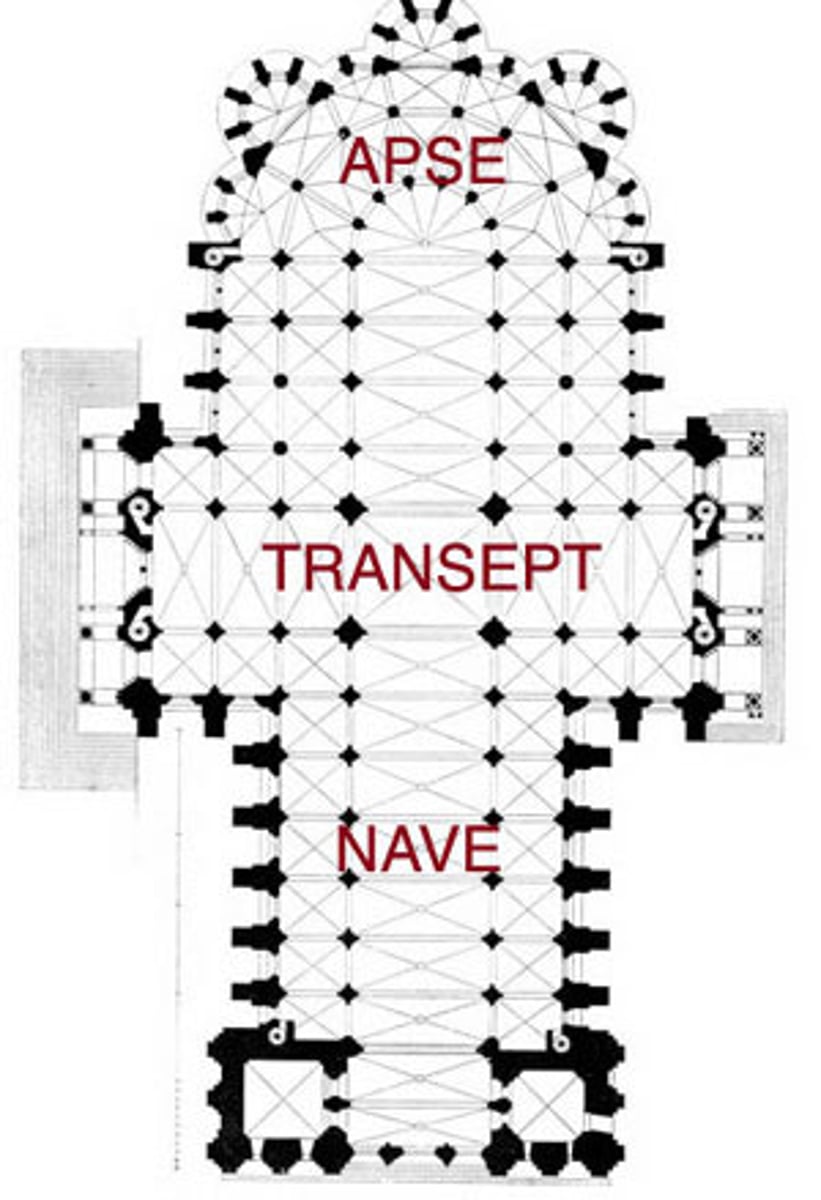
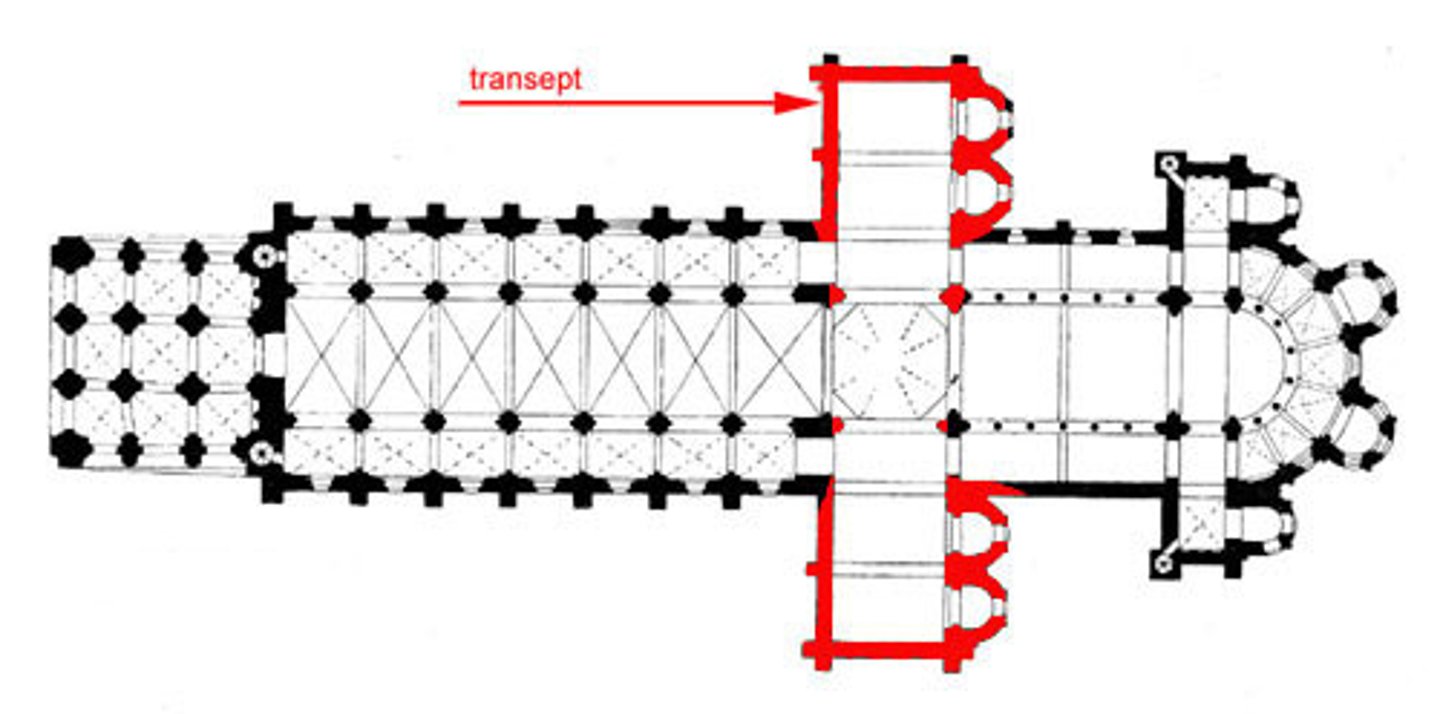
transept
-the two arms in a "latin cross" plan
nave
-space beyond the transept crossing toward the west or "front" of the church

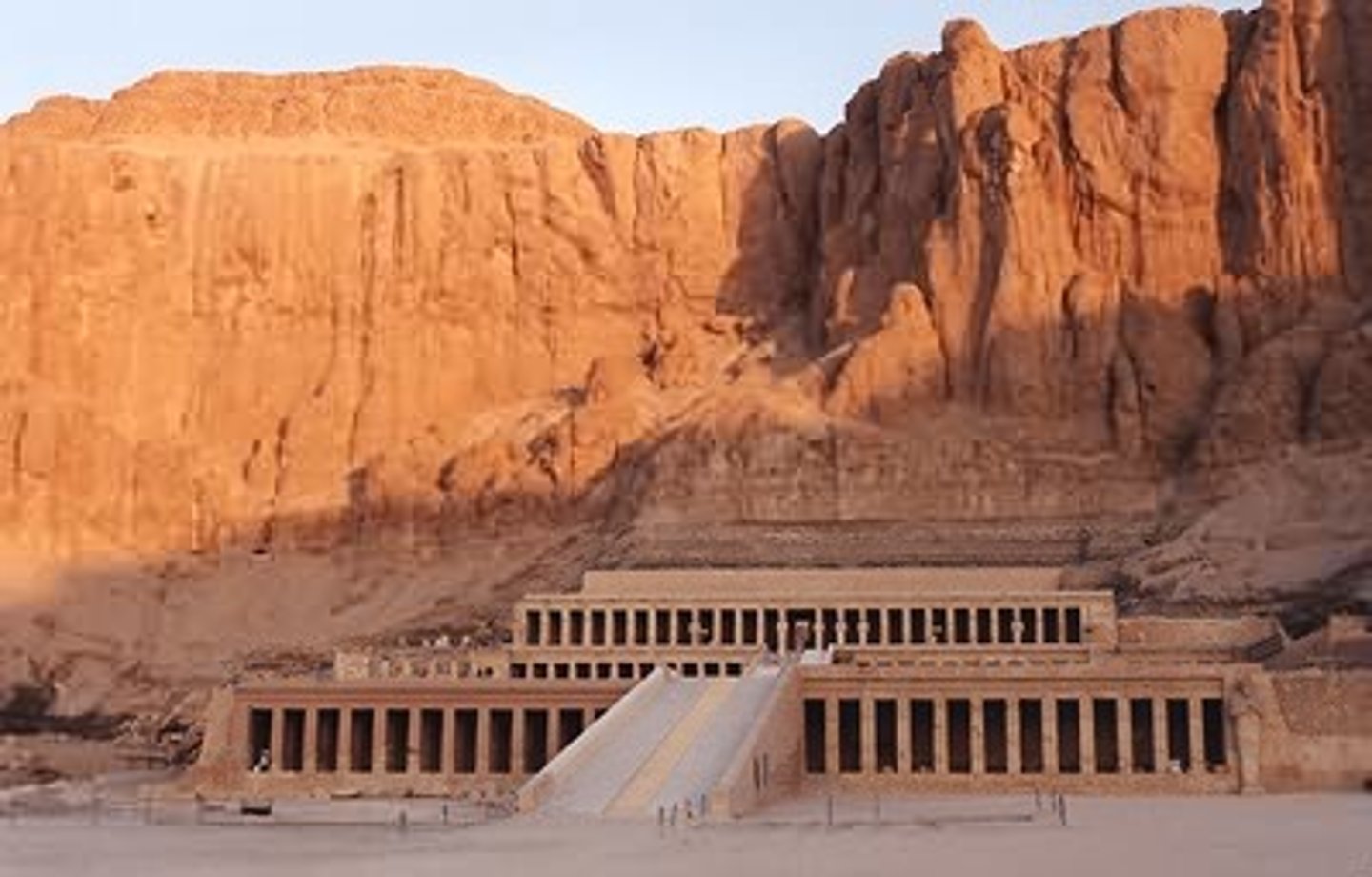
Mortuary Temple of Queen Hatshepsut

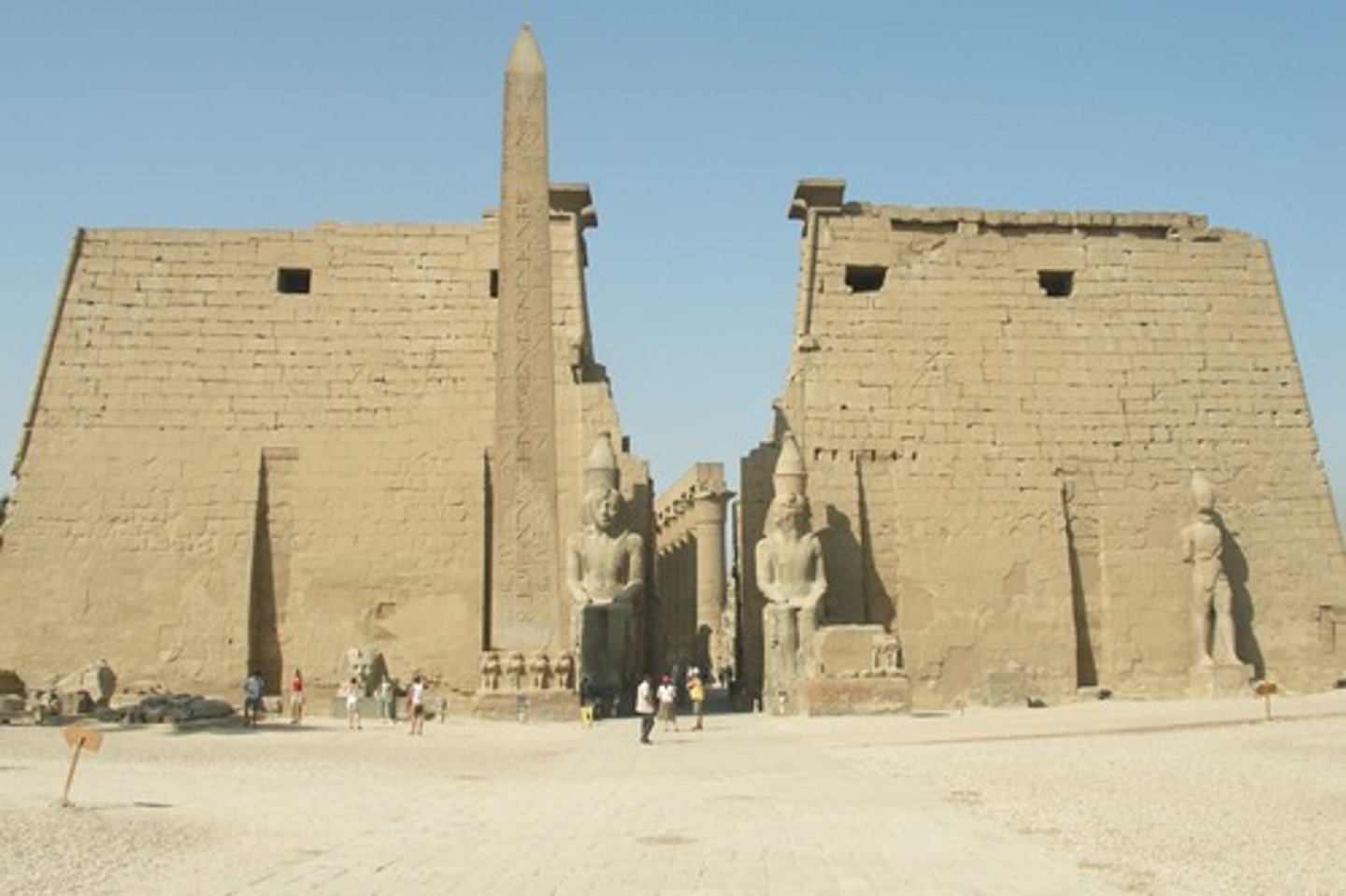
Temple of Luxor

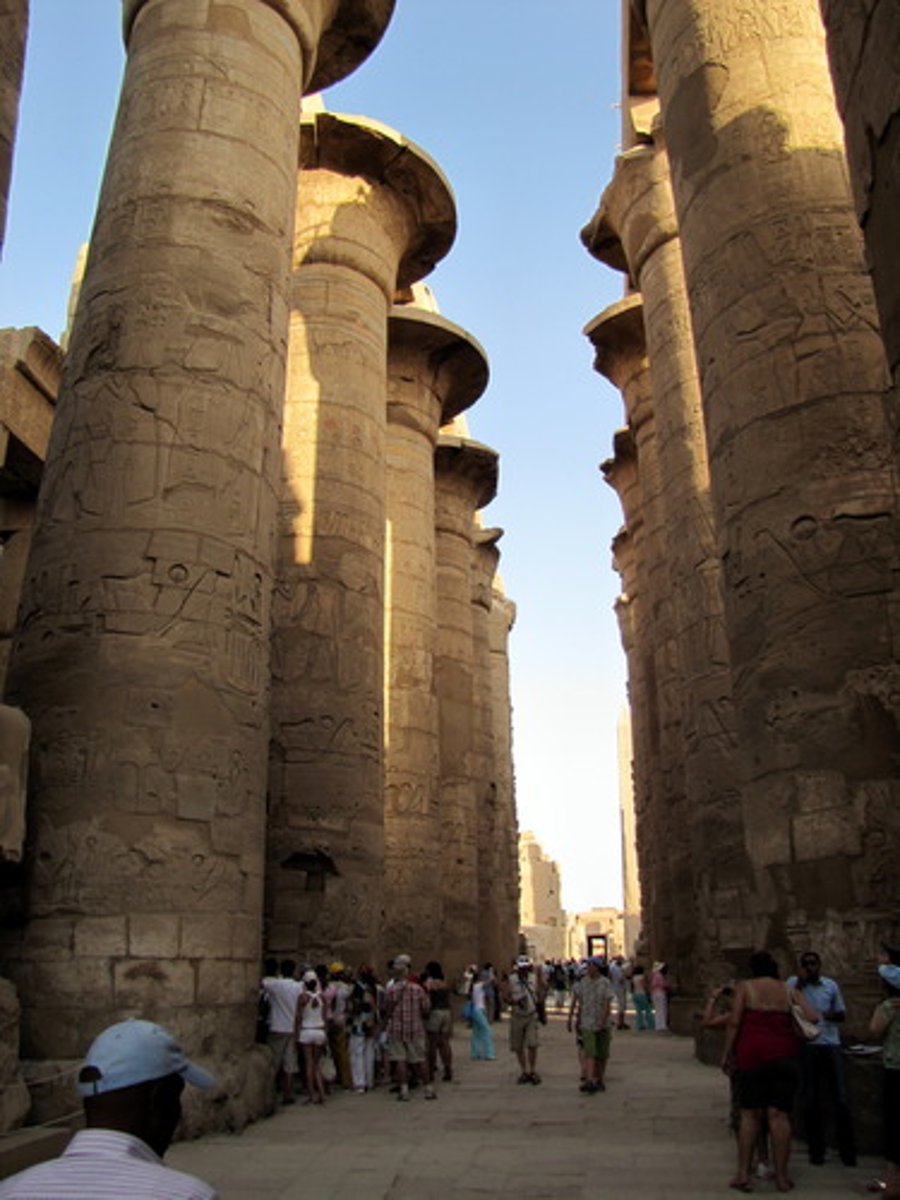
Temple of Amun at Karnak

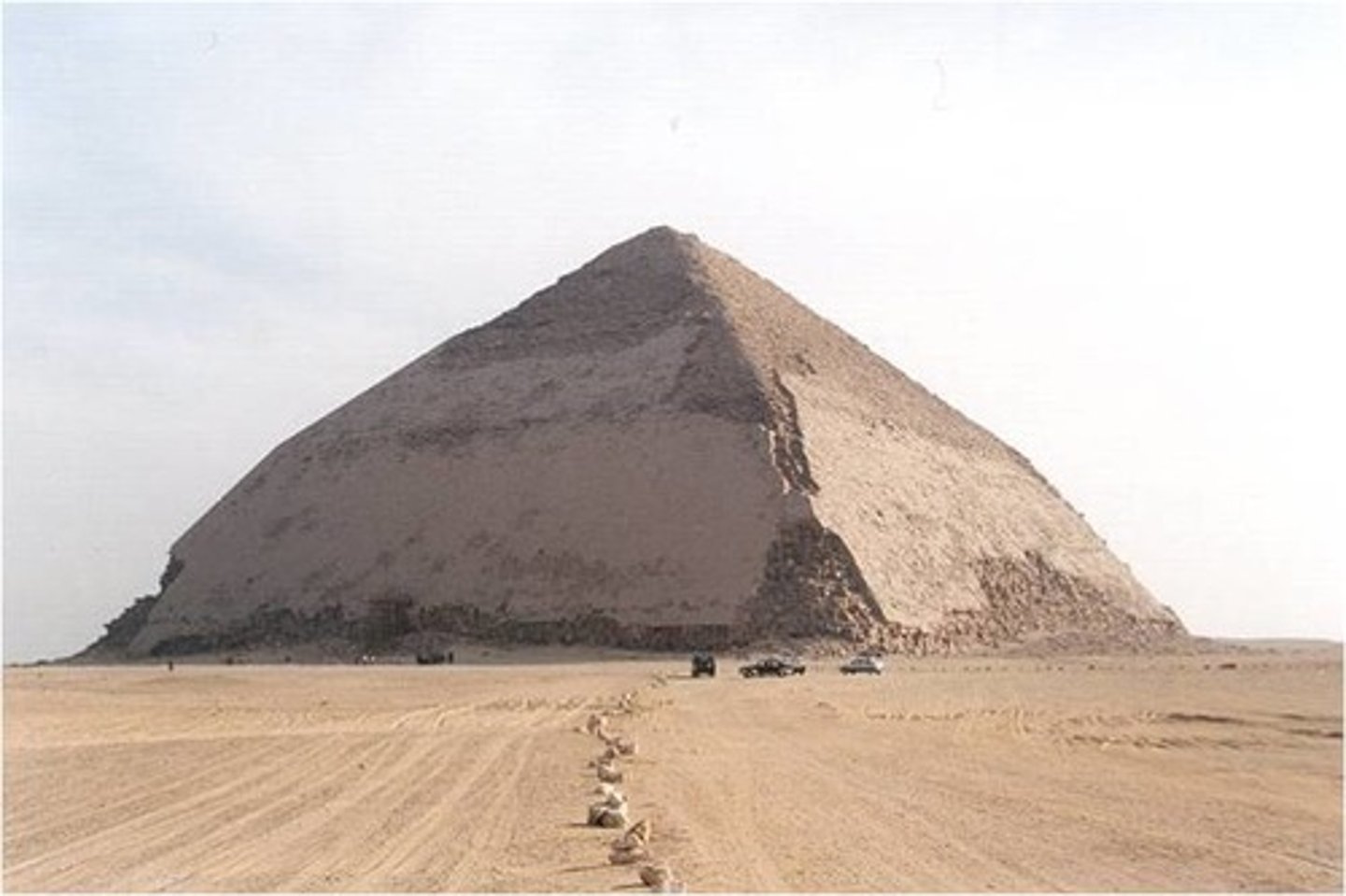
Egypt Pyramids
tombs for kings
reflective limestone
gold veneer on top
king would walk on sun rays to eternity
sealed the tomb
sculptural object
represent rays of sun