Shapes and IMFs
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the shape and bond angle of a molecule with 2 bonding pairs/regions, and no lone pairs of electrons?
Linear shape
Bond angle of 180o
What is the shape and bond angle of a molecule with 3 bonding pairs/regions, and no lone pairs of electrons?
Trigonal planar
Bond angle of 120o
What is the shape and bond angle of a molecule with 4 bonding pairs/regions, and no lone pairs of electrons?
Tetrahedral
Bond angle of 109.5o
What is the shape and bond angle of a molecule with 6 bonding pairs/regions, and no lone pairs of electrons?
Octahedral
Bond angle of 90o
What do lone pairs of electrons do to the bond angle?
Decrease it by 2.5o
What is the shape and bond angle of a molecule with 3 bonding pairs/regions, and 1 lone pair of electrons?
Pyramidal
Bond angle of 107o (109.5-2.5)
What is the shape and bond angle of a molecule with 2 bonding pairs/regions, and 2 lone pairs of electrons?
Non linear
Bond angle of 104.5o (109.5-2×2.5)
What shape does ammonia have, and why does it have this shape?
Shape is determined by electron pair repulsion
Ammonia has 3 bonding pairs, and 1 lone pair of electrons
Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs
Ammonia has a pyramidal shape with a bond angle of 107o
Electronegativity
A measure of the attraction of a bonded atom for the pair of electrons in a covalent bond
Dipole
A separation in electrical charge, so that one atom of a polar covalent bond, or one end of a polar molecule has a small positive charge, and the other has a small negative charge.
Polar covalent bond
A bond with a permanent dipole
Polar molecule
A molecule with an overall dipole, taking into account any dipoles across bonds, and the shape of the molecule.
Symmetrical (no lone pairs) molecules are not polar
What are Intermolecular forces between?
Simple molecular substances
What are the 3 intermolecular forces and their relative strengths?
Hydrogen bonds - strongest
Permanent dipole-dipole - middle
London - weakest
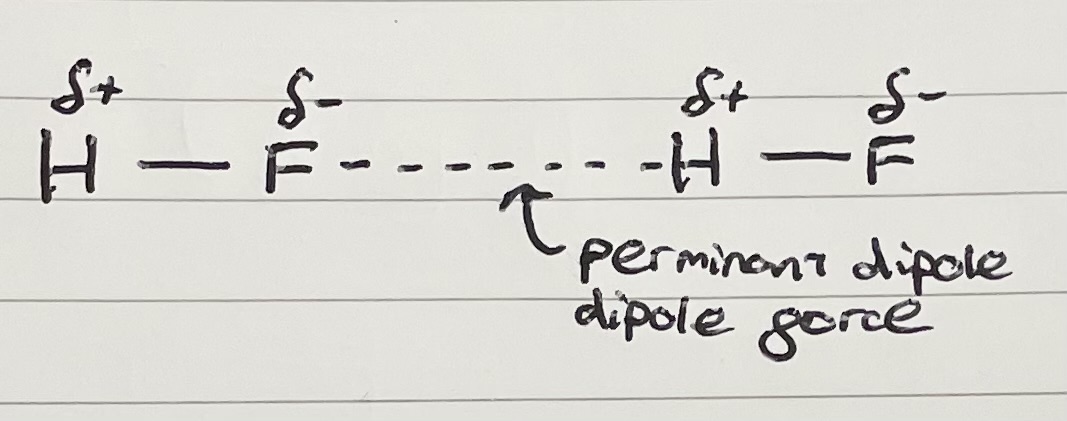
Permanent dipole-dipole force
Happens when there is a permanent dipole.
Negative dipole of one polar molecule can attract the positive dipole of a neighbouring molecule.
This forms a permanent dipole-dipole force between the molecules.
Draw an example of a permanent dipole force
Does not need to be between a H and F.
London force
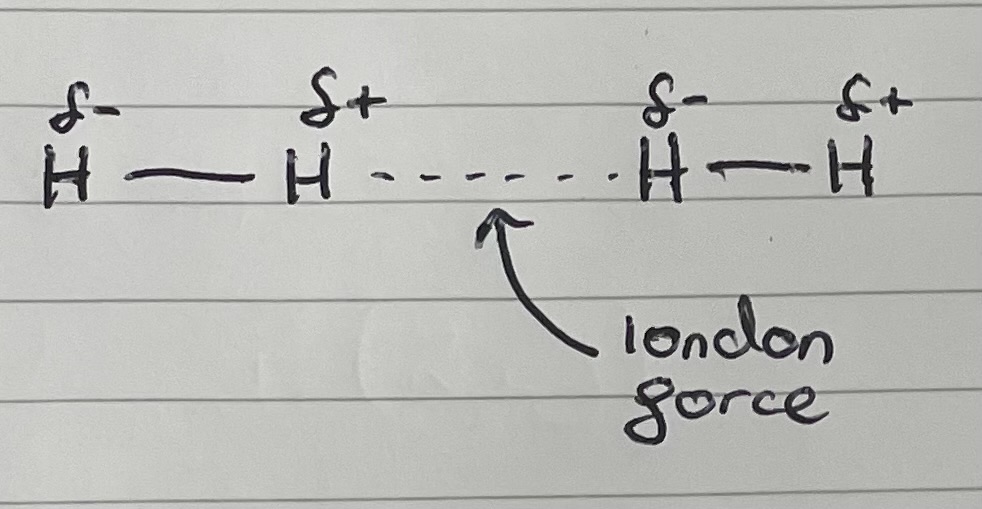
No permanent dipole
On average, electrons are in the middle of 2 atoms of equal electronegativity, but are constantly moving between them. When closer to one of the atoms, a negative dipole is induced in the atom closer to the electrons. ==> Forms induced dipoles
This interacts with the electrons in a neighbouring molecule, inducing a dipole in it.
The attraction between these oppositely charged dipoles, is called London forces
What makes stronger London forces?
More electrons
Draw an example of a London dispersion force
Hydrogen bonds
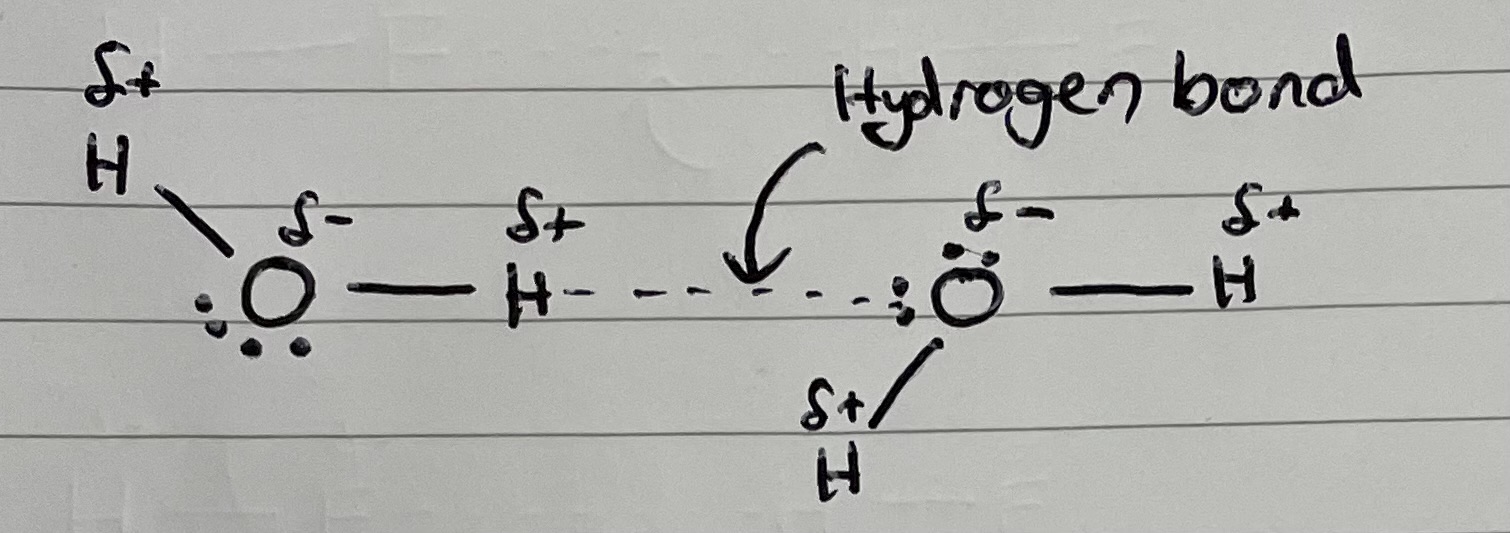
Need an O, H, or F, bonded to a hydrogen atom. This gives hydrogen a very large permanent dipole. This allows hydrogen to attract a lone pair of electrons from another o, N or F, bonded to a hydrogen.
Draw an example of a hydrogen bond
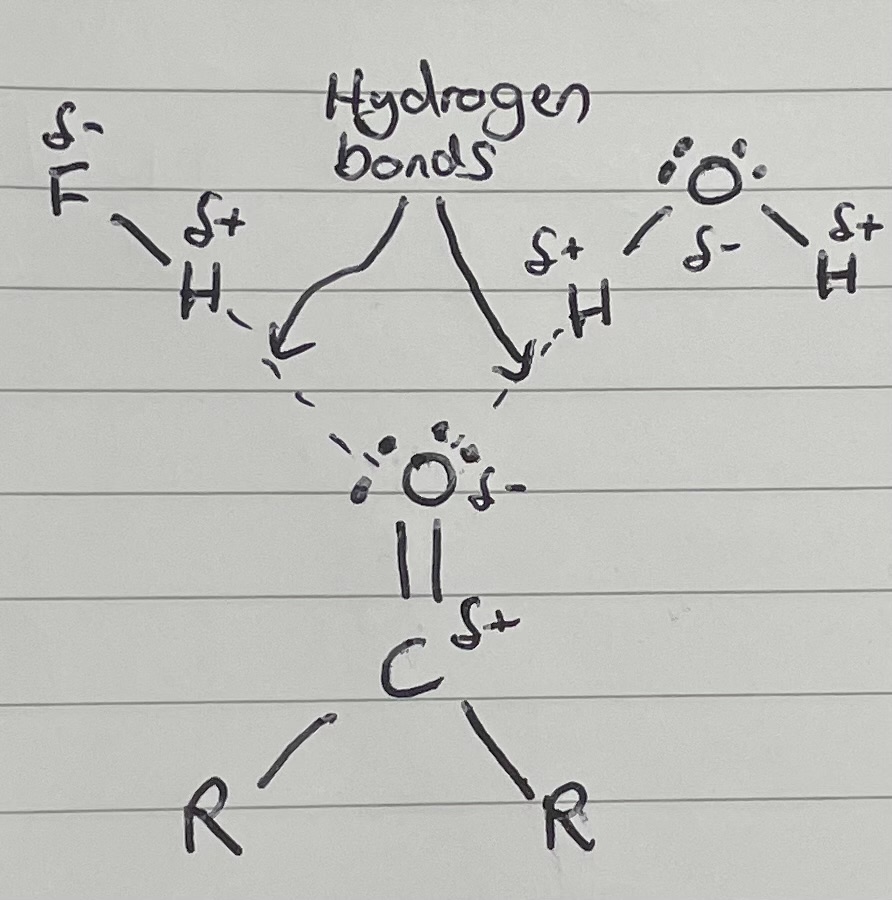
Can C=O hydrogen bond?
Kind of, it can have the lone pairs on the oxygen attracted to a hydrogen atom, but does not have a hydrogen atom to attract another O, N or F
What are the anomalous properties of water?
The solid is less dense than liquid - When the liquid turns into a solid, it formed an open lattice (molecules held slightly apart)
Relatively high melting and boiling points - Hydrogen bonds are extra IMFs (on top of London forces). This means that more energy is needed to overcome these additional bonds, hence have higher than expected melting and boiling points.
Are non-polar simple molecular substances soluble?
In non-polar solvents, IMFs form between the molecule and the solvent, weakening the IMFs of the lattice, so are soluble.
In polar solvents, there are no interactions between the solvents and lattices IMFs, so are non soluble
Are polar simple molecular substances soluble?
Depends on dipole strength, so is hard to predict. Some molecules contain parts that are polar and parts that are not, so parts of their structure can dissolve in both polar and non polar solvents.