female reproductive system
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
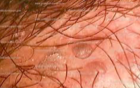
latum
flat, moist and minimally elevated lesion
seen in associatikon with 2ry syphilis
tx:
Benzathine penicillin G – 2.4 million U IM 1
dose
Doxycycline 100mg PO q 12 for 14 d or
Tetracycline 500 mg PO QID for 14 d or
Azithromycin 2000mg PO single dose
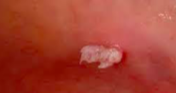
acuminata
papillary rugose and elevated lesion in anogenital region
HPV
tx:
• Cryotherapy
Surgical excision
Carbon dioxide laser
preeclampsia
new onset or worsening of existing hypertension with proteinuria after 20 wks gestation
edema
eclampsia
unexplained generalized seizures in pts with preeclampsia
criteria for preeclampsia
Blood pressure criteria for preeclampsia :
Systolic BP ≥ 140 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP ≥ 90 mm Hg (at least 2 measurements taken at least 4 hours apart) (140/90)
Systolic BP ≥ 160 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP ≥ 110 mm Hg (at least 2 measurements) (160/110)
Proteinuria
defined as > 300 mg/24 hours or
protein/creatinine ratio ≥ 0.3 or
a dipstick reading of 2
HELLP syndrome
HELLP syndrome is a serious pregnancy complication that usually occurs in the later stages of pregnancy, often in women with preeclampsia. The acronym "HELLP" stands for:
- Hemolysis: The breakdown of red blood cells.
- Elevated Liver enzymes: High levels of enzymes in the liver, indicating liver damage.
elevated tests - ALT, AST
- Low Leukocyte count (Platelets): Low levels of platelets, which are essential for blood clotting.
Symptoms can include severe headache, abdominal pain, nausea, and fatigue. It’s a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment to prevent serious complications for both the mother and baby.
0.2-0.6% of pregnancies
vaginitis
common
vaginal discharge
infectious organisms
>candida sp
>trichomonas
cervicitid (3 types)
inflammatory (acute or chronic)
STD
acute nonspecific: post partum
erosive: 2ry to physical agents
cervical neoplasms
inflammatory
complications include bleeding
PAP smear
screens cervical sample for id of pre malignant disorders
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasm (CIN)
squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL)
prevention: HPV vaccine
CIN
abnormal changes of the cells that line the cervix
not a cancer
but can become cancer over time if not treated
>do not cause any symptoms
invasive carcinoma
85-90% squamous in nature evolving from CIN
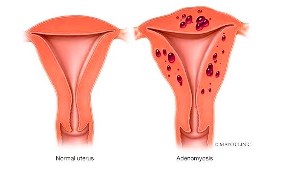
adenomyosis
presence of endometrial tissue within the myometirum
(inside uterine wall)
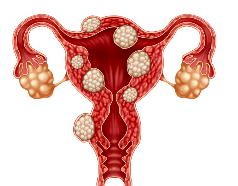
endometriosis
presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity or myometrium
endometrial polyp
sessile round pedunculated
abnormal uterine bleeding
may precede adenocarcinoma
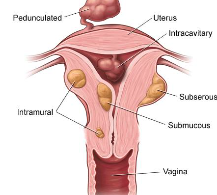
leiomyoma
most common benign tumor in females
tumor of smooth muscle (fibroids)
leiomyosarcaoma
malignant tumor derived from mesenchymal cells
>arises from the smooth muscle
>aggressive, high risk of recurrence and death
endometrial carcinoma (adenocarcinomas)
most frequent & related w/ anovoluntary cycle &/or irregular bleeding
menopausal age
associated with endometrial hyperplasia
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
fallopian tubes
inflammatory (infectious) disease which may result in abnormal scarring & stricture of the lumen
ovarian neoplasm
risk factors:
nullipairty
FHX: BRCA 1 & 2 genes
serous tumors
most frequent of the ovarian tumors
cystic or solid
teratomas
15-20% of all ovarian neoplasm
< 20 y/o
mucinous tumors
analogous to serous tumors in all respects but are considered less likely to be malignant
10% of all ovarian neoplasm