Lab practical 1 (anatomical/organelles)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
anatomical position
to stand erect facing forward, with arms at the sides, palms of the hands turned upward, feet shoulder apart
abdominal
abdomen
acromial
point/joint of shoulder
antebrachial
forearm (elbow to wrist)
brachial
arm(shoulder to elbow)
buccal
cheek (mouth)
calcaneal
heel of foot
carpal
wrist
cephalic
head
cervical
neck
crural / crus
lower leg (shin) — all of leg for crural
digital
fingers or toes
femoral
thigh
frontal
forehead
gluteal
buttocks
inguinal
groin
mammary
breast
nasal
nose
occipital
back of head
oral
mouth
otic
ear
palmar
palm of hand
patellar
knee
pelvic
pelvis
plantar
bottom of foot (sole)
popliteal
back of knee
pubic
pubis/genital
scapular
shoulder blades
sternal
breastbone/sternum
sural
calf
tarsal
ankle
thoracic
chest
umbilical
navel / belly button
vertebral
backbone/spine
lumbar
lower back
mental
chin
anterior (ventral)
front of the body / toward the front
posterior (dorsal)
back of the body / toward the back
superior
higher or located above on the body, nearer to head
inferior
lower or located below on the body, farther to the head
medial
toward midline of body
lateral
away from midline, towards the sides
contralateral
on the opposite side of the body from another structure
ipsilateral
on the same side of the body as another structure
proximal
closer to the point of attachment / origin
distal
farther from the point of attachment / origin
superficial
near the surface
deep
away from the body surface, more internal
sagittal plane
vertical division of the body into right and left portions
midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal right and left sides
parasagittal plane
divides the body into unequal right and left sides
frontal / coronal
divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) prtions
transverse (“cross section”) plane
divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts
oblique plane
divides the body at an angle (any angle)
dorsal cavity
contains the brain and spinal cord
ventral cavity
thoracic cavity: divides into pleural cavities and pericardial cavity
pleural = lungs
pericardial = heart
Abdominopelvic: divides into abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
abdominal = digestive organs, liver, kidneys, spleen
pelvic = urinary bladder, rectum, reproductive organs
important parts of cell
cytoplasm and plasma membrane
nucleus and nucleolus
membranous structures — smooth and rough ER, golgi, lysosomes
ribosomes
mitochondria
centrioles
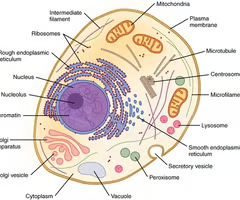
smooth ER
where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down
golgi apparatus
stack of membranes in the cell that modifies, sorts and packages proteins
lysosome
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
ribosome
site of protein synthesis
cillia
tiny hairlike extension that move together in a sweeping motion
microvilli
really tiny hairlike extensions that increase surface area (smaller than cilia)
stages of cell cycle (mitosis
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
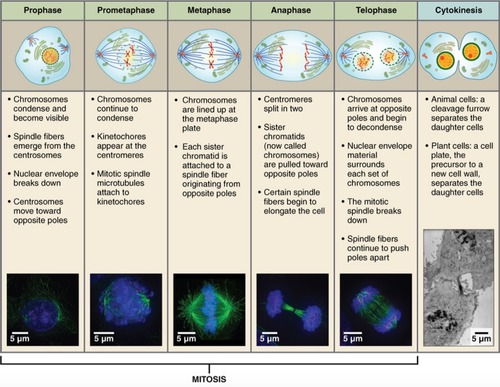
interphase
cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S and G2 phases
prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite side of the nucleus
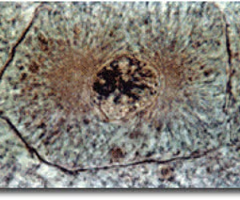
metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
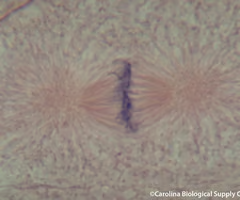
anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the chromosome pairs separate and move toward opposite poles
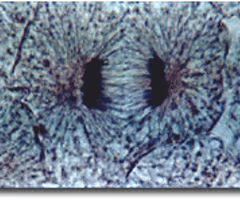
telophase
the final phase of cell division in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed
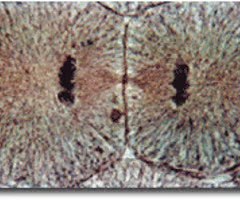
cytokinesis
the division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells after mitosis