etruscan rapid fire history stuff
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
three roman kings
Tarquinius Priscus, Servius Tullius, Tarquinius the Superb
battle of sardinian sea
540
etruscan victory
greeks lost
carthage important trading partners
hence pyrgi tablets
expansion into gulf of naples
what was the cause of the sardinian sea battle
aggressive expansionism
what battle was the end of the etruscan thalassocracy
battle of lipari
battle of himera
480 BCE — syracuse in the process of expanding
battle of cuma
474 BCE — syracuse wins
etruscan influence declines by a lot
that helmet thing
Syracuse VS athens
415 BCE Syracuse Vs Athens — adriatic
etruscans sent some help
syrause won
Rome (gens fabia) VS. Veii
477 BCE
Fabian Family VS. Veii and other E. Cities Whole family gone after 10 years
Rome vs. Veii
438-426 BCE
Fight over Fidene → access to the Tiber Asked for help from other E. Cities, but no one helped
Fall of Veii to Rome
396 BCE (siege started in 406 BCE)
End of Eturian Supremacy Completely destroyed, population enslaved, territory redistribution
Campena fell to Rome
395 BCE
Alliance of Caere with Rome Given honorary citizenship and managed to push back against Roman goals
Sack of Rome by Celtic peoples
390 BCE
40 year peace between Rome and E.
351 BCE
Hostility Resumed rome and etruria
311 BCE
Expansion inland along the Tiber
E. cities did NOT band together to fight
Roman/Samnite war ended
304 BCE
New War: Rome v. E. Cities
304-280 BCE
Fall of Arezzo
302 BCE
poorly documented
Volterra Fell
298 BCE
Perugia & Chiusi fell
295 BCE
Volsinii & Roselle fell
294 BCE
Volsinii VS. Rome
290-288 BCE
Etruscans ally with Gaelic tribes to fight Rome
284-282 BCE -
Gaul & E. Cities VS. Rome
283 BCE - Battle of Lake Vadimon
282 BCE - Another Battle
Both Losses
Tiberius Coruncanius Triumph over Vulci and Volsinii
280 BCE
Ceveteri Lost half its territory
273 BCE
Rome crush a slave revolt in Volsinii
265-264 BCE
Faliscans ultimately defeated
241 BCE
Main God (Iuno) statues moved by Rome to show dominance
ziro tomb
funerary urn + grave good like burial thing

IAB: Tomb of Orcus II 2 different tombs: Orcus I is older & Orcus II is added in Late 4 th Murina Family tombs OIII: Blinding of Cylops OII: Wheel of death procession of famous dead (from the trojan war) in the styx swamp Procession continues + Tulca (E. Demon) Procession Judged by deities of the underworld (E. Persephone has a snake crown) + Carrow (E. Demon)

AP:Dispater Stamnos most important shape for the Feliscans Made by migratory attic painter Feliscans focus on ganymede + Zues’ relationship

IAP: Calyx Krator By Nazzano Painter Portrays Herakles and his human brother (Ifyclys) V. Snake Many deities part of full grave good set

Bronze Mirror from Volterra (4 cen.) th Herakles nursing from Hera (Uniquely Etruscan) → His adoption

Embrace of Atunis and Turan 325 BCE Inverted Gender norms: Tunis pulling mantle as he is embraced mature lover Aphrodite

Relief facing city ~ Painted Terracotta Depicts 2 mythical scene of the 7 vs. Tiberus fight for power after Oedipus → both lose Lower Right corner: Tydeus bites the winners head to eat his brain + Athena with a potion Upper Left corner: Killing of Capaneus by Zeus with a thunderbolt & Polyfontus Stylistic Analysis: a mix of Archaic and severe 480 BCE ~ Temple A (built in Eturian style) Decline led to no more movement of Greek artisans → a stagnation in development

tomb of the hunter
designed to look like a pavillion/tent
THE TOMB OF HUNTING AND FISHING


what is this an example of
Caeretan Hydria; 520-500 BCE Made by Ionian Artists who migrated Decor: Herakles & Cerberus AND Herakles & Aristos Compression of 2 myths Cerberus is covered in snakes in Eturia
BLACK FIGURE POTTERY

Silenus Painter; Amphorae 2 figurative friezes sacrifice of Pollus & Achilles’ ambush of Troyes Nereids + Satyr Dancing
LOCALLY MADE BLACK FIGURE POTTERY

influx of pottery from Greece and greater migration of artisans. The fancier productions were buried in banquet sets as grave goods. This also included the creation of new shapes based on previous productions like the Nicosthenic Amphorae. IAP: Tyrrhenian Amphorae ~ Athens; 570-50 BCE Four registers: 1: tree of life/flowers 2: sacrifice of human (very violent, each figure labeled 3: tree of life & Sphinxes 4: Lions hunting cattle
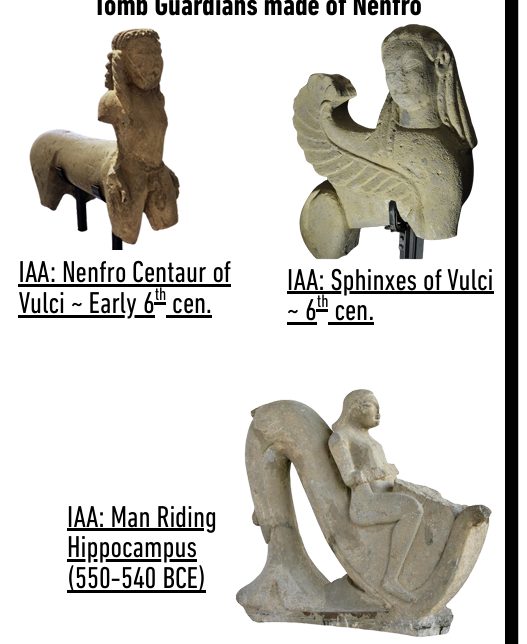
VULCI FUNERARY SCULPTURE


ACQUAROSSA RELIEF
Archaic period city with 5,000 to 7,000 people with 75 people. Monumental complex in Zone F that was annexed by a larger city 560 BCE.
1.Banquet: Male & Female Figures 2.Dancers
3.Herakles Fighting Nemean Lion & Soldiers
4.Herakles fighting cretan Bull & Hermes & Pegasus Chariot

poggio civitate two phases
Orientalizing period and the Archaic period.
Phase 1 had a small temple, aristocratic house and a workshop but was destroyed in the 7 cen. by fire.
Phase 2 had a rectangular building with open court yard, subdivided into rooms and had 2 watch towers and terracotta artistic productions

BRONZES FROM BROLIO
Bronzes as votive offerings are common in N. Eturia Spans multiple time periods from votive pit at rural sanctuaries Maybe originally part of furniture Male & Female figures

S. Valentino di Marsciano, Perugia (540-535 BCE) These tripods were a cauldron, with decorated stands, featuring scenes from Greek myths. They were used as statement pieces during Symposia to help start conversation, and were given as prizes and/or votive offerings.
Tripod A Tripod B Tripod C lid, lion/sphinx statuette and stand with lotus designs; Peleus abducting Thetis
3 registers: Herakles v. lion, Peleus abducting Thetis, Apollo kills Tityos who tries to kidnap Leto 3 registers:
Archer kneeling by bush, facing sphinxes, master of animals taming 2 lions

Chariot from Monteleone di Spoleto (575-50 BCE) Part of funerary goods → v. common in E. Tombs Made of bronze, iron, wood, and ivory inlay Mythical decoration: life of Achilles Probably a Ceremonial chariot → proof of Use


IAP: Pyxide of Pania (Chuisi, 630-20 BCE) 20cm ~ Elephant Ivory Decore in horizontal bands separated by vegetal bands Odysseus & Scylla and the escape from the cyclops; a warrior departure (mourning women)

IAP: S. Paolo Olpe - Cerveteri (630-20 BCE) 2 Scenes:
E. Animal motifs & the rejuvenation of Jason + Media, Daedalus with wings and the wedding blanket of Dionysius and Aridene

what is this an example of?
SUB GEOMETRIC CERAMIC
painter of Narce
Olla in the tomb of the ducks Maybe Greek Immigrant from Cycladic islands Features horses & waterbirds Painted tombs as well, or from the same workshop

IAP: Pyxis; Pittore della Nascita di Minerva (630-20)
Rare scene depicted signed by Kusnailisa → male slave/client of woman of the Cusna Family Proof women could be owners of production locals

IAP: Pithos con Accecament Polife (630-20 BCE) found in Cerveteri
2 figurative scenes: blinding of the cyclops: the first example of it in Eturia Fantastical Animals
bucchero sottile time period
(675-625 BCE)
Bucchero Transizionale
(625-575 BCE)
Bucchero Pesante
575 - E. 5 cen. BCE

Macchiapiana Tomb Family tomb, found in a grotto, Female urn is in position of power (on throne +Axe) Female is 20-30 years older than the male ashes.

canopo from dolciano
Bronze jar, very stylised clay lid, only example of 2 material construction in Eturia. Body is 7 cen. and head is 6 cen.

ziro tombs
Continues the cinerary urn and grave goods
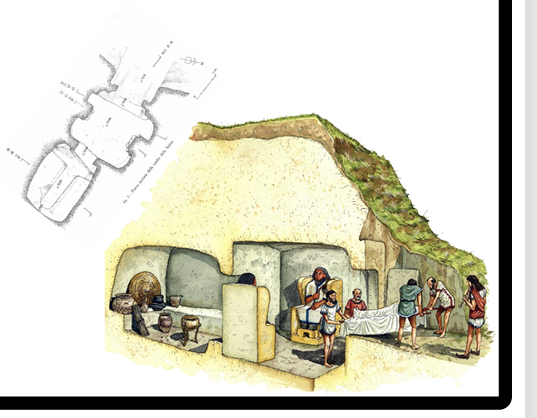
TOMB OF DA STATUES
Chamber Tomb in Ceri Large scale sculptures Antechamber and Main burial chamber Representation of 2 folks carved into the antechamber Symbol of power Model identified with model from Syria Linked as ancestors of the family to protect the lineage
REGOLINI-GALASSI TOMB
(680-650)
Del Sorbo Necropolis, Cerveteri, 680-650 BCE
Discovered in 1836 (completely intact) emphasis on retrieving “treasures,” no notes (little can be gleaned from diaries)
Tomb as an extension of the Family house New style in a mix of trench and chamber tombs Dug into the Tufa AND built up above ground Inhumed woman and Cremated Man Only rich men were cremated and placed into bronze urn → homeric traditions?

REGOLINI GALASSI TOMB!
Large Bronze items: 8 Shields; funeral bed; carriage and bedstead; cauldron and stand (local version of Eastern items) Gold and Amber Jewellery (eastern inspired) Bucchero Inscribed inkwell and mourning figures Silver vases for drinking and libation (same workshop, local production using E. artists) 6 are inscribed MI LARTHIA (Scholarly discourse on what this means and who it belongs to) D

TOMB OF THE SARDINIAN BRONZES
Vulcii - late 9 cen. (850-820 BCE)
Biconical vases Layers of vases silver vase/urn Extremely wealthy grave goods Glass, Gold jewellery, many fibula, bronze chains, statuettes Some items worn during cremation and others decommissioned for death and put in tomb 3 bronze figures from Sardinia Many with long hair, shield, conical hat, peace hand → warrior priest? Tiny stool Tiny Basket Analysis of Human Remains 2 people: adult woman and child Cremated together
J.J. Winckelmann
1717-1768 1758 → trip to Eturia Art as evolutionary pattern: freedom = Good Art Geschicht der Kunst de Altertuns (1764) → Classified E. Art too passionate; E. people = melancholic people 3 Classifications Ancient Style: Egypt related Violent Style: Peak for J.J. Imitative Style: copies Greek Ar
herodotus
lydians and half of em went to italy
hellanicus of lesbos
pelasgians (mythic people)
anticledes of athens
pelasgians + lydians
dionysus of halicarnassus
indigenous/from there
modern guy who said they were from italy
massimo pallotino
NESTOR CUP IS INSCRIBED WITH
greek like earliest inscribed thing
3 type of fibula
for cremation
for urn
decomissioned for death
campana tomb stuff

etruscans loved the odyssey possible because
connection to da sea
what did the monteleone chariot depict?

when was caertan production? + list of artifacts
artisthonos krater
heptachord painter - biconical krater
pyxide of pania
red and white shi
s. paolo olpe
aquarossa friezes go

poggio civitate friezes
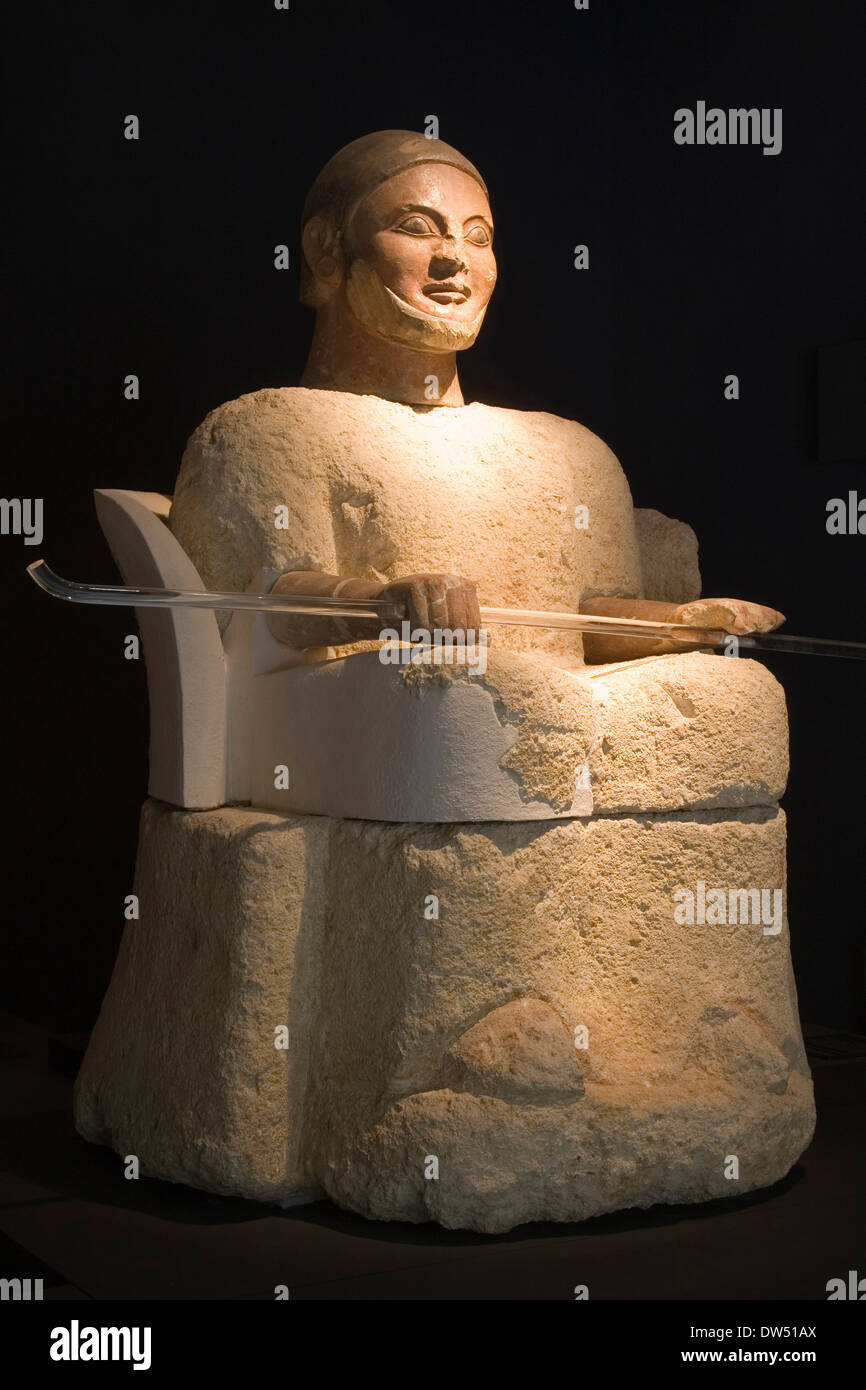


tombs during the classical period
tomb of the shields
tomb of orcus II
