Beh Sci 110 USAFA GR 1
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
critical thinking
thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions
Steps of critical thinking
examines assumptions,
appraise sources,
discerns hidden values,
evaluates evidence,
assesses conclusions.
scientific attitude
curiosity, skepticism, humility
psychology
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
behavior
actions, external/observable
mental processes
The thoughts, feelings, and motives that each of us experiences privately but that cannot be observed directly
Nature vs. Nurture
the long-standing controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors. Today's science sees traits and behaviors arising from the interaction of nature and nurture.
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
Bio approach
genetics
mutations
natural selection
genes responding to genes
Psycho approach
learned fears & expectations
emotional responses
cognitive processing
perceptual interpretations
social approach
presence of others
culture
societal
family expectations and norms
peer and other group influences
compelling models (famous people/media)
Psychology sub-fields
biological
cognitive
clinical
developmental
social
personality
legal/forensic
counseling
industrial-organizational
cognitive neuroscience
Psychology Perspectives
neuroscience,
evolutionary,
behavior genetics,
psychodynamic,
behavioral,
cognitive,
social-cultural
three roadblocks to critical thinking
hindsight bias
overconfidence
perceived order of random events
hindsight bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.
perceived order of random events
When one will believe that there is a pattern where there is none.
Theory
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
Theory functions
organizes observations
implies predictions
stimulate further research that leads to revised theory that better organizes/predicts
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
operational definition
a statement of the procedures (operations) used to define research variables.
Replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
Correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other.
Causation
A cause and effect relationship in which one variable controls the changes in another variable.
descriptive designs
study designs in which the researcher defines a problem and variable of interest but makes no prediction and does not control or manipulate anything
correlational design
A research design in which the investigator gathers information on individuals without altering their experiences and then examines relationships between participants' characteristics and their behavior or development. Does not permit inferences about cause and effect.
experimental designs
designs involving random assignment to groups and manipulation of the independent variable
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
dependent variable
The measurable effect, outcome, or response in which the research is interested.
random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
mean
average
median
the middle score in a distribution; half the scores are above it and half are below it
mode
the most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution
range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
normal curve
the symmetrical bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes. Most scores fall near the average, and fewer and fewer scores lie near the extremes.
can observed difference be generalized to population?
representative samples
less variable observations
more cases
ethics in research
informed consent
protection from harm/discomfort
maintain confidentiality
debriefing
debriefing
the post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants
informed consent
an ethical principle that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
Confidentiality
the act of holding information in confidence, not to be released to unauthorized individuals
Minimizing harm
Balance consideration of harm against telling the full truth
Be vigilant when dealing with juveniles, victims of sex crimes and those who are inexperienced with the media
Weigh whether the information is truly necessary or just panders to curiosity.
perspective taking
viewing the world from something other than one's habitual vantage point. Covers a broad range from the literal to metaphorical.
SOAR
self-assessment
objective analysis
awareness of another/alternative perspective
reflect & apply perspective taking
self-assessment
examine biases, pre-conceived ideas and their sources
Objective Analysis
seeking to evaluate based upon relevant facts, regardless of feelings in order to broaden perspective of a topic
awareness of another/alternative perspective
the way other people think, and why
reflect and apply perspective taking
how is this useful? what value is there in this process? Apply to specific instances.
biological psychology
a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
How biology and experience interact
adaptive brain is wired by out experience
nerve cells conduct electricity and talk to one another by sending chemical messages
parts of the brain have different jobs
we integrate information processes in different brain systems to construct experience with sights, sounds, meanings, memories, pain, and passion
Neuron
a specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses; a nerve cell.
86 million in an adult brain
if you don't use it, you lose it (fire together, wire together)
neurons can be reassigned
lots of neural connections occur while sleeping
cell body of neuron
the cell's life support center
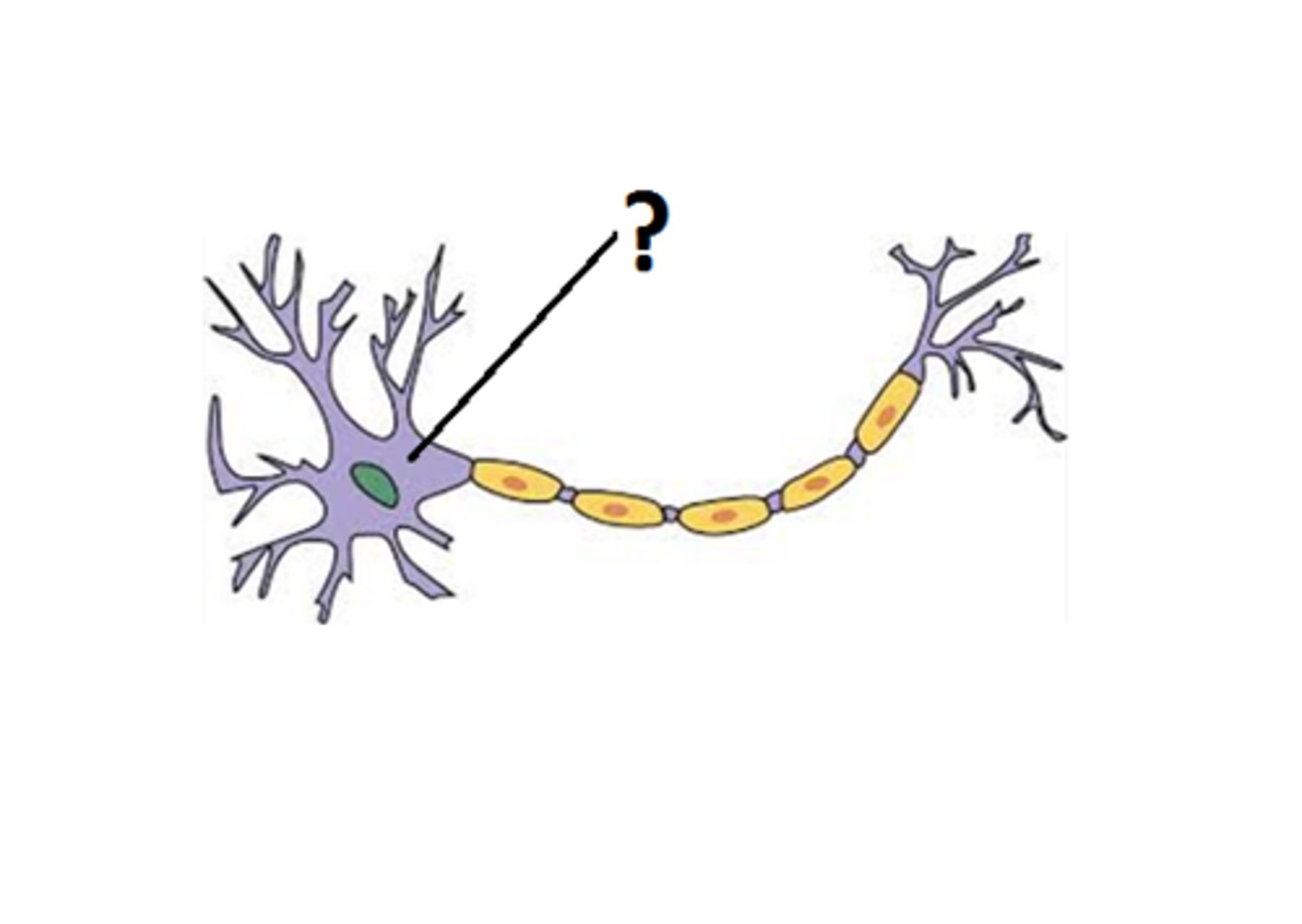
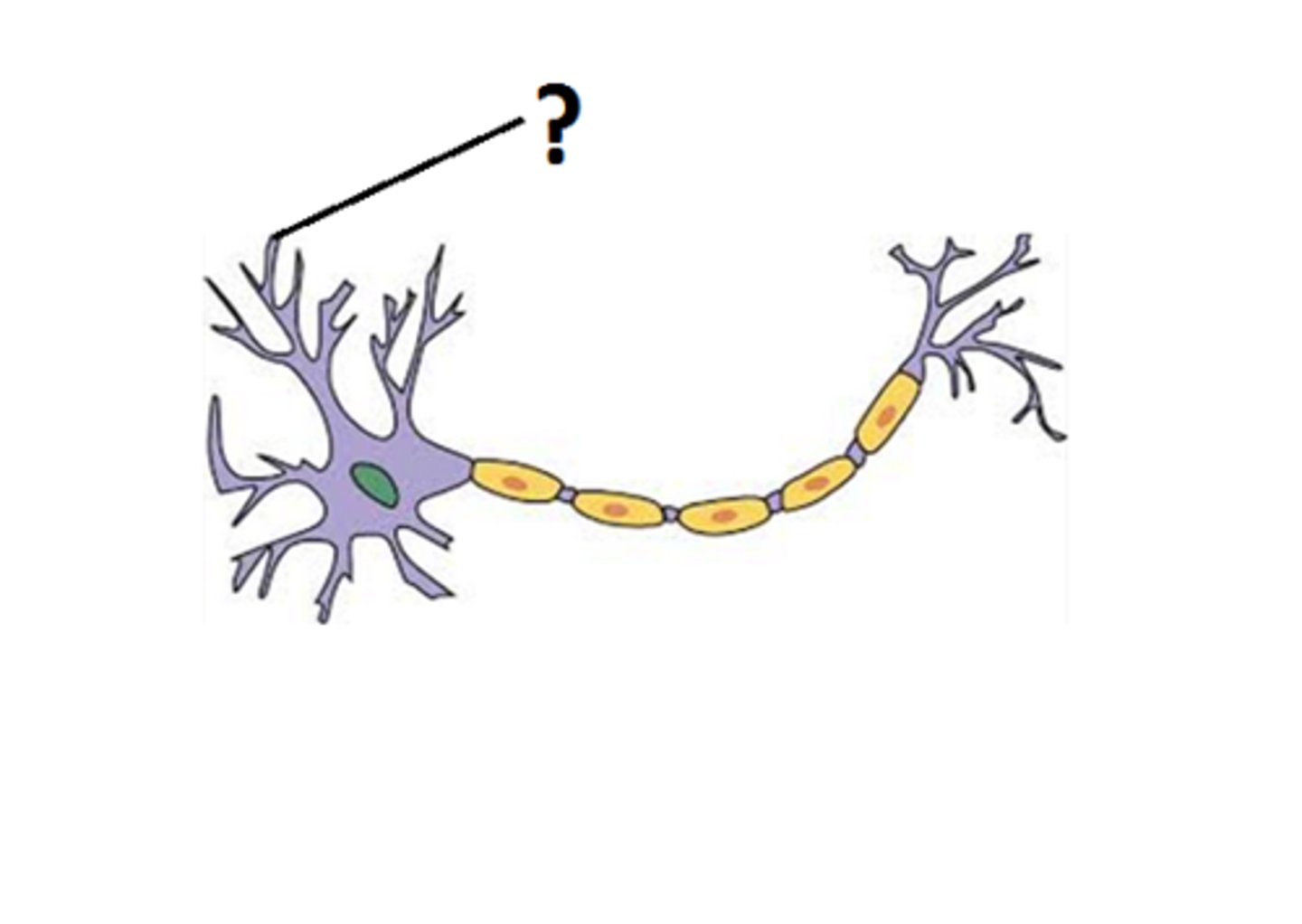
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
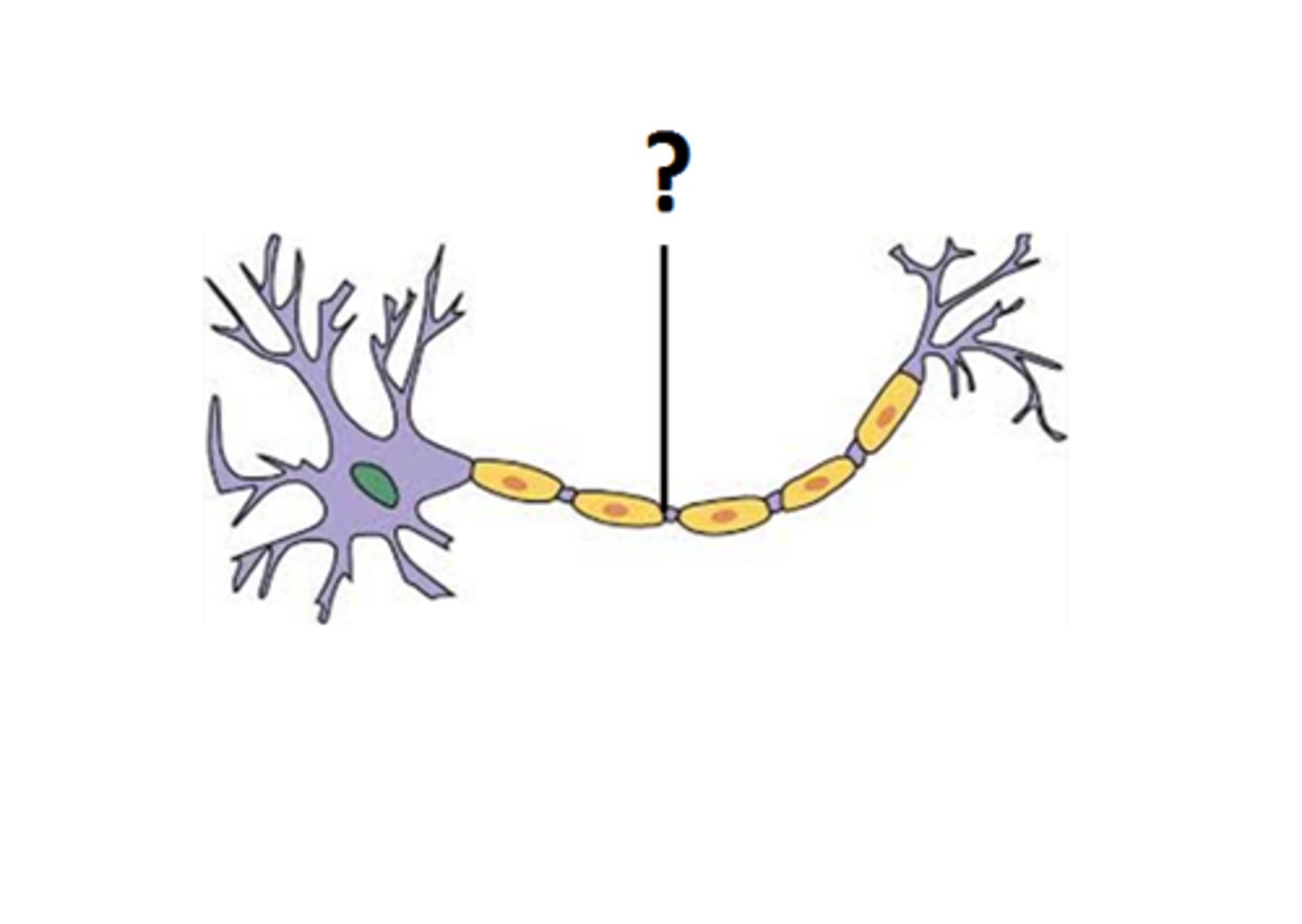
axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body to other neurons
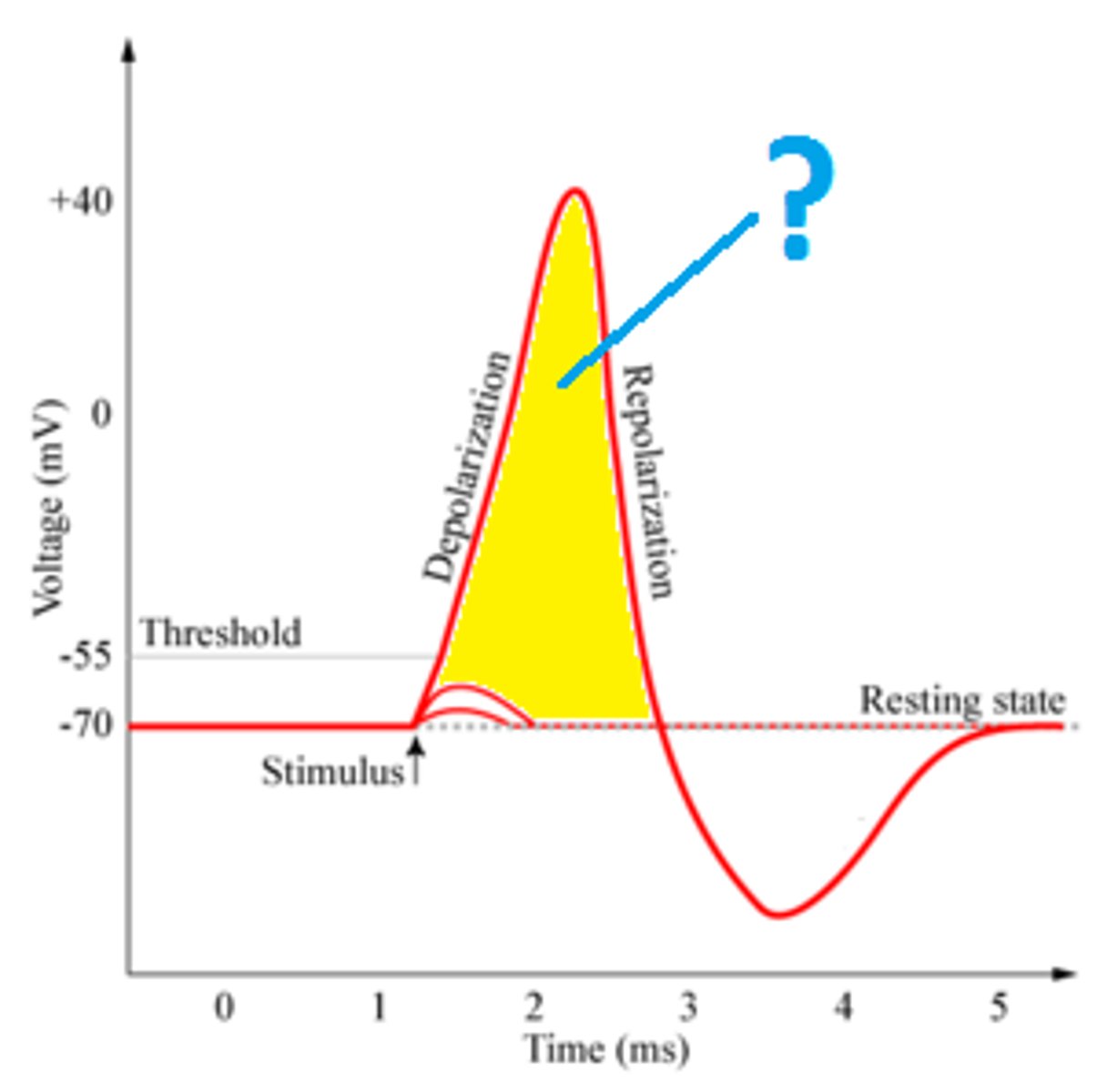
neural impulse
a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
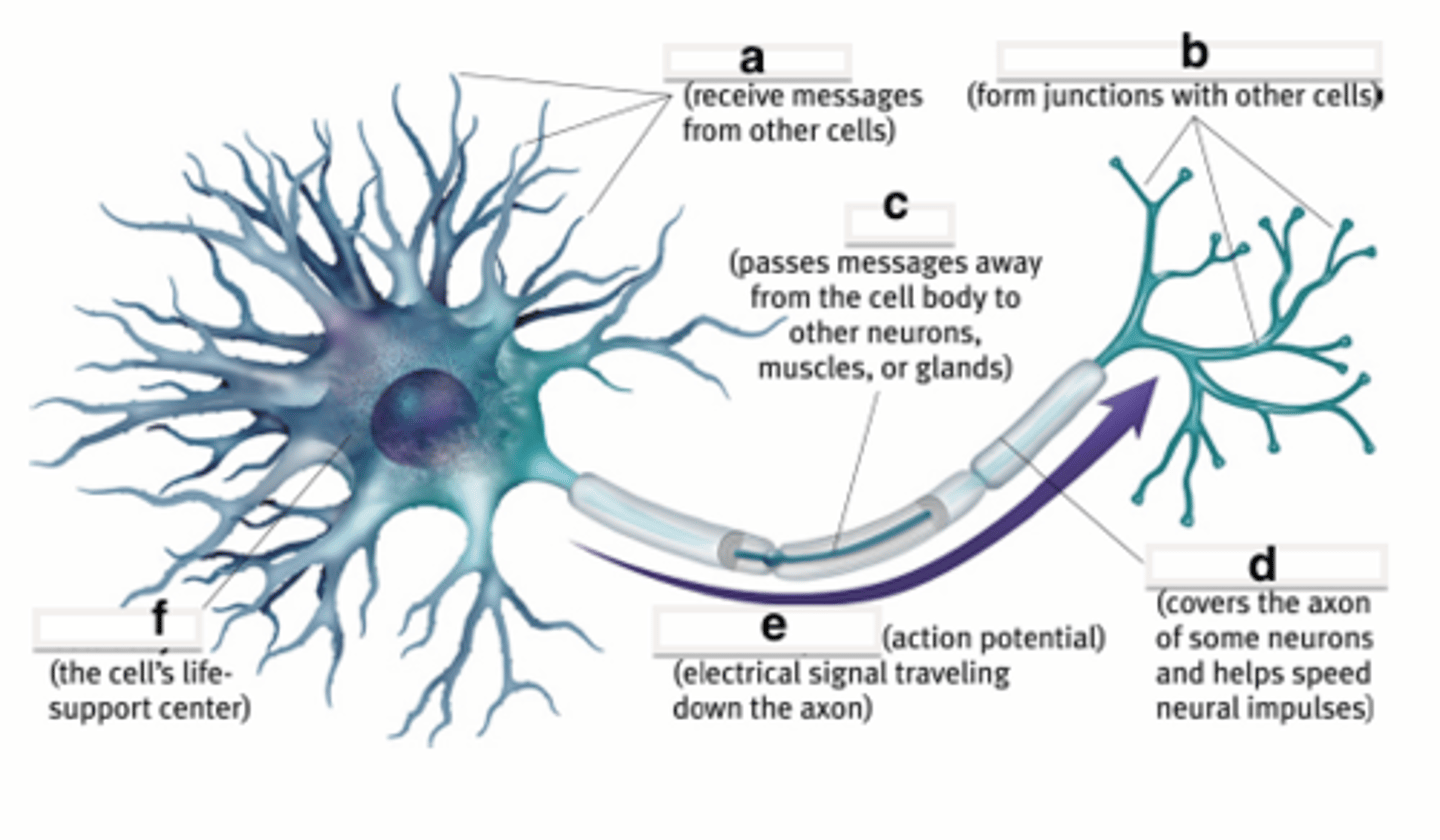
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
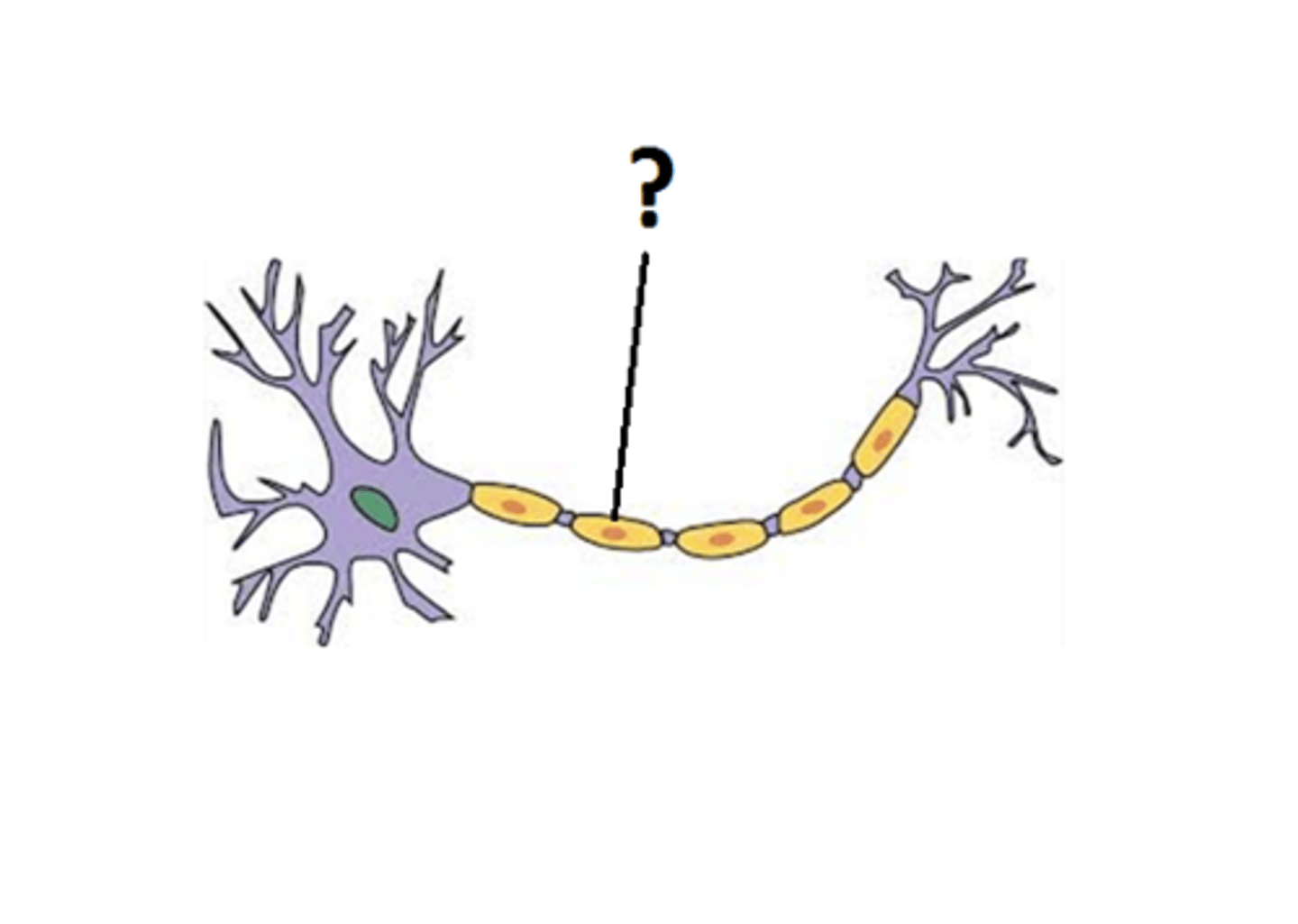
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
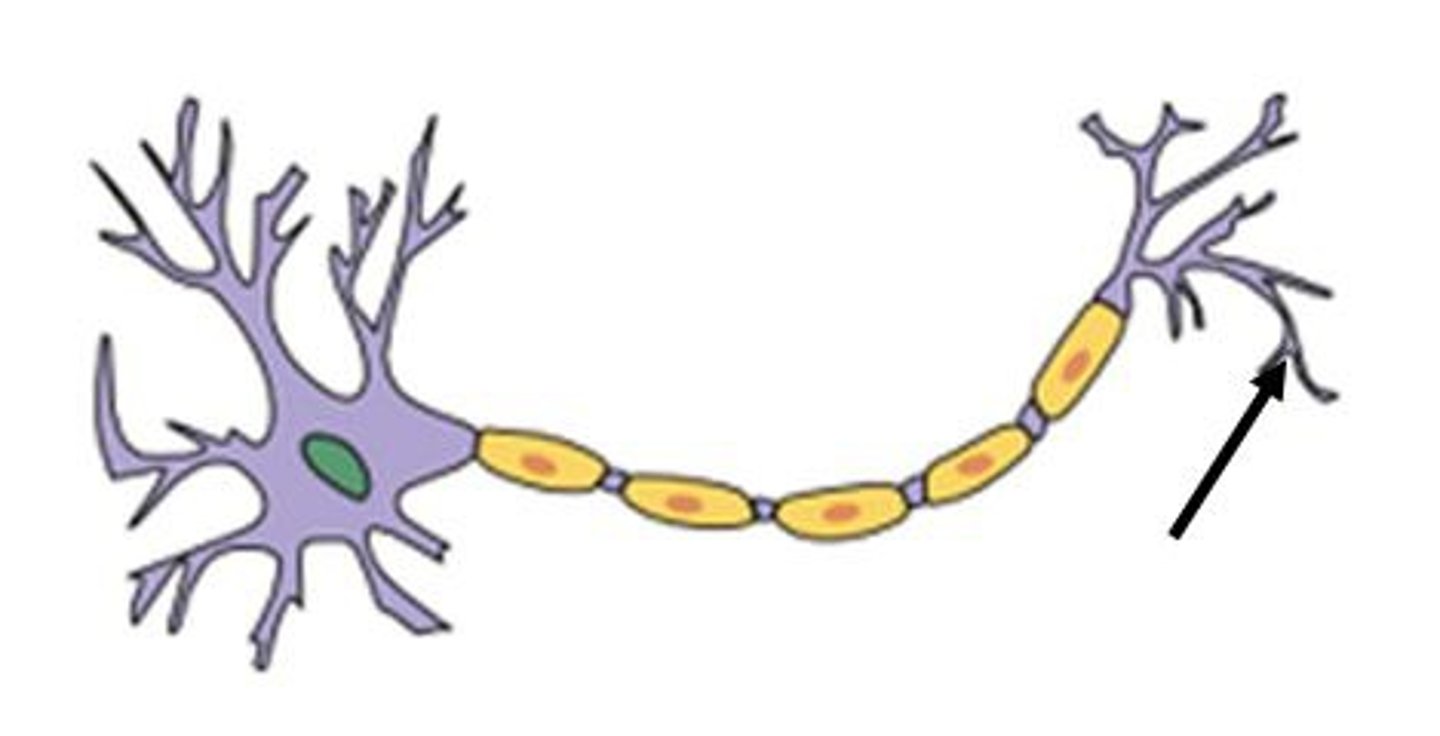
terminal branches of axon
Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons
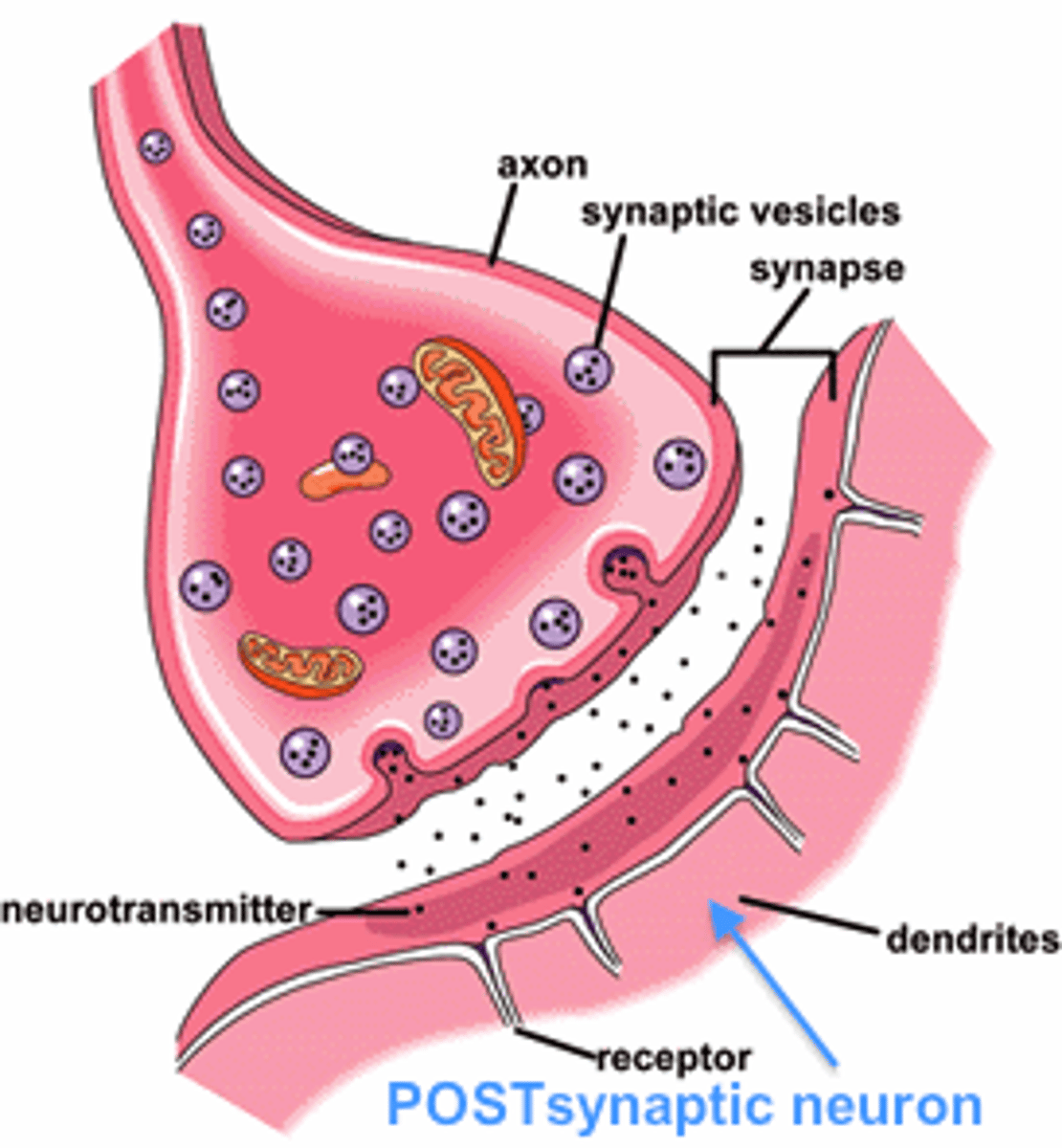
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
presynaptic neuron
neuron that sends the signal
leftover neurotransmitters are re-used in this stage
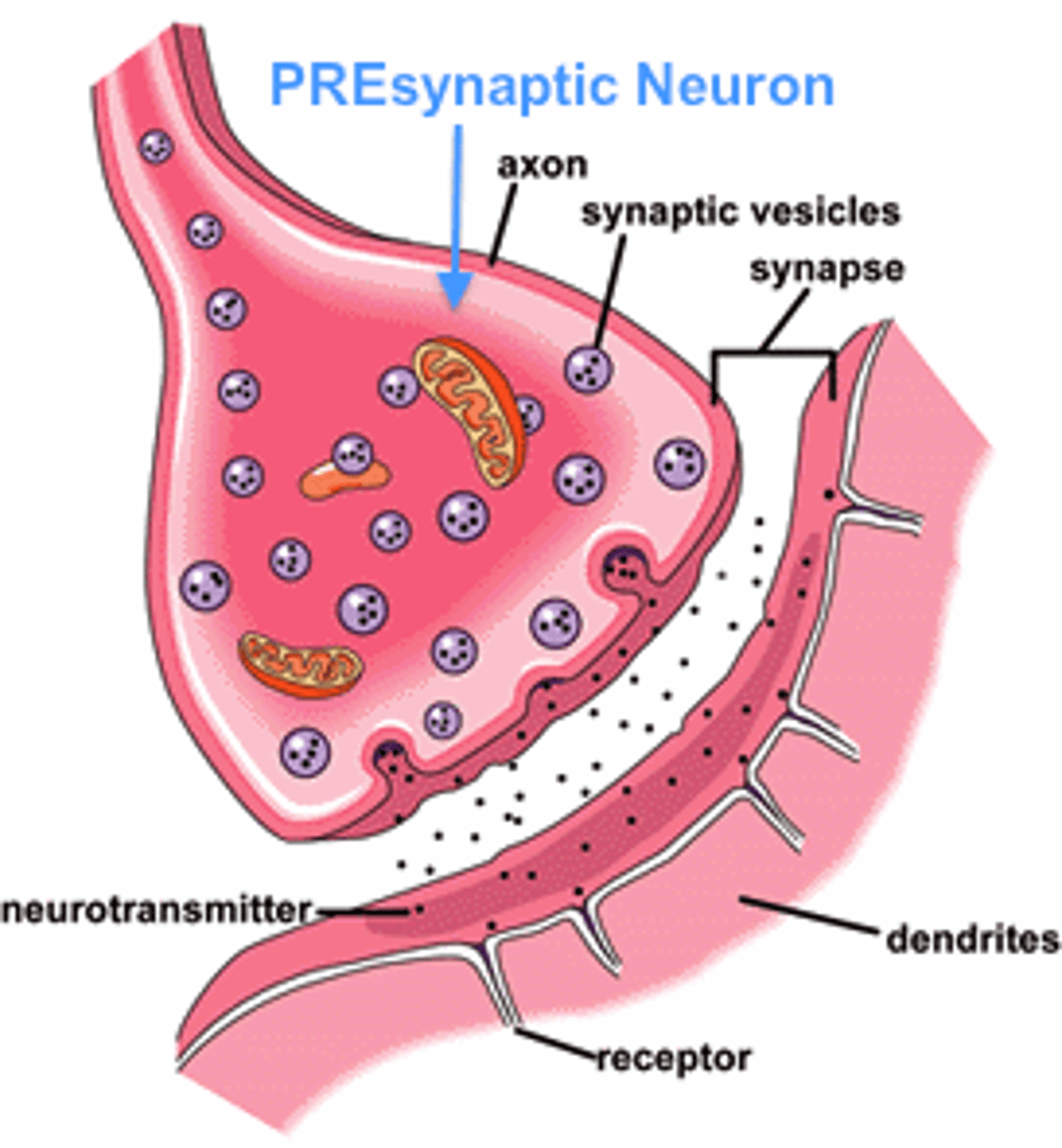
postsynaptic neuron
the neuron on the receiving end of the synapse
all-or-none response
a neuron's reaction of either firing (with a full-strength response) or not firing.
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter (like a brake in a car)
Glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory. Like gas in a car
Endorphins
"morphine within"--natural, opiatelike neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
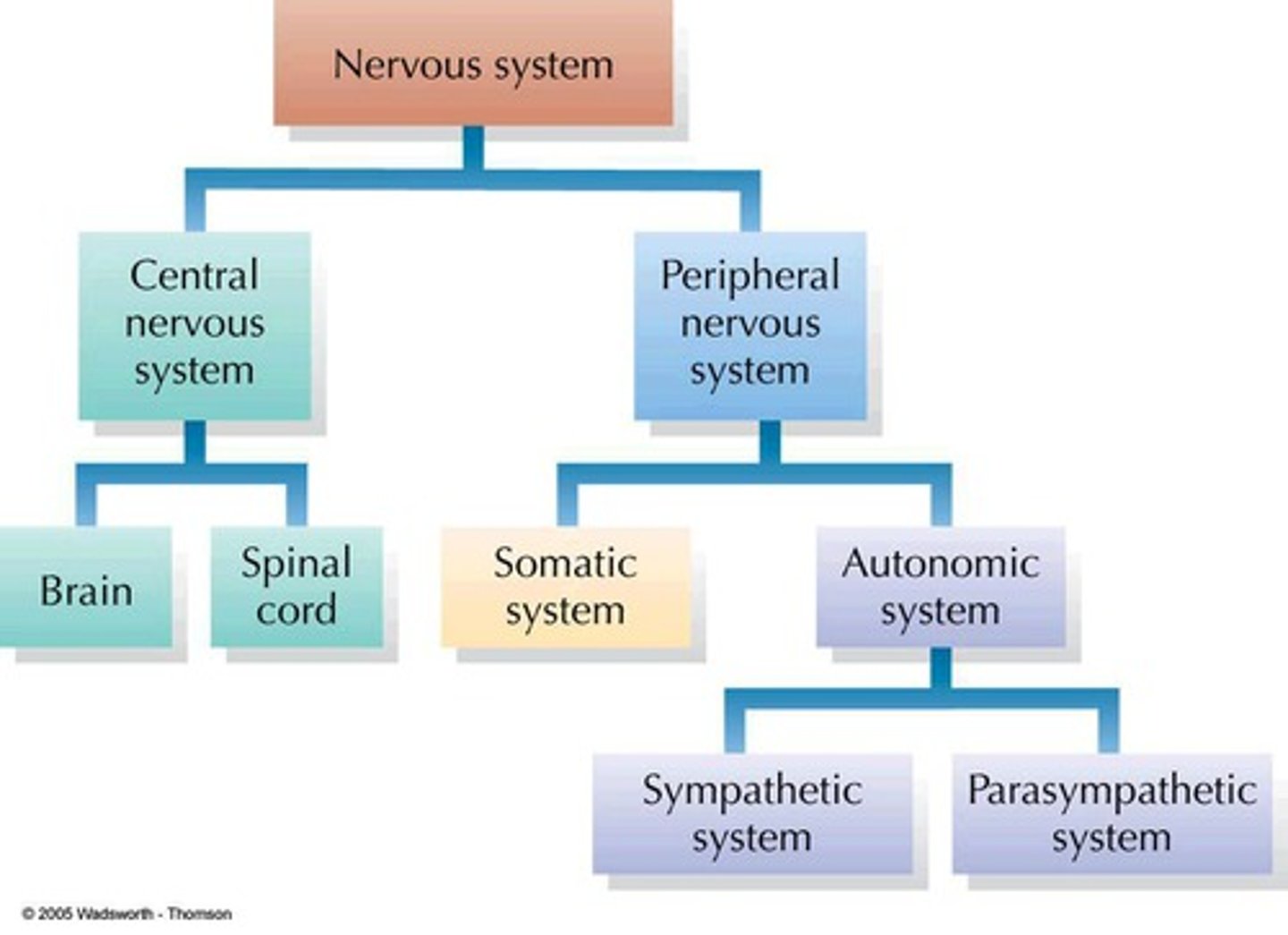
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
sensory (afferent) neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
somatic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Enables voluntary actions to be undertaken due to its control of skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
sensory input
Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes (hot stove)
motor output
controls skeletal muscles
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
brain to pituitary to other glands to hormones to body and brain
the nervous system directs endocrine secretions, which then affect the nervous system.
Medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing
Pons
movement and sleep control
reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal
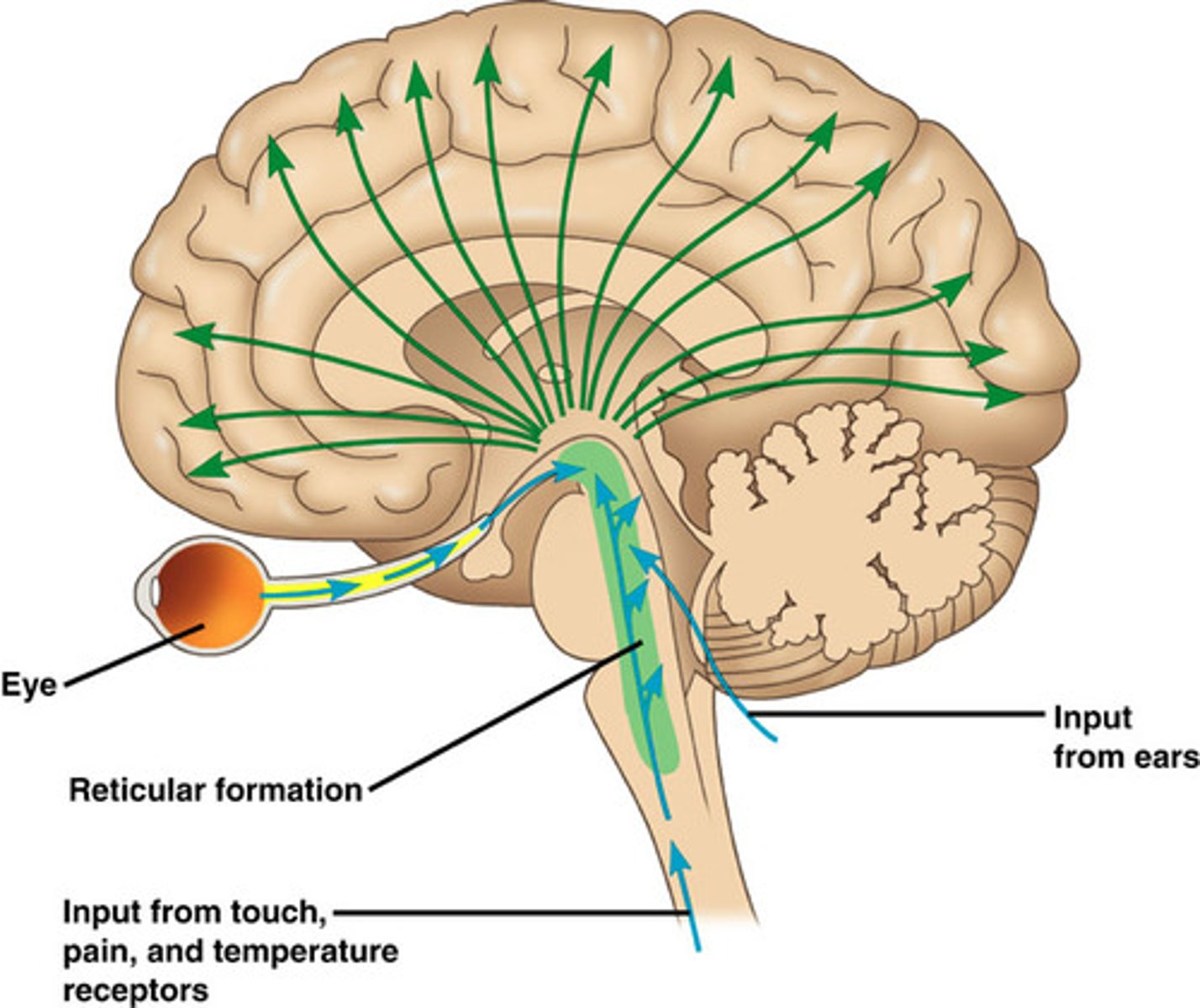
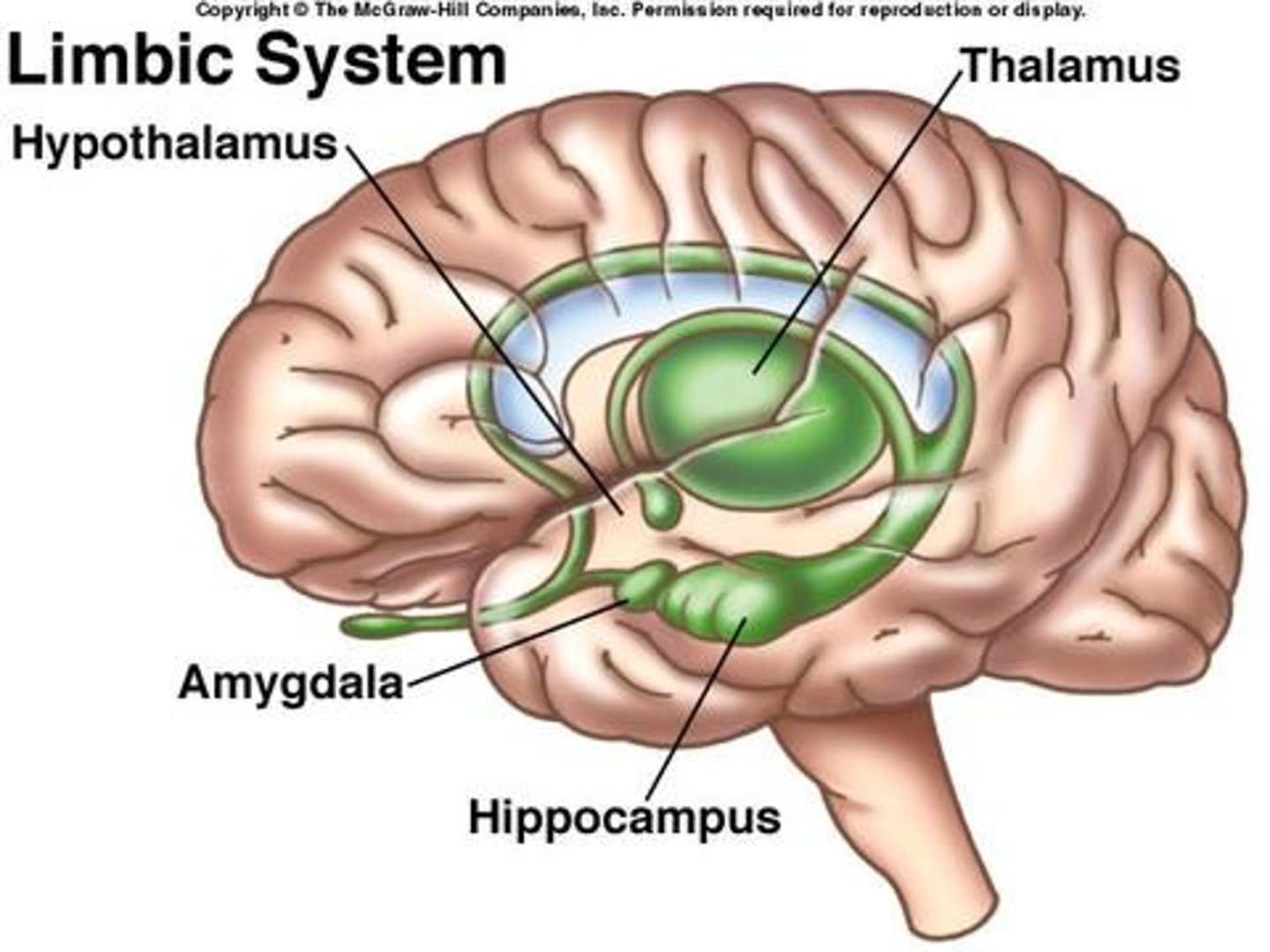
Thalamus
all senses except smell
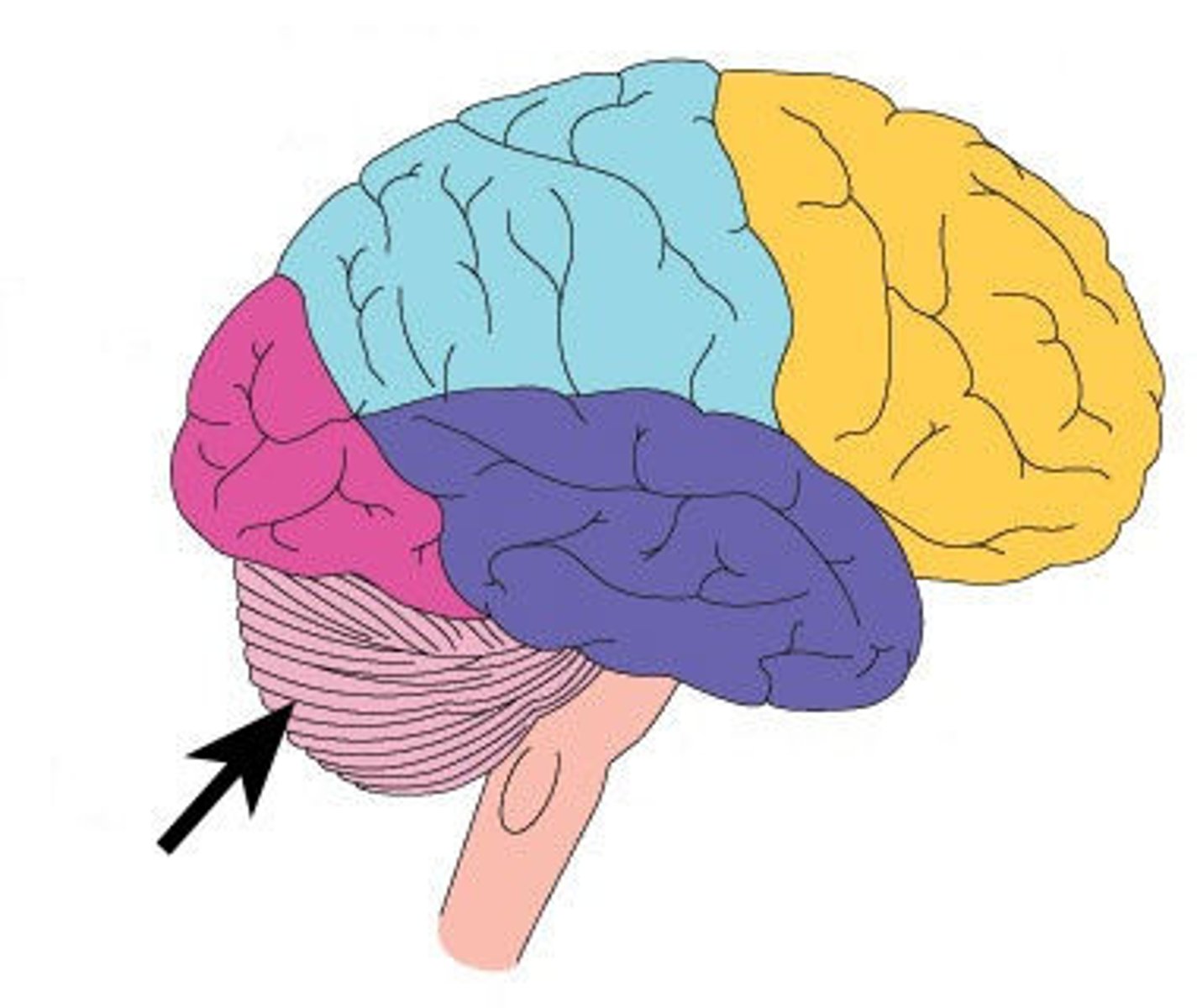
Cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance, enables nonverbal learning and skill memory judge time, modulate emotions, discriminate sounds/textures, and coordinates voluntary movement with the pons
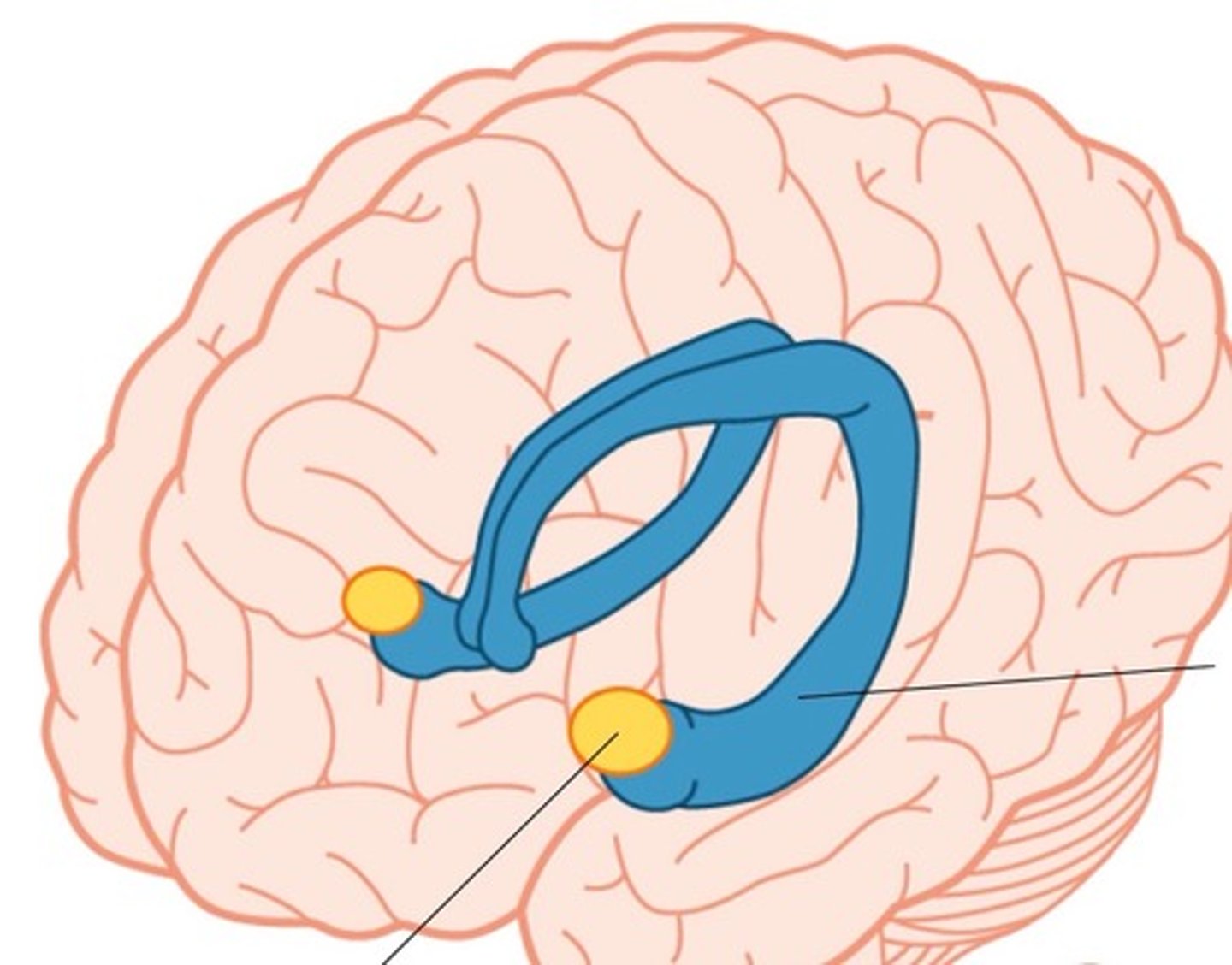
Amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
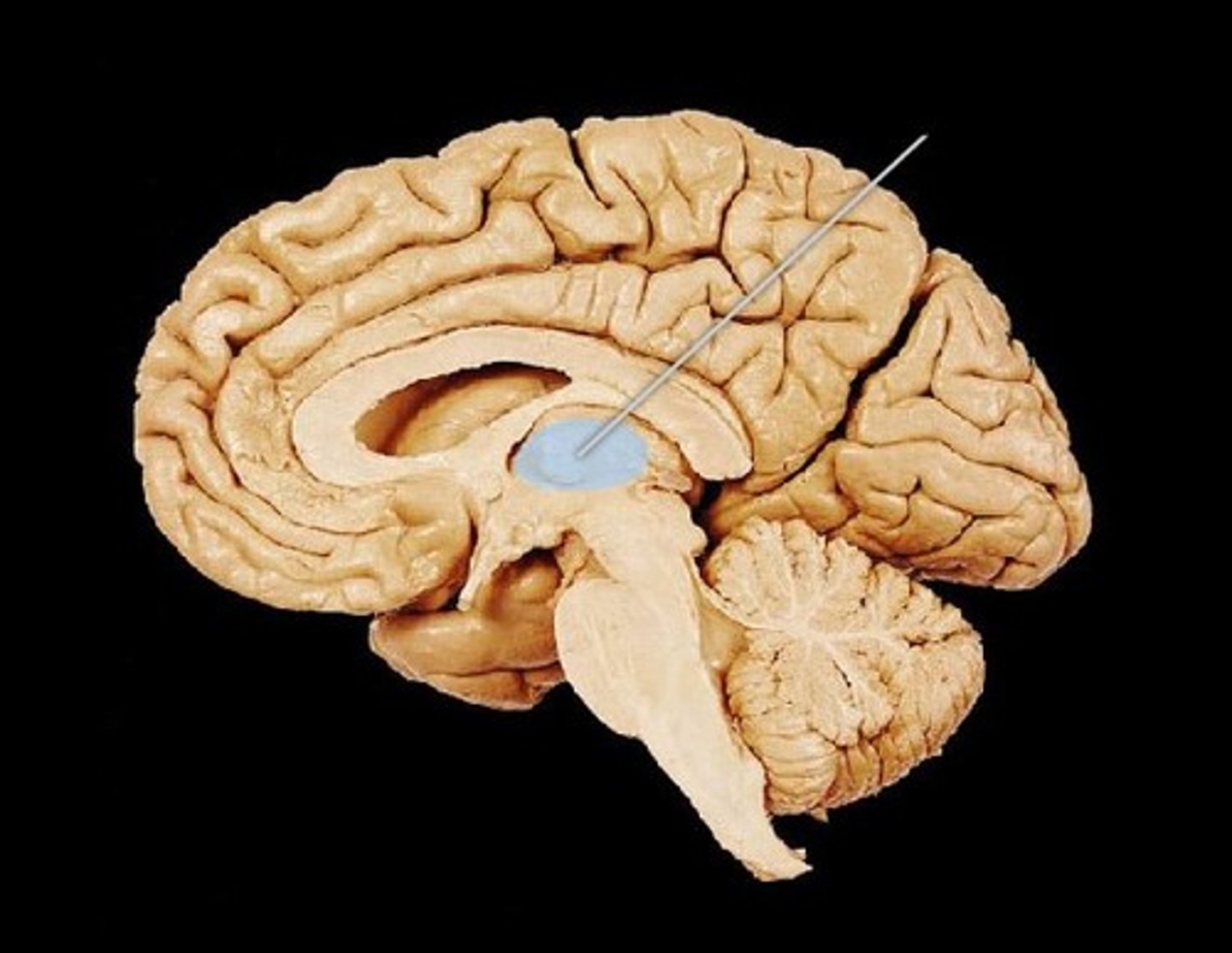
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
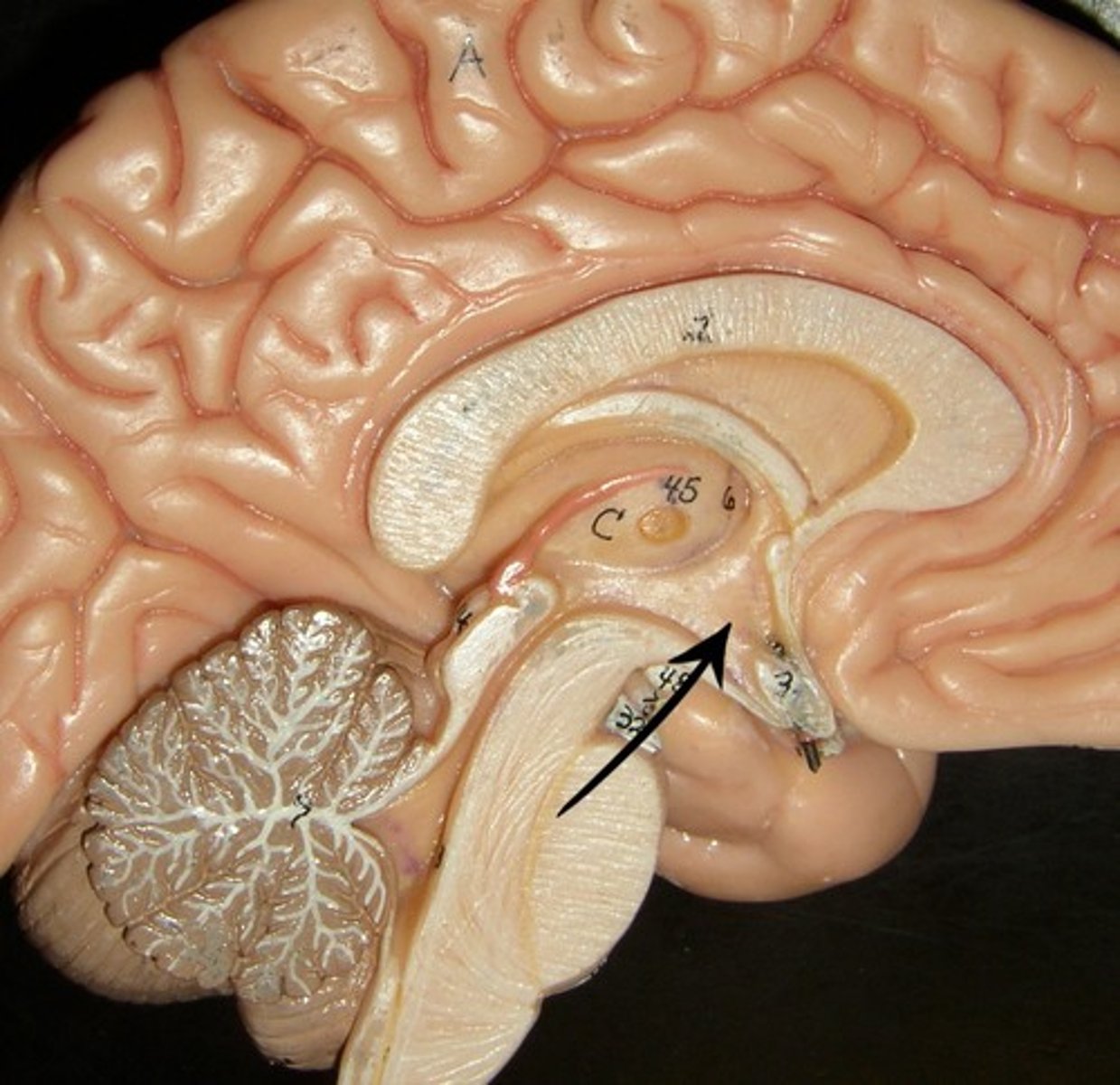
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
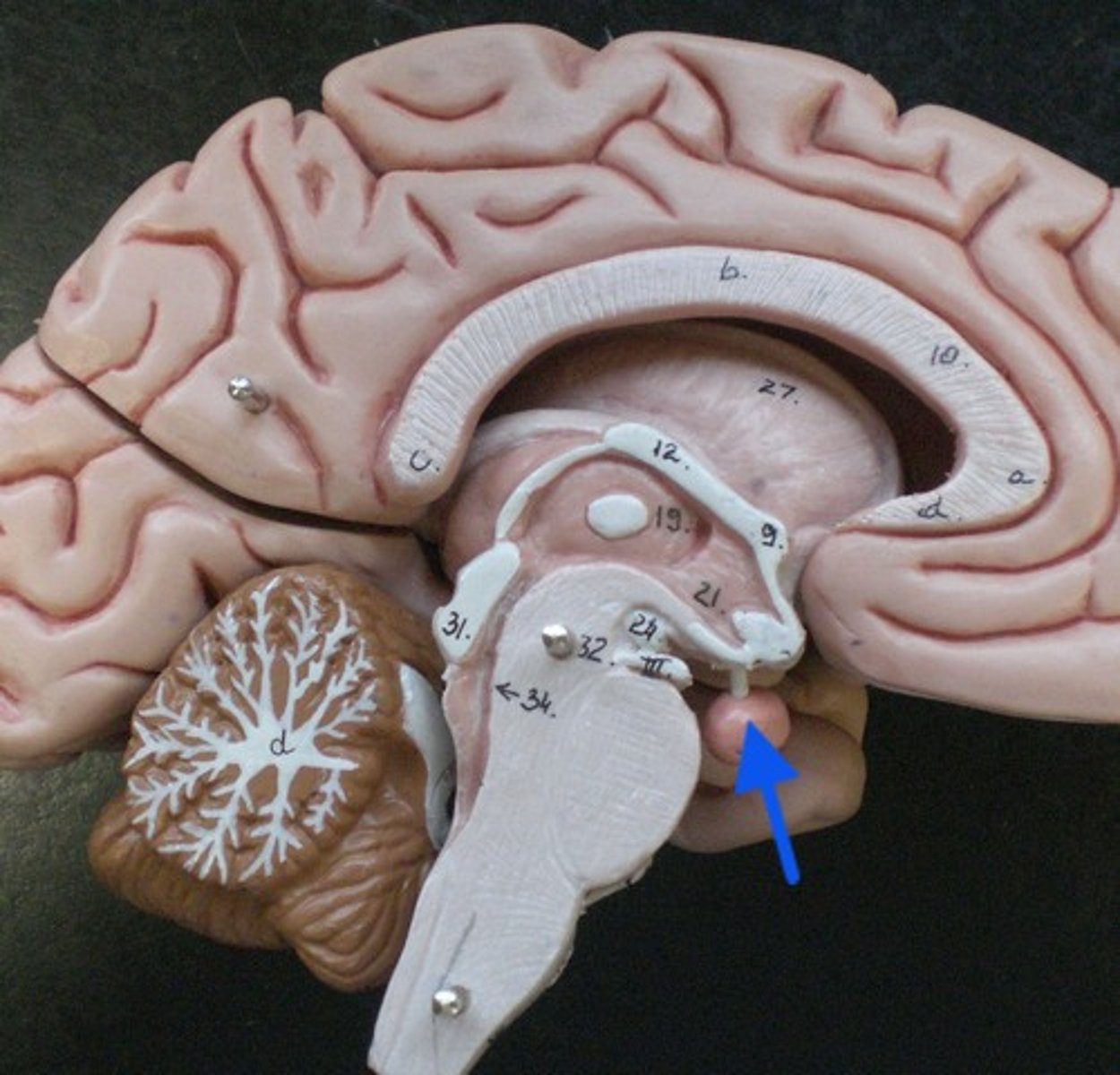
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
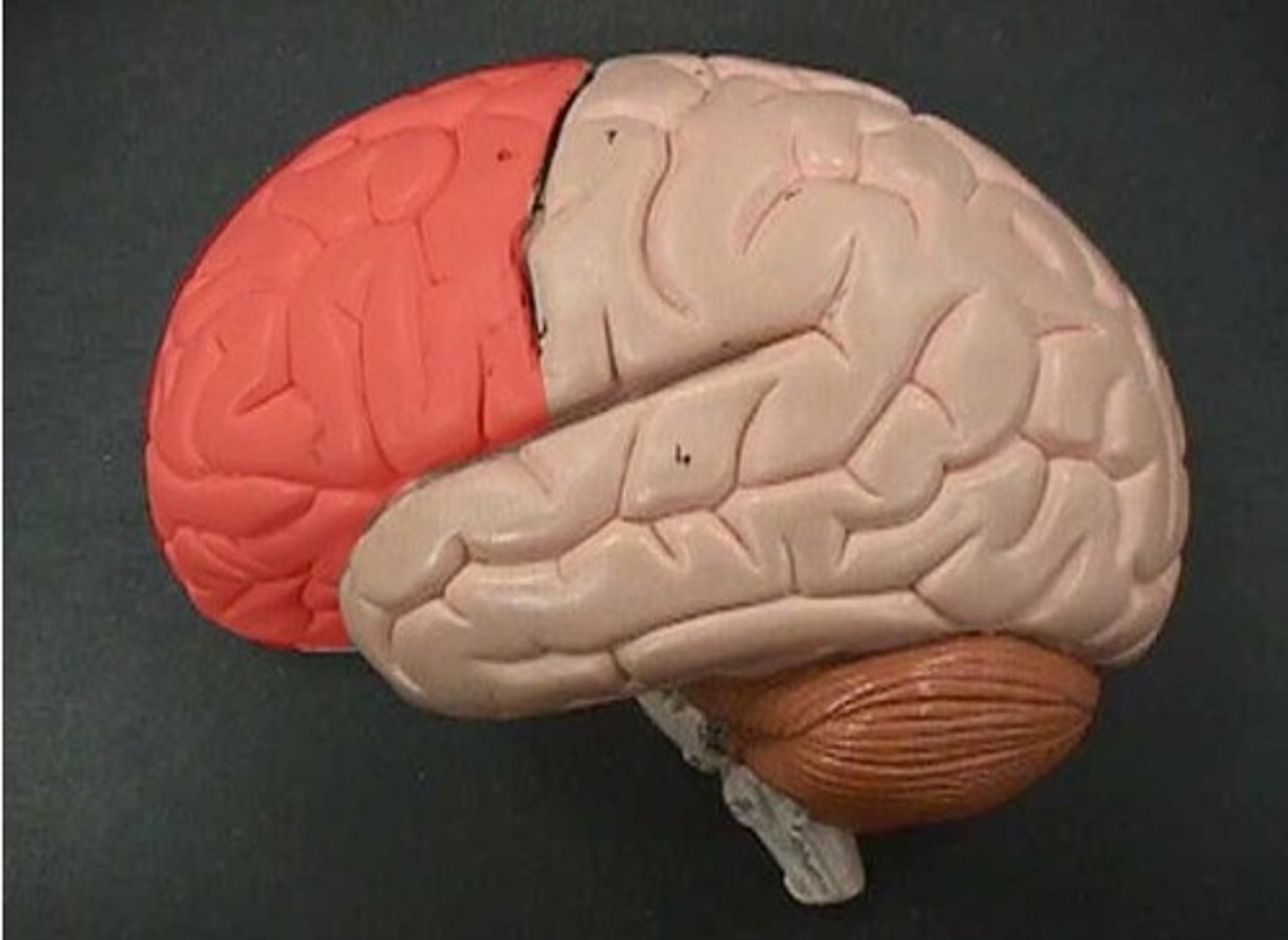
frontal lobe
speaking and muscle movements and in making plans/judgments
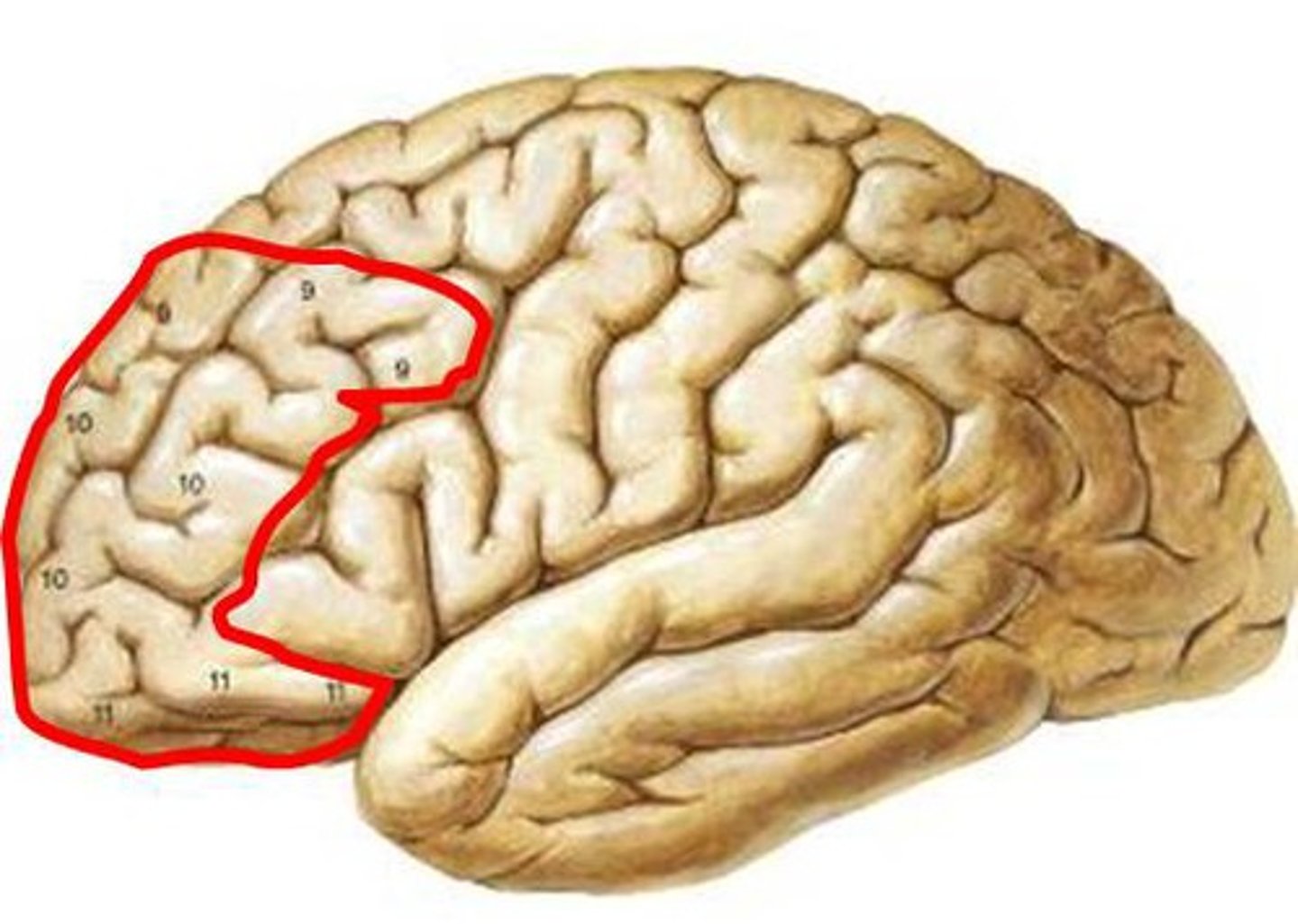
prefrontal cortex
planning complex cognitive behavior, personality expression, decision making, moderating social behavior
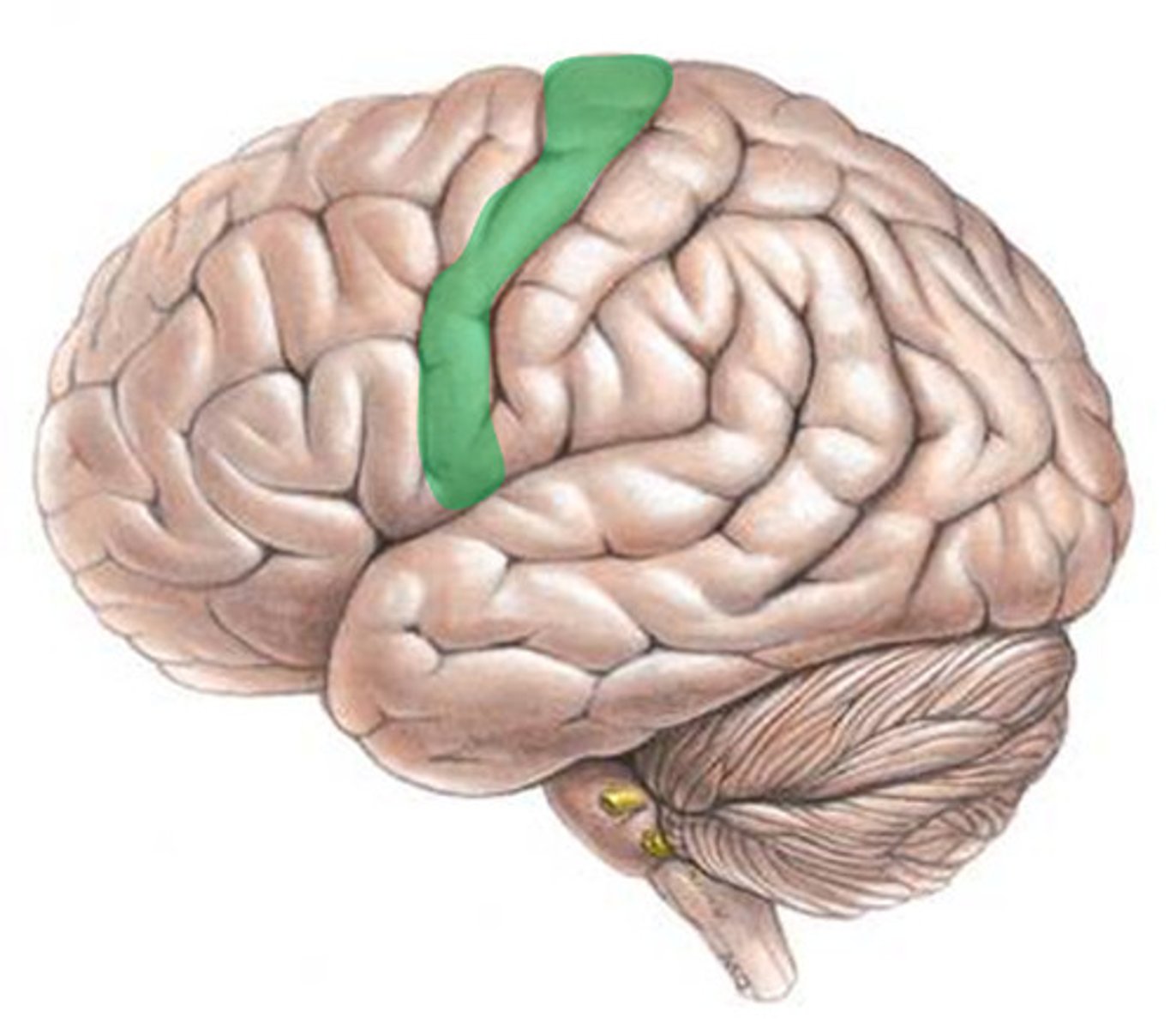
motor cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
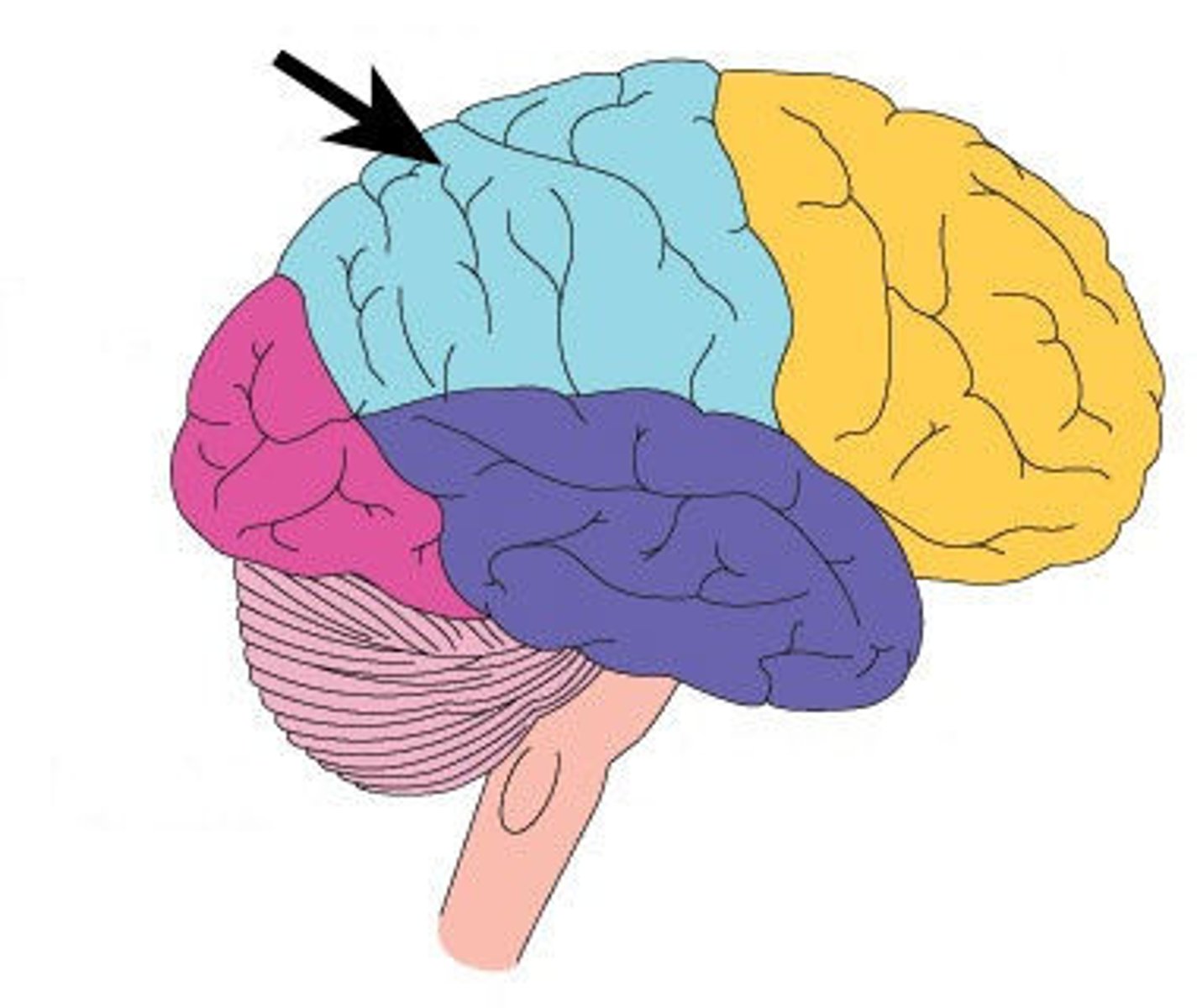
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
somatosensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
touch, temperature, body in space, pain
Occipital lobe
visual processing, where the visual cortex is
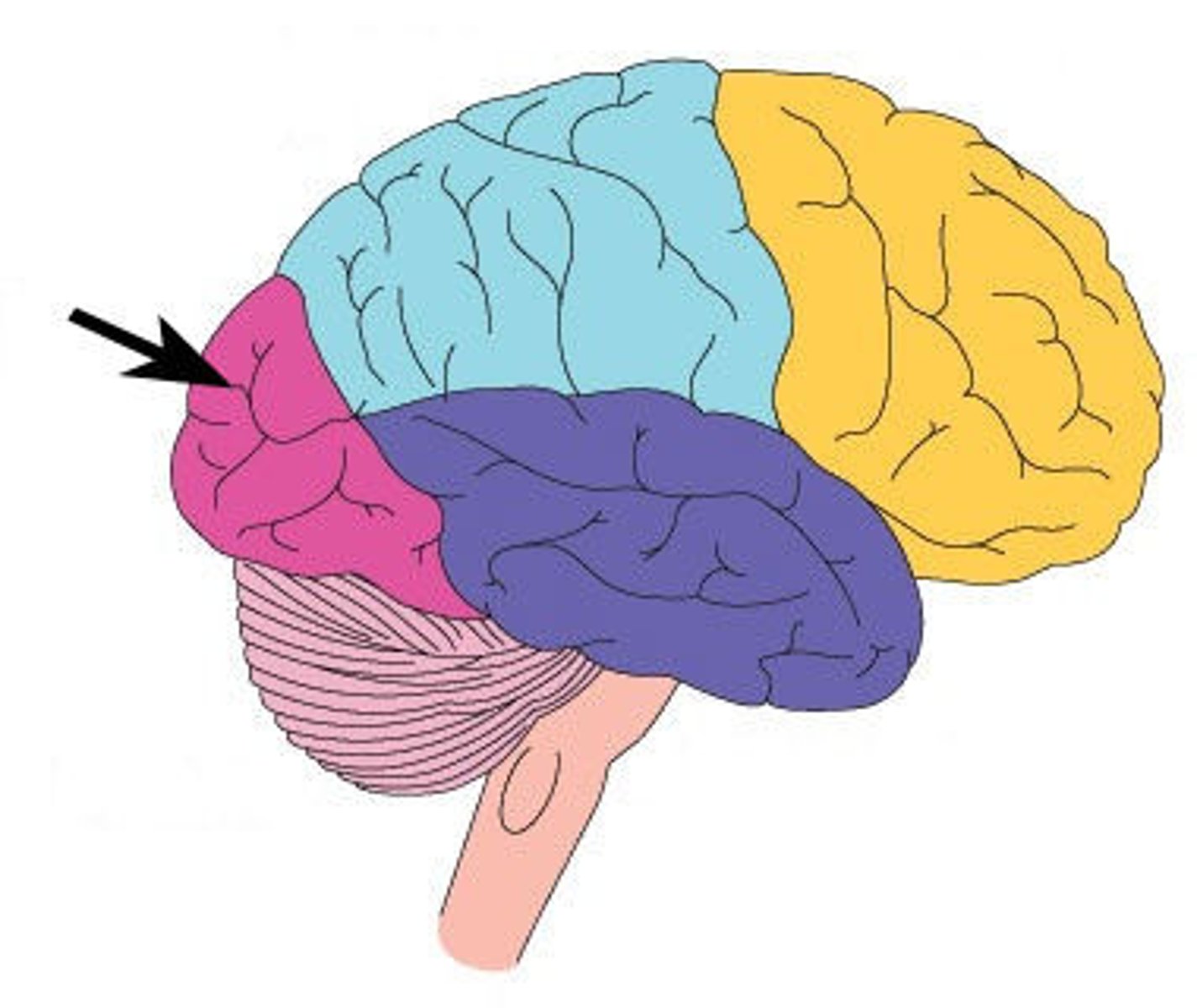
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language. -- where the auditory cortex is
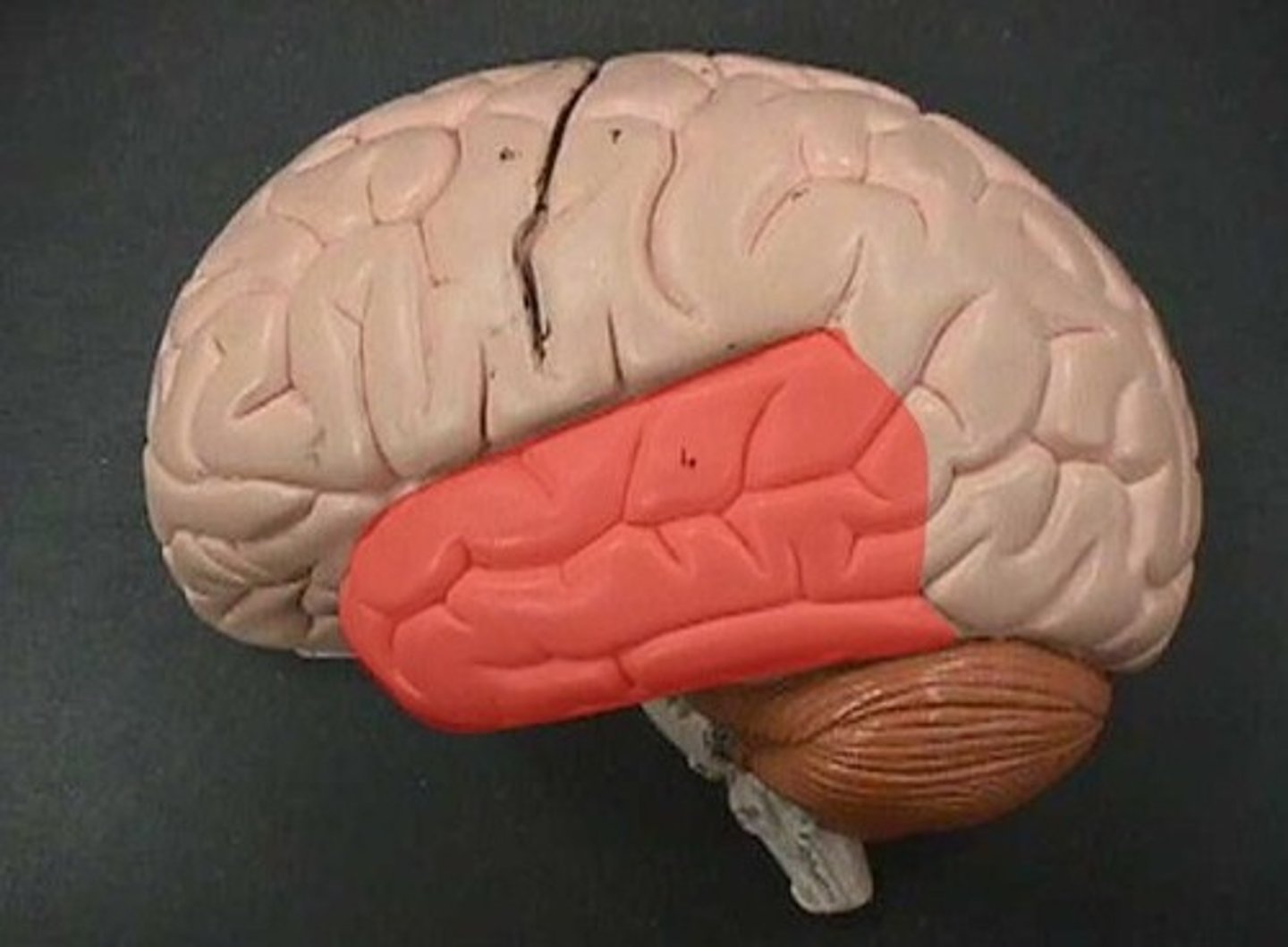
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
consciousness
our subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment
How consciousness is studied
cognitive neuroscience -- the interdisciplinary state of the brain activity linked with mental processes (including perception, thinking, memory, and language)