Psychology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Psychology
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes.

Five main goals of psychology
To describe, predict, explain, control, change, and influence behavior and mental processes.

Psychiatrists
Are medical doctors and have medical degrees, followed by several years of specialized training in the treatment of mental disorders. They can also hospitalize people, order biomedical therapies, and prescribe medications.

Psychologists
Are not medical doctors and cannot order medical treatments.

Clinical Psychology
Focuses on the causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of psychological disorders.

School Psychology
Applies psychological principles and findings in primary and secondary schools.

Health Psychology
Research psychological factors in the development, prevention, and treatment of illness; stress, and coping; promoting health-enhancing behaviors.

Biological Psychology
Explores relationships between psychological processes and the body’s physical system.

Neuroscience
Refers specifically to the study of the brain and the rest of the nervous system.

Positive Psychology
Focuses on the study of optimal human functioning and aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive.

Theory
Tentative explanation that tries to integrate and account for the relationships of various findings and observations.

Hypothesis
A tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables; a testable prediction or question.

Random selection
A process in which subjects are selected randomly from a larger group and it is important in the research participant selection process because it allows every group member to have an equal chance of being included in the study.

Meta-analysis
Pooling the effect sizes of several studies into a single analysis.
Case study
An intensive, in-depth investigation of an individual, a family, or some other social unit.

Population
The selected group of participants for the study.

Sample
A segment of the population is used to represent the group that is being studied.
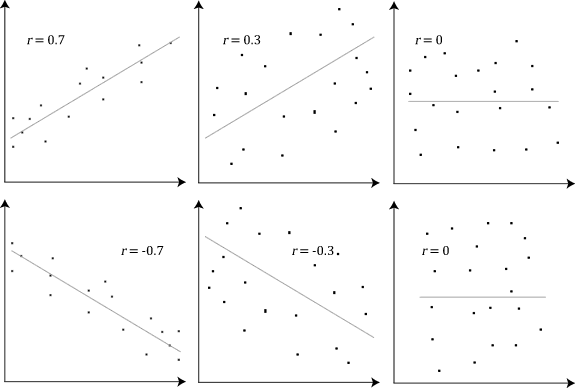
Correlational study
Examine how strongly two variables are related to, or associated with, each other. Can be used to analyze the data gathered by any type of descriptive method and is also used to analyze the results of experiments. Does not indicate causality.
Steps in the scientific method
Formulate a Testable Hypothesis
Design the Study and Collect the Data
Analyze the Data and Draw Conclusions
Report the Findings

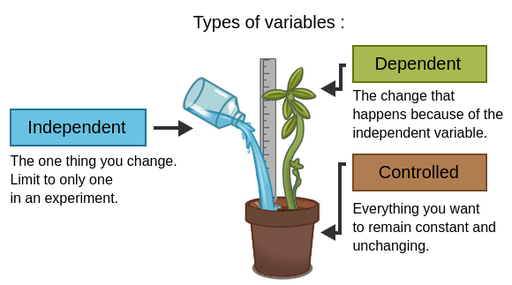
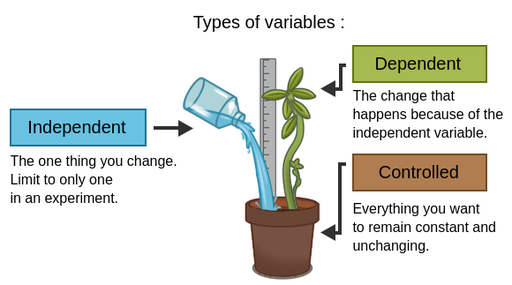
Independent variable
Factor that is purposely manipulated to produce a change in an experiment (predictor/treatment variable).
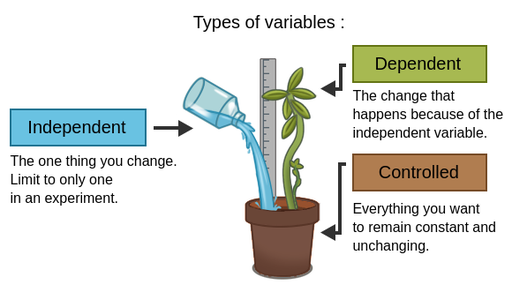
Dependent Variable
Factor that is observed and measured for change in an experiment; thought to be influenced by the independent variable (outcome variable).
Confounding Variable
External variables that are not the focus of the experiment, but could affect the outcome of an experiment (extraneous variable).
Double-blind technique/study
Both the participants and researchers interacting with them are blinded or unaware of the treatment or condition to which the participants have been assigned.

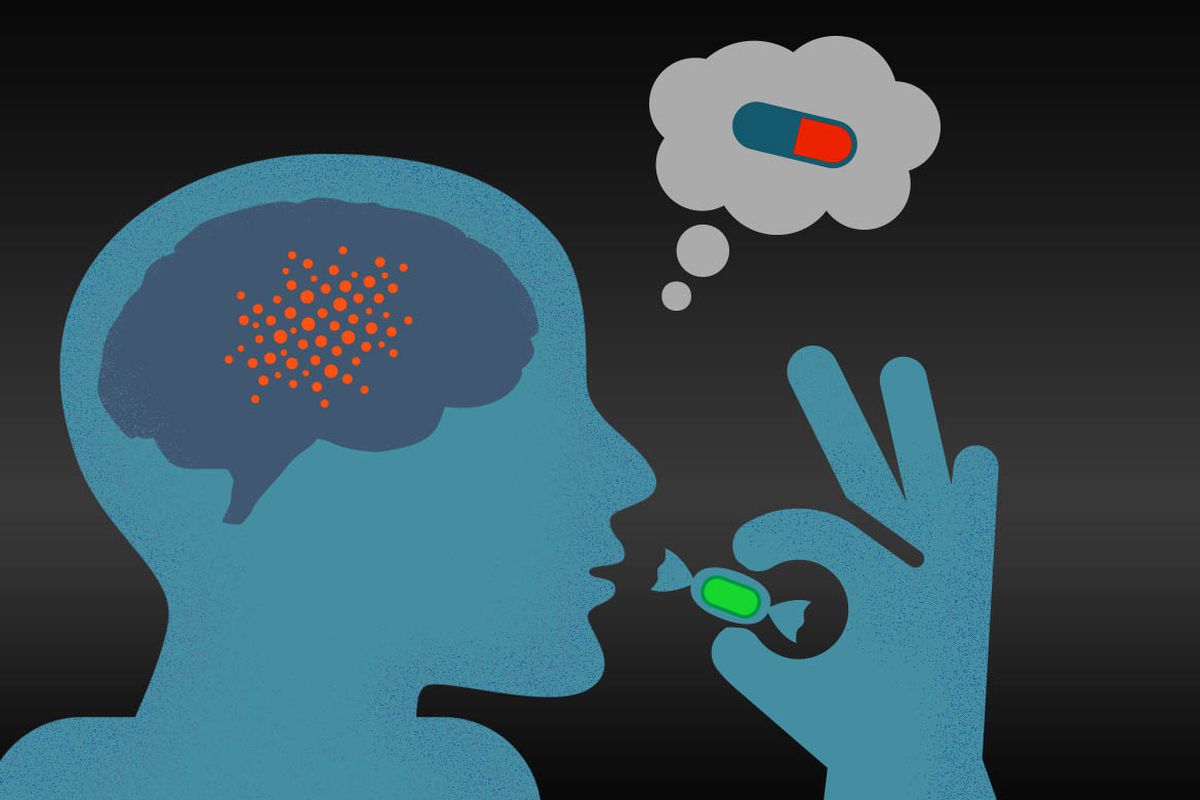
Placebo
A fake substance, treatment, or procedure that has no known direct effects.
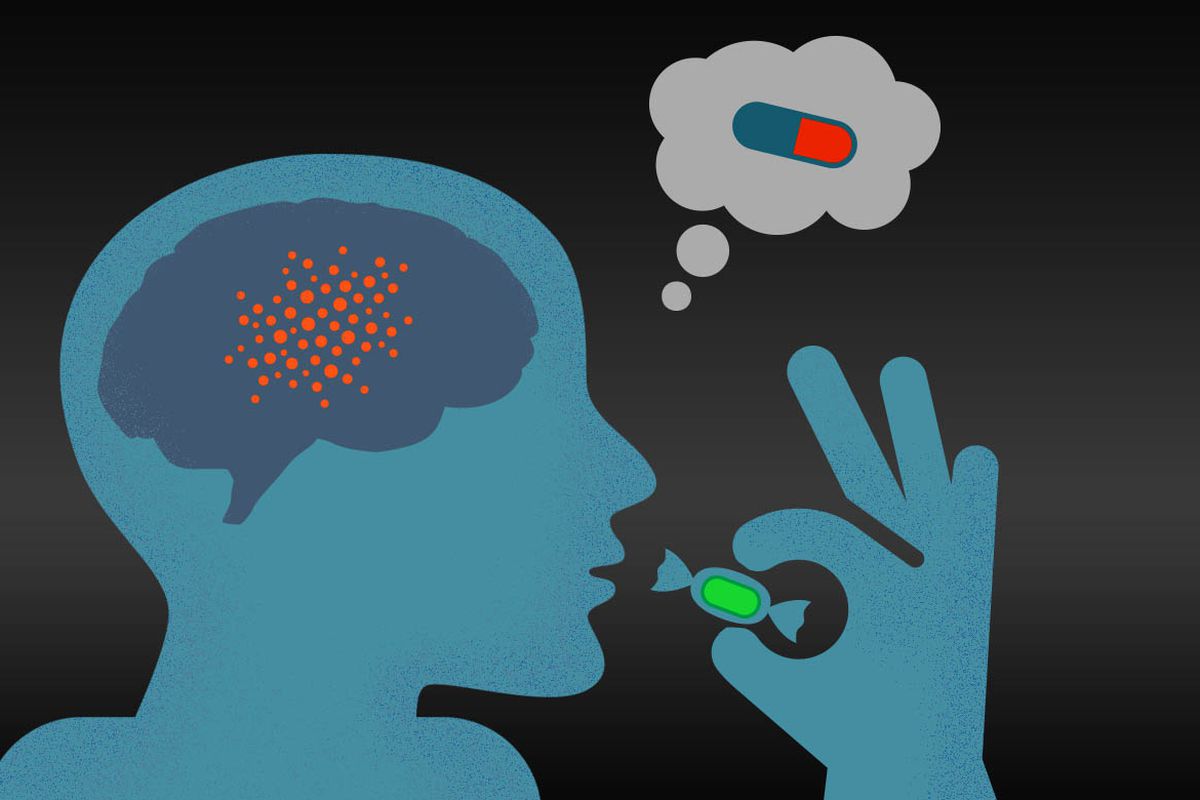
Placebo Effect
Any change attributed to the person’s beliefs and expectations rather than to an actual drug, treatment, or procedure (also called the expectancy effect).
The American Psychological Association (APA) provides ethical principles regarding research with human participants. These five key provisions include:
Informed consent and voluntary participation
Students as research participants
The use of deception
Confidentiality of information
Information about the study and debriefing
