Human Development #3
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What does the Organogenesis period mean?
a) forming organs during the first two months of prenatal (before birth) development.
b) the organs start to function by itself
c) the organs are not developing
a) forming organs during the first two months of prenatal (before birth) development.
e.g., stomach, intestines, lungs, heart, brain, spinal cord, genitals).
Hint: Genesis means the formation or creation of something
What is Thalidomide
A sedative for pregnant women, for morning sickness
True or false: It was created in July 1960, but a German company called Grunesatal
False, it was created by a company called Grünenthal
Who is praised as the hero for stopping this drug from continuing ?
Frances Oldham Kelsey. In her first month for the FDA, she refused to authorize the drug
Why: of the lack of evidence of the drugs safety
True or false: a medical specialist and expert wrote of the drug in a medical article and praised it.
False. It was actually written by the medical director of the company.
When was this drug created?
August 1960
What did this company do to the documents regarding the drug?
A) Falsification of the medical records
B) Omit information
C) asked experts to analyze the information
A) ) Falsification of the medical records
This drug was soon banned in 1962, but the effects were too late. What were the effects on children
smaller hands
smaller mouth
mental cognitive abnormalities.
This drug is still used in ________ to treat ________.
Brazil
Leprosy
True or false: Although the drug was banned four decades ago, the children in Brazil are still being born with abnormalities because of thalidomide
True
What does SIDS mean?
Sudden infant death syndrome
What is SIDS?
a condition that happens when infants stop breathing
usually during the night
and suddenly die without apparent cause.
True or false: smoker parents give their children a higher chance of getting SIDS
True
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA is what…
a) a complex molecule
b) shaped like a double circle
c) contains genetic information
d) shaped like a double helix
e) A, C, D
The answer is e) A, C, D
True or False: chromosomes come in 25 pairs
False, chromosomes come in 23 pairs.
Chromosomes are a ____________ type of structures
Threadlike type of structures
Where does each pair of the genetic information come from?
A) nowhere
B) unknown
c) cannot be known until after birth
d) from your parents
D) from your parents
_______________ are units of hereditary information
Genes
True or false, genes are composed of DNA
True
Genes act as a blueprints for cells to __________________ themselves and _______________ the proteins that maintain _________.
Reproduce
Manufacture
Life
The earliest period that gender can be predicted is the…
a) fetal period
b) embryonic
c) Germanic
a) fetal period
The genetic building blocks are… (hint: 3)
• DNA
• Genes
• Chromosomes
True or false: A Genotype is the way an individual's genotype is expressed in observed and measurable characteristics (eye color, height)
False, that is a phenotype. A Genotype consists of the actual genetic material, and their genetic information
Mitosis: is the process which each _____________ in the cell's nucleus ____________ itself.
Chromosome
Duplicates
What do the cells do in meiosis?
They divide into gametes (reproductive cells)
These cells are testes/sperm in males, ovaries/ eggs in females
These cells have _________ of the ________________ of the parent cell
Half
Genetic material
According to the Polygenic inheritance, ______ can ___________ to produce a particular characteristic
Genes
Interact
True or false: there are more than 50, 000 genes
True
The Apgar Scale and The Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale are measures of what….
Neonatal (newborn) Health and Responsiveness
The Apgar Scale is method widely used to assess the ____________ of newborns.
Health
At what minuets do they check?
1 minutes
5 minutes
The Apgar scale measures these 5 things:
Heart rate
Muscle tone
Body color
What two are missing?
Reflex irritability
Respiratory effort
The Obstetrician or nurse assesses the newborn and gives a scale, (0,1,2 on each item). What is the score you want for you baby?
7-10
Between these two, which one is the worst scale ranking for your baby?
A) 5
B) 3
B) 3, as it signifies an emergency. 5 means you have to watch for developmental difficulties
Amniotic fluid _________ and _________ the fetus inside the ammonic sac during pregnancy
surrounds
protects
What is the amniotic fluid produced by?
The mothers placenta
Name the four things ammonic fluid does
Cushioning the fetus
regulating temperature
preventing infections
allow the fetus to move and develop properly
What is contained in the ammonitic fluid?
a) the baby's urine
b) nutrients
c) hormones
d) antibodies
e) none of the above
f) all of the above
f) everything except e
A sperm fertilizes eggs (removed from a woman’s ovary) in a test tube or outside the body
These embryos are grown for several days in a laboratory, then are put into the uterus to implant
What is this process called?
InVitro (in glass, medical procedures) Fertilization
When does the postpartum period happen?
After Childbirth or delivery
What does the women’s body do during postpartum, and how long does it last?
It adjusts physically, psychologically to the process of childbearing
Last around 6 weeks
The adjustment and adaptation include these 5 things, which two are missing from the following lists:
Caring for baby
Father learning to care for baby
Father caring for mother
Recovering from childbirth
Learning to be good as a mother
Name the four Emotional and Psychological Adjustments
Hormonal change
Fatigue
Inexperience/lack of confidence with the baby
The extensive time and demands of caregiving
Hint: (H.I.F.T)
What is more severe between these two?
Baby Blues
Postpartum depression
Postpartum depression
What’s the difference between postpartum depression and psychosis
Postpartum depression
common condition
feelings of sadness, anxiety, and mood swings.
Postpartum psychosis
a rare
severe condition
have hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Why is baby blues the least severe?
Non-severe hormonal changes
Feelings of anxiety, crying and restlessness
Temporary form of depression
Usually goes away within the first two weeks after birth.
True or false: Cephalocaudal pattern is when the growth starts at the center of the body and moves outwards
FALSE: that’s the Proximodistal pattern. The Cephalocaudal pattern growth starts from the top (head), gradually to the bottom.
Fine motor skills includes what…
a) small movements in the hands
b) big movements in hands
c) big movements in the hands
a) small movements in the hands (fingers and wrists too)
walking, jumping, running are example of fine or gross motor skills?
Gross motor skills
True or False: gross motor skills involve moving the whole body
True
Drawing, writing and buttoning are examples ____________________
fine motor skills
How do you know if a gene is dominant?
the dominant gene express its self more strongly, overriding the potential influence of the other, recessive gene.
For instance, one parent has blue eyes the other has green eyes. Their child comes out with blue eyes (the blue eye) is dominant, the green is recessive
auditory, speech and grammar is controlled by what brain hemisphere?
The left side
True or false: the right side of the brain is the logical and rational side, (speech, comprehension, arithmetic, and writing).
False, those examples are for the left side.
The right side is the creative hemisphere, (controls spatial ability, artistic, and musical skills)
With newborns, they show greater electricity in the _______________ hemisphere. Why?
Left
They are listening to their parents talk (speech) and that activates the left hemisphere
________________ the term chosen to describe the narrow path, or developmental course, that certain characteristics take.
Canalization
______________________________ help protect or buffer a person from environmental extremes.
Preservative forces
How many neurons do newborns baby have?
a) 100 million
b) 1 billion
c) 100 billon
d) 10 million
c) 100 billon
Tiny gaps between neurons where connections between axons and dendrites take places is what…?
Synapses
Starting shortly after birth, a baby’s brain produces __________________ more connections b/w neurons than it can possibly use
trillions
What is an axon?
An axon is a thin fiber that connects neurons (nerve cells) to that they can communicate
Describe myelination
Encasing axons with fat cells.
Myelination…
a) insulates the nerve cells
b) helps nerve impulses travel faster
c) both
d) none of the above
c) both
Myelination for ___________________ occurs rapidly after birth and is ompleted in the first 6 months
visual pathways
the first 6 months
This branch of psychology emphasizes the importance
of adaptation, reproduction, and “survival of the fittest”
in explaining behaviour
Evolutionary Psychology
What does Evolutionary Psychology focus on
it focuses on the conditions that allow individuals to survive or to fail
True or False: It believes natural selection favours behaviours that increase organisms’ reproductive success and their ability to pass their genes on the next generation.
True
Amniocentesis is a procedure performed when?
Prenatally
After birth
During birth
Prenatally, specifically between the 12th and 16 week (during the fetal period)
What is Amniocentesis?
a sample of amniotic fluid is taken by syringe and tested
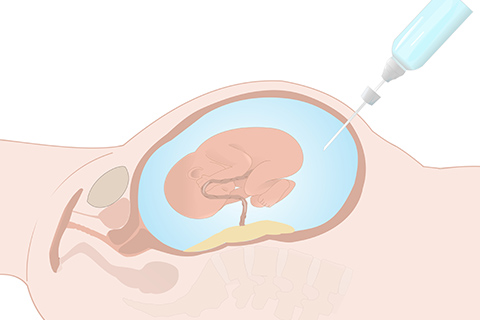
The purpose of Amniocentesis is to discover if the baby is suffering from what…
any chromosomal
or metabolic disorder
Infertility is the inability to conceive a child after ________ months of regular intercourse
a) 8 months
b) 6 months
c) 10 months
d) 12 months
d) 12 months
How many other infertile interventions are there besides in vitro fertilization?
a) 5
b) 6
c) 4
d) 3
c) 4. There are four other infertile interventions
True or False: Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) – eggs are fertilized in the laboratory then any resulting
zygotes are transferred to a fallopian tube. (Success rate approximately 25%)
No. That is the zygote intrafallopian transfer.
The GIFT is when a doctor inserts eggs and sperm directly into a woman’s fallopian tube. (Success rate almost 30%.
Hint: Gametes are reproductive cells. Intra means inside. The fallopian tube is where fertilization happens.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) – frozen _____________ is placed directly into the ___________. (Success rate
10%)
frozen
uterus.
Hint: Intra means inside.
Hint: Insemination = putting male sperm into woman or female animal through sexual activity or other methods)
What is the success rate for Intrauterine insemination?
a) 25%
b) 10%
c) 5%
d) 10%
d) 10%
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) – a single ______________ is injected by ____________ into an egg and the ___________ is returned to the uterus. (Success rate approximately 25%)
sperm
pipette (a slender tube)
zygote
Teratology is the field that investigates what?
a) birth defects
b) respiratory complications with the baby
c) any/all complications with the baby
a) birth defects
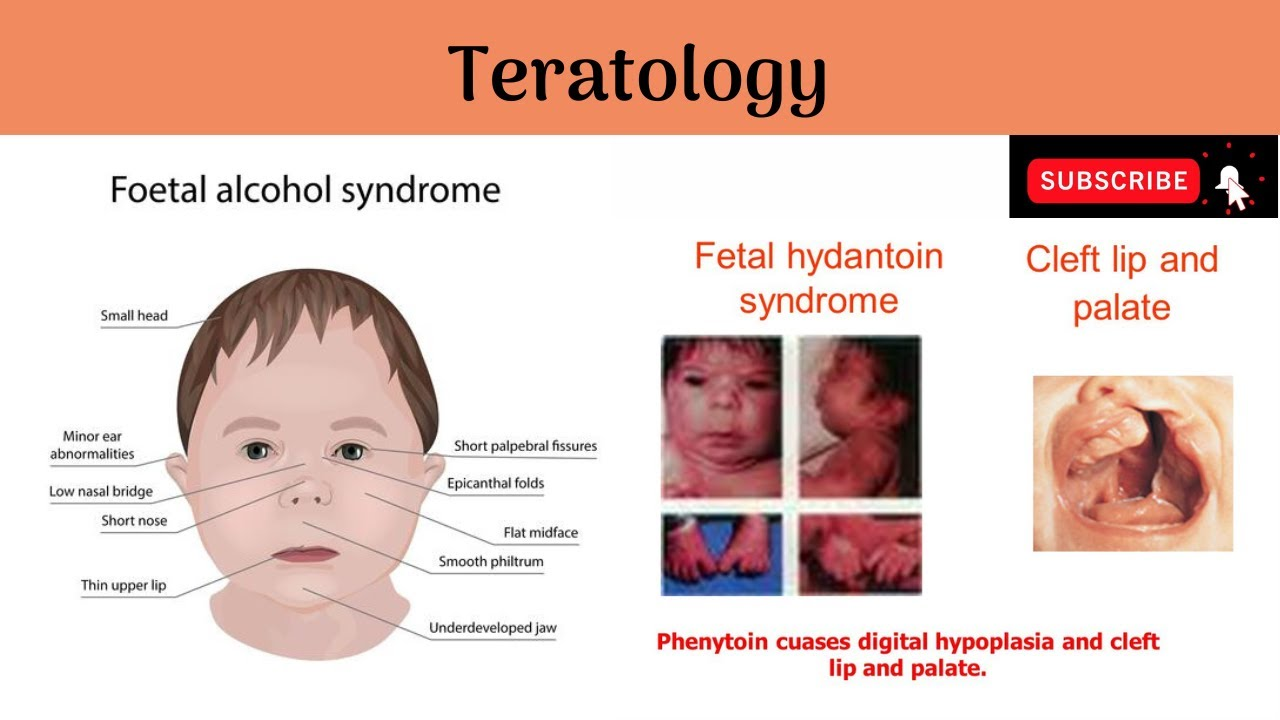
______________ any agent that causes a birth defecft
Teratogen
True or false: numerous teratogens exist, thus almost every fetus is exposed to at least some
True
Do all teratogens cause a birth defect?
a) Specific teratogens do not usually cause a specific birth
defect
b) yes all do
c) no
d) it’s unknown
a) Specific teratogens do not usually cause a specific birth
defect
How long will it take for the effects of tetragon to show up, and how much % will appear at birth?
may take a long time for the effects of a teratogen to show up.
Only about 50% of all potential effects appear at birth.
A Neuron is a ____________ cell that handles _________ processing at the cellular level
nerve
information
Charles Nelson used _______ electrodes attached to
babies’ scalps
a) 126
b) 127
c) 128
d) 129
c) 128
What did Nelson find?
a) the newborns brain waves are active when hearing their mothers voice
b) the newborns brain waves are active when hearing their fathers voice
c) the newborns brain waves are active when hearing someone’s voice
a) the newborns brain waves are active when hearing their mothers voice
they can distinguish their mother’s voices from another woman’s, even while they’re asleep.
What is another thing that Charles Nelson found in babies that are 8 months old?
Babies can distinguish a picture of a wooden toy they were allowed to feel, but not see, from pictures of other
toys.
How many kids on average a week die from SIDS?
a) 3
b) 4
c) 5
a) 3
To prevent SIDS… you
a) put the baby on its stomach when they’re sleeping
b) put the baby on its back when they’re sleeping
c) put the baby on its stomach when they’re sleeping
b) put the baby on its back when they’re sleeping
What is the Sucking Reflex, and when does it disappear?
when newborns automatically suck an object placed in their mouth.
• Helps newborns get nourishment before they have associated a nipple with food.
• Disappears after 3–4 months.
The Rooting reflexes is…
a) when the infant’s cheek is stroked or the side of the mouth is touched.
b) when the infant’s head is stroked or the side of the head is touched
c) when the infant’s arm is stroked or the side of the arm is touched
a) when the infant’s cheek is stroked or the side of the mouth is touched.
In response, the infant turns its head towards the
side that was touched, to find
something to suck.
How long does this take to disappear?
3-4 months
The Moro reflex is a neonatal __________ response that occurs in response to a _________, ________ noise or movement
startle
intense
sudden
True or False, the grasping reflex is when something touches the infant’s palms and the infant responds by grasping tightly.
True, the grasping reflex is when something touches the infant’s palms and the infant responds by grasping tightly.
The Fagan est measures the infants process certain information… what are they? (hint: there is 4)
Encoding the attributes of objects (color, size, shape, etc) to understand the object.
Knowing similarities and differences between objects
Creating mental representations
Retrieving those representations.
The Fagan test is for what age?
12 months of age
What do you do with the Fagan test?
a) pair two objects together
b) pair two pictures together
c) pairt two words together
b) pair two pictures together
What percent is Genetic influence on genetics and on environ?
a) 70/30
b) 70/40
c) 40/70
d) 30/70
a) 70/30
Reaction range is the range of possible _____________ for each ______________, suggesting the importance of an environment's restrictiveness or richness.
phenotype
genottype