chapter 8 periodicity
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
order of the periodic table
increasing atomic number
structure of the periodic table
alkali metals
alkaline earth metals
transition metals
below the staircase metals
in the staircase metalloids
above the staircase non metals
noble gases
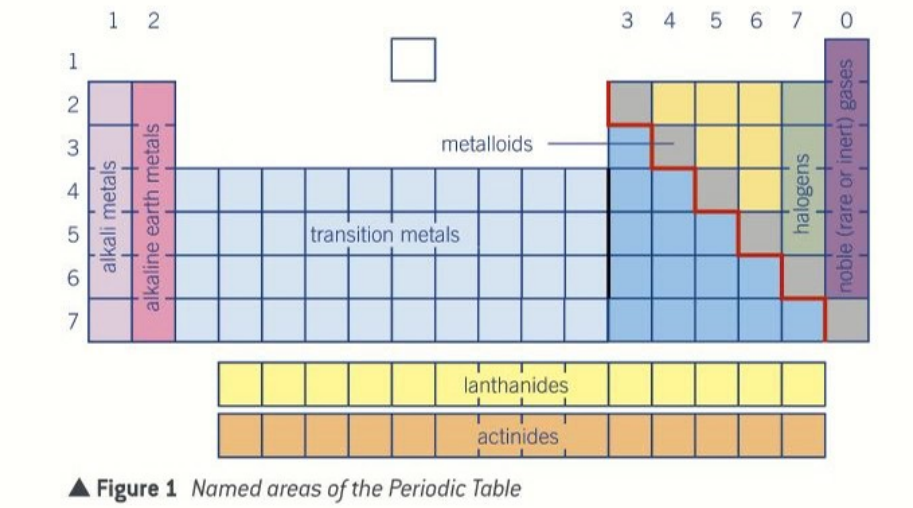
the staircase on the periodic table
left = non metals
right= metals
on the stairs metalloids
what are metalloids
elements that have a combination of metallic and non metallic properties
properties of metalloids
shiny
conducts electricity
e.g silicon
history of the periodic table
dimitri mendeleev left gaps in the periodic table for undiscovered elements. newly discovered element fit the gaps he left years ago and he accurately predicted their properties
blocks of the periodic table
s,d,p and f
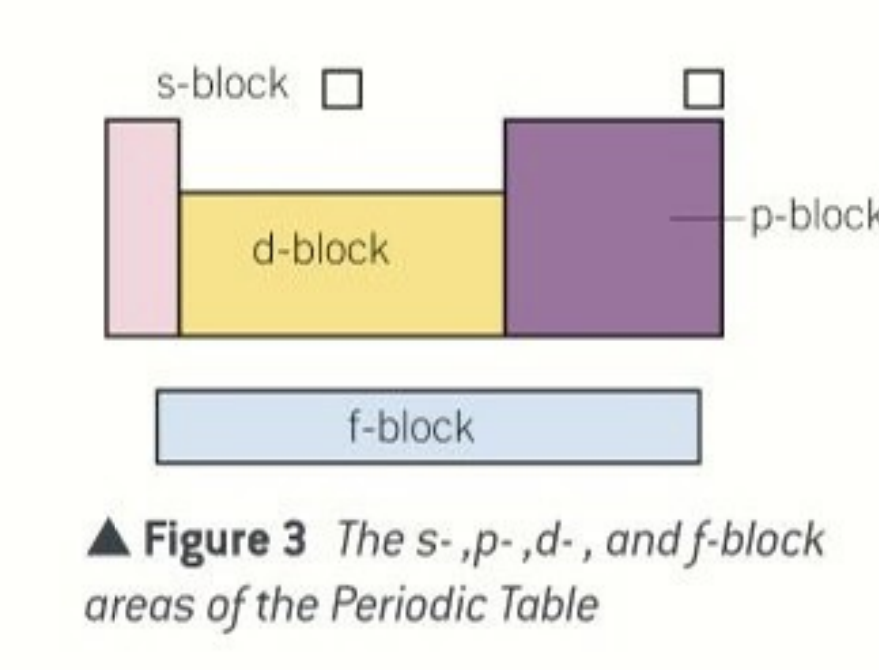
s orbital block
elements in the s orbital have their highest energy electrons in the s orbital e.g sodium
d block
elements in the d block have their highest energy electrons in the d orbital e.g iron
p orbital block
all elements in the p block have their highest energy electrons in the p orbital e.g carbon
characteristics of transtition metals
form compounds where they have partly filled orbitals
exceptions to the rule of transition eleements and why
scandium and zinc are not transition metals because they do not forma any compounds where their d orbitals are partly filled
origins or the terms s,d,p,f
when elements are heated they give out light energy at certain wavelengths. thi makes line appear in the spectrum of light.
s,d,p,f were words used to describe the lines
s= sharp
d=diffuse
p=principle
f= fine
groups
verticle column of elements
simalar properties
same number of electrons in outer main shells
reactivity
metals get more reactive going down
non metals get less reactive going down
d orbital block elements are unreactive
why helium and hydrogen are atypical
helium and hydrogen
helium;is not a p block element but is placed with noble gases
hydrogen; forms +1 ions like group 1 metals but does not react similarly because its not a metal so its placed on its own
periodicity
the repetition of properties of elements in each period
properties of elements in period 3 in group 1,2,3
Na, Mg, Al form ionic compounds and have gaint stuctures
properties of elements in period 3 group 4
silicon 4 electrons in the outer shell and forms bonds with 4 other silicon atoms. so it has a gaint covalent structure
silicon is a metalloid so it has both metallic and non metallic properties
properties of period 3 elemnts in group 5,6,7
P,S,Cl get reduced to form ionic compounds or share electrons to form covalent compounds
general trends across period 3
melting poin increases until group 5 where is dcreases
shielding stays the same
nuclear charge increases
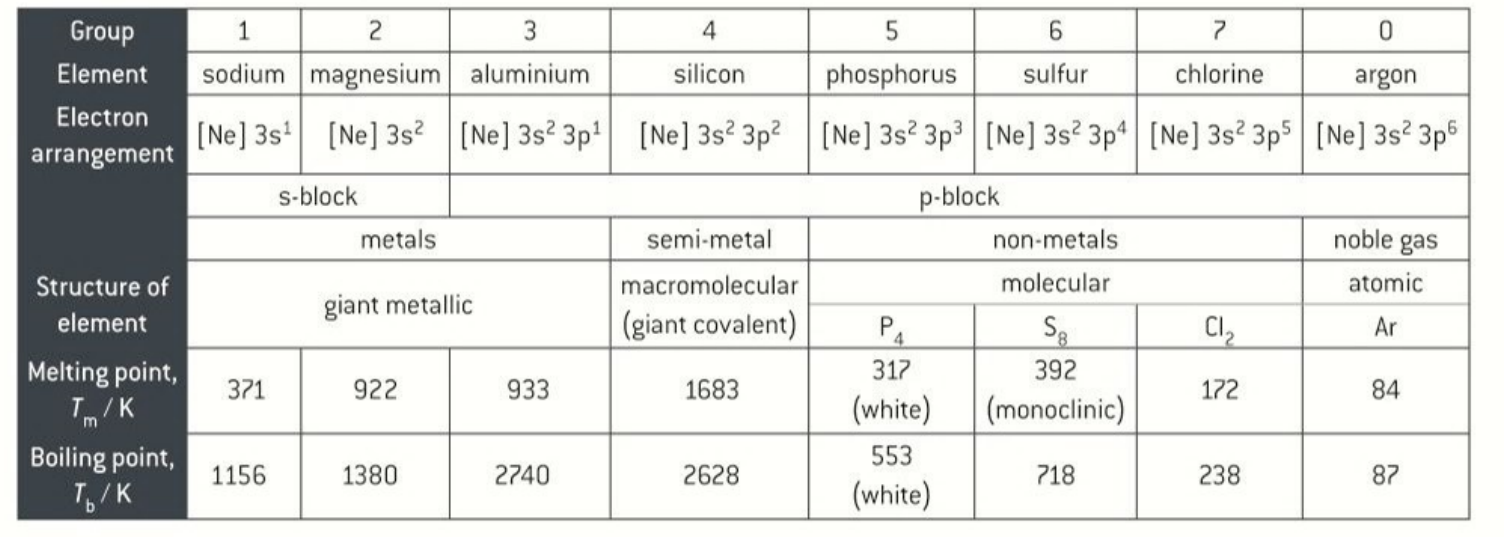
trends in melting and boiling points of period 3 group 1 to group 4 elements
increases because they have metallic structures
high melting and boiling points
except silicon which is a gaint covalent structure
trends in melting points period 3 group 5 to group7 elements
low melting points
simple/molecular structures
why does the melting point increase from sodium to aluminium
strength of metallic bond increases
charge on the ion increases
more delocalised electrons
why do the non metals in period 3 have low boiling points
molecular structure
smaller van der waals forces
more electrons so they cant pack as closely together
why is silicon the exception
gaint structure with a high melting point
so stronger van der waals forces
there are more electrons
and they can pack closely together because 1 Si atom bonds to 4 others
define atomic radii
half the distance between the centres of a pair of atoms used
why is the term atomic radius used
there is no clear point at which the electron cloud density drops to 0
how are the sizes of atoms measured
using their atomic radii
what does the atomic radius depend on?
the type of bond formed
e.g covalent, ionic, metallic, and the strength of van der waals
why are noble gases left out of comparisons of atomic sizes
noble gases do not bond covalently with one another because they have full outer main shells
general trend in atomic radius
periodic property
atoms get larger down any group
decreases across each period
there is a jump when starting the next period
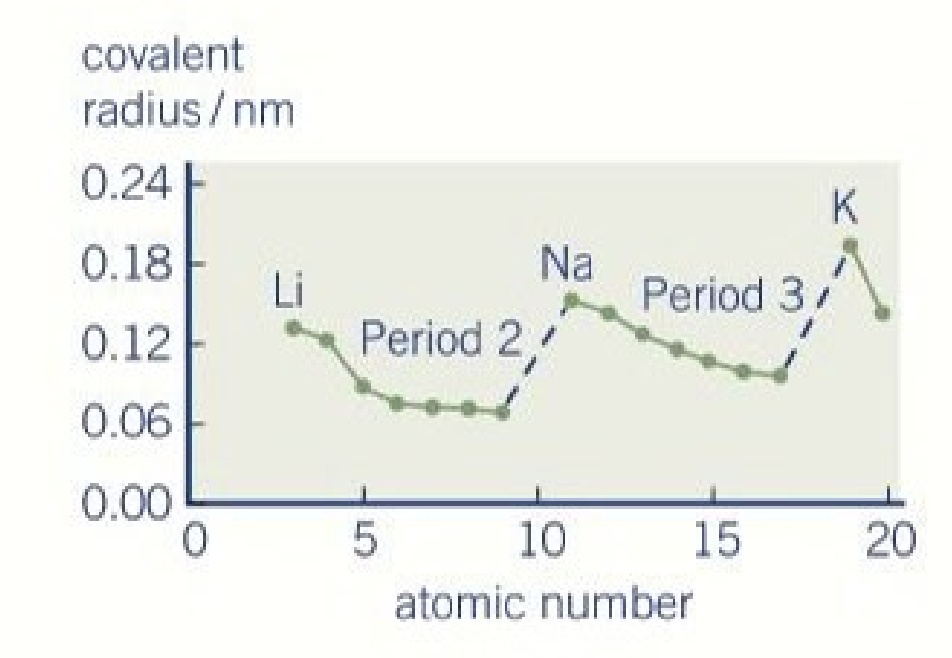
general trend in atomic radius across a period
the size atoms decreases across a period
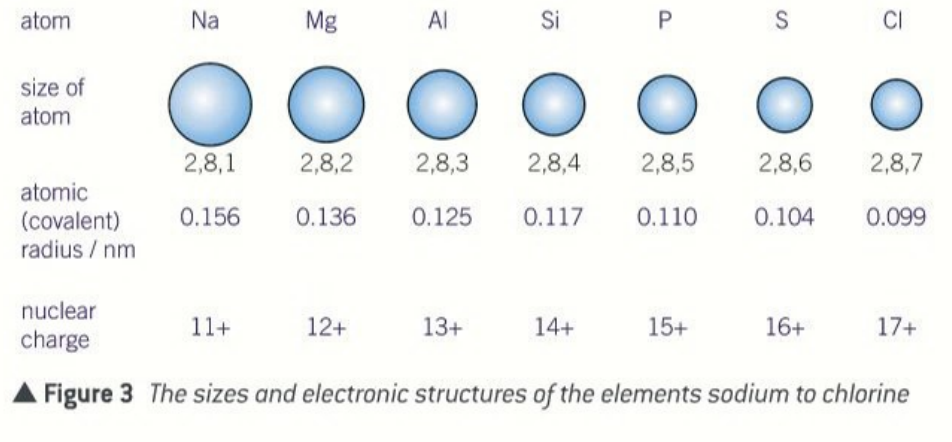
why does the atomic radius decrease across a period
there are more protons
increased nuclear charge
increased pull towards the nucleus
same shielding
why does the atomic radius increase down a group
more shielding
greater distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus
define first ionisation energy
energy required to convert 1 mol of gaseous atoms of an element into 1 mole of gaseous cations
general trend in first ionisation energy of the first 20 elements across a periods
increases
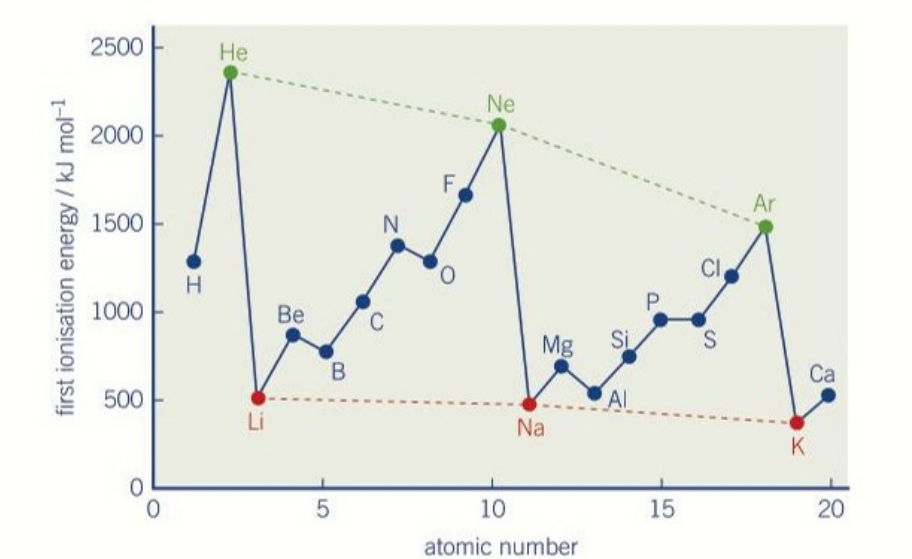
the discovery of argon
Willian ramsey discovered argon
and the whole group of noble gases
general trend in first ionisation energy of the first 20 elements down a group
decreases
why does first ionisation energy increase across a period
more protons
same shielding
gets harder to lose one electron
why does the first ionisation energy decrease going down
more shielding going down
greater distance between the nucleus and valence electron
easier to remove valence shell electron
why is there a drop in ionisation energy from 1 period to the next
new main shell
bigger atomic radius
weaker attraction of valence shell electron to the nucleus
exception between group 2 and 3 first ionisation energy
first ionisation energy decreases from 2 to 3 because the valence electron(3p) is removed from a higher energy level than in group 2 so magnesium has a higher first ionisation energy than aluminium.
exception between group 5 and 6 first ionisation energy
group 5 has spin pair repulsion group 6 does not

successive ionisation energy
Reduced electron shielding.
Increased effective nuclear charge on the remaining electrons.
Decreased distance of remaining electrons from the nucleus.
Significant jumps when electrons are removed from a lower energy shell.

why does magnesium have a higher melting point than sodium
greater nuclear charge
smaller atoms
more delocalised electrons
stronger attraction between ions and delocalised electrons
phosphorus
P4
oxidation state 3 +
covalent molecular structure with weak van der waals