CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 12: Respiration
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
uses of energy in the body of humans
-muscle contraction
-protein synthesis,
-cell division
-active transport
-growth,
-the passage of nerve impulses
-maintenance of a constant body temperature
aerobic respiration
the chemical reactions in cells that use oxygen to break down nutrient molecules to release energy

Investigate the uptake of oxygen by respiring
organisms in arthropods
-Used for growth
-cell division
-active transport
Investigate the uptake of oxygen by respiring
organisms in germinating seeds
Needed for aerobic respiration to provide energy for embryo
the effect of temperature on the rate of respiration of germinating seeds
Suitable temperature is required for enzymes to function in seed to produce energy for germination
anaerobic respiration
the chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules to release energy without using oxygen. Releases much less energy per glucose molecule than aerobic respiration. Product formed is lactic acid which is later broken down into carbon dioxide and water when there is presence of oxygen
lactic acid
An organic acid that builds up in muscles and blood during vigorous exercise causing an oxygen debt
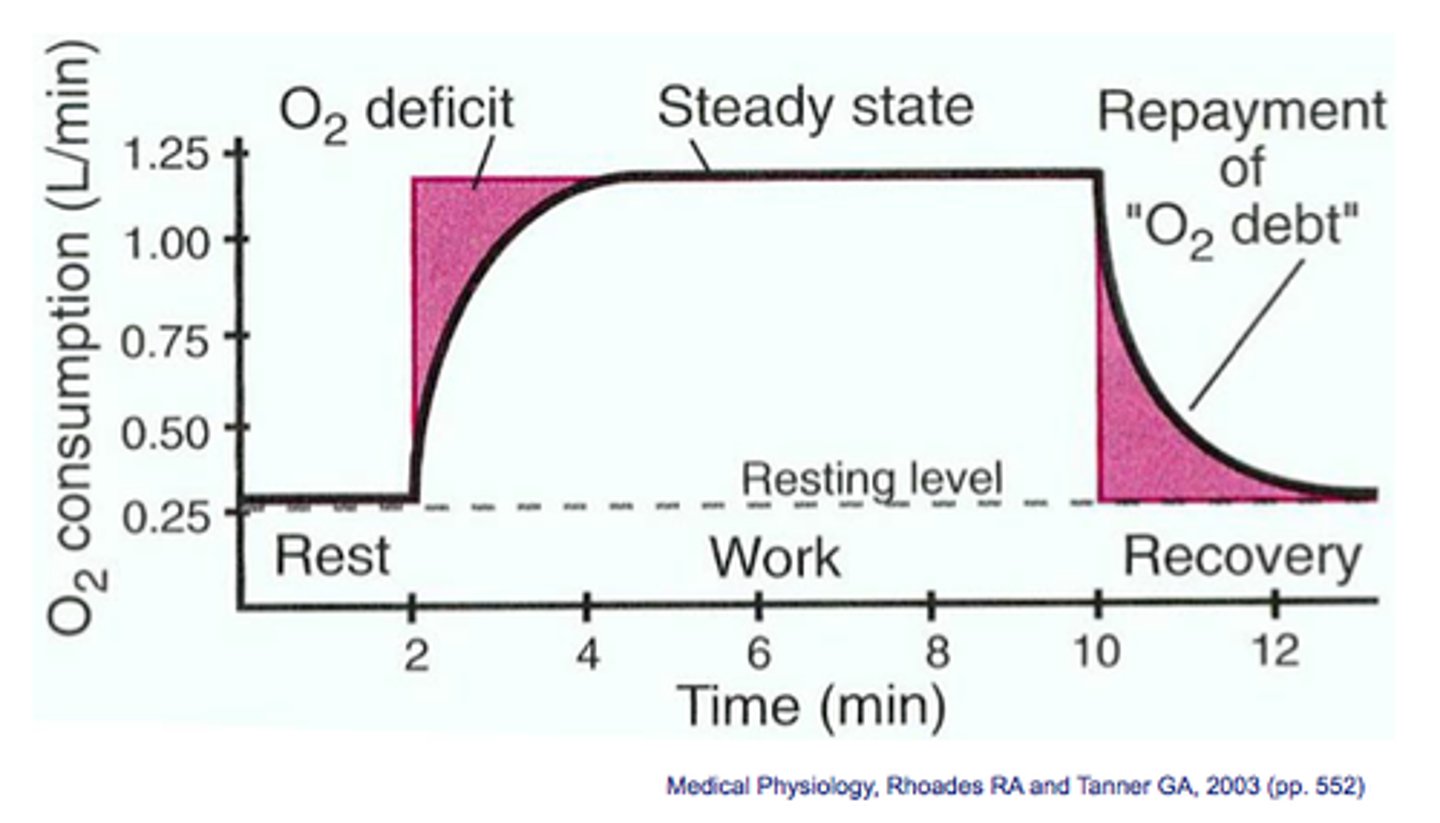
how the oxygen debt is removed during recovery
- aerobic respiration of lactic acid in the liver
- continuation, after exercise, of fast heart
rate to transport lactic acid in blood from
muscles to the liver
- continuation, after exercise, of deeper
breathing supplying oxygen for aerobic
respiration of lactic acid