X-ray Equipment (Ch. 6 part 1)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What are the two types of things that medical x-ray equipment be classified as?
Diagnostic or therapeutic
What do diagnostic x-ray units include?
General procedures, head procedure, fluoroscopy, cardiac Cath. etc
What do therapeutic x-ray units include?
Treatment
What can tube current range from for diagnostic units?
10 to 1200 mA
What can exposure time range from for diagnostic units?
0.0001 to 10 seconds
What can potential difference range from for diagnostic units?
25 to 150 kVp
What does tube current range from for therapeutic units?
Below 20 mA
What does the exposure time range from for therapeutic units?
1 to 60 minutes
What does the x-ray energy range from for therapeutic units?
4 to 40 meV
What is the x-ray table designed for?
To support the patient for their exam
____ is no the primary purpose of the x-ray table, although some institutions permit pads
Comfort
True or false: the x-ray table must be radiolucent
True
What is the most common x-ray table top that is radiolucent called?
Bakelite or carbon graphite fiber
The x-ray table can be ____ or _____
Flat or curved
Is flat or curved x-ray tables more common?
Flat
Where are curved x-ray tables usually found?
On fluoro tables
What can the curved x-ray table also be called?
Dished
What are the two advantages of the curved x-ray table?
More comfortable
Allows the body part to be placed closer to the film (decrease in OID), therefore increasing the spatial resolution of the radiograph
What are the three disadvantages of the curved x-ray table?
Difficult to keep the patient in an oblique or lateral position
Useless for tabletop radiography
Unable to perform decubitus or cross-table exams
The x-ray table must include a space for a tray to hold the film cassettes and grid, known as the?
Bucky tray
The Bucky tray must be clean and is _____ to scratch
Hard
Most x-ray tables are moveable, however some _____ table tops still exist
Stationary
Most in-table grids are reciprocating, which means?
They will blur out grid lines
In most modern x-ray tables, both the ____ and the ____ move to best position the patient
Tabletop and grid
What are the types of x-ray tabletops?
Motor driven
Floating
Fixed
Tilting
What are tilting x-ray tables used for?
Fluoro or R & F (radiographic and fluoroscopic) rooms
How are tilting tables described?
By the angle that the table tilts in each direction
Tilting tables tilt ____ in an upright position/feet down
90 degrees
Tilting x-ray tables tilt ____ in the opposite direction(from 90)/head down
15-30 degrees
Most x-ray tables are at a fixed height which is?
30 to 40 inches (75 to 100 cm)
Why would you want to lower the x-ray table?
To allow the patient to get on and off the table easily
Why would you want to raise the x-ray table?
To allow for radiographers to have a comfortable working height
What four things are included in ancillary equipment?
Foot board
Shoulder supports
Hand grips
Compression bands
When are foot boards used in radiology?
For gastrointestinal studies
When are shoulder supports used in radiography?
When the head is tilted down
When are compression bands used in radiography?
Used to restrain the patient during an exam
What are the 5 types of tube supports?
Overhead
Floor-to-ceiling
Floor
Mobile
C-arm
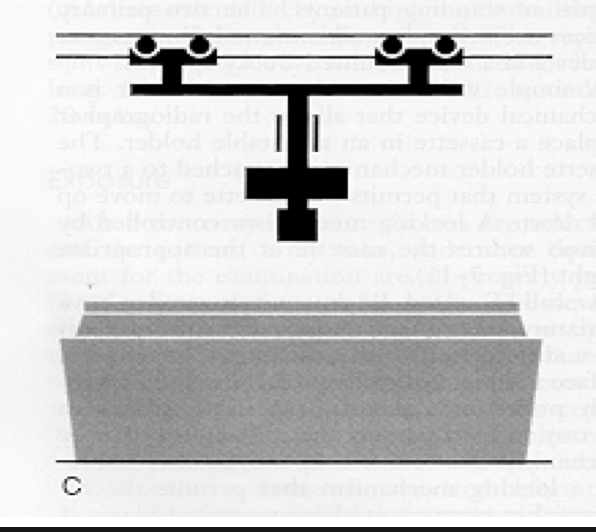
What is this an image of?
Overhead suspension system
What are overhead suspension systems also called?
The ceiling system
The overhead suspension system contains ____ sets of rails in the ceiling and a telescoping column attached to the tube
Two
The overhead suspension system can rotate ____ around the column
360 degrees
The overhead suspension system can roll or pitch up to ___ transversely or side to side
60 degrees
The overhead suspension system track allows the tube to be moved anywhere in the room, making it the most ____ and most _____ system
Flexible, expensive
The overhead suspension system “detents” lock at specific places around the room at what distances?
40 and 72 inches
The floor-to-ceiling suspension system consists of ____ rail on the ceiling, ___ rail on the floor, a telescoping arm for transverse positioning, and a column that slides up and down for vertical movement
One
The floor-to- ceiling suspension system is cheaper and _____ flexible than overhead systems
Less
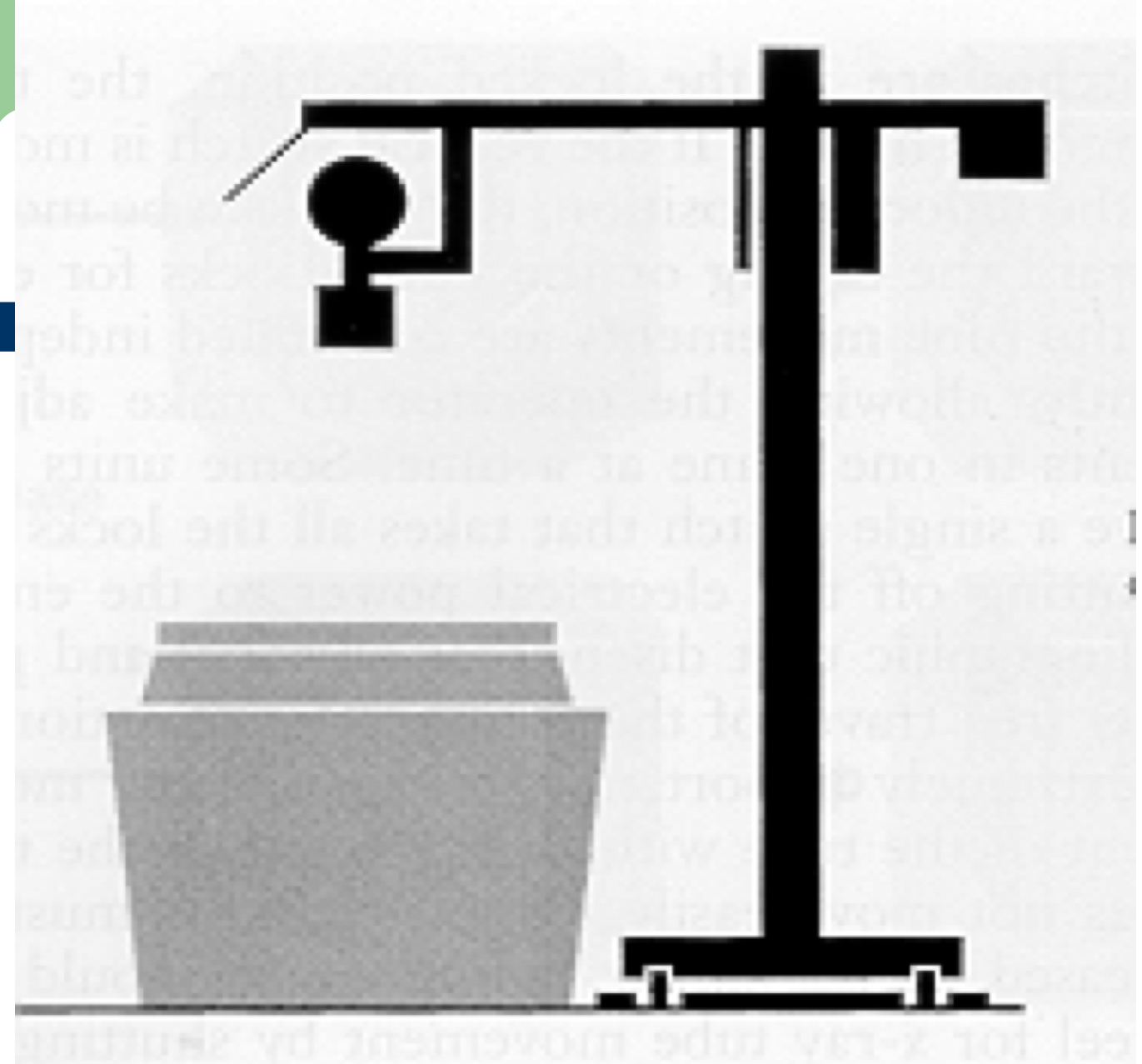
What is this an image of?
Floor suspension system
Where are floor-to-ceiling suspension systems usually found?
In rooms with high ceilings
What does the floor suspension system consist of?
A tube support column mounted on a rail system on the floor
The floor suspension system can be tipped over unless ______
Counterbalanced
The floor suspension system can angle, but some units ____ allow pivoting at the column
Do not
What system needs more space between the table and wall than any other system?
Floor suspension system
What are mobile systems considered?
Portables
What do mobile systems consist of?
A tube, suspension system, and power source and are mounted on wheels
What does the C-arm tube suspension system consist of?
A tube and image reception that are fixed at the opposite ends of the C
Some c-arm’s are fixed/stationary and some are _____
Mobile
C-arm’s are very ____ and move in every direction
Flexible
C-arms have both fluoro and _____ capability
Still-shot
When is a mobile C-arm used?
During surgical procedures
What are the 5 types of specialized (dedicated) equipment?
Head units
Upright units (chest stands)
Chest units or chest changers
Panoramic units or Panoramic Tomography (“Panorex”)
Mammography, Tomography, CT, MRI, etc
What are head units also called?
“Franklin head units”
Head units are like a floor-to ceiling mounted ____?
C-arm (aka U-arm)
What are head units used for to radiograph?
Cranium, facial bones, and cervical spine
Head units do not include a ____, so instead the pt will sit between the tube and image receptor
Table
What are upright units used for?
Chests, c-spines, sinuses, AC joints, weight bearing studies, etc
Chest units or chest changers consist of an _____ with an automatic film feed from a storage box (100 14×17 films) to receive a magazine
Upright bucky
Chest usints or chest changers are great for doing ______, but lousy for doing anything else
Upright chest film
What are panoramic units or panoramic tomography used for?
Dental or mandibular x-rays