Plant Cell Wall Structure and Biosynthesis: Key Components and Processes
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the three main components of the plant cell wall?
Cellulose, Hemicellulose, and Pectin.
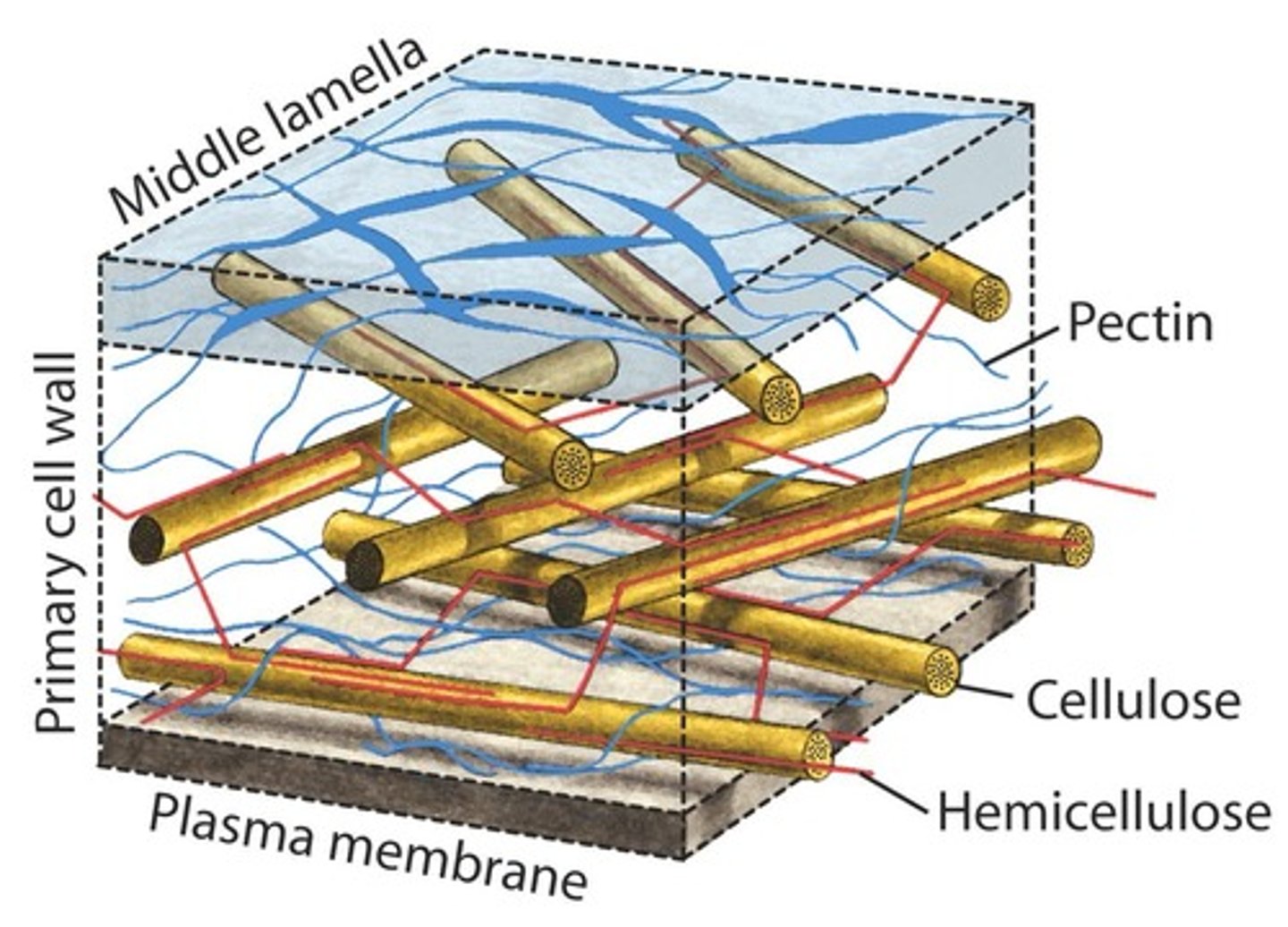
What is cellulose?
A polysaccharide composed of linear chains of glucose with β (1→4) linkages, forming microfibrils.
What is the role of hemicellulose in the cell wall?
It links cellulose and regulates cell wall extensibility and growth.
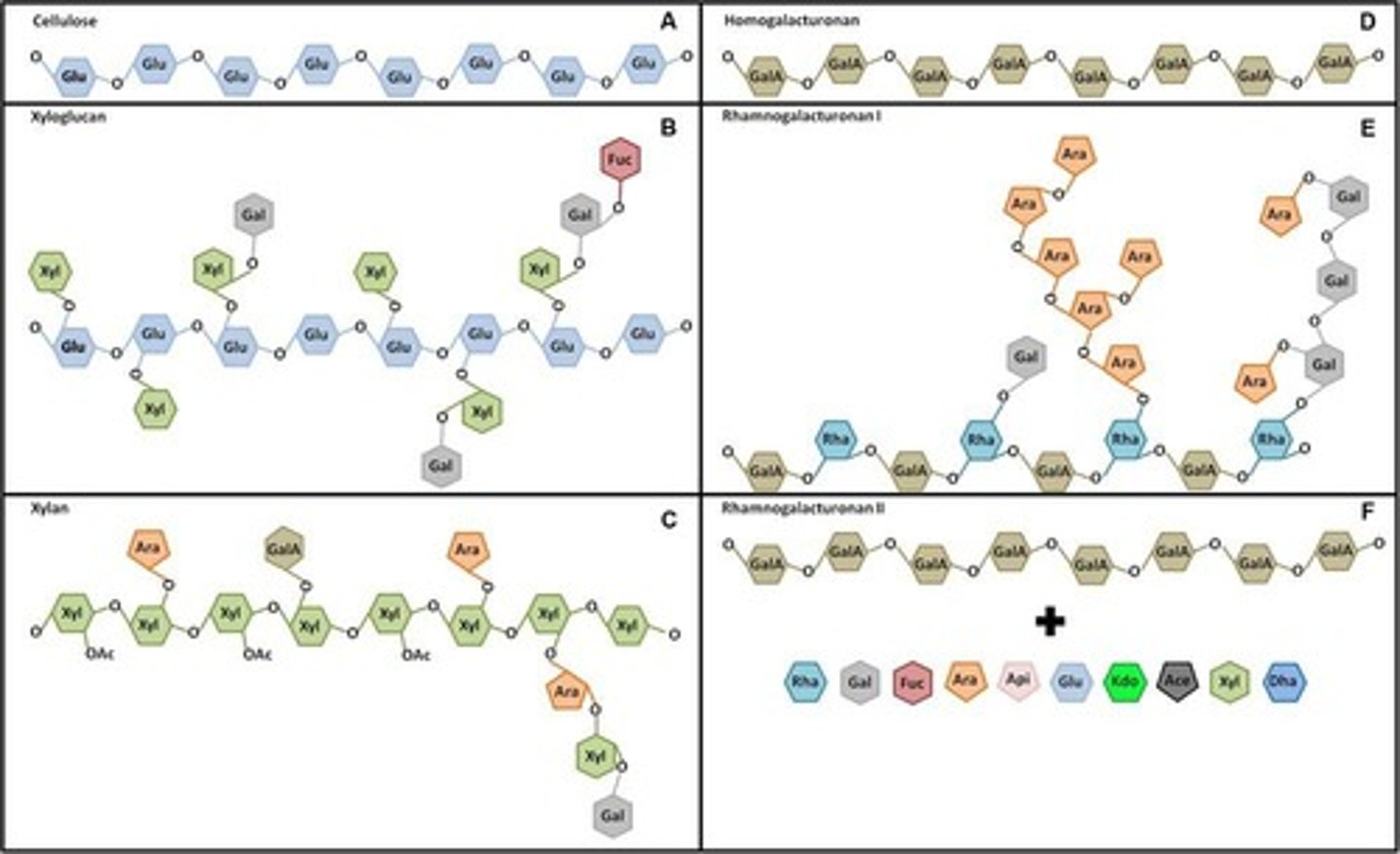
What are the principal constituents of hemicellulose?
Xyloglucans in eudicots, Glucuronoarabinoxylan in certain monocots, Mixed-linked glucans in Poales, and Glucomannans in gymnosperms.
What are pectins?
A diverse group of polysaccharides that form gels and determine cell wall porosity.
What are the two fundamental constituents of pectins?
Homogalacturonan (HG) and Rhamnogalacturonan (RGI & RGII).
How do pectins affect cell wall porosity?
They create pores with diameters ranging from 4.0 to 6.8 nm, allowing the passage of salts, sugars, amino acids, and hormones.
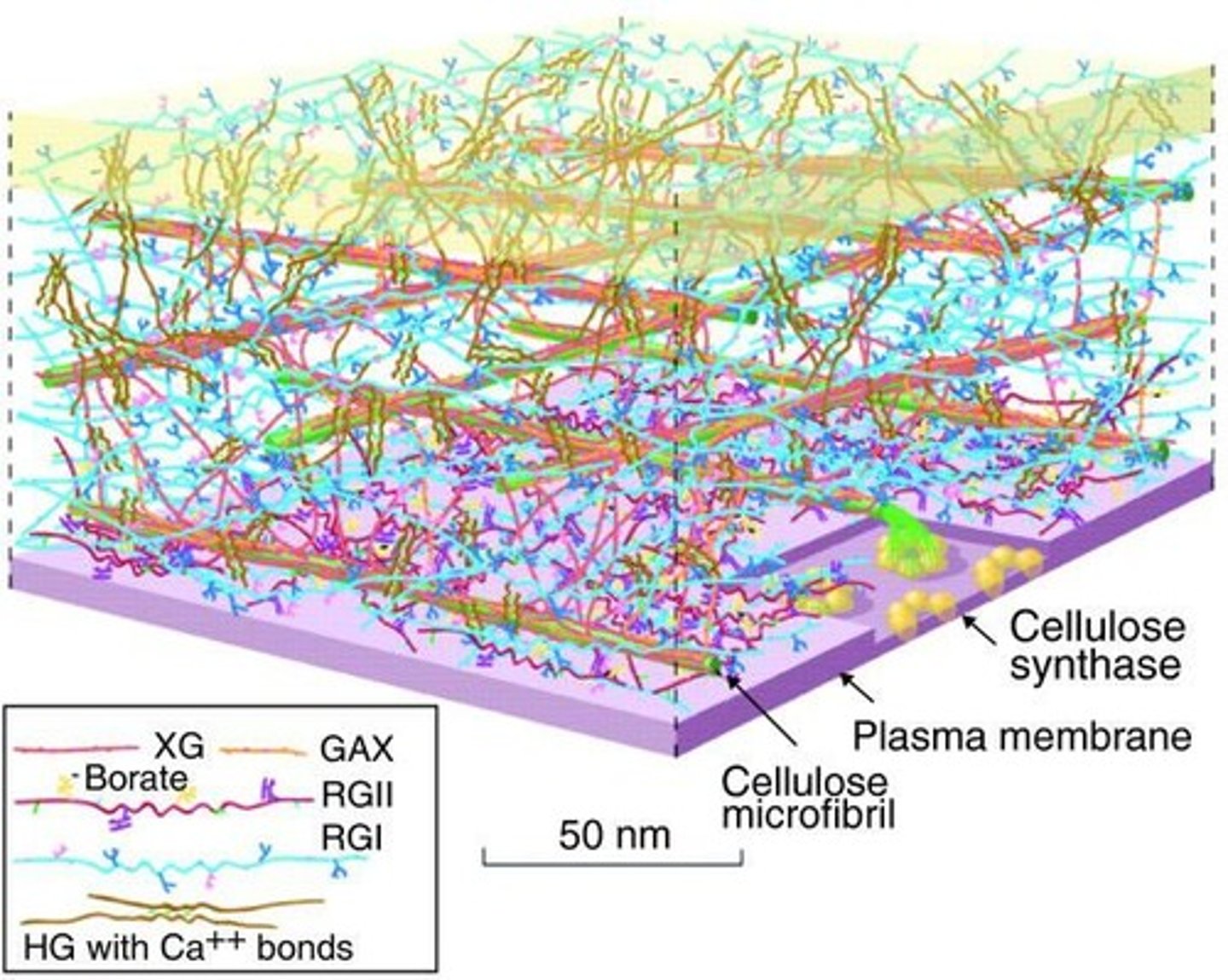
What is the significance of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall?
They constitute 20 to 30% of the dry weight of a typical primary wall and are the most abundant polymer on Earth.
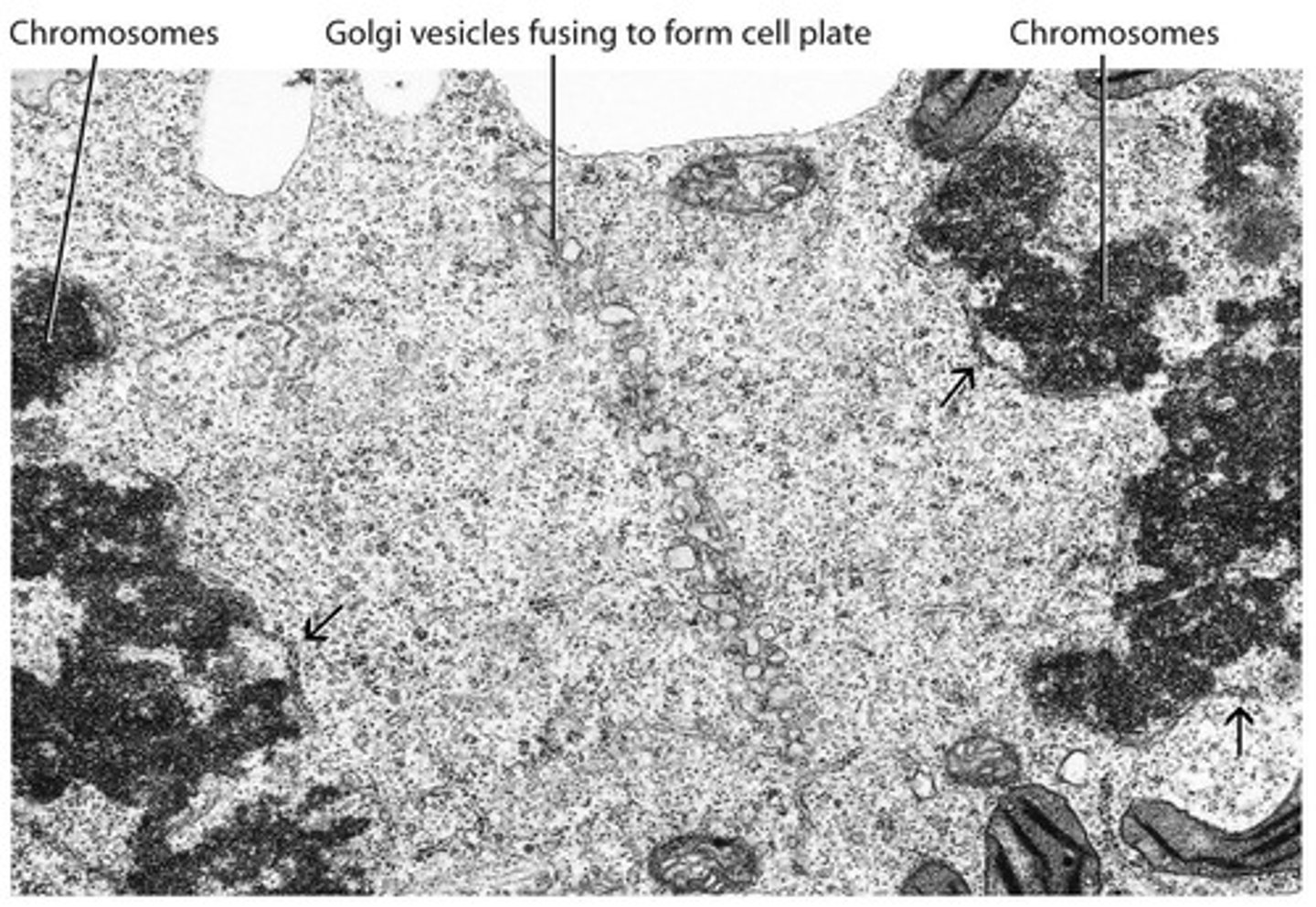
How does the cell wall form during cytokinesis?
The new cell wall, middle lamellae, and plasmalemma form from the center out, controlled by the phragmoplast.
What is the function of the middle lamella in plant cells?
It acts as a cementing layer between adjacent plant cells.
What is the role of primary plasmodesmata?
They facilitate communication and transport between adjacent plant cells.
What is the composition of the primary cell wall?
It includes cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, and proteins.
What is the structure of cellulose in the cell wall?
Cellulose forms microfibrils that wind together to create fine threads, contributing to the wall's strength.
What is the role of the cytoskeleton during cell wall formation?
It controls movement and organization during the formation of the new cell wall.
What is the significance of lignin in plant cell walls?
Lignin provides rigidity and resistance to degradation in secondary cell walls.
How do pectin fragments contribute to plant cell signaling?
They may play a role in signaling processes within the plant.
What is the relationship between hemicellulose and cellulose?
Hemicellulose forms hydrogen bonds with cellulose, linking its fibers.
What is the primary function of the cell wall?
To provide structural support and protection to plant cells.
What is the process of plasmolysis in plant cells?
It occurs when cells lose water in a hypertonic solution, causing the plasma membrane to pull away from the cell wall.
What is the significance of the extracellular medium in plant cells?
It is the location of many metabolic reactions and interactions.
What is the composition of the cell plate?
The cell plate is comprised of the plasmalemma, cell wall (cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin), and middle lamella (pectin).
What is the endomembrane system?
The endomembrane system is a network of the endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear envelope, Golgi bodies, and their transport and secretory vesicles, plasma, and vacuolar membranes.
What are the three major components of the primary cell wall?
The primary cell wall consists of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectins.
How is cellulose synthesized?
Cellulose synthesis involves the synthesis of the enzyme making cellulose, followed by the synthesis of cellulose itself, guided by cortical microtubules.
What role do structural proteins play in primary cell walls?
Structural proteins make up about 10% of the dry weight of walls and are highly specific for certain cell types and tissues.
What are Hydroxyproline-rich proteins (HRGPs) associated with?
HRGPs are mainly associated with phloem, cambium, and sclerenchyma.
What is the function of expansins in cell walls?
Expansins function as wall-loosening agents to promote cell expansion.
What is callose and its significance?
Callose is a linear (1→3) β-D glucan deposited between the plasma membrane and the existing cellulosic wall, associated with developing sieve pores and rapid response to stress.
What characterizes secondary cell walls?
Secondary cell walls are much thicker, more rigid, and contain cellulose, hemicelluloses, low levels of pectins, and lignin.
What are the main components of lignin?
Lignins are phenolic polymers formed from the polymerization of p-coumaryl, coniferyl, and sinapyl alcohols.
What is the role of lignin in plant cell walls?
Lignin provides strength, stiffness, water-proofing, and plays a role in water transport and acts as an anti-microbial agent.
What is cutin and its function?
Cutin is an insoluble lipid polymer that, along with waxes, forms the protective cuticle of plants.
What is suberin and its role in plant cells?
Suberin is an insoluble lipid polymer that restricts the apoplastic movement of water and solutes and forms a barrier to microbial penetration.
What are the two domains of suberin?
Suberin has a polyphenolic domain and a polyaliphatic domain, which are incorporated within the primary cell wall.
What is the significance of plasmodesmata in plant cells?
Plasmodesmata are channels that allow for communication and transport between plant cells.
What is the function of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs)?
AGPs likely play a role as messengers in cell-cell interactions during differentiation.
What is the process of lignification?
Lignification is an irreversible process controlled by phytohormones, where lignin is deposited in cell walls.
What is the role of cortical microtubules in cell wall synthesis?
Cortical microtubules guide the synthesis of the cell wall, particularly in the deposition of cellulose.
What is the function of glycine-rich proteins (GRPs)?
GRPs are localized in the modified primary walls of early tracheary elements and are synthesized by xylem parenchyma cells.